Food From The Land
Due: Oct 27, 2025, 2:45 PM
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(done)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Hunter Gatherer Society
Nomadic groups searching for food from the land around them
Neolithic Revolution
10,000 BCE, transition to settled agriculture
Domestication
Taming an animal and keeping it. Coddling it to the point where it cant survive on its own. It becomes completely reliant on humans.
Irrigation
Using channels/pipelines to water to farmland consistently
Columbian Exchange
Exchange of humans, plants and animals between the western and eastern continents. 15 and 16th century
New World
The new world is North and South America
Old World
the old world was made up of Europe, Asia, Africa, and Oceania
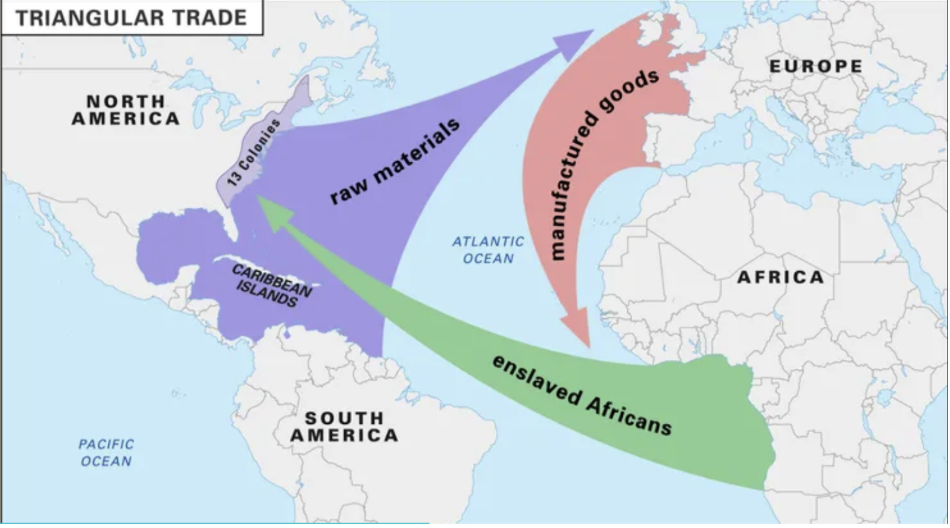
Triangle Trade
Triangle Trade- Slaves —> Africa to new world, Raw Materials —> New world to Europe, Manufactured goods —> Europe to Africa
Plantation Agriculture
Large farms with a single cash crop grown.
Crop Rotation
Growing different crops in the same area over a few growing seasons
Urbanization
People move into cities, Railways expand and working class is created which experiences low wages and poor living conditions.
Green Revolution
The mechanization of farming. Crop yields increased by 45%, 1965-2015. Prevents famine.
Genetically Modified Organism
Selective breeding of plants to create desirable traits in the produce
Monoculture
Using one crop over a large area that is used for profit
Soil Degradation
When soil loses its nutrients
Corporatization
To change a government organization into a privately owned company.
Agribusiness
Large corporations make technology for farming and create larger industrial farms that are mechanized.
Organic
Food grown without the use of pesticides, herbicides, synthetic fertilizers, and without GMOs
Cash Crops
Crops that are grown to be sold for profit; they can't be eaten, e.g. cotton
Urban Farming
Growing crops near and in cities and making the distribution of crops easier.
Todd the Dog
The dog from the documentary “The biggest little farm” who inspired the couple to move from the city to a farm
Canada Land Inventory
A survey of all land in Canada that gives land a rating for farming. The survey was taken from the 1960s to the 1980s
Land Classification
A survey of all land in Canada that gives land a rating for farming. The survey was taken from the 1960s to the 1980s
Agroecology
The approach to farming that prioritizes biodiversity in farms
Class 1 Land
Best farming land, deep soil, good in any weather
Class 2 Land
Good farmland, can do well in most climates
Class 3 Land
Land is okay, had some climate limits that can possibly make farming difficult
Class 4 Land
Average land, short growing season, poor soil quality
Class 5 Land
Not good, very short growing season, hilly, thin soil, poor drainage
Class 6 Land
Only capable of sustaining grasses, improvement practices are not feasible
Class 7 Land
Can not be used for farming
Food Sovereignty
Communities control their own food systems
Why do we need to classify Canada’s farmland?
We classify Canada’s farmland to identify its suitability for crops and to protect valuable agricultural land.
Over time, the number of farmers decreases yet the amount of food produced increases. Why is that?
Farms get bigger, farms get bought up by big corporations.
How does the Colombian Exchange affect agriculture in both the Old World and New World?
It introduced new animals and plants to both sides of the world
What is the difference between a genetically modified crop and an organic one?
GMO crops have had their DNA alerted to make specific traits happen while organic crops have not and do not use fertilizers or pesticides.
What is monocrop agriculture? Why is it bad?
Monocrop agriculture is a farming practice that includes only one crop on a whole farm. It can deplete the soil by repeatedly growing the same crops that take the same nutrients from the soil
What is a cash crop?
A cash crop is a crop grown to be sold for profit rather than for the farmer or livestock, wheat, cotton, tobacco etc.
List 3 characteristics of the plantation system.
Monoculture, large acreage, and Heavy labor intensify.
What factors led European colonizers to create the system of racial slavery across the Americas?
Europeans wanted cheap labor for farms and mines, so they enslaved Africans and justified it by racism
What are 3 alternatives to conventional agriculture that a farmer can use to increase food production while decreasing environmental impact?
Organic Farming, Permaculture (Farms that imitate nature,) Conservation Agriculture (Cover Crops, Crop rotation)
Why is food sovereignty important?
Allows communities to ensure access to healthy food at a reasonable price
Pros of Agribusiness
An increase in crop yields prevents famine
Cons of Agribusiness
Energy intensive, uses crude oil, crops may lack important vitamins and minerals, pesticides, reliant on synthetic fertilizers, soil degradation, drives out small-scale farms
What are 4 common agroecological techniques? What are their respective benefits? (BE FAMILIAR WITH THOSE CASE STUDIES)
Agroforestry - Using trees to provide shade for crops, helps retain water
Cover crops - used on cash crops to suppress weeds and increase nutrients in soil
Crop Rotation - Rotate crops on a plot of land, it increase the nutrients in the soil and crop yields.
Heritage crops - Older variations of crops, more resistant to disease