Chapter 21: Solid and Hazardous Waste
21.1 What Are Solid and Hazardous Waste, and Why Are They Problems?
Wasting Resources
- Solid Waste
- Industrial Solid Waste
- Mining
- Agriculture
- Industry
- Municipal Solid Waste
- Hazardous or toxic waste
- Threatens human health or the environment
- Poisonous
- Reactive
- Corrosive
- Flammable
- Developed countries produce 80-90%
- Solid waste and hazardous waste
- About 3/4 of unnecessary resource waste
- Create air and water pollution, land degradation
What Harmful Chemicals Are in Your Home?
Cleaning
- Disinfectants
- Drain, toilet, and window cleaners
- Spot removers
- Septic tank cleaners
Paint Products
- Paints, stains, varnishes, and lacquers
- Paint thinners, solvents, and strippers
- Wood preservatives
- Artist paints and inks
General
- Dry-cell batteries (mercury and cadmium)
- Glues and cement
Gardening
- Pesticides
- Weed killers
- Ant and rodent killers
- Plea powders
Automotive
- Gasoline
- Used motor oil
- Antifreeze
- Battery acid
- Brake and transmission fluid
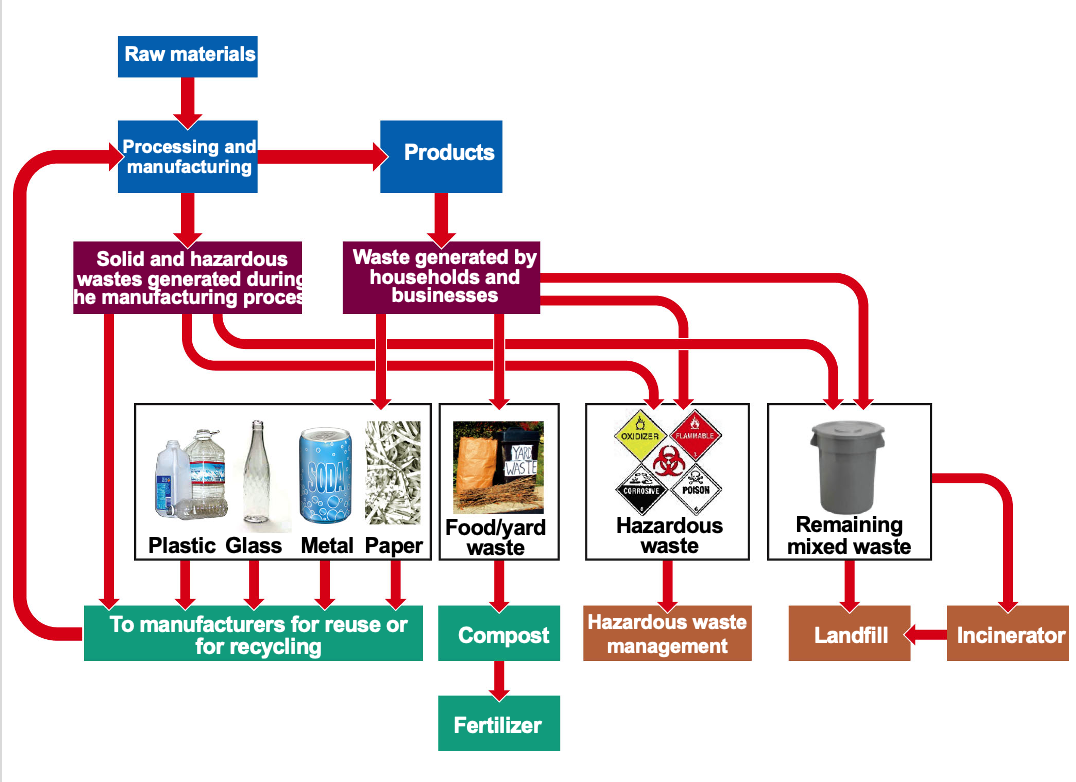
21.2 How Should We Deal with Solid Waste?
Dealing with Solid Waste
Waste management
Waste reduction
Integrated waste management
First Priority
Primary Pollution and Waste Prevention
- Change industrial processes to eliminate the use of harmful chemicals
- Use less of a dangerous product
- Reduce packaging and materials in products
- Make products that last longer and are recyclable, reusable, or easy to repair
Second Priority
Second Pollution and Waste Prevention
- Reuse
- Repair
- Recycle
- Compost
- Buy reusable and recyclable products
Last Priority
Waste Management
- Treat waste to reduce toxicity
- Incinerate waste
- Bury waste in landfills
- Release waste into the environment for dispersal or dilution
What Can You Do?
Solid Waste
- Follow the three Rs of resource use: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle
- Ask yourself whether you really need a particular item, and refuse to package where possible
- Rent, borrow, or barter goods and services when you can, buy secondhand, and donate or sell unused items
- Buy reusable, recyclable, or compostable things, and be sure to reuse, recycle, and compost them.
- Avoid disposables, and do not use throwaway paper and plastic plates, cups, eating utensils, and other disposable items when reusable or refillable versions are available
- Use email or text messaging in place of conventional paper mail
- Read newspapers and magazines online
- Buy products in bulk or concentrated form whenever possible
Reducing Resource Use, Waste, and Pollution
- Redesign processes and products to use less material
- Redesign processes and products to generate less waste
- Make products easy to repair, reuse, remanufacture, compost, or recycle
- Eliminate or reduce unnecessary packaging
- Use fee-per-bag waste collection systems
- Establish cradle-to-grave laws
21.3 Why Is Reusing and Recycling Materials So Important?
Reuse
- Reuse: Clean and use materials over and over
- The downside of reuse in developing countries
- Salvaginf automobiles parts
- Rechargeable batteries
What Can We Do?
- Buy beverages in refillable glass containers instead of cans or throwaways bottles
- Use reusable plastic or metal lunchboxes
- Carry sandwiches and store food in the refrigerator in reusable containers instead of wrapping them in aluminum foil or plastic wrap
- Use rechargeable batteries and recycle them when their useful life is over
- Carry groceries and other items in a reusable basket, a canvas or string bag, or a small cart
- Buy used furniture, computers, cars, and other items instead of buying new
- Give away or sell items you no longer use.
There Are Two Types of Recycling
- Primary, closed-loop recycling
- Second recycling
- Types of wastes that can be recycled
- Preconsumer: Internal waste
- Postconsumer: external waste
Bioplastics
- Plastics from soybeans: not a new concept
- Key to bioplastics: catalysts
- Source
- Corn
- Soy
- Sugarcane
- Switchgrass
- Chicken feathers
- Some garbage
- CO2 from coal-burning plant emissions
- Benefits
- lighter, stronger, cheaper, and biodegradable
Trade-Offs: Recycling
Advantages
- Reduces air and water pollution
- Saves energy
- Reduces mineral demand
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Reduce solid waste production and disposal
- Helps protect biodiversity
- Can save landfill space
- An important part of the economy
Disadvantages
- Can cost more than burying in areas with ample landfill space
- May lose money for items such as glass and some plastics
- Reduces profits for landfill and incinerator owners
- Source separation is inconvenient for some people.
We Can Encourage Reuse and Recycling
- Encourage reuse and recycling
- Government
- Increase subsidies and tax breaks for using such products
- Decrease subsidies and tax breaks for making items from virgin resources
- Fee-per-bag collection
- News laws
- Citizen pressure
21.4 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Burning or Burying Solid Waste
- Waste-energy incinerators
- 600 Globally
Tradeoffs- Incineration
Advantages
- Reduce trash volume
- Less need for landfills
- Low water pollution
- Concentrates hazardous substances into asking for burial
- The sale of energy reduces the cost
- Modern controls reduce air pollution
- Some facilities recover and sell metals
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build
- Costs most than short-distance
- hauling to landfills
- Difficult to the site because of citizen opposition
- Some air pollution and CO2 emissions
- Order or poorly managed facilities can release large amounts of air pollution
- Outputs approach that encourages waste production
- Can compete with recycling for burnable materials such as newspaper
Tradeoffs- Sanitary Landfills
Advantages
- No open burning
- Littler order
- Low groundwater pollution if sited properly
- Cna be built quickly
- Low operating cost
- Can handle a large amount of water
- Filled land can be used for other purposes
Disadvantages
- Noise and traffic
- Dust
- Air pollution from toxic gases and trucks
- releases greenhouse gases (methane and CO2) unless they are collected
- Slow decomposition of wastes
- Output approach that encourages waste production
- Eventually, leaks can contaminate groundwater
21.5 How Should We Deal with Hazardous Waste
We Can Use Integrated Management of Hazardous Waste
- Integrated management of hazardous wastes: produce less, convert to less hazardous substances, rest in long-term safe storage
- Increase the use of post-consumer hazardous waste.
We Can Detoxify Hazardous Wastes
- Collect and then detoxify
- Physical methods
- Chemical methods
- Use nonmagnetic
- Bioremediation
- Phytoremediation
- Incineration
- Using a plasma arc torch
Phytoremediation
- Rhizofiltration: Roots of plants such as sunflowers with dangling roots absorb pollution.
- Phytostabilization: Plants such as willow trees and popular can absorb chemicals and keep them from reaching groundwater or nearby surface water
- Photodegradation: Plants can absorb toxic organic chemicals and break them down into less harmful compounds which they store or release slowly into the air
- Phytoextraction: Roots of plants can absorb toxic metals
We Can Store Some Forms of Hazardous Waste
- Burial on land or long-term storage
- Deep well disposal: disposal of fluids
- Surface impoundments: holds an accumulation of liquids
- Secure hazardous landfill: a built-on or depression of the ground to hold waste.
United States
- 1979: Resource Conservation and recovery act
- 1980: Comprehensive Environmental, compensation, and liability act
- The pace of cleanup has slowed
- Superfund is broke