Overview of Injections for Optometry (Part I)
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Landgraf's FOSD II Lecture UMSL School of Optometry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Intralesional
Subconjunctival
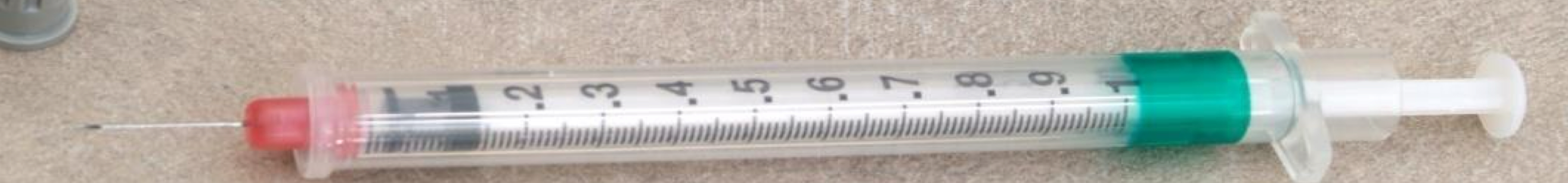
What 2 types of injections use this syringe?

chalazion clamp
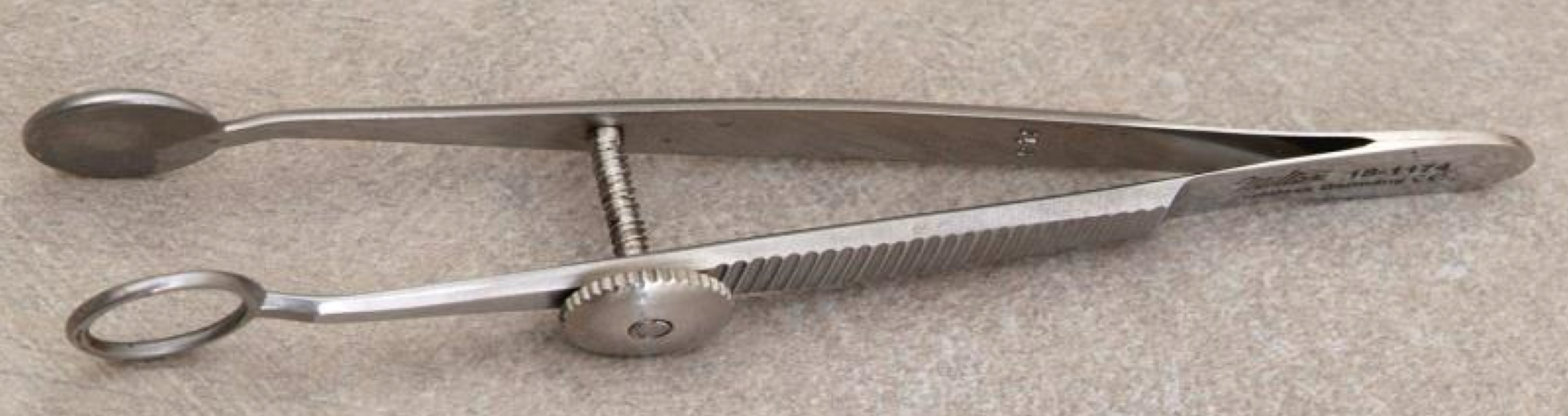
What is the name of this tool?

Intralesional Kenalog
What type of injection & medication do we use for a chalazion?
IV NaFl & ICG
IV IM subcutaneous epinephrine, Epipen
IM Benadryl
IV IM promethazine
What 4 injections are used for IVFA & anaphylaxis? (Medication & Type of injection)
IV IM subcutaneous epinephrine, Epipen
What type of injection & medication is used for IVFA anaphylaxis?
Gentamycin
Cefazolin
Vancomycin
Penicillin G
Tobramycin
Erythromycin
Polymixin B
What are the 7 types of subconjunctival antibiotic injections used to treat uveitis & corneal ulcers?
Kenalog
Methylprednisone
What are the 2 types of subconjunctival steroids used to treat uveitis & corneal ulcers?
subcutaneous
Xylocaine ± epinephrine
What type of injection is given for local anesthesia? What type of local anesthesia is given in this form of injection?
TB
HIV
HBV
HCV
What 4 pathogens are under increased awareness in OSHA control?
TB
What pathogen under increased awareness with OSHA is NOT bloodborne?
7 days
How long can Hepatitis B survive in dried up blood?
60-150 days
How long does it take to develop symptoms if exposed to Hepatitis B?
Within 24 hours
If exposed to Hep B, how soon should you receive a vaccine for it to be effective at preventing disease?
False—very fragile; < 24 hours
True/False: HIV is very durable and will survive outside the body for 7 days.
True
True/False: OSHA Exposure to Blood Borne Pathogens Standards are concerned with employees, not the patients.
Exposure Control Plan
What type of plan is required by OSHA in work environments that has controls in place for pathogen exposures?
Engineering
Work Practice
Preventative
What are the 3 types of controls in place in the Exposure Control Plan required by OSHA in the workplace?
Needlestick injuries
Mucous membrane contact
Non-intact skin contact
What are the 3 easiest exposure concerns for bloodborne pathogens?
Sharps containers
New sharps
“no touch” techniques
What are 3 engineering methods utilized for controlling bloodborne pathogens?
Hand washing
Do not recap needles
What are 2 work practice methods for controlling bloodborne pathogen spread?
Gloves
Wash hands before & after gloving
What are 2 personal protective equipment methods used to control bloodborne pathogen spread?
Labels (biohazard bags for gloves, band-aids, gauze, etc.)
Training
Education on Universal Precautions
What are 3 communication methods used to control bloodborne pathogens?
Universal precautions
Assumption that every patient has HIV, HBV, or HCV
HBV
HAV
Influenza
What are the 3 main vaccines made available to at-risk employees?
TB screening
What screening method is made available to at-risk employees of bloodborne pathogens?
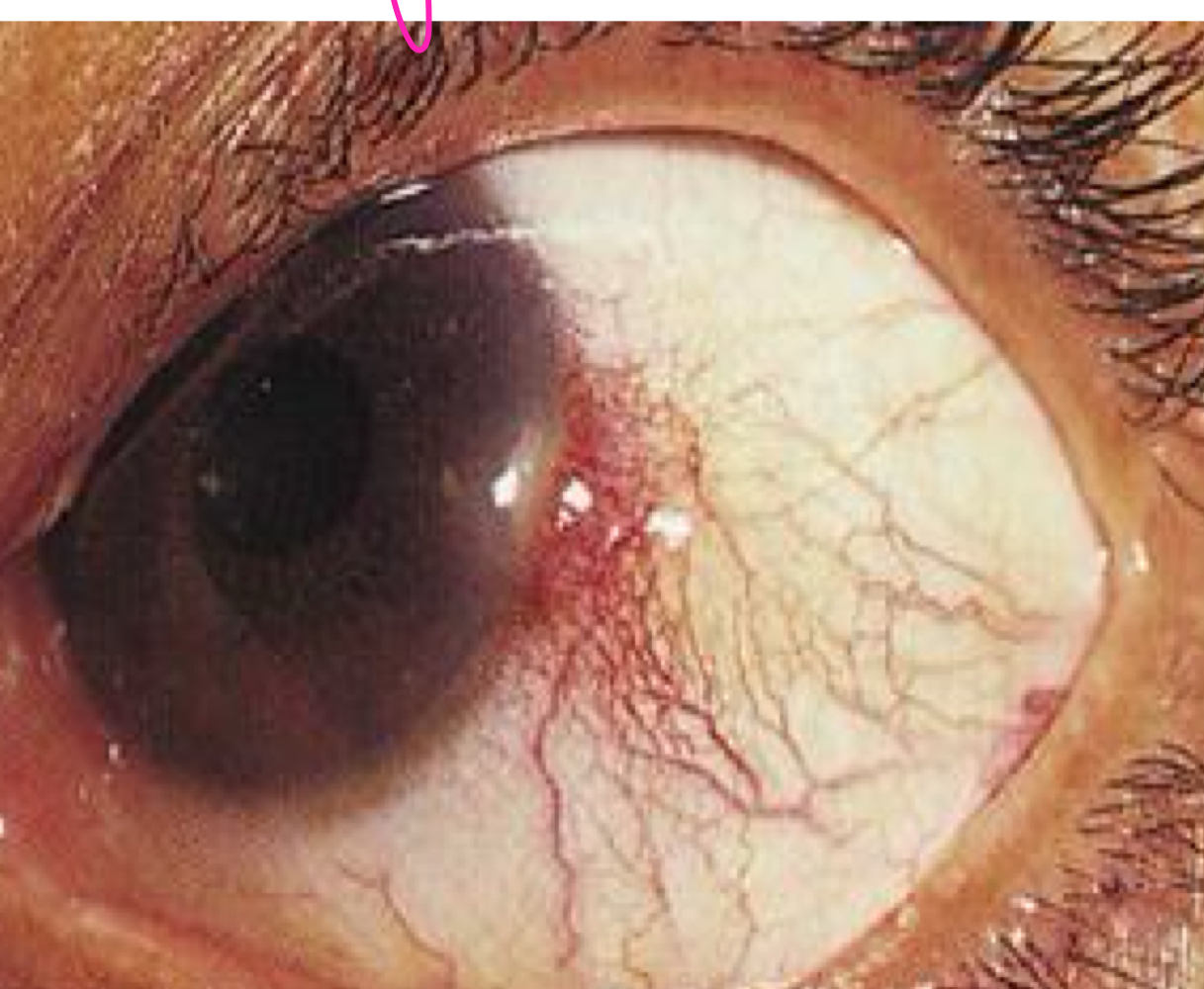
phlyctenule
What type of eye manifestation can occurs from undiagnosed TB as shown in the image?
Autoclaving
2% gluteraldehyde
3% hydrogen peroxide
1:10 bleach
What are the 4 ways in which we can properly sanitize surgical instruments?
Contact with mucous membranes
What exposure to instruments requires high levels of disinfection?
20 minutes
15 minutes
10 minutes
Identify the amount of time required to properly disinfect instruments in the following solutions.
a. 2% gluteraldehyde
b. 1:10 bleach
c. 3% hydrogen peroxide
Needlestick Safety & Prevention Act
From 1991-2001, there was a large number of percutaneous injuries involving contaminated sharps by healthcare workers. Half of these were not reported. What did this prompt within public health?
Needlestick Safety & Prevention Act
Act effective & adopted in 2001; Controls that isolate or remove the bloodborne pathogens hazard from the workplace; Solicitation of input from non-managerial employees; requires sharps injury log
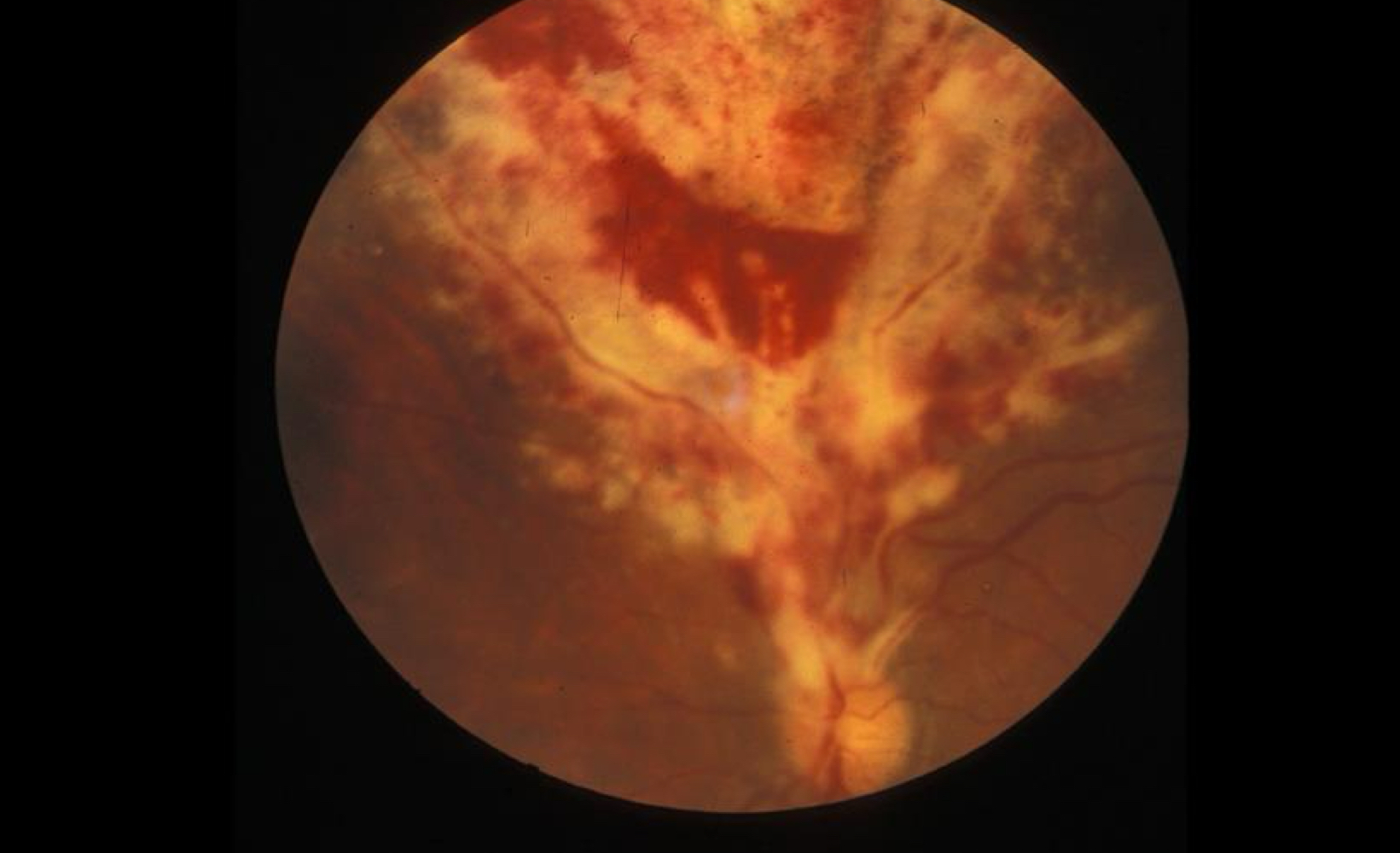
CNV Retinitis
What ocular manifestation shown in the image is caused by the HIV virus?
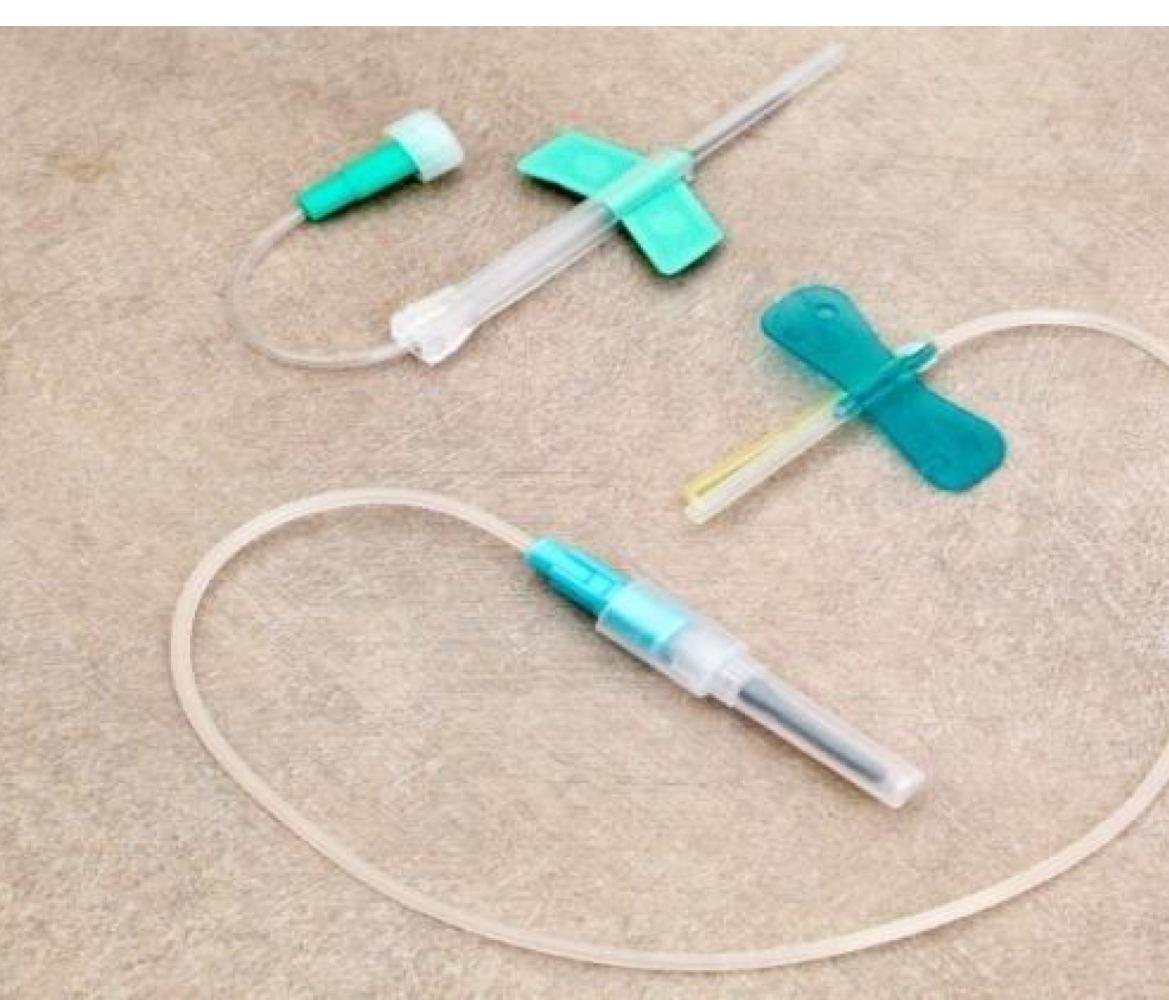
Sharps with Engineered Sharps Injury Protections (SESIP)
Built-in safety feature or mechanism that effectively reduces the risk of an exposure incorporated into the needlestick safety and prevention act (ex. protective sleeve pushed onto a needle)
IV injection; Subcutaneous
What injection moves the fastest through the blood stream? Slowest?
Ask about allergies
What is important to ask about prior to giving an injection?
SC
What type of injection is the shallowest—IM, IV, or SC?
IM
What type of injection is the deepest—IM, IV, or SC?
Type I Hypersensitivity
What type of hypersensitivity is correlated with anaphylaxis from IV NaFl?
Take a great history
What is the best way to avoid anaphylaxis from IVFA IV?
Asthma
Atopic
Allergies
What 3 conditions should you inquire about during your history before an NaFl IV injection?
Hives
Itching
Angioedema
What are the cutaneous signs associated with anaphylaxis to IV NaFl? (3)
Wheezing
Tachypnea
Cyanosis
Tightness in throat
Shortness of Breath
What are the respiratory signs associated with anaphylaxis to IV NaFl (5)?
Respiratory signs
What type of signs would signal you to call EMS and inject epinephrine?
Trendelenberg position
What position should you put a patient in that is having signs of anaphylaxis from NaFl IV?
1/1000 epinephrine IM
What is the dosage and injection type used in an Epi-Pen?
IM diphenhydramine ± epinephrine
What allergy injection can be used for urticaria and itching during an allergic reaction?
Gauge
Diameter of a needle
18g
Which is the larger needle—18g or 30g?
30g; 18-25g
What gauge of needle is used for ocular injections? What gauges are used for IM/IV?
Bevel Down
How should the bevel of a needle be oriented for a subconjunctival injection?
1”
What length of needle should be utilized for IM injections?
3/8”
1/2”
1”
What are the 3 lengths of needles available for injections?
cubic centimeters (cc)
What units are syringes measured in?
1 cc
What volume of syringe is used for TB injections, as well as ocular, subconjunctival, and intralesional injections?
3 cc
5 cc
10 cc
What volumes of syringes are used for IM injections? (3)
Informed consent
What form should be filled out by the patient prior to every procedure done in office?
Procedure explanation
Potential side effects
Alternative treatments
What 3 things are discussed in Informed Consent forms?