Medical Imaging
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is the wavelength of X-rays?
Short wavelength
10^-8m → 10^-13m
Label the diagram of an X-ray tube?

Describe what happens at the cathode in the X-ray tube?

Electrons are produced at the heated cathode by thermionic emission
This gives the electrons enough energy to overcome the attractive force from the nucleus and escape from the metal cathode
These free electrons form a cloud near the cathode and are then accelerated towards the anode by a large potential difference applied across the tube.
The cathode is often shaped to focus the emitted electrons into a narrow beam directed at the anode target.
Why does the X-ray tube need to be a vacuum?
So there is no energy lost in collisions between the electrons and air particles
Describe what happens at the anode in the X-ray tube?

The anode is positively charged to produce a force on the negatively charged electrons causing them to be accelerated
When the electron hits the anode it rapidly decelerates- This converts 99% of the kinetic energy into heat and the rest (1%) produce X-rays which are directed outside the X-ray window
Why is the anode often made from tungsten and what is the purpose of rotating the anode and circulating oil around it?
Tungsten has a high melting point and a relatively large nucleus
Rotating the anode allows it to cool down, dissipating the heat
Describe the energy transfers that take place in the X-ray tube?
An electron, accelerated through a p.d, V gains kinetic energy eV
Since one electron emits 1 X-ray photon from the principle of conservation of energy. the maximum energy of a photon from an X-ray tube must be equal to the maximum Kinetic energy of a single electron
hf= eV
Planck constant X Frequency = elementary charge X voltage
How can the minimum wavelength of an X-ray photon produced in an X-ray tube be determined?
hf= eV
hc/λ = eV
Therefore, λ= hc/eV
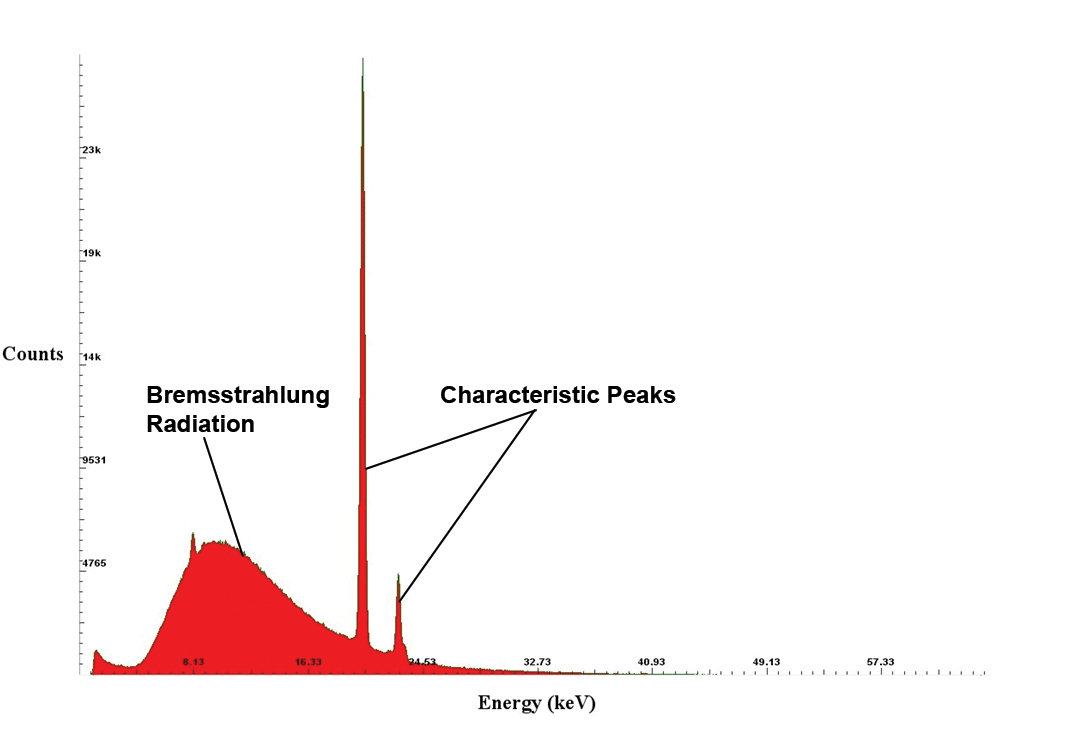
What is braking radiation (Bremsstrahlung) and what is it used for?
X-ray photons with a range of energies are produced at each p.d.
This is because the emitted electrons undergo a range of decelerations when they interact with the nucleus of the target anode
Higher voltages produce higher energy photons→ these X-rays are used for medical imaging
What are K-lines and how are they produced?
Characteristic lines show the X-rays photons when an incident electron interacts with an inner electron of the tungsten (anode) and excites it to a higher energy level or ejects it from the atom
As an electron falls back to fill in the gap, a photon with the energy difference is emitted
(not used in medical imaging)
List the braking radiation and K-lines on the characteristic X-ray spectrum shown?
What is attenuation?
The decrease in intensity of an electromagnetic radiation as it passes through matter
Describe the simple scatter attenuation mechanism?
Include a diagram
X-ray photon interacts with an electron in the atom, but has less energy than the energy required to remove the electron, so bounces off without any change to its energy

Describe the photoelectric effect attenuation mechanism?
Include a diagram
X-ray photon is absorbed by one of the electrons in the atom. The electron uses this energy to escape from the atom.
Upto 100keV

Describe the Compton scattering attenuation mechanism?
Include a diagram
X-ray photon interacts with an electron within the atom, The electron is ejected from the atom, and the x-ray photon is scattered away as a low energy photon
0.5MeV- 5.0 Mev

Describe the pair production attenuation mechanism? (why must energy be greater than 1.02MeV?)
Include a diagram
X-ray photon interacts with the nucleus of the atom. It disappears and the EM energy of the photon is used to create an electron and positron pair
Only if energy is greater than 1.02 MeV (minimum energy needed to create rest mass of both particles)

Which attenuation method is the most dominant in hospital X-ray machines and why?
The Photoelectric effect attenuation method
Hospital X-ray machines typically use 30-100keV supplies which is the same as the photoelectric effect
How is an X-ray image formed? (which absorbs more, Bone or soft tissue?)
As X-rays pass through the body, denser tissues absorb more radiation, appearing white
Whereas less dense tissue allows for more radiation to pass through, appearing darker
(Bones absorb more X-rays than soft tissue and muscles)
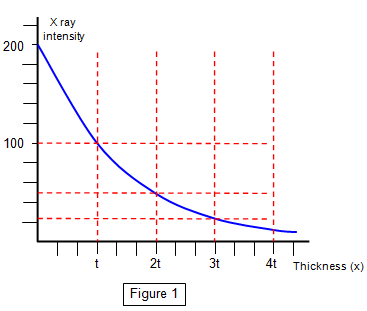
State the equation for transmitted intensity?
I = I(o) e^ - α x
Transmitted intensity= Initial intensity before absorption X e^- attenuation coefficient X thickness
Which 3 things does transmitted intensity depend on?
Energy of photon
Thickness of substance
Type of substance
What would a graph of Intensity against thickness look like?
What would a graph of ln (Intensity/ Initial intensity) against thickness look like? (what is the gradient equal to)
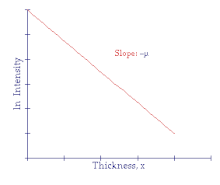
Gradient= -α (- attenuation coefficient)
Why is it necessary to use a contrast medium in an X-ray image?
They are used to improve the visibility of internal structures in X-ray images (soft tissue has low absorption coefficients)
How does a contrast medium work?
The altering of the way X-rays are absorbed by increasing/ decreasing X-ray absorption, making them standout against surrounding tissue
What is the relationship between atomic number and attenuation coefficient for the photoelectric effect mechanism?
Attenuation coefficient is proportional to the cube of the atomic number
α is directly proportional to Z³
Give an example of how iodine is used as a contrast medium?
They are used in liquids, e.g. to view the blood flow
An organic compound of iodine is injected into the blood vessels so that doctors can diagnose blockages in the blood and in the organs from an X-ray image
Give an example of how barium is used as a contrast medium?
They are used in the digestive system
it is given to a patient in the form of a white liquid mixture, which the patient swallows before an X-ray image is taken
Pale regions on the X-ray image is where the barium has accumulated
What type of image is produced in a CAT scan?
A 3D image
Label the diagram of a CAT scan?

What shape is the beam produced by the X-ray tube?
A fan-shaped beam
Why is a thin beam used in a CAT scan?
It irradiates a thin slice of the patient, and the X-rays are attenuated by different amounts by different tissues
Describe the process to produce a 2D slice, and then how it is converted to a 3D image?
Each time the X-ray tube and detectors make a 360 degree rotation, a 2D image (slice) is produced
By the time the X-ray tube has made one complete revolution, the table has moved about 1cm through the ring, where the process repeats and another slice is produced
After all 2D slices have been acquired, they can be manipulated into a 3D image of the patient by a computer
What are the advantages of a CAT scan over a conventional X-ray image?
CAT scans create 3D images, that doctors can assess the shape, size and position of disorders such as tumours
CAT scans can distinguish between soft tissue of similar attenuation coefficients
What are the disadvantages of a CAT scan over a conventional X-ray image?
It is much more expensive and time consuming
CAT scans can be prolonged, and so exposure to ionising radiation (X-ray) is much more riskier than a typical X-ray scan
Patients must remain still, to not blur the image which can be difficult with young patients
What is a gamma camera scan used for?
It detects gamma photons emitted from a radioactive medical tracer which is injected into the patient
Label the diagram of a gamma camera?

What are the features of a radio-pharmaceutical and its function in a gamma camera scan?
Radio-isotope which is chemically combined with other elements e.g. Tc-99m
Produces gamma photons inside the body when injected
What are the features of a Collimator and its function in a gamma camera scan?
Honeycomb of long, thin tubes made from lead
Photons arriving at an angle to the axis of the tubes are absorbed (to prevent a blurry image), and the ones along the tube are passed through to the scintillator
What are the features of a scintillator and its function in a gamma camera scan?
Made up of sodium iodide
A single gamma photon striking the scintillator produces into thousands of visible light photons (1 in 10 chance of occurring)
What are the features of a photo-multiplier and its function in a gamma camera scan?
Hexagonal pattern of tubes, which are connected to a computer, which produces the final image
A single photon of light entering a photo-multiplier is converted into an electrical pulse/ voltage which is displayed on a screen
Which radio-isotope is commonly used in a gamma scan?
Tc-99m
Why does Tc-99m need to be produced on site at a hospital and why is it used for gamma scans?
It is an extremely unstable isotope- this is because the nucleus stays in a high energy state. The isotope emits gamma photons with a half life of 6 hours,which minimises radiation exposure, but its short half-life means it must be produced on site
It can be combined with other chemical compounds to target specific organs
Why might a gamma scan be more preferable than a CAT scan or X-ray image?
It produces an image that shows the function and processes of the body rather than just its anatomy
Label the diagram of a photo-multiplier tube?

What does PET stand for?
Positron emission tomography
What is a positron?
An Anti-electron, with the opposite charge of an electron, but the same mass
What is antimatter?
It is made up of anti-particles, which have the same mass, but opposite charges and sometimes quantum number
What is a neutrino?
A neutral, mass-less lepton that interacts very weakly with matter
Describe what happens when matter and anti-matter interact?
They annihilate each other, the particle and antiparticle are both destroyed
Their masses are converted into energy (due to E=mc²)
Usually 2 gamma photons are produced in opposite directions to conserve momentum
Give an example of a positron emitting pharmaceutical and write its decay equation and how it works?
Fluorine-18, which decays into a nucleus of Oxygen 18, a positron, a neutrino
The positron eventually annihilates an electron inside the patient and 2 gamma rays are emitted
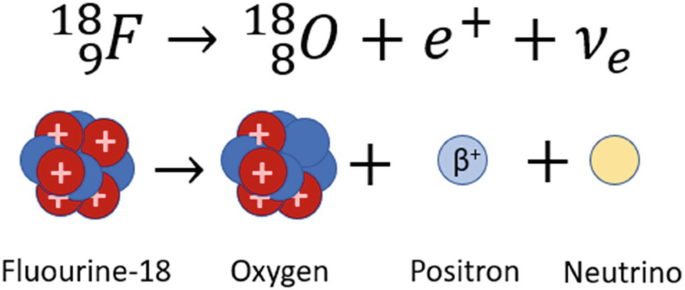
What is the particle that PET scanners detect?
Gamma photons
Describe how gamma photons are detected, after they are produced by the annihilation of a positron and electron?
Include a diagram
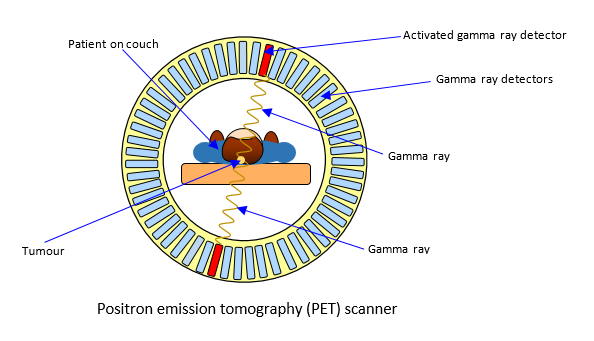
The patient is injected with Fluorine-18, after annihilation occurs, 2 gamma rays are emitted
in the ring of detectors, each detector consists of a photo multiplier tube and a scintillation, which produces a voltage for every gamma photon
These form an image on a computer, when the gamma rays are detected by the gamma scan cameras
What are the uses of a PET scan?
It can help plan complex heart surgery
Observe functions of the brain
Diagnose cancers and disorders
Explain how detectors and computers locate the point where the pair of gamma photons have originated?
The computer can determine the point of annihilation from the difference in arrival times of the photons at the 2 opposite gamma detectors
The speed of the photon, is c, so the location can be calculated
What type of image is produced in a PET scan?
3D functional image
What are the advantages of a PET scan?
Non-invasive technique (not subjected to risk of surgery)
Can be used to assess new medicine and drugs on organs
What are the disadvantages of a PET scan?
Very expensive, because of the facilities required to produce medical tracers
What happens when a beam of ultrasound is incident at a boundary between 2 substances? (Acoustic impedence)
Include a diagram
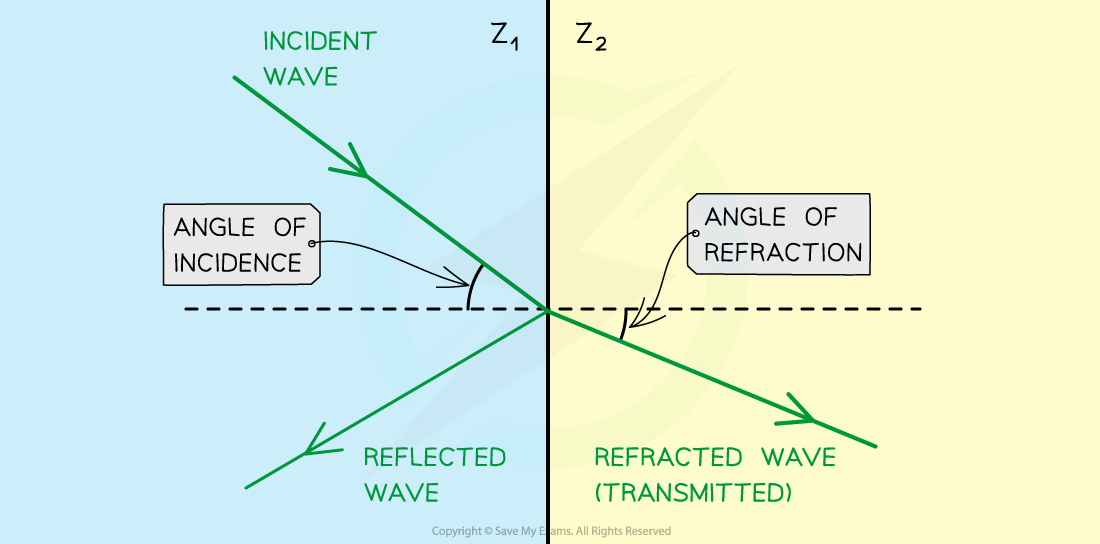
A proportion of its intensity will be reflected and the remainder will be refracted
Z(1)- low speed
Z(2)- high speed
How is acoustic impedance defined?
The product of the density of the substance and the speed of the ultrasound in that substance
State the acoustic impedance equation and its units?
Z= p X c
Acoustic Impedance= density X speed of ultrasound in substance
kgm^-2s^-1
State the equation that can be used to calculate the intensity reflection coefficient when the beam of ultrasound is incidental normally at the boundary?
I(r)/I(o) = (Z(2) - Z(1) / Z(2) + Z(1))²
Intensity reflection coefficient = acoustic impedance of 2 substances²
Explain why it is necessary to use a coupling gel in an ultrasound scan, explain how the gel works?
Normally, almost 99% of the incident ultrasound would be reflected at the skin
However, the gel fills the air pockets between the transducer and the skin, which ensures that almost all the ultrasound enters the patient’s body by refraction
This allows for negligible reflection to occur at the boundary between the 2 substances
What is ultrasound?
A longitudinal sound wave which goes beyond human hearing
Greater than 20kHz
What frequency of ultrasound is normally used in ultrasound imaging and why?
1-15 MHz
This allows for the ultrasound to be refracted as it travels between the substances, but also reflected at the boundary between the 2 substances
What are the advantages of ultrasound imaging?
It is not very ionising, making it harmless
It is quick
It is a non-invasive technique, surgery is not necessary
What is the name given to the device which is used to generate and detect ultrasound?
Ultrasound Transducer
Describe the piezoelectric effect?
Include a diagram (For applying forces, and applying voltages)
Some crystals produce an e.m.f when they are compressed or stretched. This piezoelectric effect is a reversible process, meaning when an external p.d. is applied across the opposite faces of the crystal, the electric field can compress or stretch the crystal

If the p.d. was in the opposite polarity, the crystal would expand
if the crystal was stretched, a p.d. would be induced in the opposite polarity
Draw a labelled diagram of an ultrasound transducer?
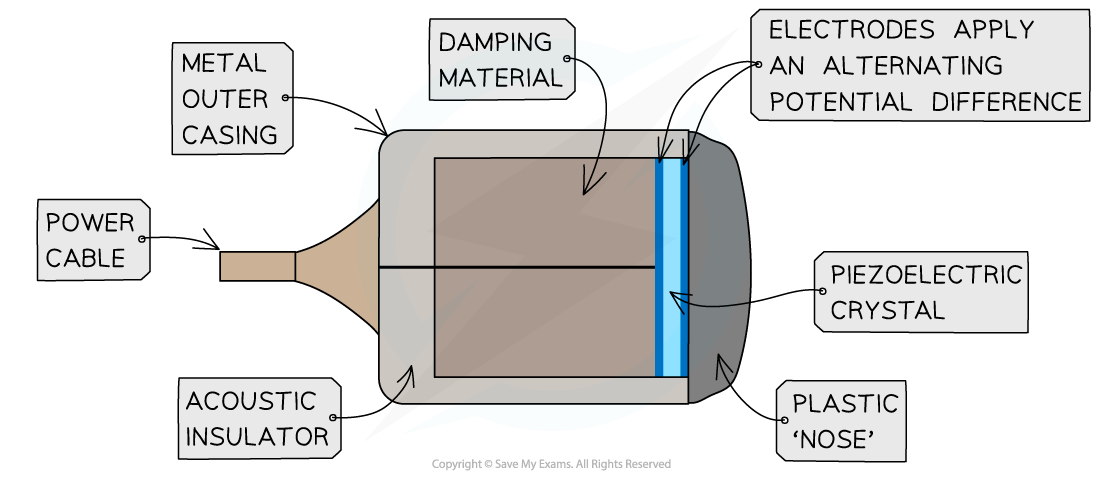
Describe how an ultrasound transducer produces and detects ultrasound pulses?
A high frequency, alternating p.d. is applied across opposite faces of a crystal. This repeatedly makes the crystal compress and expand in an oscillation
The oscillating frequency is the same as the natural frequency of the oscillation of the crystal→ creating intense ultrasound signals
The same ultrasound is used to detect ultrasound, because only ultrasound incident on the crystal will make it vibrate → these vibrations create an alternating p.d. which is detected by electronic circuits
Describe what happens when a pulse of ultrasound is incident on a boundary between 2 materials in the body? (bone and muscle)
Each pulse will be partly reflected and partly transmitted at the boundary between the 2 different tissues
What is an ultrasound A-scan and name some uses? (Amplitude scan)
A single transducer is used to record along a straight line through the patient
It can be used to measure distance between lens and the retina in the eye or the thickness of bone
How is thickness of a material calculated from an A-scan?
The time interval for the ultrasound pulse to travel from the front of the transducer to the material and then back to the transducer
The total distance is 2L, L can be calculated if the average speed of the ultrasound is known
speed divided by time/2
What is an ultrasound B-scan? (Brightness scan)
Provides a 2D image on a screen, the transducer is moved over the patient’s skin, the output of the transducer is connected to a computer
For each position, a row of dots are produced on a digital screen, each dot is a boundary between 2 tissues
The brightness of the dots is proportional to the intensity of the reflected ultrasound pulse
Transducer moved in various positions to create a 2D image
What is the Doppler effect, and how is it used in ultrasound imaging in medicine?
The frequency of ultrasound changing when it is reflected off a moving object
Used to evaluate blood flow
In the Doppler imaging technique, what is responsible for producing the change in frequency of the ultrasound?
The movement of the blood cells
Frequency increases when the red blood cells move towards the transducer
Frequency decreases when the red blood cells recede away from the transducer
What is shown in a Doppler ultrasound image?
A colour coded image showing the direction and speed of blood flow
Produce a diagram to show the basic principle behind the Doppler ultrasound?

State the equation that can be used to determine the change in observed ultrasound frequency?
∆f = 2 f v cos θ / c
observed ultrasound frequency = 2 X original ultrasound frequency X speed of moving blood cells x angle from blood vessel / speed of ultrasound in the blood
What are the advantages of the Doppler effect?
It can reveal blood clots
Evaluate the amount of blood flow to a transplanted kidney/ liver