POM FINALS ASTHMA TO EPISTAXIS (josh copy)
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is the 3 characteristics of asthma?
Hyper-responsive airways
Inflammation
Excessive mucus production
What type of drugs is not given to px with asthma
Beta-blockers
decade of life asthma most common
1st decade
Second peak of asthma occurs during
3rd to 4th decade
gender risk of asthma occurs on?
both male and female
describe asthma
Atopic tendency with multiple allergic reactions
What are the 3 etiology of asthma
Extrinsic
Intrinsic
Lifestyle/environmental
Extrinsic etiology of asthma
Pollen, feces of house-dust mites, pet fur
Intrinsic etiology of asthma
Atopy w/ raised IgE levels, asthma gene (Chr. 11), bronchial hyper-reactivity
Lifestyle/environmental etiology of asthma
Exercise (>cold air), stress, smoking, drugs (NSAIDs, B-Blockers), pollution, viral infections (URTI)
What has a notorious allergic effect?
Protein
Triad of asthma
Edema
bronchoconstriction
mucous plugging affecting the bronchioles
Cause of asthma in pathogenesis
Mast cell degranulation
What is released during mast cell degranulation?
Histamine and prostaglandin
Symptoms of asthma
Nocturnal cough
Wheezing
Inability to breath w/ cyanosis and coma
(Status asthmaticus)
Life threatening features: Cyanosis,
apnea, confusion, exhaustion
Treatment in terms of medical for asthma
Beta2 Agonist - Salbutamol
Beta2 Agonist + Inhaled steroid ○ Add long-acting B2 Agonist
Add (Theophylline, leukotriene antagonist high-dose inhaled steroid)
Add oral steroids and nebulizers
What is monitored in patient with asthma
Peak expiratory flow
Device used to measure peak expiratory flow
Peak flow meter
Describe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Group of lung diseases leading to damage of lung tissue w/ persistent and progressive limitation of air flow
2 common cause of COPD
Chronic bronchitis
Emphysema
Other term for chronic bronchitis
Blue bloater
Other term for emphysema
Pink puffer
Other cause of COPD due to lifestyle
Smoking
Etiology of COPD
Smoking (Active and Passive)
Atmospheric Pollution
Alpha 1 - Antitrypsin Deficiency (Pulmonary Protective Protease)
Congenital form
COPD due to chronic bronchitis
Damage to the respiratory epithelium with ulceration
COPD due to emphysema
Airspace dilation and loss of elastic tissue within the alveolar walls leading to gas trapping, over inflation, and limitation of expiratory airflow
SS of COPD
Chronic cough
Excessive sputum production
Shortness of breath
Expiratory wheeze
3 complications of copd
Respiratory failure
Right heat failure
Pneumothorax
T/F: Bronchodilators for COPD do offer the same degree of relief
F; do not offer; Temporal relief only
Treatment for COPD
Cessation of smoking
Antibiotics, bronchodilators, inhaled and oral steroids
Non-invasive ventilation
Oxygen concentrator
Influenza and pneumococcal vaccination
Rely on low oxygen tension to drive their respiration and should not be given high-flow oxygen over long periods of time
Do we sedate COPD patients?
NO!
COPD has inflamed _
primary and secondary bronchi
Most common malignancy in western world
Lung Cancer
Incidence decreases on who and increases on who?
Decreasing incidence in males
Increasing incidence in females
What is the main cause of lung cancer?
smoking (90%)
Other causes of lung cancer
Passive smoking
Air pollution
Coal and asbestos exposure
What are the 2 major groups of lung cancer?
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Describe sclc
Centrally located, rapid growth rate, and metastasis early
describe nsclc
slow growth rate, metastasizes later
Horner’s syndrome is seen on patients with?
Lung cancer
Describe horner’s syndrome
miosis, partial ptosis, hemifacial anhidrosis
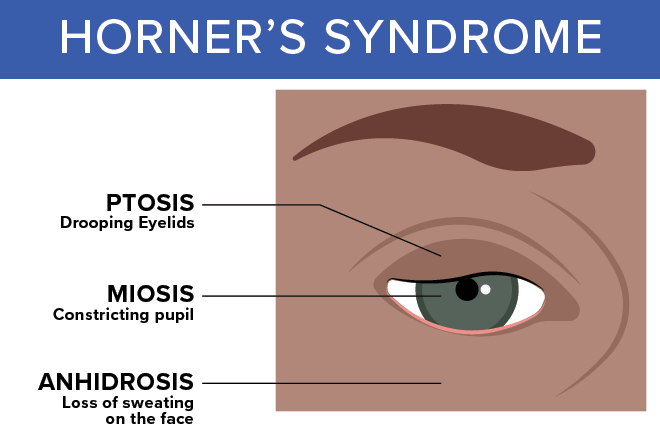
drooping eyelids
pstosis
miosis
constriction of pupil
hemifacial anhidrosis
loss of sweating of face (one side only)
Local signs and symptoms of lung cancer
Persistent cough
Prolonged chest infection
Chest pain increased by breathing and coughing
Hemoptysis
Progressive dyspnea
Hoarse voice
Horner’s Syndrome
Distended neck veins (superior vena caval obstruction)
Systemic signs and symptoms
Finger clubbing
Weight loss
Malaise
Anemia
Ectopic hormone production (e.g. ACTH)
Lung cancer spreads through (metastatic spread)
Bone pain
Neurological deficits
Jaundice
Treatment for patients with lung cancer
Curative surgery - 20%
Majority, palliative
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Supportive therapy
Analgesia
Advice on how to stop smoking
These are evident/present on people with lung cancer
Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction (CLAD)
Distended neck veins
Horner’s syndrome
Color of lungs on patients with lung cancer
Charcoal
Inhaled foreign body percentage occurence
27%
IFB more common in?
Adults or lederly
Causes of inhaled foreign body
Close proximity to airway
Small instruments used
Supine position
Sedation-induced reduction in cough reflux
What part of the lung is affected during IFB
Right main bronchus to right lower lobe of the lung
IFB can develop risk for
Lung abscess
Pneumonia
When small object is inhaled, this affects?
Lungs
When larger object is inhaled, this affects?
Above the vocal cords
How to prevent iFB
Use of rubber dam
Placement of pharyngeal sponges
Restraining cords on instruments
Avoidance of over sedation
Training in instrument handling
TX for IFB
Removal
Antibiotics
Describe pulmonary embolism
Due to a blockage of a portion of the arterial system in the lungs
Cause of pulmonary embolism
Most commonly due to a blood clot shed from a deep vein thrombosis in the lower limb
Prolonged immobilization
Less common on fat, air, amniotic fluid
Pulmonary embolism is common in people that are?
Bedridden due to immobilization
Pathogenesis of pulmonary embolism
Embolus impacts and obstructs a portion of the pulmonary arterial circulation resulting in collapse of the alveoli in the area and decreasing the efficiency of gas exchange
Clinical features of pulmonary embolism
Sudden onset of chest pain
Acute shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
Collapse
Sudden death
This clinical feature causes sudden death in pulmonary embolism (common)
Amniotic fluid embolism
Treatment for pulmonary embolism
Thrombolysis
Anticoagulation (Warfarin, coumadin)
Describe rhinitis
Inflammation of the lining of the nose
Causes of rhinitis
Allergies
Cigarette smoke
Changes in temperature
Exercise
Stress
Reaction by the body which happens in some people who are sensitive to chemical substances from various things present in the environment
Allergy
What are the 4 types of rhinits
Seasonal allergic rhinitis
Perennial allergic rhinitis
Non-allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis
Caused by pollen in the air from plants, grasses or trees; Symptoms present during times of peak pollen levels
Seasonal allergic rhinitis
Chronic rhinitis, year-round problem; Caused by indoor allergens such
as dust and animal dander
Perennial allergic rhinitis
Allergic cause cannot be
identified
Thought to occur because of
abnormal regulation of nasal
blood flow
Non-allergic rhinitis
Symptoms are mostly in the nose
and eyes
Due to airborne particles of dust,
dander, or plant pollens
Allergic rhinitis
When the cause is pollen, it is considered as?
Seasonal allergic rhinitis/hayfever
Over-sensitive immune response, reacts to substances (allergens) that are generally harmless and in most people do not cause an immune response
Allergy
Allergen example
Pollen or dust
1st exposure produces
Abs
2nd exposure produces
Ab-mediated release of histamine
Determination of Ige can be done through?
Blood test
Other determination test
Intradermal allergy test reactions
Best treatment for allergy
avoid what causes the allergic symptoms or reduce exposure
Medication options for allergies
Short-acting antihistamines
Relieve mild to moderate symptoms, may cause drowsiness
Loratadine (Claritin) - non-drowse
Long-acting antihistamines
Less drowsiness e.g. Fexofenadine, and Citirizine
Nasal corticosteroid sprays
If symptoms are not relieved by antihistamines alone
Decongestants
Helpful in reducing nasal congestion (should not be used for long periods)
Neozep, can cause hypertension (shoots up bp sa px with hypertension)
Cromolyn sodium
Nasal spray (Nasalcrom) for treating hay fever
Eye drop preparations are for itchy, bloodshot eyes
Leukotriene inhibitor
Helps control asthma and relieve symptoms of seasonal allergies
Describe epistaxis
A nosebleed is a loss of blood from the tissue lining of the nose
Where is epistaxis occuring?
One nostril only!
If 2 nostril bleeding, this indicates?
High blood pressure
Season epistaxis prevalent
Winter
Air moving through the nose can also dry out the membranes and can form
Crust
T/F: These crusts bleed when irritated by rubbing, picking, or blowing the nose
T
Most nosebleeds occur on the front of the _
nasal septum
Rationale for front nasal septum
It contains many fragile, easily damaged blood vessels
Less commonly, nosebleeds may occur _
higher on the septum or deeper in the nose.
Higher septum or deeper in nose indicates _
Such nosebleeds may be harder to control
Frequent nosebleeds may also be a sign of _
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (also called HHT or Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome)
T/F: Blood thinners do not worsen nosebleed
F; Blood thinners such as Coumadin or aspirin may cause or worsen nosebleeds
Causes of epistaxis
Allergic rhinitis, colds, sinusitis, deviated septum
An object stuck in the nose
Barotrauma
Blowing the nose very hard
Chemical irritants
Direct injury to nose, including a broken nose
Nose picking
Overuse of decongestant nasal sprays Repeated sneezing
Surgery on the face or nose
Taking large doses of aspirin or blood-thinning medicine
Upper respiratory infection
Very cold or very dry air, low humidity Prolonged use of decongestant Rebound rhinitis
Repeated nosebleeds may be a symptom of another disease such as
high blood pressure, allergies, a bleeding disorder, or a tumor of the nose or sinuses.