CH 26- Secondary Growth
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
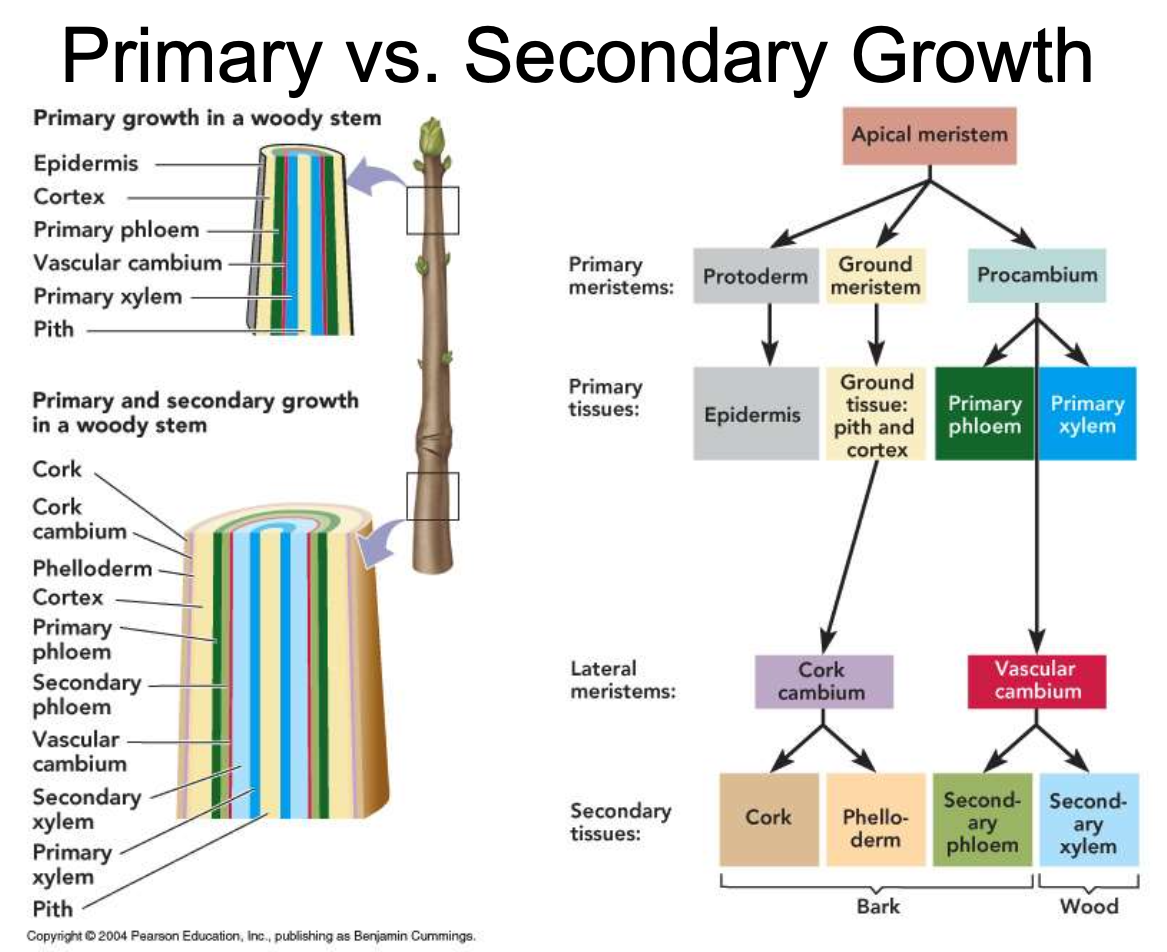
Secondary growth
Occurs in woody plants
all gymnosperms
20% of dicots
5% of monocots
Occurs in stems and roots after they are no longer growing in length
Lateral meristems
Produce secondary growth
Cylinders rather than clusters of undifferentiated stem cells
Secondary growth is radial
New cells are added bidirectionally (toward center and surface)
Cambia
Cambial cells are derived from cells that dedifferentiate
Cambium means “to exchange”
Cambia forms 2 lateral meristems
Vascular cambium
Cork cambium
Vascular cambium
Derived from the cortex and procambium
Produces secondary xylem and phloem
Cork cambium
Forms from parenchyma cells and phloem
Produces new dermal tissue
Stem Vascular cambium
Produces secondary xylem and phloem
Vascular cambium cells arise from residual procambium cells (between 1 xylem and phloem)
Can also arise from parenchyma cells between vascular bundles
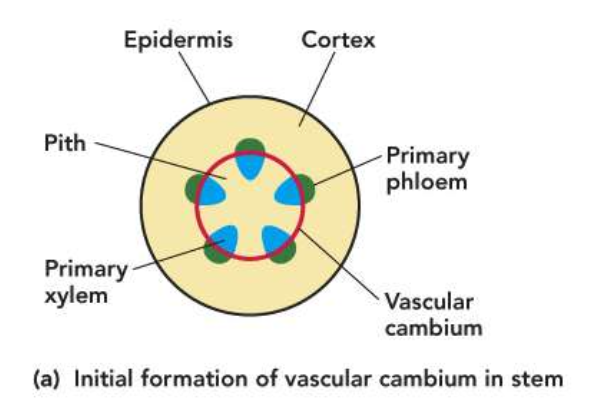
Root Vascular Cambium
First forms a discontinuous series of sections that eventually form a closed ring
Pericycle cells become part of the vascular cambium
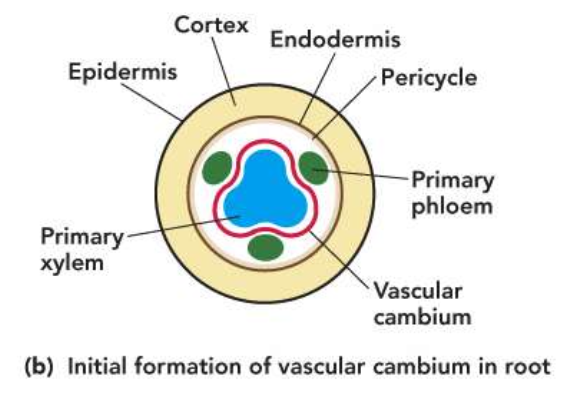
The secondary xylem and phloem
• Expand the plant’s conducting capacity
• Replace older cells that no longer conduct
• Vascular cambia produce much more xylem than phloem
Secondary Xylem
Wood!
Consists of largely dead cells
Only the more recently formed layers of secondary xylem conduct water and minerals
Primary and older secondary xylem become inactive (vessels have broken columns of water; trac
Secondary Phloem
One more recent layers of living secondary phloem conduct food
Primary and older secondary phloem become stretched and broken as vascular cambium push them outward
Secondary growth
• Enhances conduction and support
• Function of cells in secondary xylem and phloem is the same as that of primary tissues
• Secondary xylem tends to have thicker walls (lignin constitutes up to 25% of dry weight of wood)
• Lignin is the second most common organic compound on Earth
After several years of growth
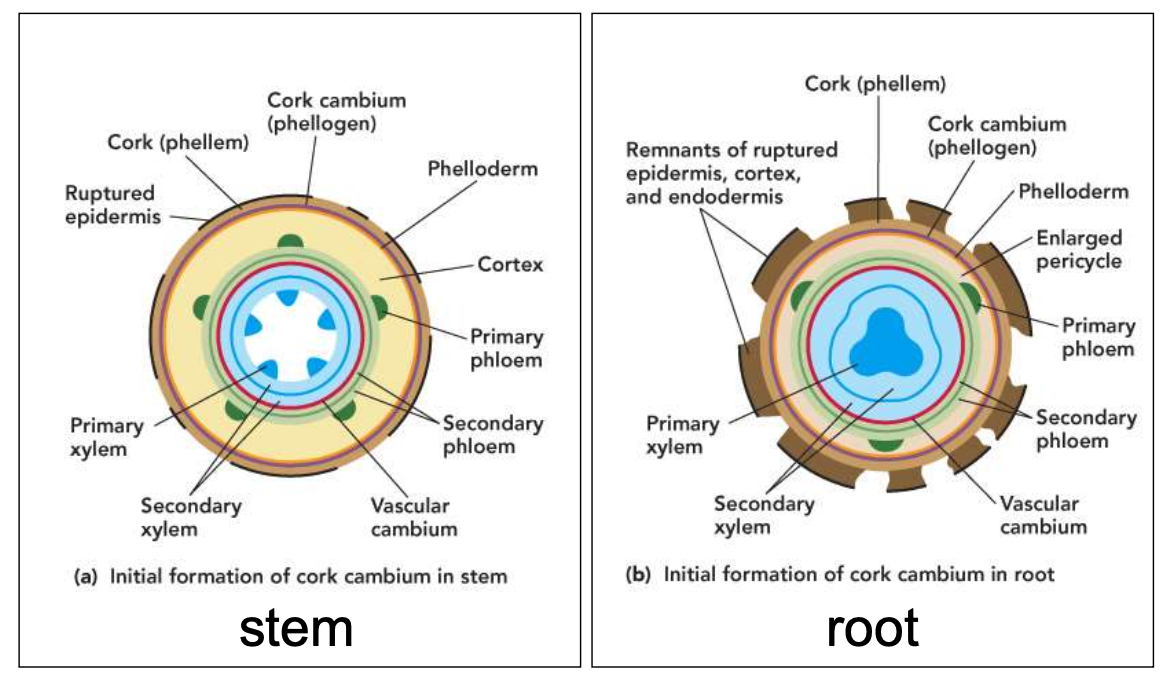
Cork cambium
2 types of dermal tissue in vascular plants:
Epidermis
Periderm
During secondary growth, epidermis and cortex are replaced by periderm
Periderm
Is produced by the cork cambium
It consists of:
Cork (phellum)
Phelloderm
Cork cambium cells (phellogen)
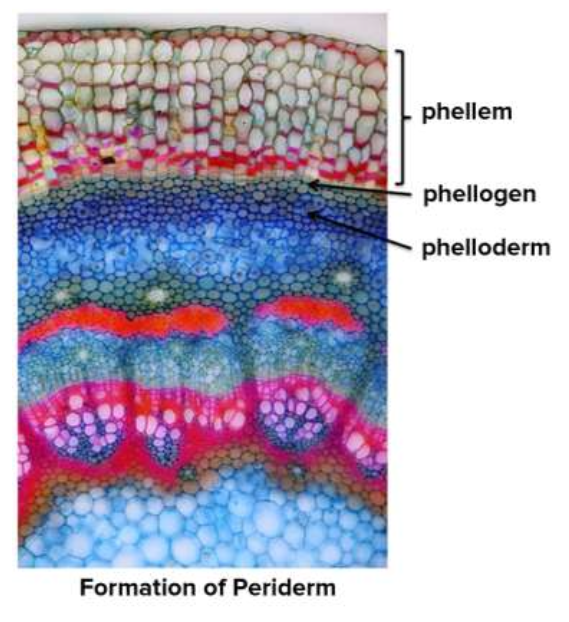
Cork phellum
Forms to the outside of the cork cambium
Consists of dead cells when mature

Phelloderm
Forms to the inside of the cork cambium
Consists of a thin layer of living parenchyma cells
Unlike vascular cambium, cork cambium does not grow in diameter (forms inside old one each year or so)
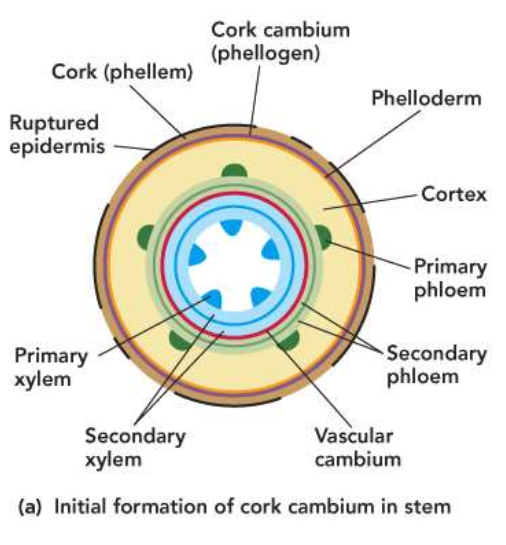
Stem cork cambium
• First cork cambium arises from parenchyma cells in cortex
• Each new cork cambium arises from cortex tissue to the inside
– until cortex is used up
• Expansion causes cortex to break apart and fall off stem
• Subsequent cork cambia arise from secondary phloem to the inside
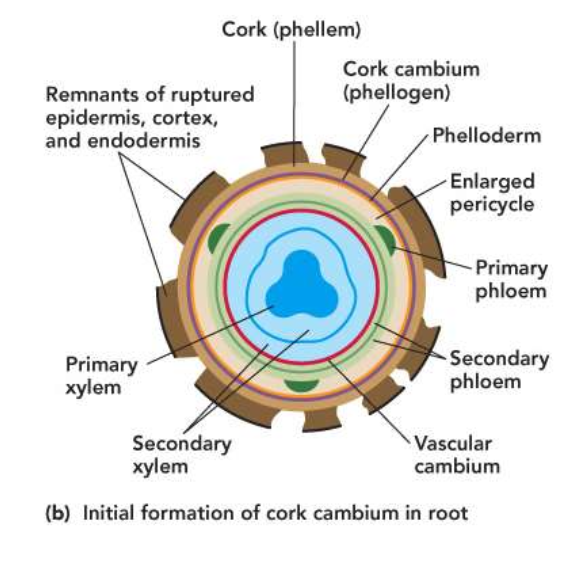
Root cork cambium
Endodermis and pericycle
Endodermis-filtering no longer needed
Pericycle-no more branch roots
Outer layer of enlarged pericycle gives rise to the first cork cambium forms periderm
Bark
Consists of all tissues external to the vascular cambium
Two distinct regions:
Inner bark
Outer bark
Typically thinner than the woody portion of the stem
Pattern s are variable but characteristic for different species
Essential for tree viability
Inner bark
Living secondary phloem, dead phloem between the vascular cambium and inner-most cork cambium, and any remaining cortex
Inner bark carries sugar and other organic molecules
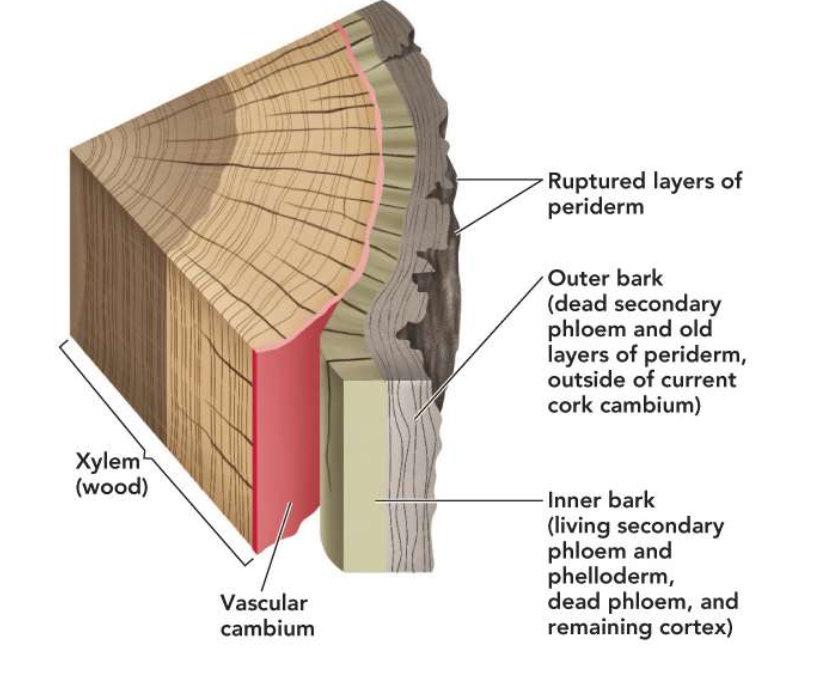
Outer bark
dead tissue (includes dead secondary phloem, all layers of periderm outside of most recent cork cambium)
Dead outer bark provides protection
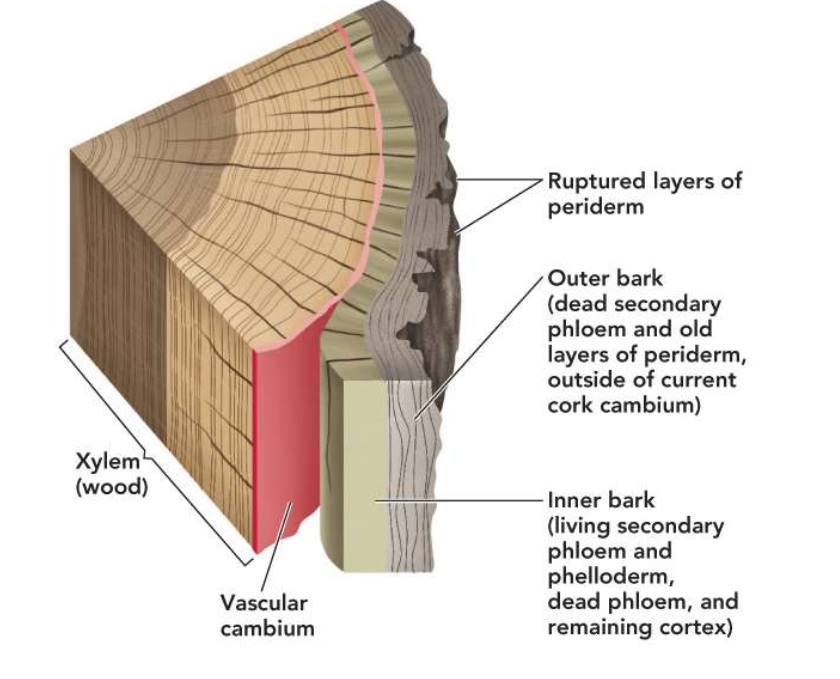
Primary and secondary growth
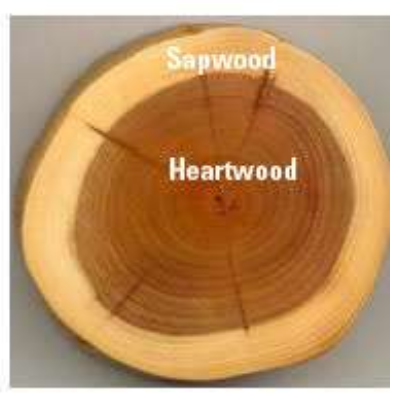
Heartwood
Older non-conducting rings of xylem found in the center of the trunk or root
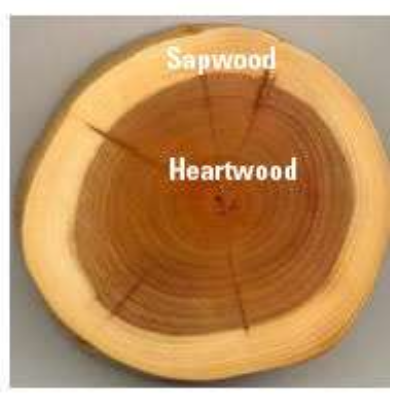

Sapwood
Consist of the outer xylem rings that still conduct water and minerals
Antibacterial and antimicrobial compounds protect heartwood from rotting

Growth rings in wood
• Yearly growth of xylem forms rings
• The sizes of the cells that make up these rings varies with season
• Cells tend to be small in late summer and large in the spring
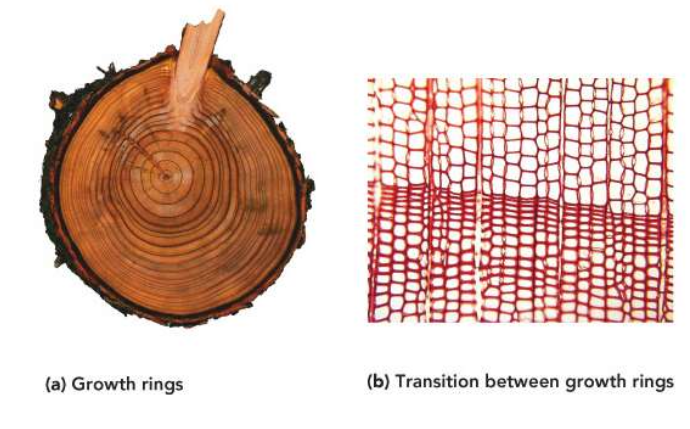
Dendrochronology
• Science of tree ring dating and climate interpretation
• Tree rings provide information about tree and climate variations
Reaction Wood
Develops to counterbalance wind and gravity
• Tension wood (dicots)
• Compression wood (gymnosperms):
Tension wood (dicots)
Forms on the upper side of leaning trunks or branches-pulls

Compression wood (gymnosperms)
Forms on the underside of trunk or branches-pushes

Protrecting the Outside at a cost
• Cork cambium forms protective layers of tissues preventing water loss, infection by disease and predation
• Cork cambium cannot grow in diameter and must reform inside the old one (toward a source of water and nutrients)
• Cork cells enlarge and become coated and impregnated with suberin
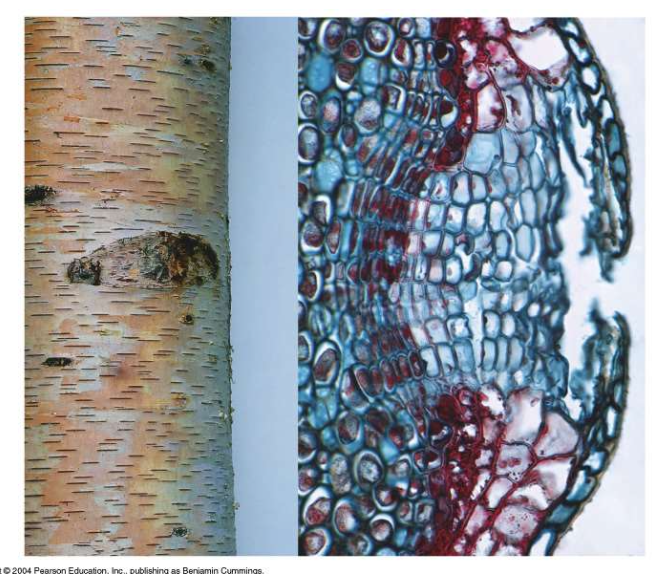
Lenticels
Small openings in outer bark of stems and roots that allow gas exchange which is blocked by suberin

Antimicrobials
Latex
Resins
Flowering plants - produce forms of latex
• Milky substance
• Blocks entry of disease-causing organisms
• Contains compounds with growth inhibiting
properties
Pines and SVP’s - produce resins
• Flow through canals in secondary xylem and phloem, periderm and leaves (turpentine and rosin mix)