AP Psych: The Biological Perspective
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sept 2023 Class notes: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1ZM_2C41RfGZuP6Tfa7VOQlrLRKLkkxDqoCysyg8lCWw/edit?usp=sharing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Nervous System
Extensive network of specialized cells that carry information to and from ALL parts of the body.
Neuroscience
Deals with the function and structure of the neurons, nerves, and nervous tissue in relationship to learning and behavior.
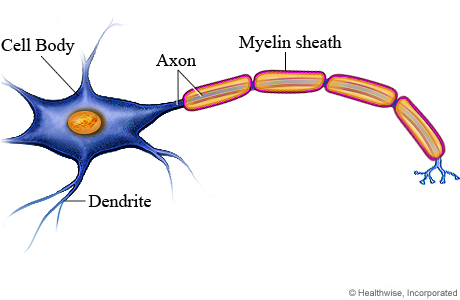
Neuron
The basic cell that makes up the nervous system and which receives and sends messages within that system.
Dendrite
Branch-like structure that receives messages from other neurons.
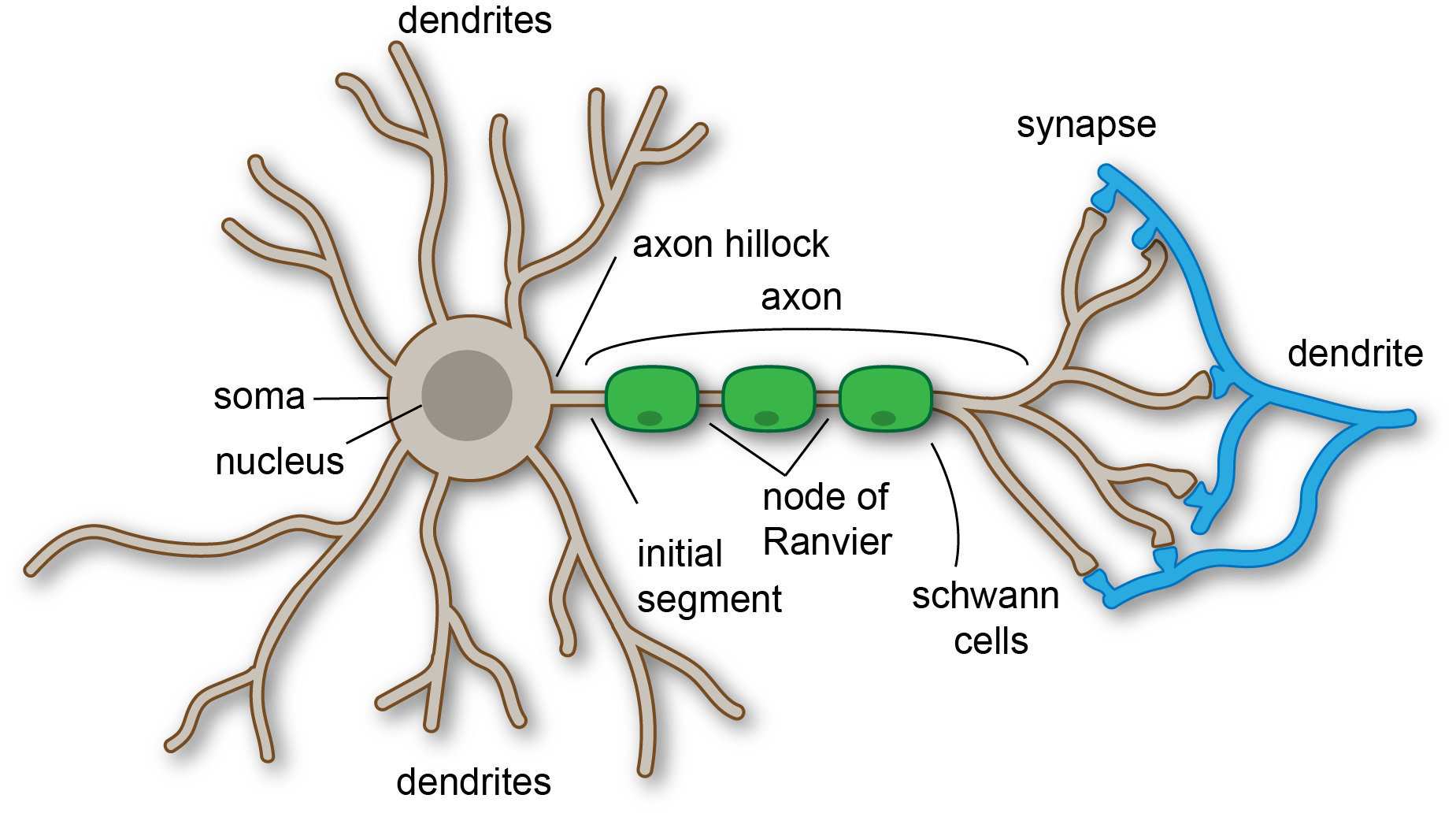
Soma
The cell body of the neuron, responsible for maintaining the life of the cell.
Axon
Long tube-like structure that carries the neural message to other cells. Can never touch eachother.
Glial Cells (brain cells)
Give support to the neurons to grow on, give nutrients to neurons, and produce myelin (to coat and protect axons).
Myelin Sheets (brain cells)
Fatty substances made by glial cells that coat the axons on neurons to insulate, protect, and speed up neural impulse. Clean up waste and dead neurons
Ions= charged particles
How do they differ inside and outside neurons?
Inside neurons= negatively charged potassium ions
Outside neurons= positively charged sodium ions
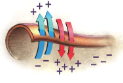
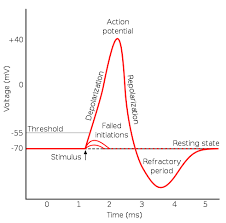
Resting potential
When neurons are NOT firing a neural impulse, POLARIZED.
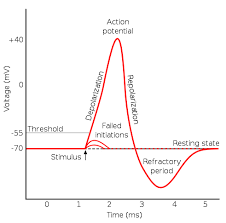
Action potential
When a neuron releases a neural impulse the electrical charge reverses in the axon, DEPOLARIZED.
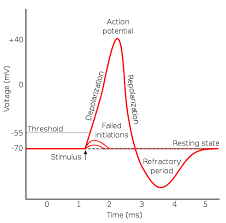
All-or-None
Neurons must fire completely or not at all (similar to a gun).
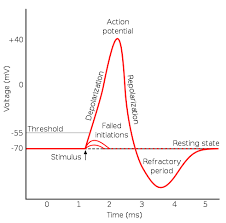
Refractory period
After a neural impulse is fired the cell is depolarized and must go through a rest period to re-polarize in order to fire again.
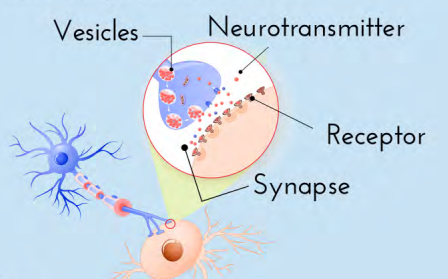
Axon terminals: Synaptic knob: Synaptic vesicles
Branches at end of axon.
Synaptic knob/terminal button: rounded areas on the end of axon terminals.
Synaptic vesicles: sack-like structures found inside the synaptic knob containing chemicals.
Messages sent through neurotransmitters.
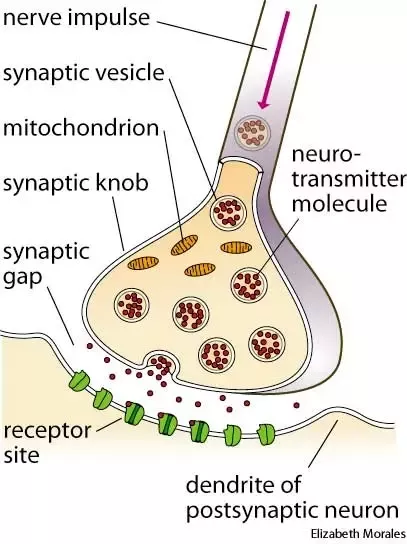
Neurotransmitters
Chemical found in the synaptic vesicles which, when released, affect the next cell. Wrong amount= chemical imbalance.
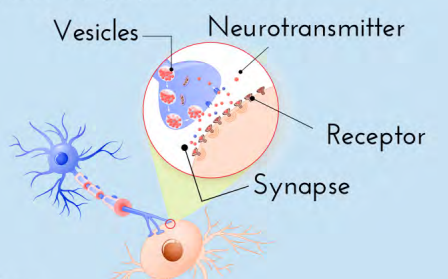
Synapse/Synaptic gap
Fluid filled space between axon terminal and dendrites of two different cells.
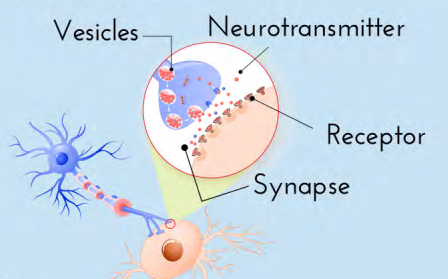
Receptor sites
Proteins on the dendrite (or muscles or glands) that are shaped to allow only certain neurotransmitters to bind there (like a reserved parking spot).
When all are full the neurotransmitters must return to synapse.
Excitatory neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter that causes receiving cells to INCREASE firing.
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter that causes receiving cells to DECREASE firing.
How do agonist chemical substances affect neuronal communications?
Mimic or enhance the effects of neurotransmitters on the receptor sites of the next cell, INCREASING or DECREASING the activity of the cell.
EX: Opioid drugs like heroin
Reuptake
When neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles.
Post Synaptic= receiving neuron
Pre Synaptic= sending neuron
Nerves
Bundle of axons in the body that travel together through the body.
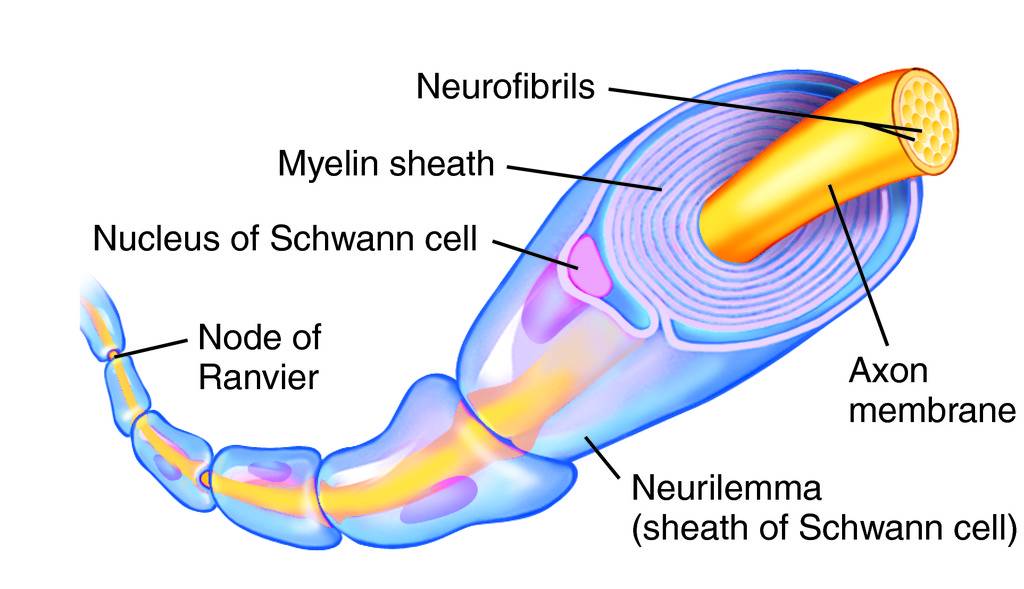
Neurilemma (Schwann’s membrane)
Tunnel where damaged nerve fibers can repair themselves, protect peripheral nerve fibers.
Sensory neuron
Neuron that carries info from the senses to the central nervous system. Afferent neurons (“a” for approaching CNS).
Motor neuron
Carries messages from the central nervous system to the muscles. Efferent neuron (“e” for exiting CNS).
Interneuron
In the center of the spinal cord, receives info from the sensory neurons and sends commands to the muscles via motor neurons (relay neuron).
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord.
Spinal cord
Long bundle of neurons that carries messages to and from the body to the brain. Responsible for fast, lifesaving reflexes.
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves and neurons are not contained in the brain and spinal cord but that run through the body.
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system (PNS) (Sensory vs Motor Pathways)
Nerves that carry info from the senses to the CNS and from the CNS to the VOLUNTARY muscle of the body.
Sensory pathways: nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS, consisting of sensory neurons (afferent).
Motor pathways: nerves coming from CNS to the VOLUNTARY muscles, consisting of motor neurons (efferent).
Autonomic Nervous System (PNS) (Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic divisions)
Nerves that control all the INVOLUNTARY muscles, organs, and glands.
Sympathetic Division (fight or flight): responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal.
Parasympathetic Division: restores to normal functioning after arousal, day-to-day functions.
Deep Lesioning (clinical study)
Insertion of a thin insulated wire into the brain through which an electrical current is sent that destroys the brain cells at the tip of the wire, mainly done on animals.
Electrical Stimulation of the Brain (ESB) (clinical study)
Milder electrical current that causes neurons to react as if they have received a message.
Human Brain Damage (clinical study)
Can show where function or thought occur (or doesn’t) (not causing damage, done as a case study).
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Machine designed to record the brain wave patterns produced by electrical activity of the surface of the brain.
Usually used to diagnose sleep issues.
Computed Tomography (CT/CAT Scan)
Brain-imaging method using computer controlled X-rays of the brain, but won’t show function only solid mass/bone in brain.
Can show issues in brain structure like tumors or blood clots.
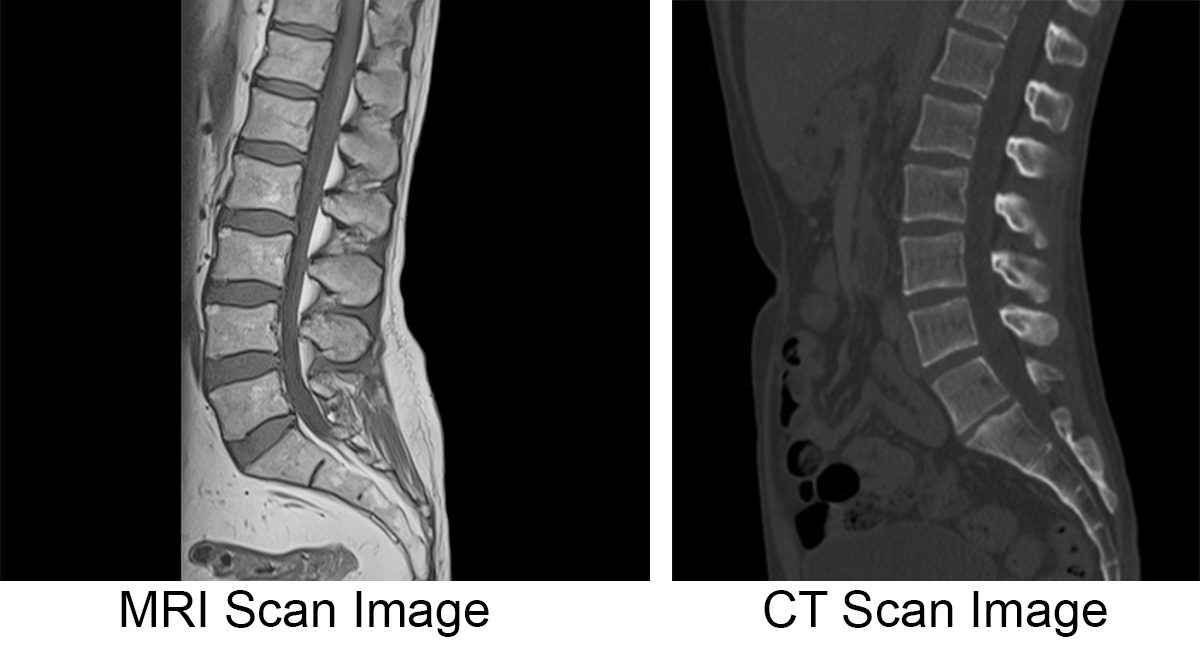
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce detailed images of the brain.
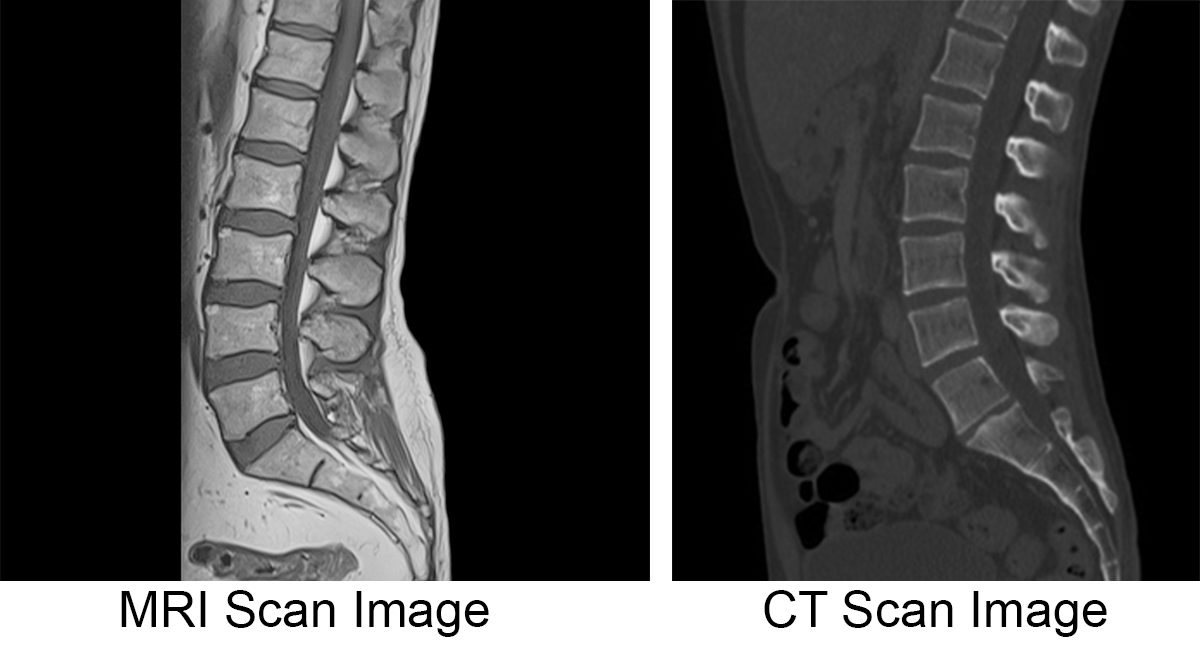
Functional MRI (fMRI)
A computer makes a sort of “movie” of changes in the activity of the brain using images from different time periods.
Shows structure and function, shows where brain oxygen levels change as subject completes tasks
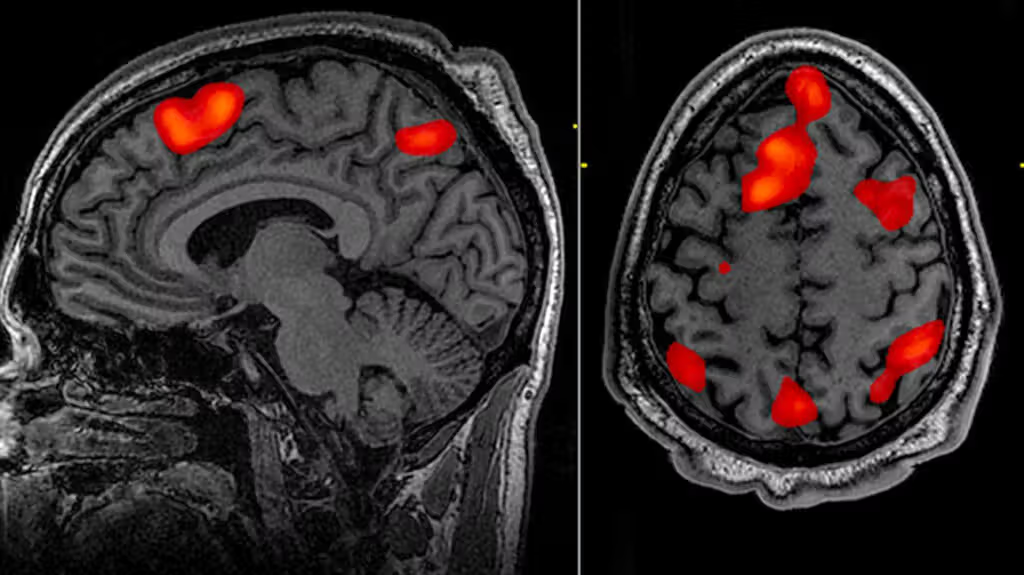
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Brain-imaging method where radioactive sugar is injected into a subject and a computer compiles a color-coded image of activity in the brain with lighter colors indicating more activity. Shows what part of the brain is NOT functioning.
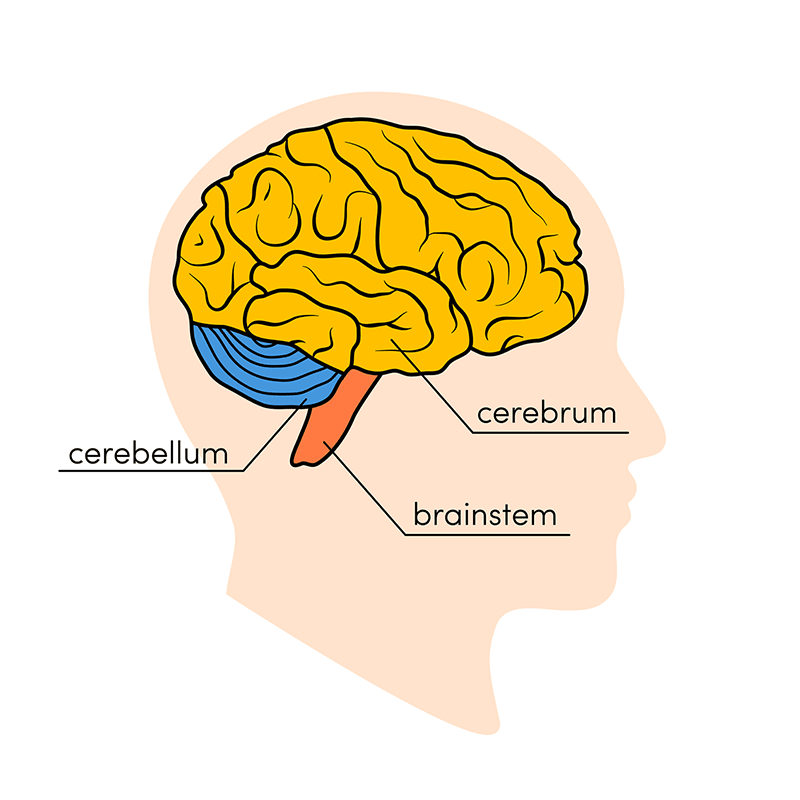
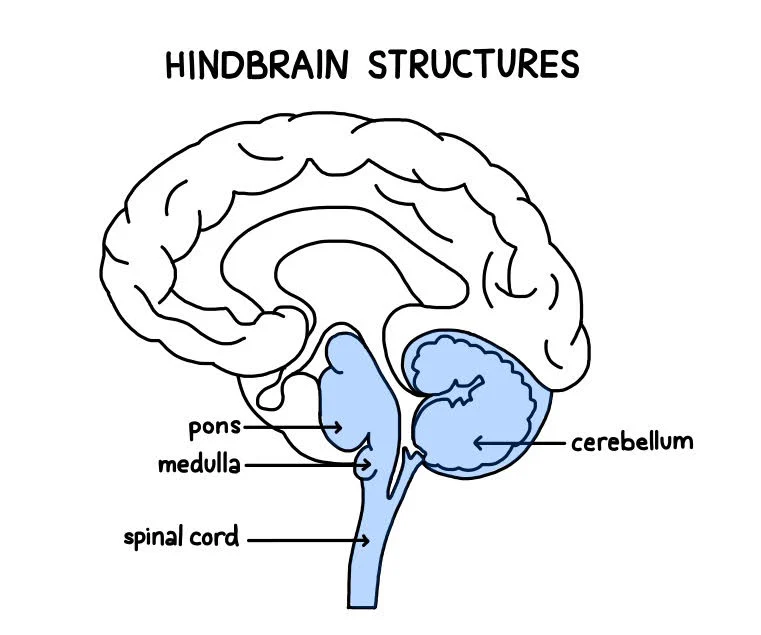
Medulla (Brain Stem/Hindbrain)
First large swelling at the top of the spinal cord, forming the lowest part of the brain. Responsible for life-sustaining functions (breathing, swallowing, digesting, and heartbeat).
Alcohol poisoning stops last (breathing)
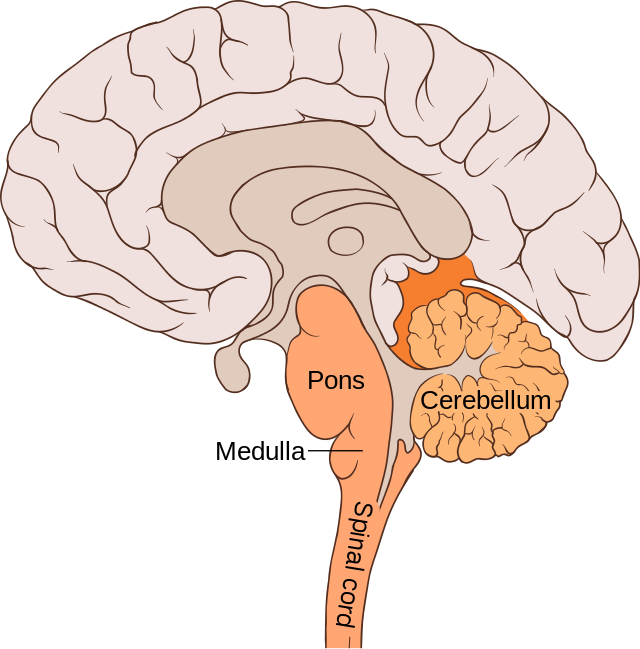
Pons (Brain Stem/Hindbrain)
Larger swelling above the medulla that connects the top of the brain to the bottom. Plays a part in sleep, dreaming, left-right body coordination, and arousal (alertness).
Keeps you aware even when asleep (can be woken up by a sound or sunlight), blacking/passing out= no awareness.
Pons: Pillow: Sleeping and Dreaming
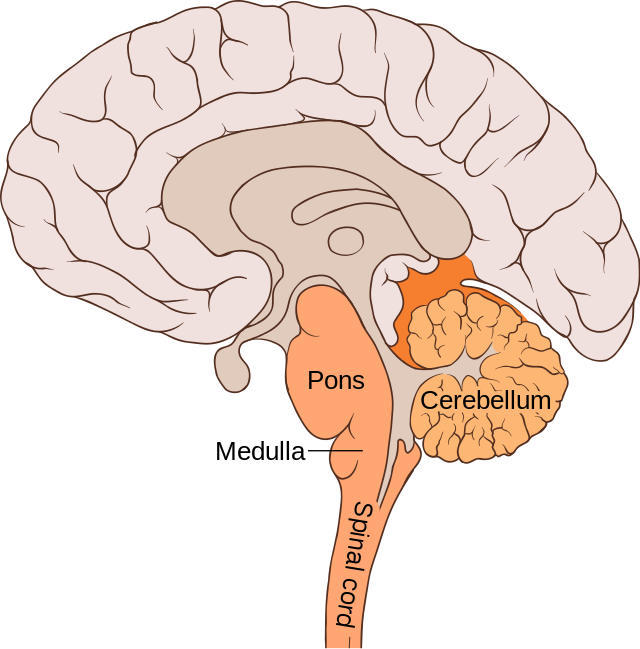
Cerebellum (Brain Stem/Hindbrain)
Part of the lower brain behind the Pons that controls and coordinates involuntary, rapid, fine motor movement and balance (“little brain”).
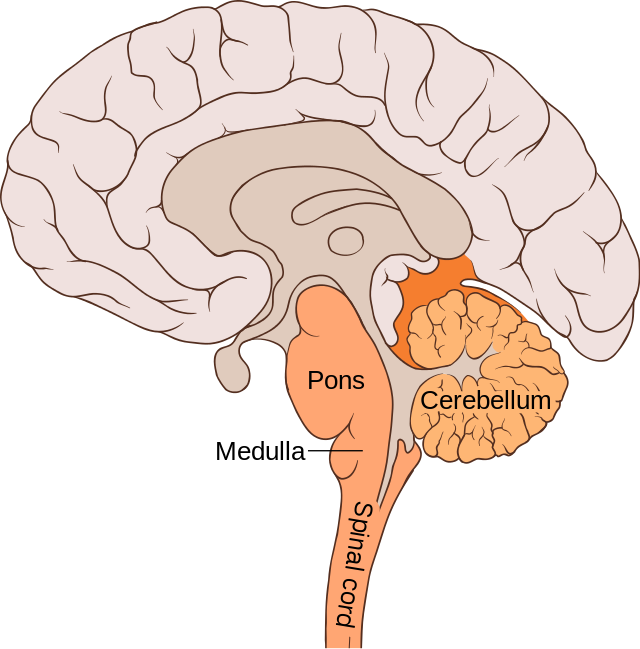
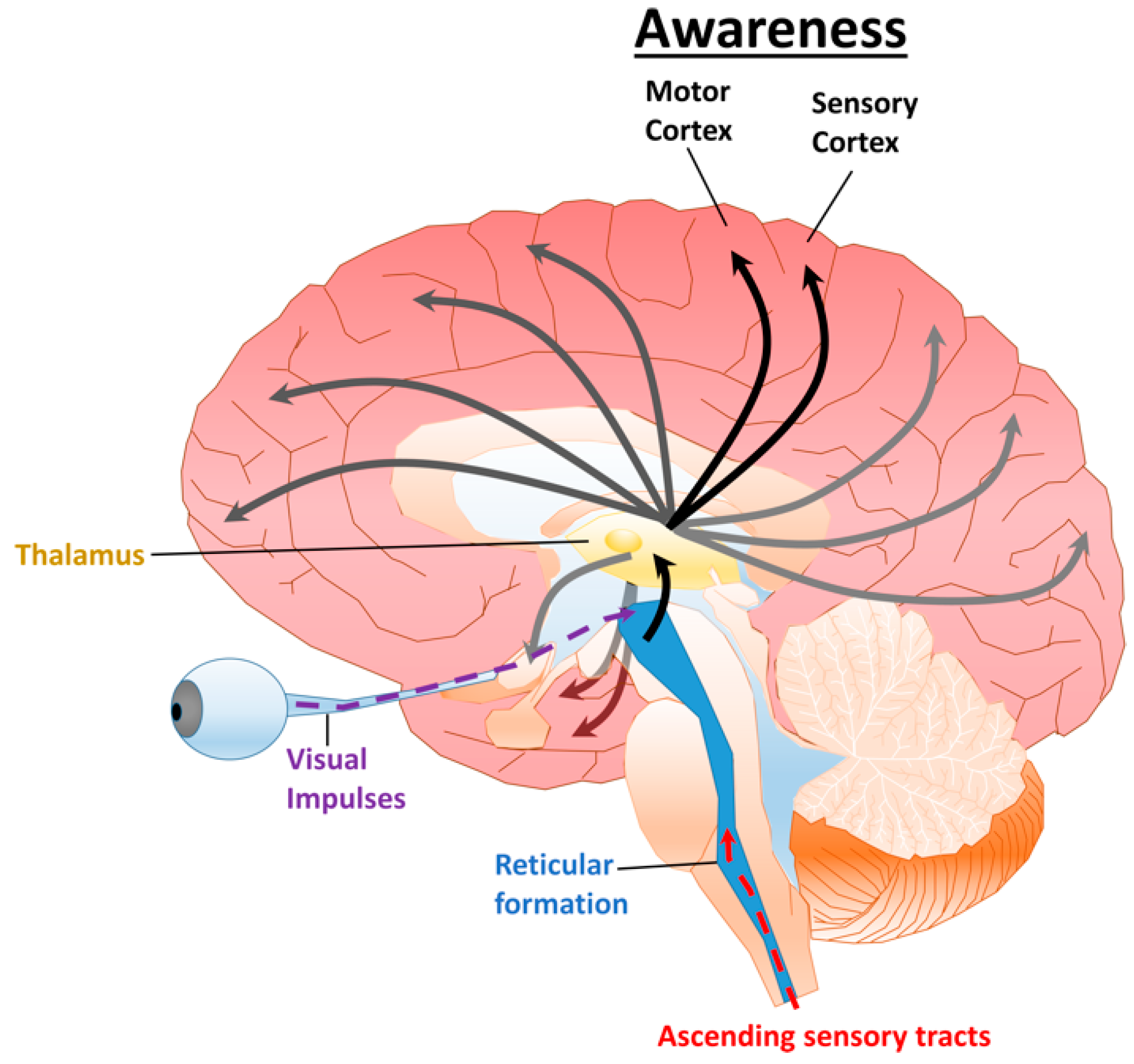
Reticular Formation (RF) (Brain Stem/Hindbrain) (Reticular Activating Device)
Neurons that extend from hindbrain to midbrain; from middle of the medulla and the Pons to slightly beyond.
Reticular Activating Device: selective attention and arousal/alertness to incoming stimuli.
Acts as sensory filter, determines which incoming info will reach the cerebral cortex
Limbic System (under cortex)
Several brain structures under the cortex, involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation.
Hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
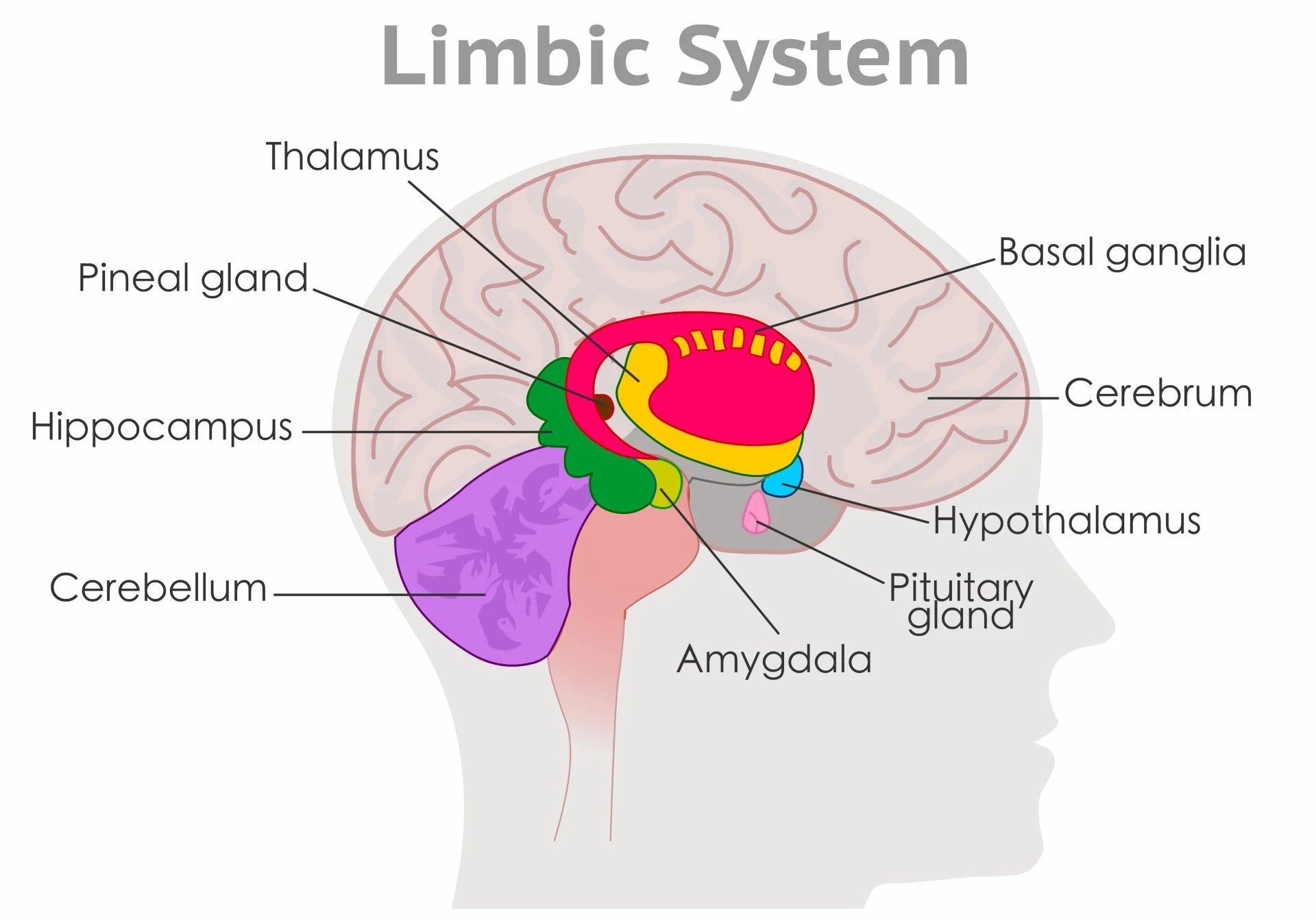
Thalamus
Limbic System. Center of brain/midbrain.
Relays sensory info (except for smell; olfactory bulbs) from the lower part of the brain (spinal cord) to proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory info before sending to its proper area.
Olfactory bulb
Two projections under the front of the brain that receive info about smell from the receptors in nose.
Hypothalamus
Limbic System. Center of brain/midbrain.
Small structure in the brain located below the thalamus and directly above the pituitary gland, responsible for motivational behavior such as sleep, hunger, thirst, body temp. and sex.
(hypo= below in latin, hypothalamus= below the thalamus)
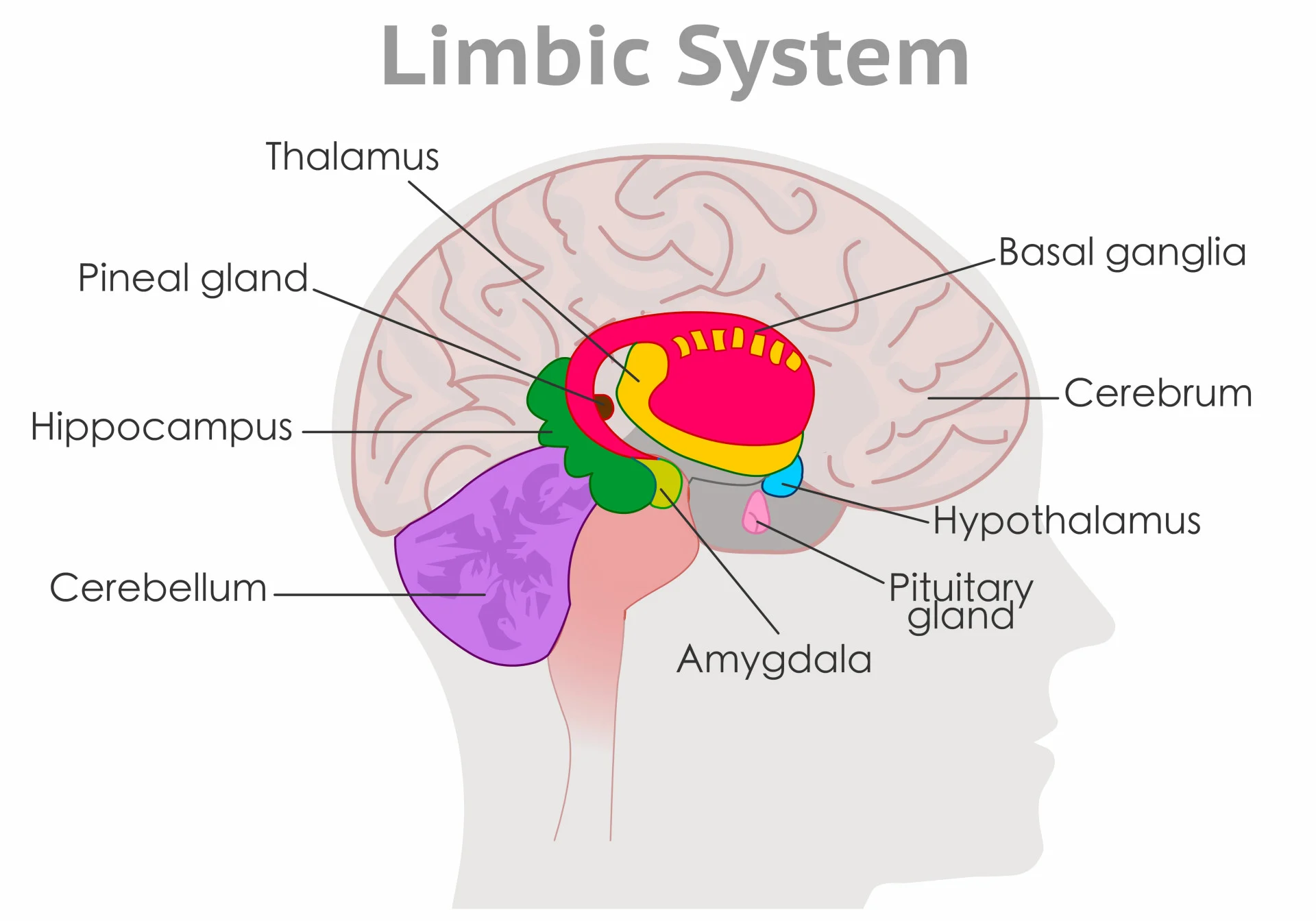
Hippocampus
Curved, inside each temporal lobe. Responsible for formation of long-term memories and the storage of memory for location of objects and new info (Hippos have good memories).
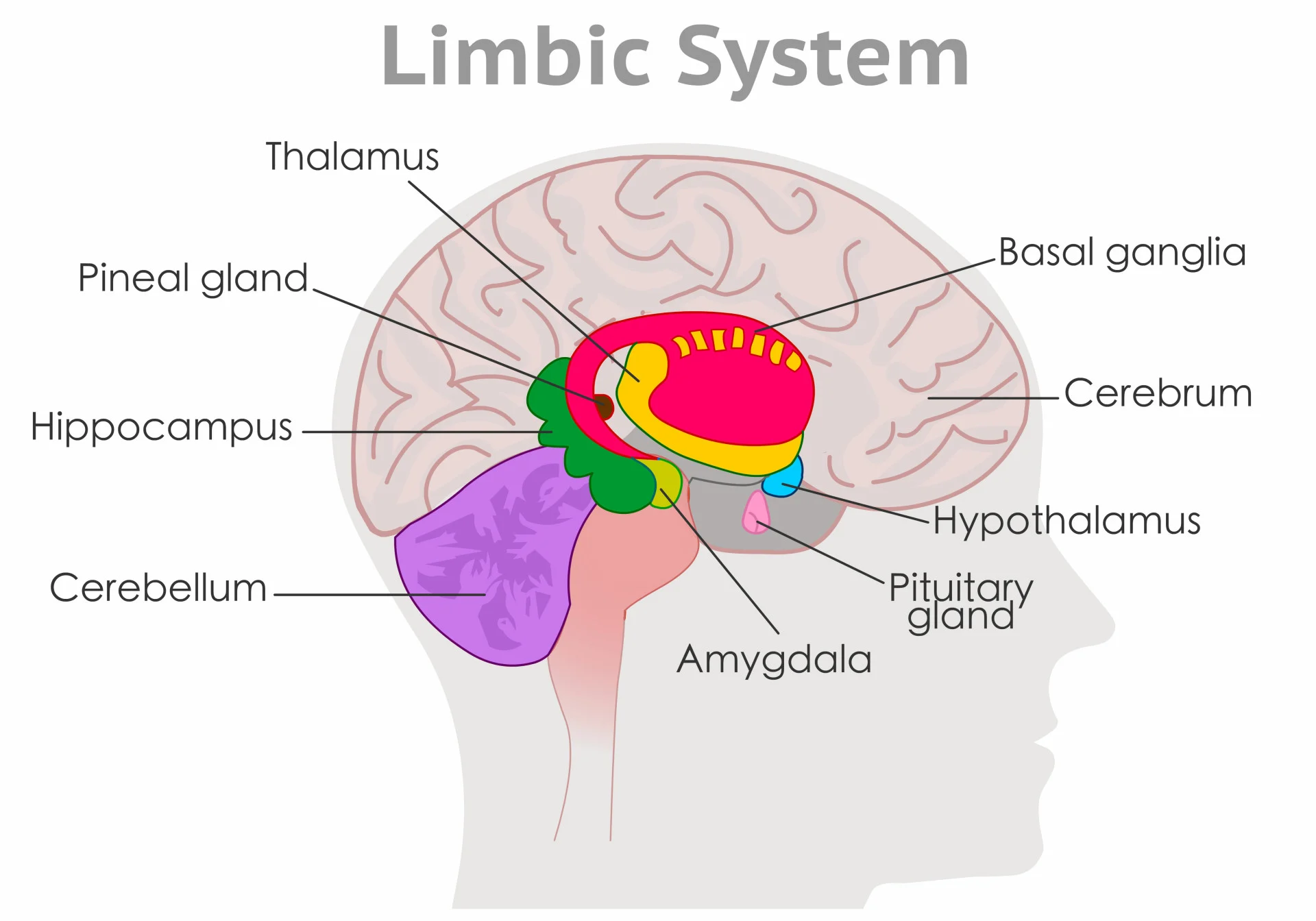
Amygdala
Near hippocampus. Responsible for fear responses and memory of fear; anger and sex drive.
Cortex
Outermost covering of the brain, made up of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. Gray Matter. Made up of 4 lobes.
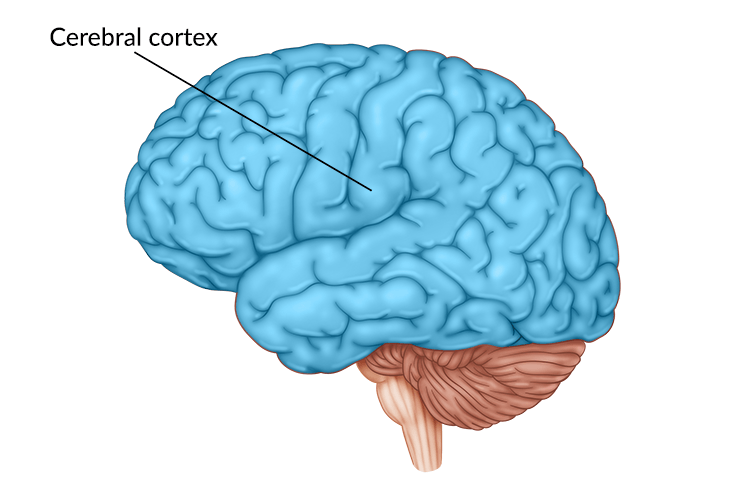
Corticalization
Wrinkling of the cortex.
Cerebral hemisphere
Two sections of the cortex on the left and right sides of the brain.
Corpus callosum
Thick band of neurons connecting the right and left cerebral hemisphere.
Brain plasticity
Brain’s ability to wire and re-wire synaptic connections.
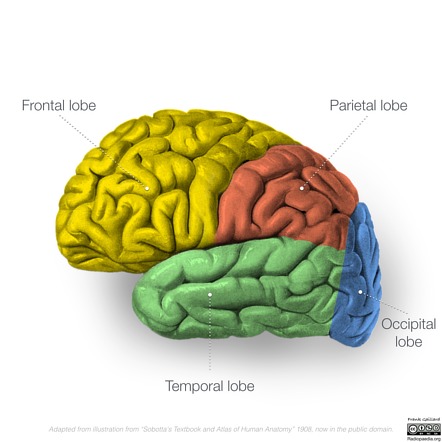
Occipital lobe
Section of brain in rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere, containing the visual centers of the brain (eyes in the back of your head).
Primary visual cortex & Visual association cortex
Occipital Lobe
Primary visual cortex: processes visual info from eyes.
Visual association cortex: identifies and makes sense of visual info (acts as an assistant to primary cortex).
Parietal lobes
Sections on the top and back of the brain in each cerebral hemisphere containing centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations.
Somatosensory cortex
Part of parietal lobes. Neurons in the front of the parietal lobes responsible for processing info from the skin and internal body receptors for touch, temperature, body position, and possibly taste.
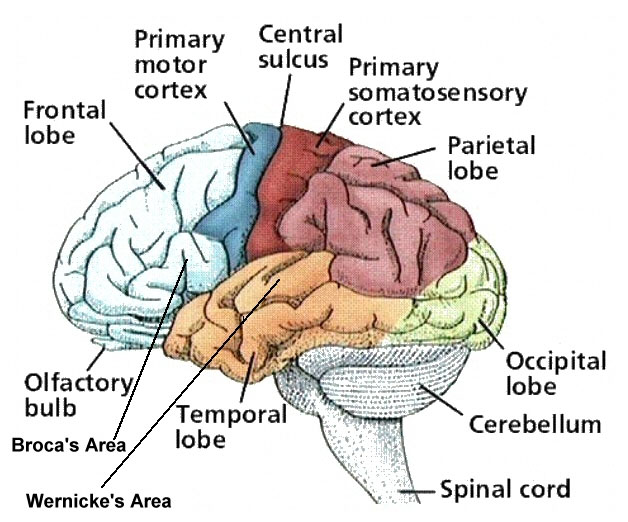
Frontal lobes
Front and top of brain. Responsible for higher mental processes, decision making, speech, and muscular movement.
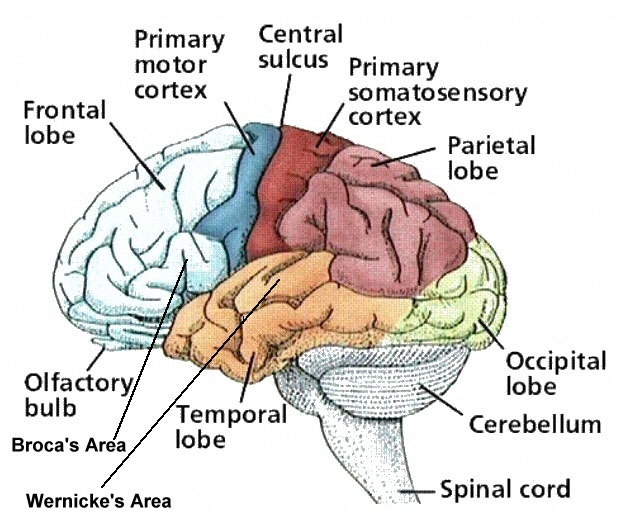
Motor cortex
Part of frontal lobe. Responsible for sending motor commands to the muscles of the somatic (voluntary) nervous system.
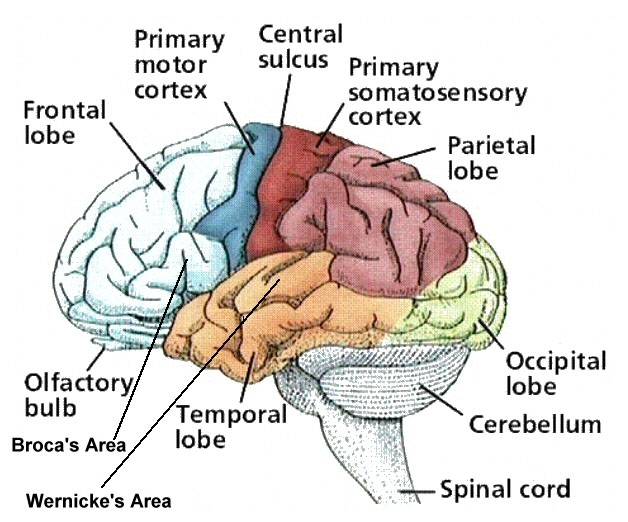
Prefrontal cortex
Executive of the brain in frontal lobes. Controls decision making, planning, judgement, and self control.
Temporal lobes
Behind temples. Responsible for sense of hearing and meaningful speech.
Primary auditory cortex & auditory association cortex
Temporal lobe.
Primary auditory cortex: processes auditory info from ears.
Auditory association cortex: identifies and makes sense of auditory info.
Olfactory cortex
Temporal lobe. Smell
(NOT the same as olfactory bulbs).
Association areas
Areas in each lobe of the cortex responsible for coordination, interpretation of info, and higher mental processing.
Association Areas: Broca’s aphasia
Condition resulting from damage to Broca’s area (left frontal lobe, produces speech), affected person is unable to speak fluently and likely to mispronounce words, and speak haltingly.
Left Hemisphere= language, logic, mathematics
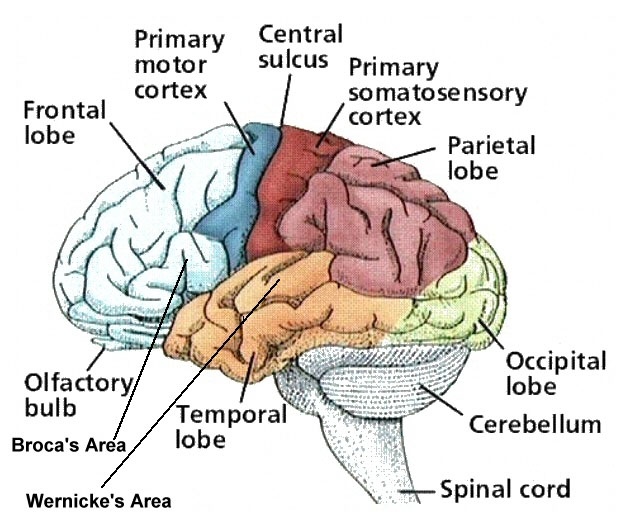
Association Areas: Wernicke’s aphasia
Condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (left temporal lobe, understands speech), affected person unable to understand or produce meaningful language.
Left Hemisphere= language, logic, mathematics
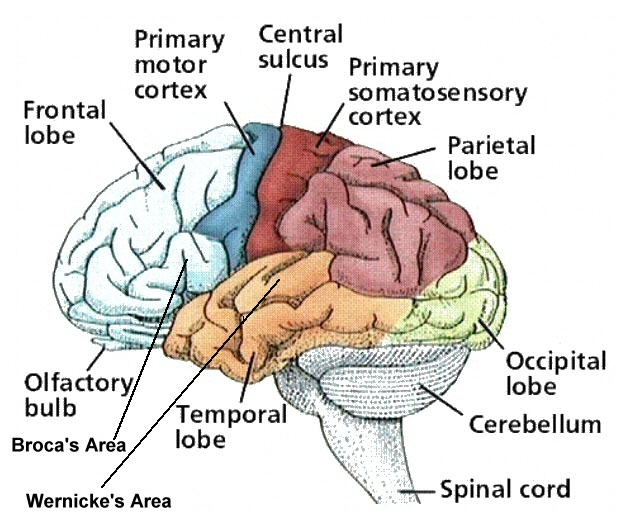
Cerebrum
Upper part of the brain consisting of two hemispheres and the structures that connect them.
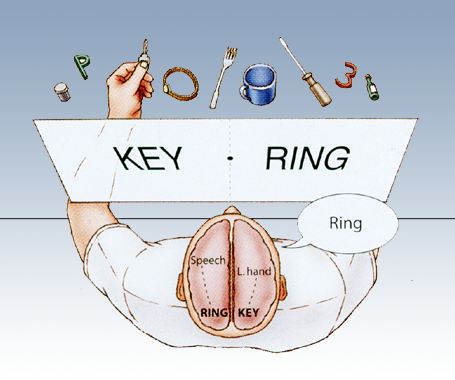
Split Brain Research (R. Sperry & M. Gazzangia)
Case study of patients with severed corpus callosum (connects the brain hemispheres, and sends messages between them). Study shows specialization in right & left hemispheres.
Usually only severed to help severe epilepsy.
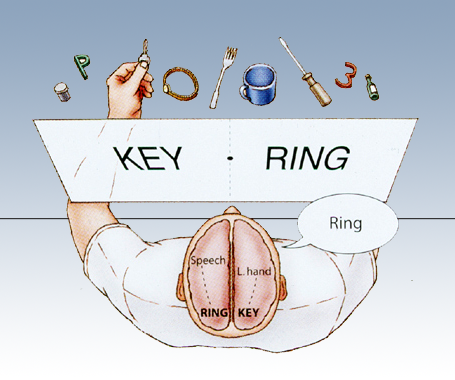
Lateralization (result of split brain research)
Two hemispheres of the brain have special functions. Right hemisphere = left side of the body. Left hemisphere =right side of the body.
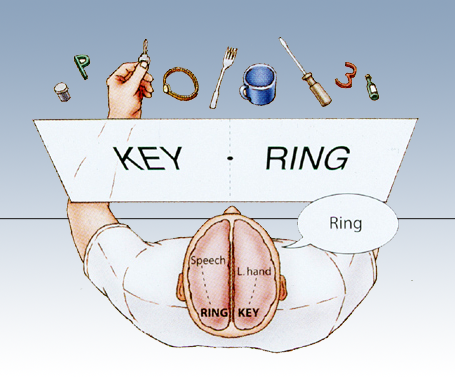
Right vs. Left side of the brain (functions) (results of split brain research)
Left side:
Language, writing, logical thought, analysis, and math abilities.
Processes info sequentially
CAN speak
Right side:
Emotions, expressions, spatial perception, recognition of faces, patterns, melodies.
Processes info globally
CANNOT speak
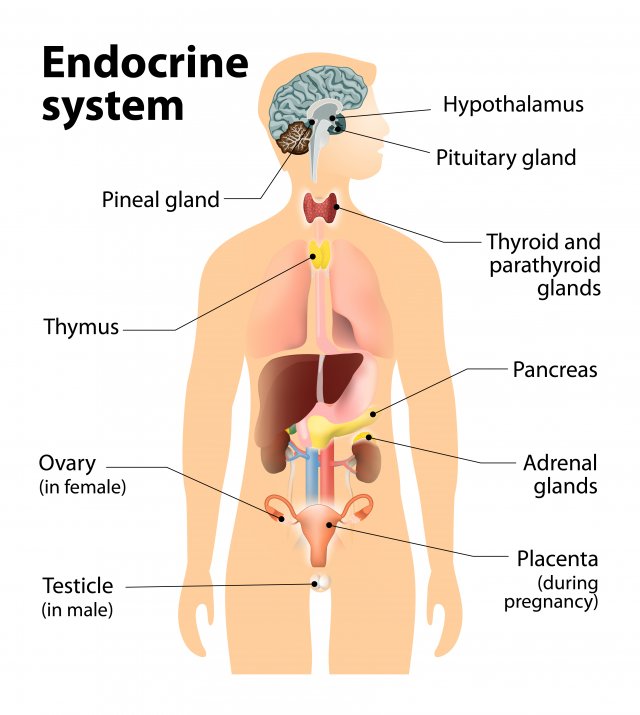
Endocrie glands
glands that secrete hormones (chemicals) DIRECTLY into bloodstream (slower than nervous system which uses neurotransmitters).
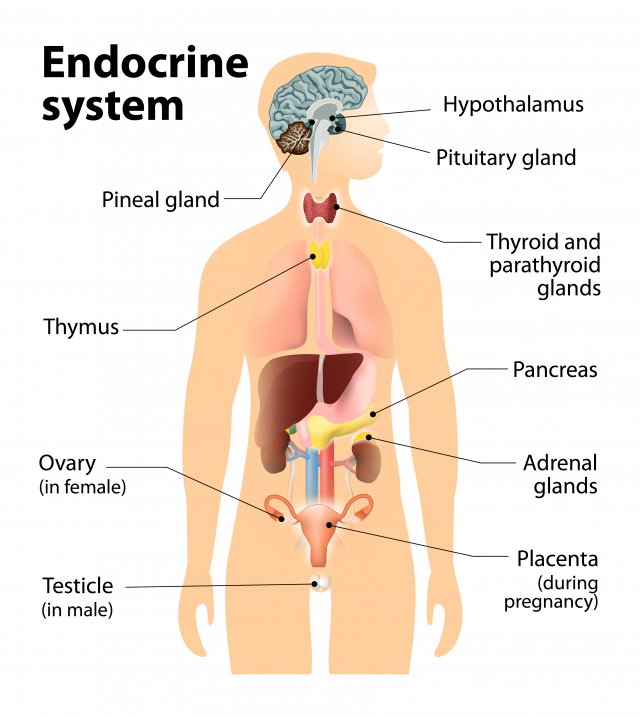
Pituitary gland
In hypothalamus. Secretes human growth hormones and influences all other hormone-secreting glands. Master Gland.
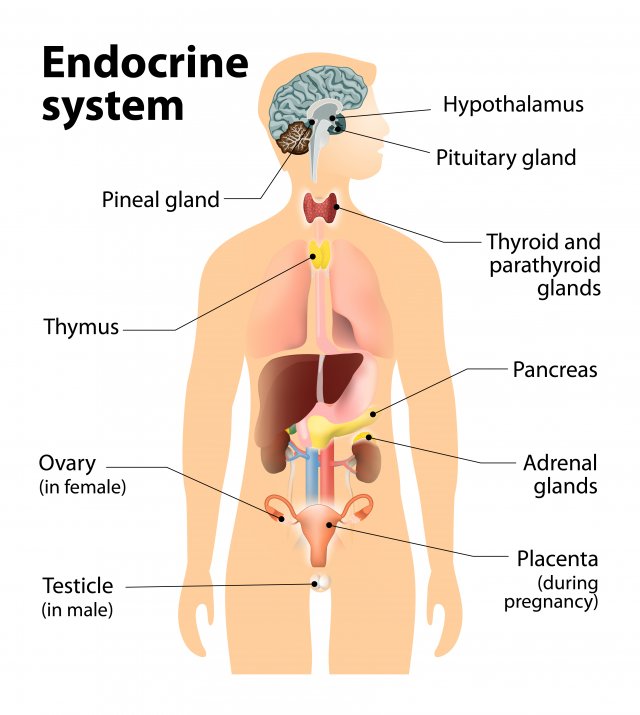
Pineal gland
Base of cerebrum. Secretes melatonin (sleep inducing hormone).
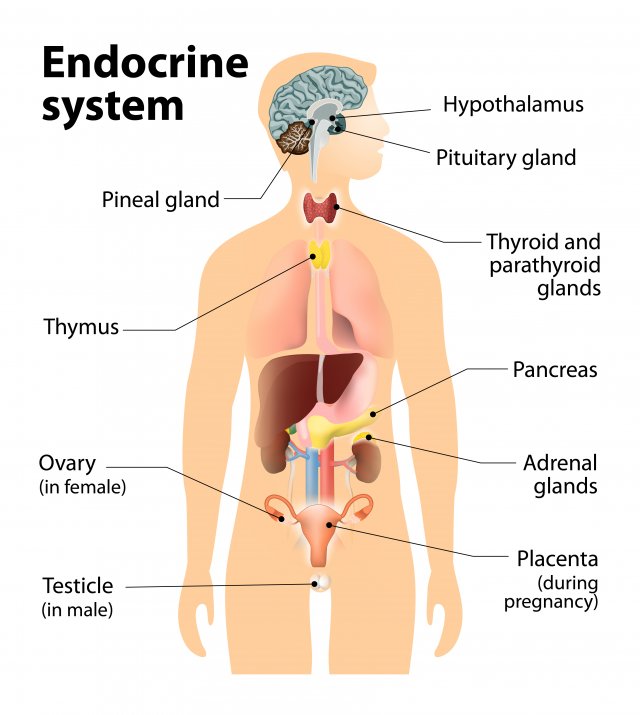
Thyroid gland
In the neck. Regulates metabolism through thyroxin.
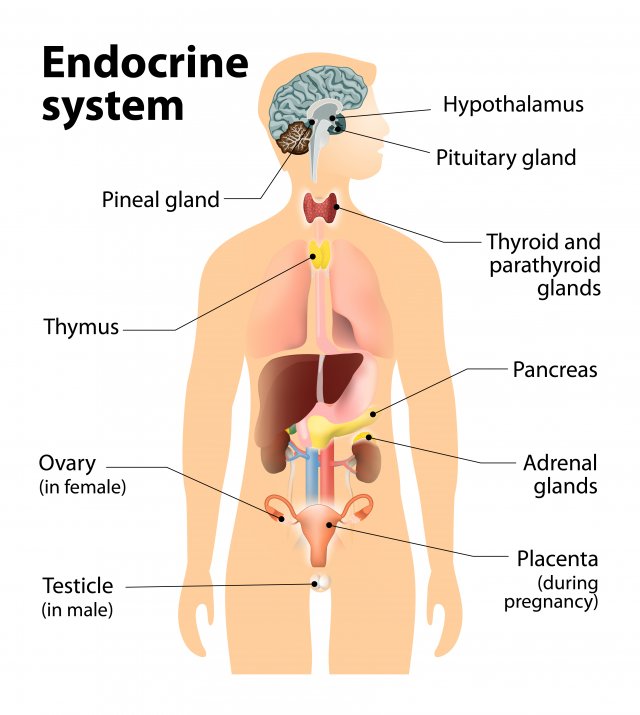
Pancrease
Controls levels of sugar in the blood (diabetic vs hypogycemic).
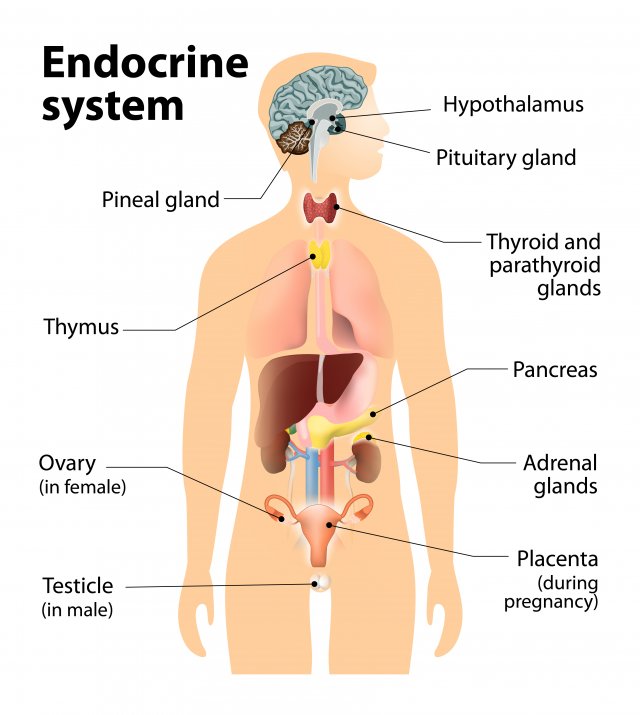
Gonads
Sex glands, secrete hormones that regulate sexual development/behavior and reproduction.
Ovaries= female gonads (estrogen)
Testes= male gonads (testosterone)
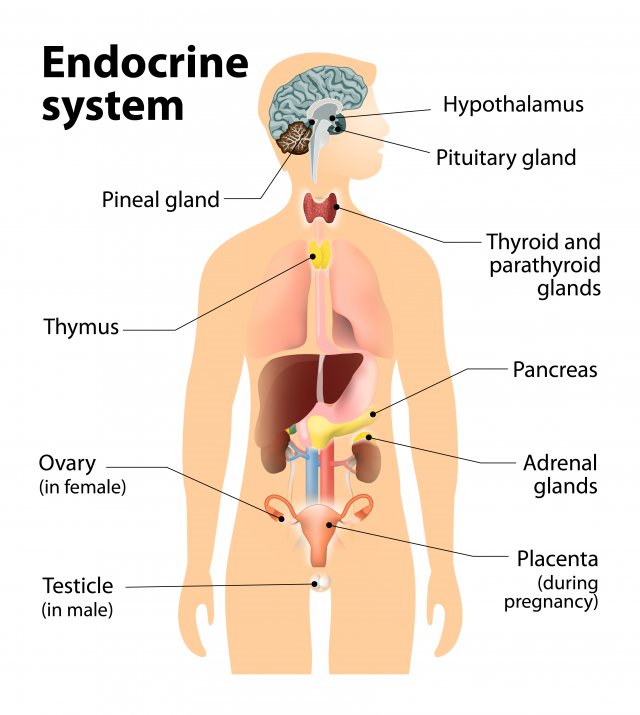
Adrenal glands
Top of each kidney, secrete +30 hormones. Deal with stress (fight or flight), regulate salt intake, and provide a second source for sex hormones.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter.
Functions: voluntary muscle movements, memory
Disorder: ACh producing neurons deteriorate with Alzheimers
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter.
Functions: pleasure, muscular control, learning attention
Disorder: high levels associated with schizophrenia
Endorphins
Neurotransmitter.
Functions: natural pain relief
Disorder: low levels can cause chronic pain; fibromyalgia
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter.
Functions: alertness and arousal
Disorder: low levels correlate with depression
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter.
Functions: appetite, sleep, mood
Disorder: low levels correlate with depression
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Neurotransmitter
Function: primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Disorder: low levels associated with anxiety and seizure disorders
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter
Function: primary excitatory neurotransmitter
Disorder: high levels associated with seizure disorders
4 parts of hindbrain
Medulla, Pons, Reticular Formation, and Cereblum.
Brainstem= Pons and Medulla
Difference between neurotransmitters and endocrine glands/hormones?
Neurotransmitters: quick, operate in the synapses between neurons, act between receptor sites of receiving neurons.
Hormones: slower, operate in the bloodstream, many receiving sites throughout body.
How do antagonist chemical substances affect neuronal communications?
BLOCK or REDUCE a cell’s response to the action of other chemicals or neurotransmitters.
EX: caffeine, blocks adenosine
Sympathetic Division (fight or flight)
Part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal.
Parasympathetic Division:
Part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Restores to normal functioning after arousal, day-to-day functions.