biochem WEEK 2 lecture 3
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
amino acids intro, derivative/modifications, peptide bonds
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
12.5
arginine (R) side chain pKa
3.9
aspartic acid (D) side chain pKa
8.3
cysteine (C) side chain pKa
4.2
glutamic acid (E) side chain pKa
6.0
histidine (H) side chain pKa
10.0
lysine (K) side chain pKa
10.1
tyrosine (Y) side chain pKa
8
N terminus (-NH3+) pKa
4
C terminus (-COO-) pKa
+1
amino (N-term, lysine (K))charge when pH is below pKa
0
hydroxyl (serine(S), threonine(T), tyrosine(Y)) charge when pH is below pKa
0
SH (cysteine(C)) charge when pH is below pKa
0
carboxylate (C-term aspartic acid(D), glutamic acid(E)) charge when pH is below pKa
+1
imidazole (histidine(H)) charge when pH is below pKa
+1
Guanidinium (arginine(R)) charge when pH is below pKa
0
amino (N-term, lysine (K))charge when pH is above pKa
-1
hydroxyl (serine(S), threonine(T), tyrosine(Y)) charge when pH is above pKa
-1
SH (cysteine(C)) charge when pH is above pKa
-1
carboxylate (C-term aspartic acid(D), glutamic acid(E)) charge when pH is above pKa
0
imidazole (histidine(H)) charge when pH is above pKa
0
Guanidinium (arginine(R)) charge when pH is above pKa
Ala, Ile, Phe
three amino acids with non-polar side chains (from least to most hydrophobic)
gly, ala, pro, val, leu, ile, met
amino acids with aliphatic non-polar side chains, not many H bond donors or acceptors in R groups
glycine
AA has no side chain, alpha carbon is not a chiral center
proline
AAs side chain makes a ring by bonding with its main chain Nitrogen, rigidifies and provides structure
isoleucine
AA has aliphatic non polar side chain, is one of two amino acids with a chiral side chain (B carbon)
threonine
AA has uncharged polar side chain, is one of two amino acids with a chiral side chain (B carbon)
Ser, Thr, Cys, Asn, Gln
amino acids with uncharged polar side chains, have plenty of H bond donors and acceptors
cysteine
AA can form disulfide bridges, AA side chain has S which is a good nucleophile, is good in coordinating metals
Lys, Arg, His
amino acids with positively charged side chain
histidine
AA often involved in acid base catalysis, side chain s good in coordinating metals, has a pKa of around 6 so at a neutral pH it is in both its protonated and deprotonated state
Asp, Glu
amino acids with a negatively charged side chain, side chains are very hydrophilic, carboxylates can often coordinate metals (usually Mg2+ and Ca2+)
Phe, Tyr, Trp
amino acids with aromatic side chains that can absorb UV light
Tyr, Trp
two amino acids with aromatic side chains that can absorb much more light than Phenylalanine
-NH3+
amino group at a pH below pKa
-OH
hydroxyl group at a pH below pKa
-SH
SH group at a pH below pKa
-COOH
carboxylate group at a pH below pKa
-NH+
Imidazole group at a pH below pKa (leave out aromatic ring stuff)
-NH2+
guanidinium group at a pH below pKa (just part that changes)
-NH2
amino group at a pH above pKa
-O-
hydroxyl group at a pH above pKa
-S-
SH group at a pH above pKa
-COO-
carboxylate group at a pH above pKa
N
Imidazole group at a pH above pKa (leave out aromatic ring stuff)
NH
guanidinium group at a pH above pKa (just part that changes)
enantiomer
a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror images of one another but cannot be superimposed one upon the other
L
configuration AA enantiomer R group points away, bolded up or dashed down
D
configuration AA enantiomer R group points towards, dashed up or bolded down
L-configuration
configuration all AAs in proteins (except one) have
below
dotted bonds point (above/below) plane of projection for the L configuration
above
dotted bonds point (above/below) plane of projection for the D configuration
GABA, histamine, dopamine
biologically active amino acid derivatives act as as neurotransmitters and are not incorporated into polypeptide chains of proteins
thyroxine
biologically active amino acid derivative important for cell-to-cell communication, hormone used to regulate metabolism
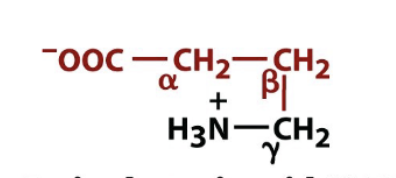
GABA
biologically active amino acid derivative
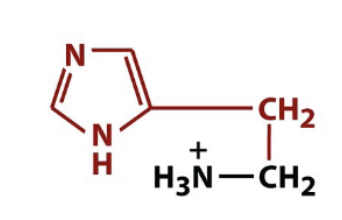
histamine
biologically active amino acid derivative
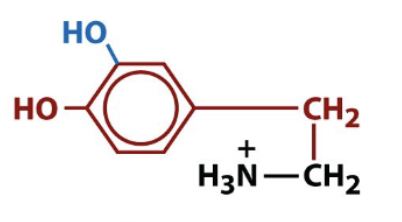
dopamine
biologically active amino acid derivative
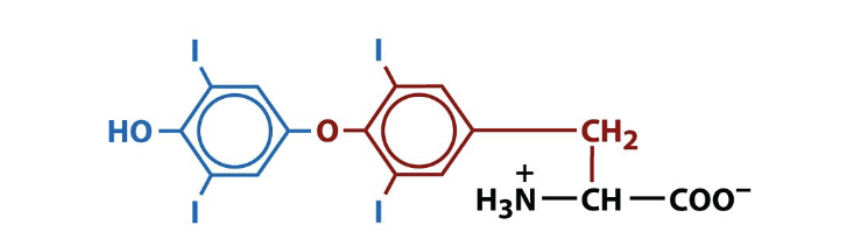
thyroxine
biologically active amino acid derivative
L-DOPA
deficiencies in dopamine production is associated with parkinson disease, what is the intermediate given to Parkinson patients?
cysteine
not genetically encoded, amino acid side chain modification in which thiol groups are oxidized forming a covalent bond “disulfide” bridge between this AAs residues
tyrosine
dopamine is derived from:
post translational modifications
done by specialized enzymes to make non standard amino acids in proteins
O-phosphoserine
amino acid side chain modification via phosphorylation, important for signal transduction
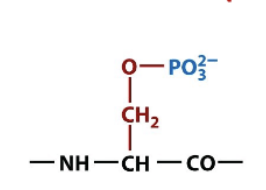
4-hydroxyproline
amino acid side chain modification via hydroxylation, major component of protein collagen for connective tissue
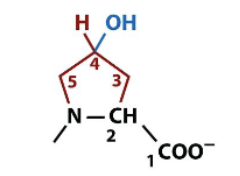
glutamate
amino acid that undergoes carboxylation to make a non standard AA
histidine
amino acid that undergoes methylation to make a non standard AA
lysine
amino acid that undergoes acetylation to make a non standard AA
Ser, Thr, Tyr
signal transduction: protein kinases phosphorylate these AAs side chains
protein kinases
attach phosphoryl groups (phosphorylate) to Ser, Thr, Tyr
protein phosphatases
remove phosphoryl groups (dephosphorylate) from Ser, Thr, Tyr
protein glycosylation
common type of modification of side chains on protein surface in which one or more sugars are attached to one or more specific residues
secreted and membrane associated
almost all of these proteins in eukaryotes are glycosylated
extracellular matrix (ECM)
formed by protein glycosylation, mixture of oligosaccharides and proteins between cells, key to cell positioning, crucial in complex precesses such as wound healing
O-glycosylation, N-glycosylation
two major types of glyosylation:
O
type of glycosylation, oligosaccharide is attached to side chain of Ser or Thr
N
type of glycosylation, oligosaccharide is attached to side chain of Asn
Ser, Thr
amino acids that undergo O-glycosylation (oligosaccharide attached to side chain O)
Asn
amino acid that undergoes N-glycosylation (oligosaccharide attached to side chain N)
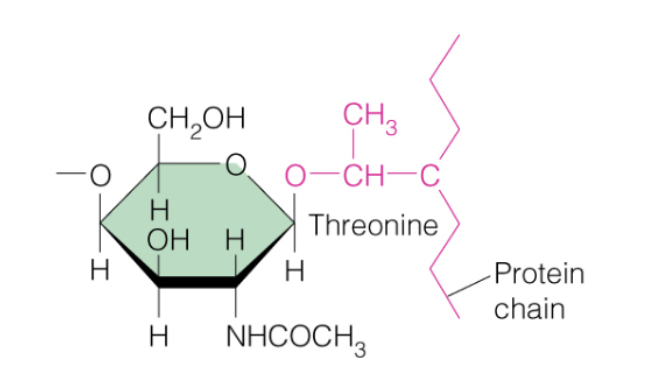
O-glycosylation
What kind of amino acid modification occurred in this picture?
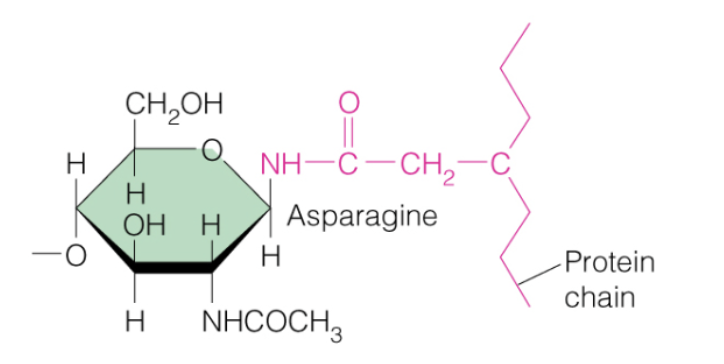
N-glycosylation
What kind of amino acid modification occurred in this picture?
pentasaccharide core
where all N linked glycans are added to during glycosylation forming a complex antenna
peptide bond
formed via condensation of two amino acids forming long polypeptide chains, process carried out by the ribosome
N term → C term
direction in which AAs are added forming polypeptide chains
aspartame
dipeptide used as an artificial sweetener, condensation of L-aspartic acid and methylated L-phenylalanine
L-aspartic acid, L-phenylalanine
condensation of these two amino acids results in the oligopeptide/dipeptide aspartame
L-phenylalanine
the condensation of two amino acids results in the dipeptide aspartame which is used as an artificial sweetener, which one is methylated?
reduced
most abundant form of the oligopeptide glutathione (GSH) which is highly reactive with free oxygen helping maintain reduced environment in cells
glutathione (GSH)
reduced form of this oligopeptide is highly reactive with free oxygen maintaining the reducing environment in cells
Glu, Cys, Gly
three AAs that make up glutathione (GSH) which is highly reactive with free oxygen helping maintain reduced environment in cells (order in proper linkage)
Glu, Cys
three AAs that make up glutathione (GSH) which is highly reactive with free oxygen helping maintain reduced environment in cells, these two are linked in a strange way via their side chains