Lecture 39: The Immune System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Identify invaders, eliminate or neutralize threat
these are the two challenges of fighting off bad things in our body
innate immune system
is immune system is in all multicellular plants and animals, 1st line of defense, always on, in the epithelial lining around host cells to destroy pathogens
generic
The innate system recognizes _____ elements common to many pathogens
evasion
In the innate immune system , the limited set of elements recognized makes _____ possible
specific
The adaptove immune system recognizes ____ features in individual pathogens
Toll-like receptors
these are expressed in macrophages and dendritic cells, expressed mostly on plasma membrane, but some on internal membranes, bind PAMPs to fight pathogens
macrophages and dendritic cells
Toll like receptors are expressed in ____ and ____ cells
mostly on plasma membranes, but some on internal membranes
where are Toll Like receptors expressed (location)
internal
receptors on the internal compartments of toll-like receptors identify _____ pathogens
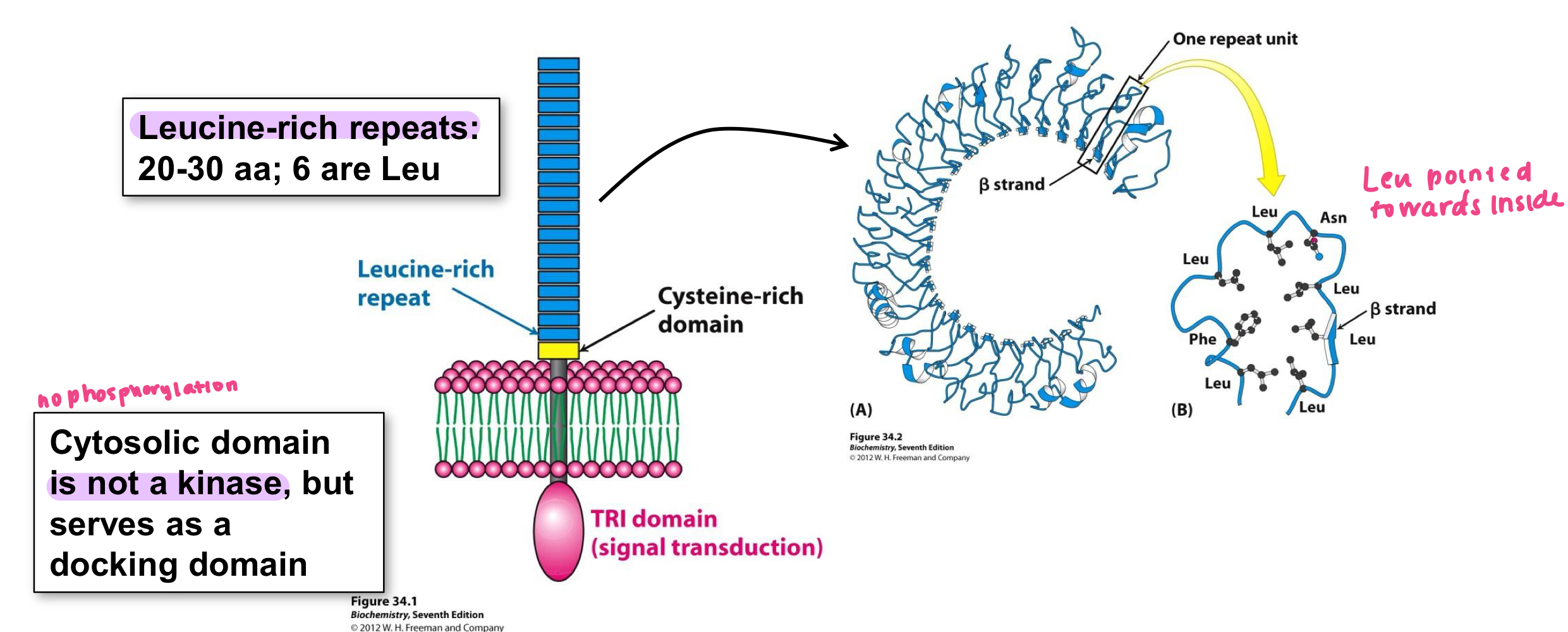
Leucine
Leucine residues are positioned towards the inside of the C where they congregate together
The toll-like receptor contains many ____-rich repeats that curve into a C-shape
PAMPS
Toll-like receptors bind _____
PAMPS
these are pathogen associated moelcular patterns, found on invading organisms and are a critical component
invading organisms
PAMPS are found primarily on ______ ______ and are usually a critical component of that organism
Dimerization, fever, endocytosis
When toll like receptor binds the PAMP, it causes _______________, which initiaes signal transduction to have __________, inflammation, and ____________ of the pathogen
adaptive immune system
this immune system is focused on fighting specific pathognes, has humoral (antibodies) and cellular (killer T cells)
humoral immune response (antibodies)
cellular immune response (killer T cells)
what are the two systems in the adaptive immune system
antibodies
these are called immunoglobulins, they bind antigens, and we make a lot of them in order to specifically target antigens
antigens
antibodies bind ______
antigen
this is the foreign macromolecule that antibodies bind to
epitope
this is the site of the antigen where the antibody binds to
Fab, Fc
these are the 2 subunits of an antibody
Fab
ab= antigen binding
these fragments bind the antigen on the antibody
Fc
c= constant
these fragments mediate the effector response for the immune system
2 light chains, 2 heavy chains
these are the chain components of an antibody
disulfide bonds
these are the bonds that bond the Fab and Fc units together
immunoglobulin fold
this is a beta sandwich held together bya disulfide bond
IgG
4 per heavy chain
2 per light chain
this antibody has 12 immunoglobulin domains
Fab
The antigens bind on which subunits?
IgG
what is the most common antibody in serum
IgA (dimer)
this immunoglobulin is found in external secretions such as tears or saliva
IgM (pentamer)
this immunoglobulin is the first responder
IgD (monomer)
This immunoglobulins function is not clear, but seems to be key in activating basophils
IgE (monomer)
this immunoglobulin acts in allergic responses
flexible
antibodies are ____________(flexible/stiff)
crosslinking, two spots
antibodies being flexible are good because it allows from _________-________________ and for the natibody to bind an antigen in ________ ____________
Avidity
this is how two binding sites helps on antibodies, by allowing the bond to stay present for a lot longer
on the ends of the Fab subunits
Where are the variable regions on an antibodY?
hypervariable loops
these are found on the loops on the end of each beta sandwich, allows different antigens to bind to different antibodies (specificity)
pre-determined, doesn’t, amplified
Specificity of antibodies is ______-______________, as the body __________(does/doesn't) know beforehand what it is going to bind to, and when an antigen enters, an ab is selected, then ____________
some or all
antigens may interact with ____ or ____ groups
recombination
We get millions of antibodies from so few genes via __________________ in antibody producing cells
variable, antibodies
By recombining different _________________ regions, we can get various different combinations of those regions to get almost infinite amount of ______________
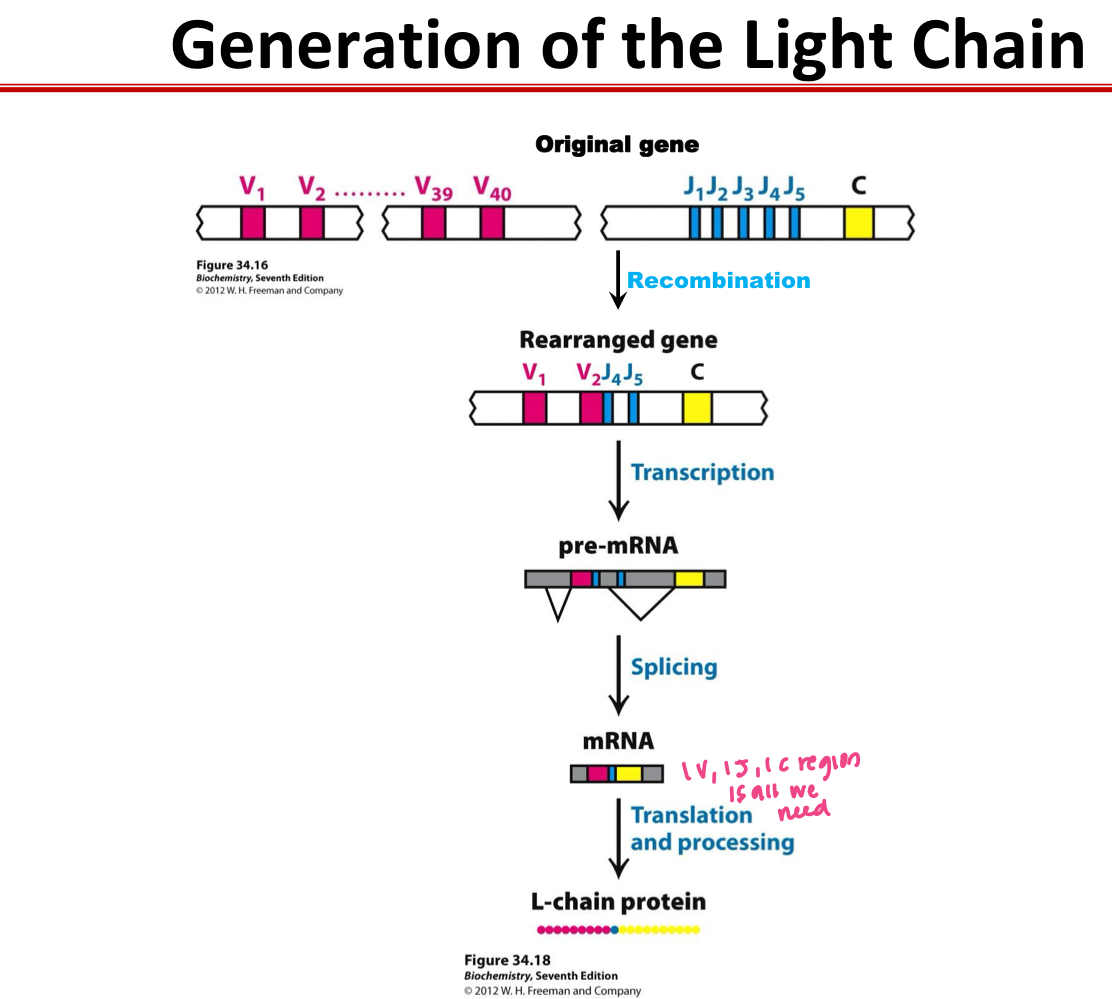
V,D,and J
generation of the light chain combines 1_ , 1_, and 1_ region
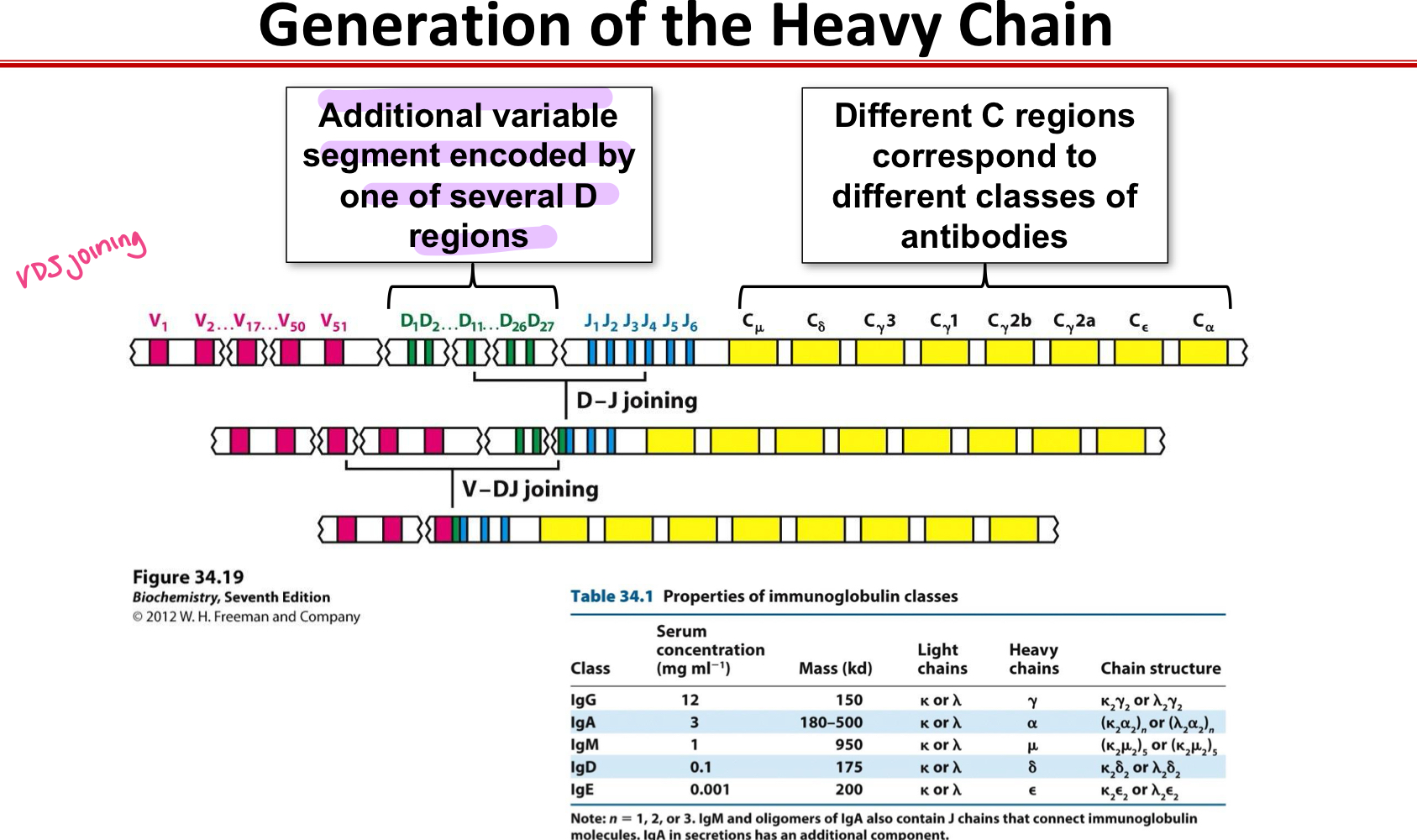
D
the generation of the heavy chain is similar to the generation of the light chain, except it also includes a __ region
C
Different ____ regions correspond to different classes of antibodies
B cells
these are antibody producing cells, each one undergoes a different recombination, and each B cell has a set variable region
V(D)J recombination
this type of recombination is what happpens in B cells that allows specific B cells to use variable regions to get specific antibodies that bind to specific antigens
IgM
all antibodies are originally _____(IgM)
one, cell surface
wach immature B cells produces ____ kind of antibody, nad thousands of copies of this antibody are attached to the _____ _____
phosphorylation, activated, proliferate
when B cells are activated, the IgM is on the outside of the cell, and the antigen binds to the antibody leading to _______________ inside of the B cell, which allows teh B cell to be ______________, and it starts to ______________
class switching
this is what happens after the proliferation of a certain B cell, which allows the IgM antibody to switch to IgG, IgA etc
does not
class switching (does/does not) change antigen specificity
variable, constant
in class switching, the ____ region stays the same, but the _____ region changes
recombination
OVERVIEW:
precursor cells undergo _______ to produce immature B cells
selection and activation
immature B cells under go ____ and ______ to become activated B cells
class switching
after B cells are activated they can undergo _____ _____