macroeconomics
5.0(1)Studied by 80 people
Card Sorting
1/49
Last updated 10:32 PM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
What is economic growth?
an increase in the amount of goods and services produced per head of the population over a period of time.
2
New cards
what is the uk's long run trend of economic growth?
2.5% is the gov'ts aim to have sustainable growth for the long run
3
New cards
why would gov'ts aim to increase economic development before economic growth?
this is because in emerging markets and developing economies economic development will improve living standards, life expectancy, literacy rates
4
New cards
Income vs wealth
Income is assets EARNED (e.g. cars, houses, money etc) while wealth is assets already OWNED.
5
New cards
consumer spending
C
spending on goods/services
spending on goods/services
6
New cards
gov't spending
G
public sector demand
public sector demand
7
New cards
investment
I
spending on capital goods
spending on capital goods
8
New cards
exports
X
overseas markets
overseas markets
9
New cards
imports
M
goods bought overseas
goods bought overseas
10
New cards
national income = ?
y= GDP
11
New cards
savings
S
Deferred spendings - not spent
Deferred spendings - not spent
12
New cards
leakages/ withdrawals
spending (income) that flows out of the circular flow.
T = taxation
S = savings
M = imports
T = taxation
S = savings
M = imports
13
New cards
injection
income going into circular flow
G = gov't spending
X = exports
I = investments
G = gov't spending
X = exports
I = investments
14
New cards
How to achieve equilibrium
injections = withdrawals
X+G+I = S+T+M
X+G+I = S+T+M
15
New cards
what does it mean if national income is rising
I+G+X > S+T+M
inflation
inflation
16
New cards
what does it mean if growth is declining
I+G+X < S+T+M
recession
- increase gov't spending
- reduce tax
- lower interest rates
recession
- increase gov't spending
- reduce tax
- lower interest rates
17
New cards
circular flow of income
A simplified model of the economy that shows the flow of money through the economy.
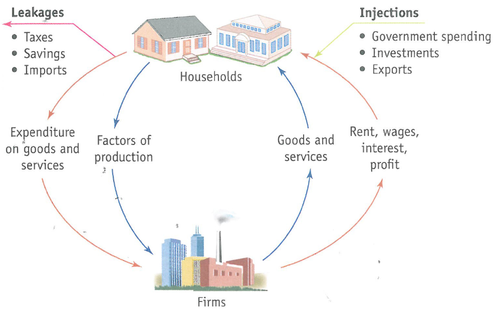
18
New cards
what does national income measure
national income is the total value of goods and services a country purchase. it is the output in one year and can be measured by GDP, GNI and GNP
19
New cards
What is nominal GDP?
the production of goods and services valued at current prices
20
New cards
Define the circular flow of income model. Why is this model important?
- model that represents the exchange between firms and households
- benefits both of them mutually
- represents the flow of money and goods in the economy
- benefits both of them mutually
- represents the flow of money and goods in the economy
21
New cards
What does investment spending represent spending on ?
Productive physical capital
22
New cards
When is unemplyment likely to occur?
When savings are greater than investments
- leakages > injections
- leakages > injections
23
New cards
Real GDP = ?
Nominal GDP x 100/price index
24
New cards
What is real GDP?
Ajusted for inflation expressed at current prices (chosen by base year)
25
New cards
Nominal vs real GDP
- GDP goes up when prices go up - inflation (nominal)
- GDP goes up when more/better goods & services are produced (real) - measures 2nd type of growth - controls inflation - if price hasnt changed
- GDP goes up when more/better goods & services are produced (real) - measures 2nd type of growth - controls inflation - if price hasnt changed
26
New cards
Measure of living standards = ?
Real GDP/ real GDP per capita
- declines during a recession - increase in unemployment
- declines during a recession - increase in unemployment
27
New cards
What is purchasing power parity ?
- when the buying ability of different currencies is = across countries , the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium
- the purchasing power of the $
- the purchasing power of the $
28
New cards
The problems w/ using GDP per capita as a measure of economic performance
- GDP per capita is average - takes no account of inequaity i.e. the way money is distributed
- the informal sector - price of goods & services deliberstely not declared
- subsistence and barter
- exchange rate differences (PPP)
- quality of goods - certain goods improve over time
- social indicators impact living standards
- the informal sector - price of goods & services deliberstely not declared
- subsistence and barter
- exchange rate differences (PPP)
- quality of goods - certain goods improve over time
- social indicators impact living standards
29
New cards
The happiness agenda - criticisms
- definition of happiness is subjective
- measurement
- policy implementation
- does income actualy correlate w/ happiness
- measurement
- policy implementation
- does income actualy correlate w/ happiness
30
New cards
How do we measure inflation?
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- a measurement of the price level in the economy based on the prices of a collection of products (basket)
- a measurement of the price level in the economy based on the prices of a collection of products (basket)
31
New cards
What is inflation?
a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
32
New cards
What is inflation rate?
Annual rate of change of the avg. price of goods & services
33
New cards
What is disinflation?
If inflation reduces from 3% to 2%, prices are still going UP, just at a slower rate than before.
34
New cards
What is deflation ?
Prices are FALLING
- decline in general price level in the economy - leads to a spiral
- decline in general price level in the economy - leads to a spiral
35
New cards
What is the process of calculating CPI ?
- living costs and food survey :
- 7,000 families are asked to keep a record of what they spend over 2 week. Used to produce typical basket of 700 goods & services.
- each year basket changes to reflect consumers change
- the basket of goods & services is weighted. - what is more important ( proportion of total expenditure)mfoe each good/service.
- second survey records how much these goods & services have changed
- 7,000 families are asked to keep a record of what they spend over 2 week. Used to produce typical basket of 700 goods & services.
- each year basket changes to reflect consumers change
- the basket of goods & services is weighted. - what is more important ( proportion of total expenditure)mfoe each good/service.
- second survey records how much these goods & services have changed
36
New cards
Main causes of inflation ?
- Demand pull inflation
- cost push inflation
- administered prices
- cost push inflation
- administered prices
37
New cards
What is demand push inflation?
Aggregate demand from customers - scarcity
38
New cards
What is cost push inflation ?
Cost rising for businesses - raw materials and components costs & overseas suppliers - rising imports due to falling exchange rates
39
New cards
What is administered prices?
Changes in regulated prices - bills - changes in taxes
40
New cards
CPI weighting
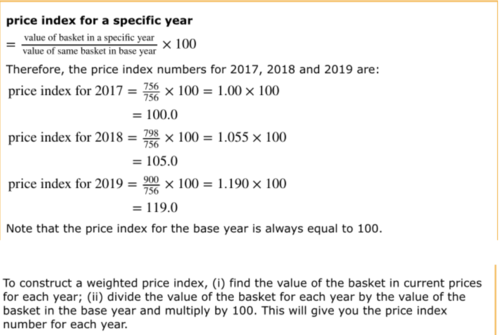
41
New cards
CPI basket
contains the goods and services represented in the index, each weighted by its relative importance
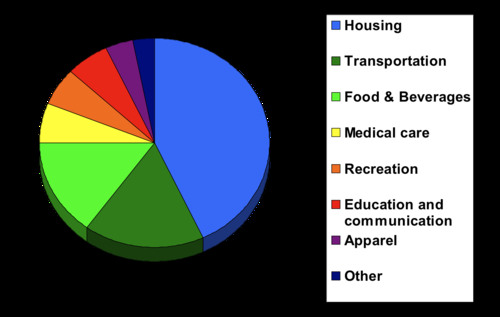
42
New cards
Price value = ?
Price value = A(pxw) + B(pxw) + C(pxw) + D(pxw) = Pv
43
New cards
Index for year x = ?
Index for year x = price value of year x /price value of base year X100
44
New cards
Percentage change when comparing with base year = ? ( calculating index)
(New - old)/ old X 100
45
New cards
CPI measurement problems
- changes in quality - measuring price change doesnt measure quality
- changes in expenditure - spending patterns change quickly
- potential sampling error - not all households could answer survey accurately
- changes in expenditure - spending patterns change quickly
- potential sampling error - not all households could answer survey accurately
46
New cards
CPI vs RPI
- population base - RPI excludes high and low income households
- housing costs - CPI includes actual rents but not owner occupiers housing costs
- housing costs - CPI includes actual rents but not owner occupiers housing costs
47
New cards
GPD deflator
Nominal gdp/real gdp X 100
48
New cards
What is trade surplus?
Exsist when value of exports is > value of imports
49
New cards
What is meant by a fall in GDP at constant prices?
constant-price GDP factors out the impact of inflation and allows for easy comparisons by converting the value of the dollar in other time periods to present-day dollars.
When GDP declines for two consecutive quarters or more, by definition the economy is in a recession
When GDP declines for two consecutive quarters or more, by definition the economy is in a recession
50
New cards
What is the possible impact on the distribution of income of negative economic growth ?
High levels of inequality are linked to economic instability, financial crisis, debt and inflation