Lab Practical Final (2025)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
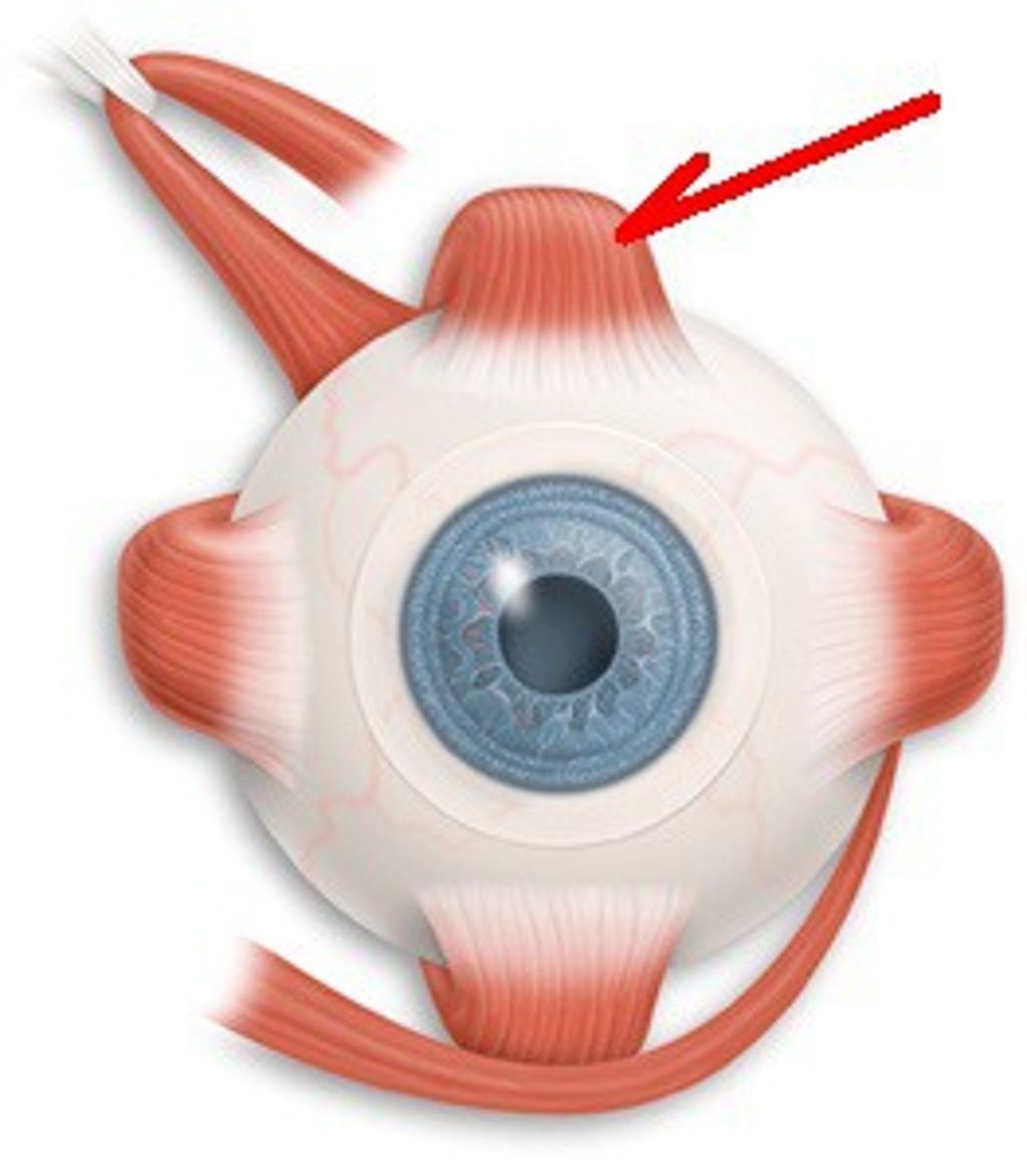
Superior Rectus
Moves eye upwards
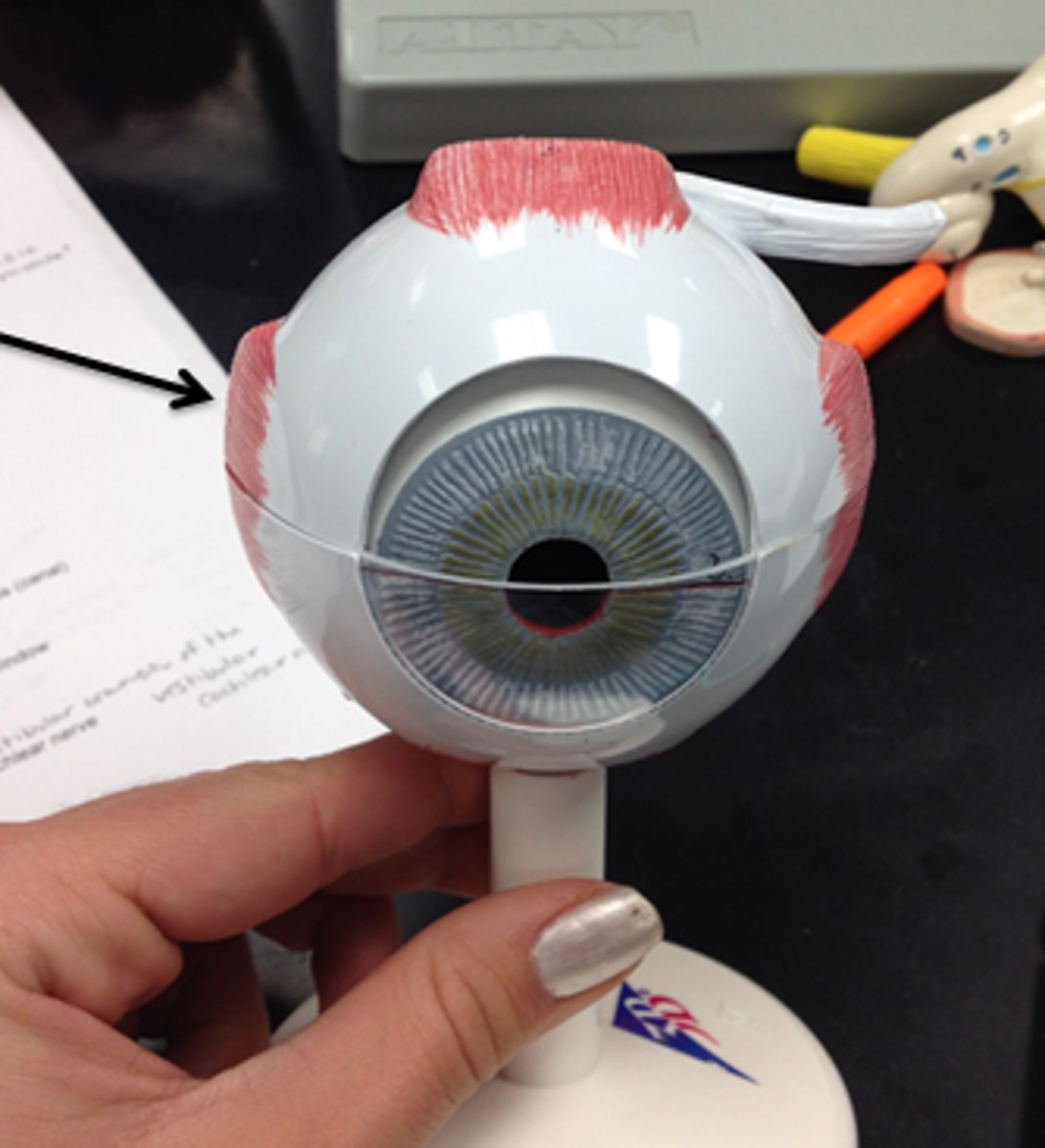
Inferior Rectus
Moves eye downwards

Lateral Rectus
Moves eye laterally (to ears)
Medial Rectus
Moves eyes medially (to nose)

Superior Oblique
Moves the eye both downward and laterally
Inferior Oblique
Moves the eye both upward & laterally
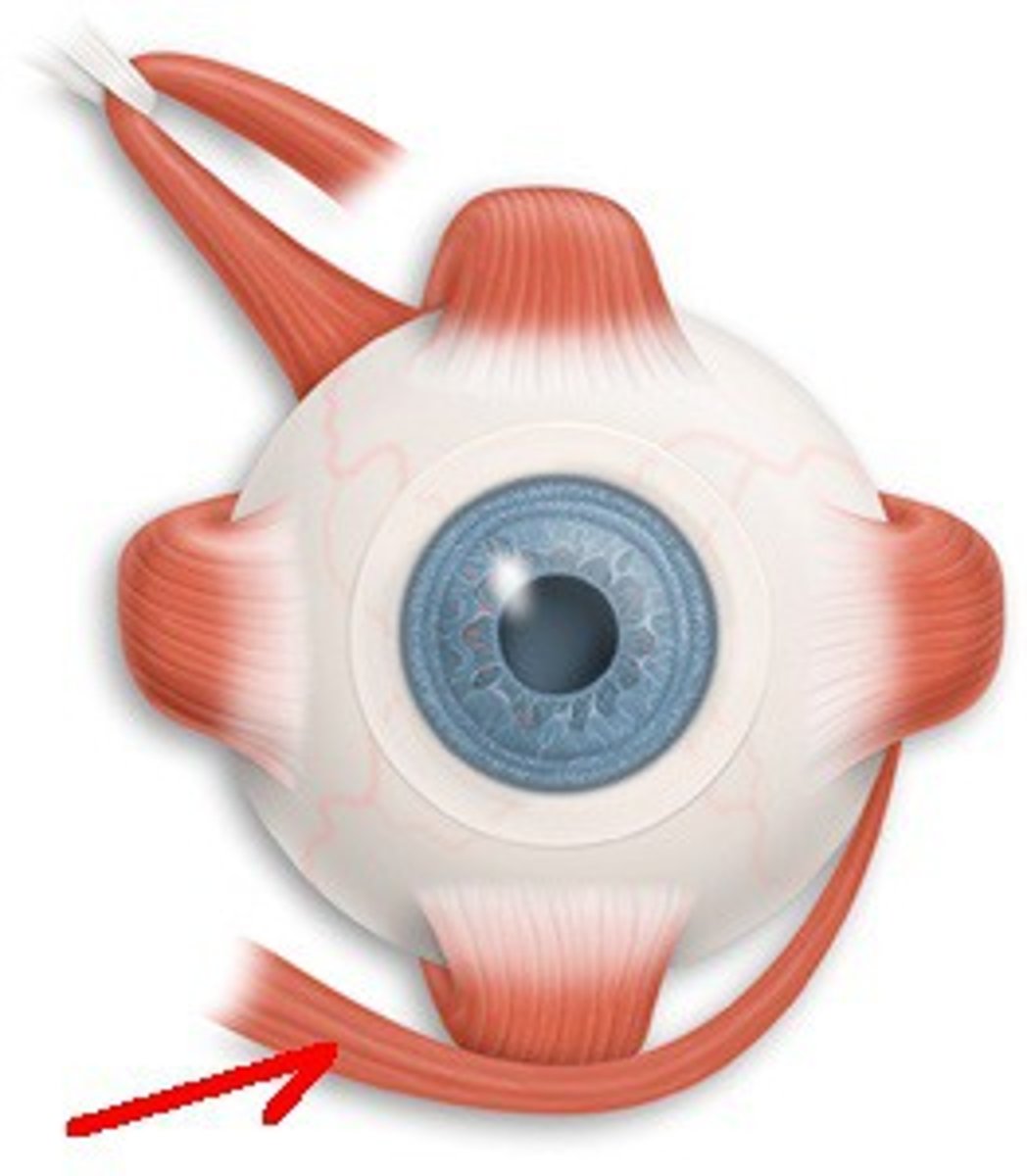
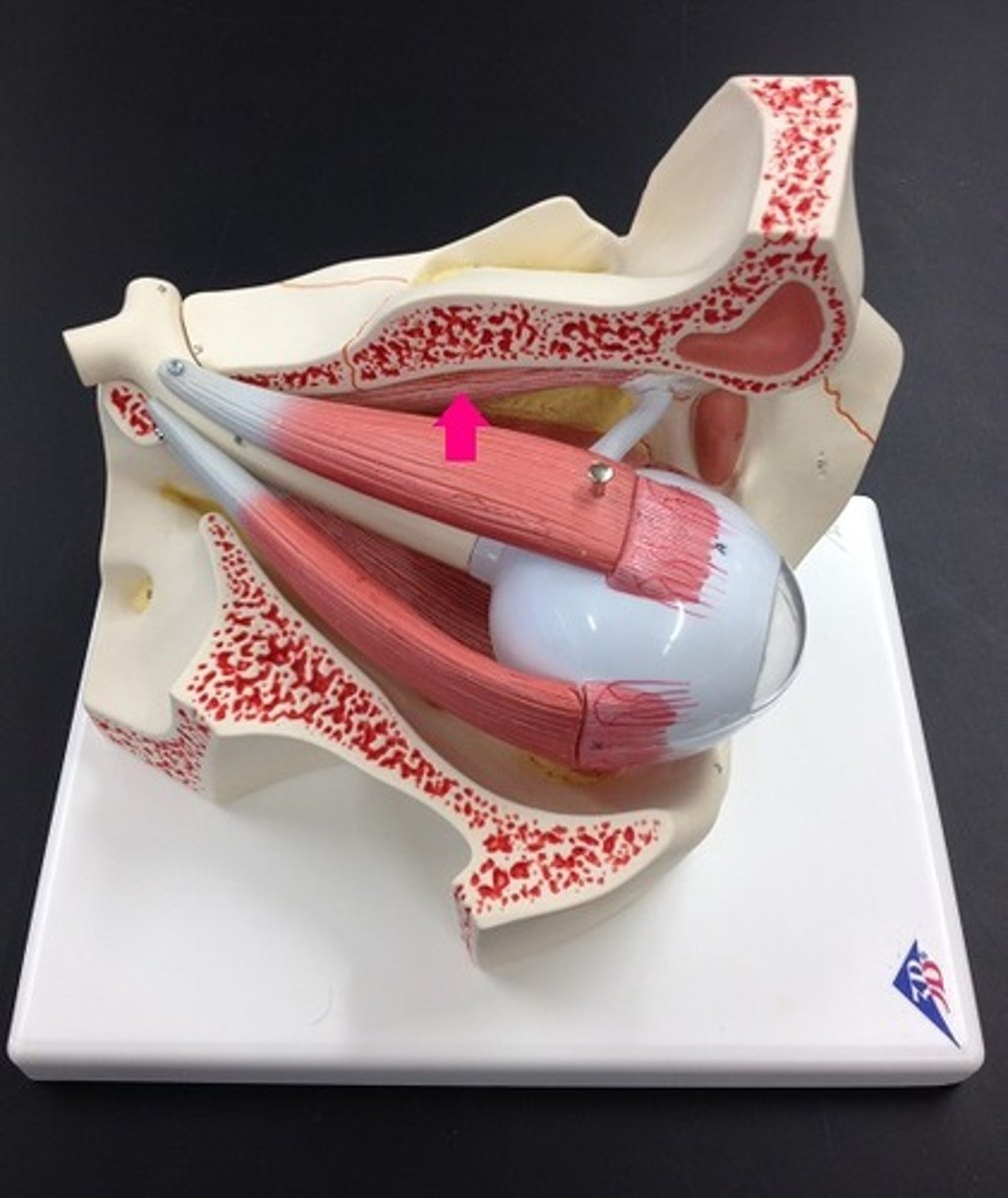
Accessory structures of the eye
protect the eyeball, no role in vision
-eyebrows, eyelashes, upper and lower eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extrinsic eye muscles
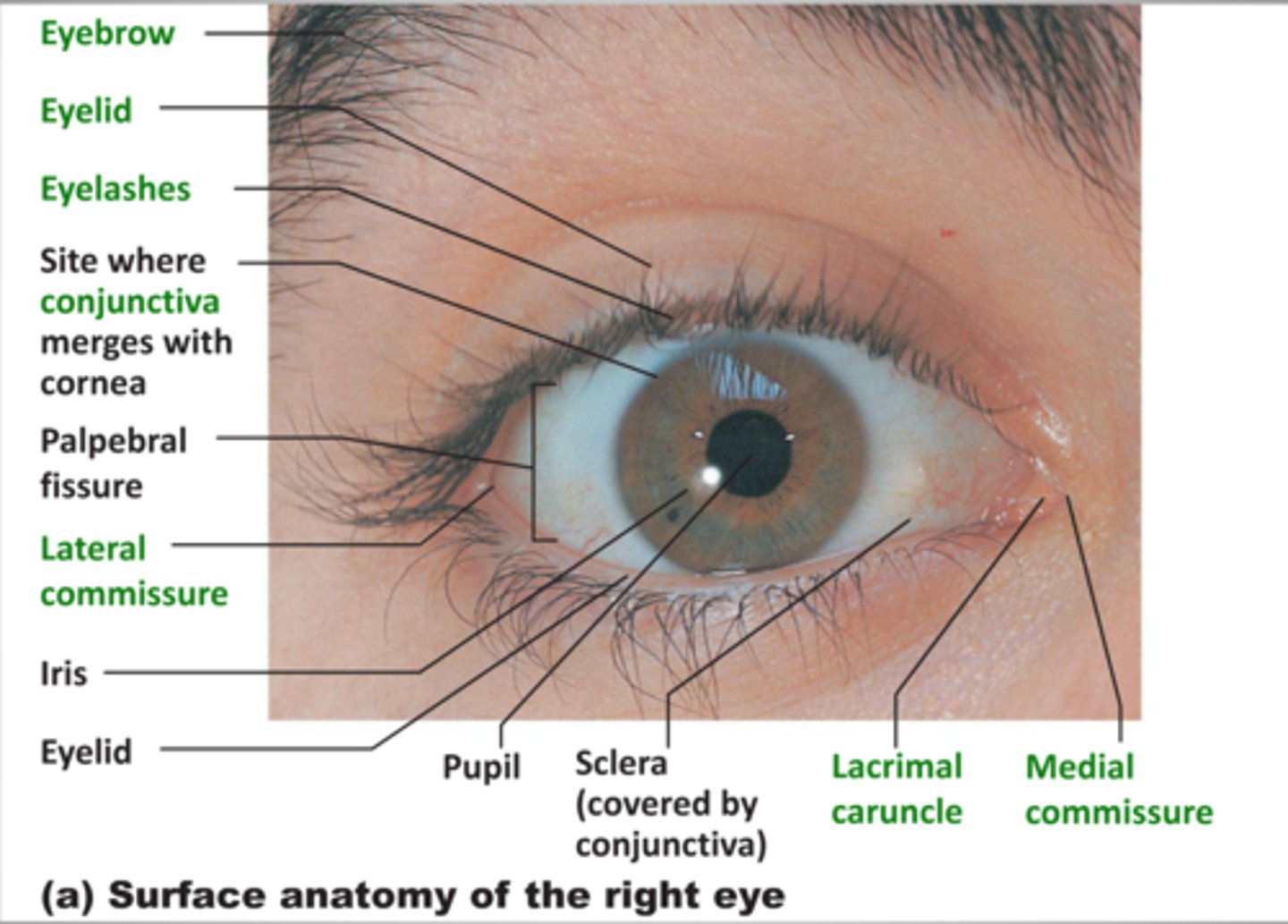
Eyebrows (accessory structures of the eye)
superior to each orbit, act as partial filters. They protect our eyes from sweat and sunlight
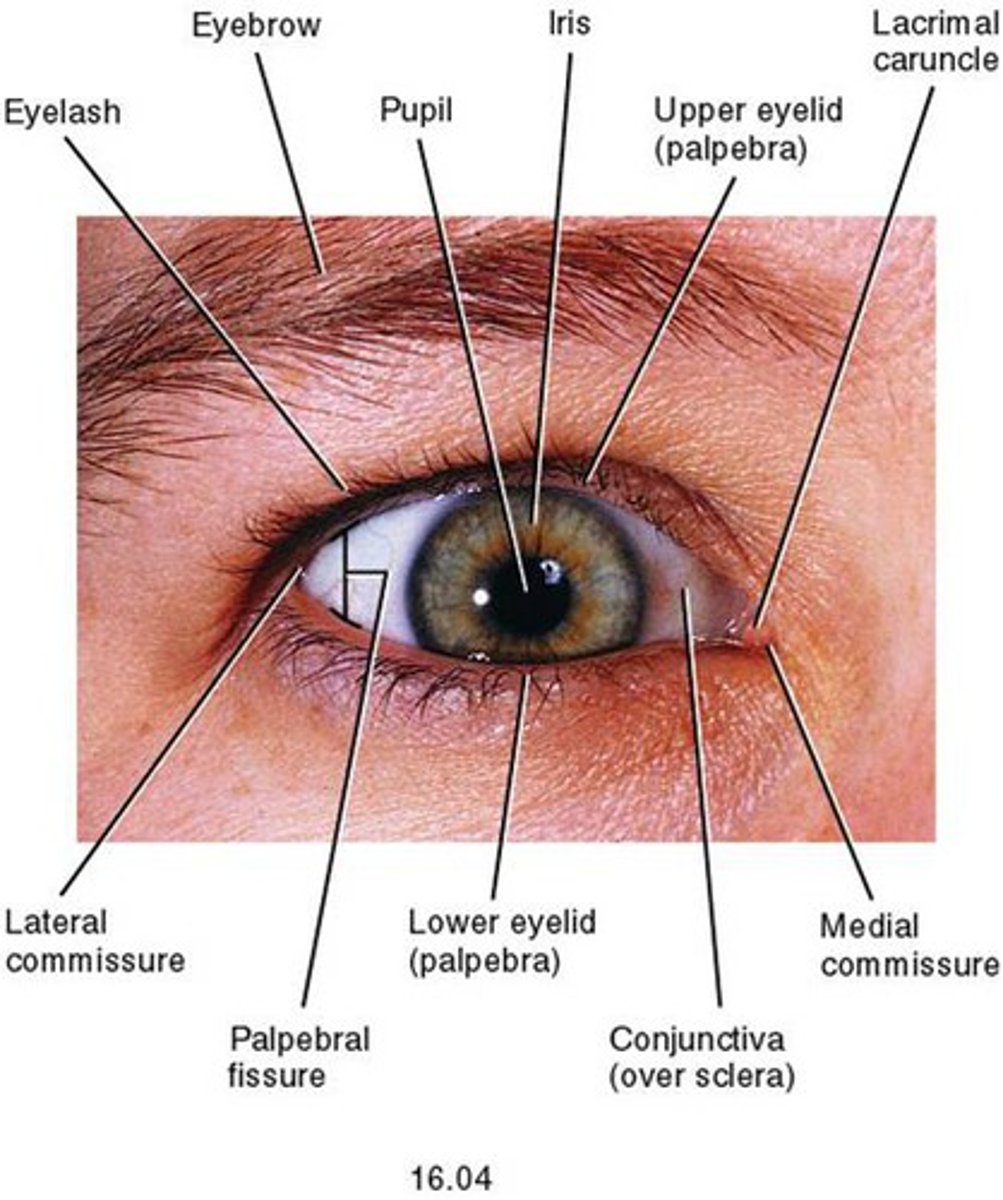
Upper and lower eyelids (palpebrae)
Protects our eyes from bright lights and foreign objects. shades our eyes during sleep and lubricates the eyeballs by spreading lubrication around from mucous membranes
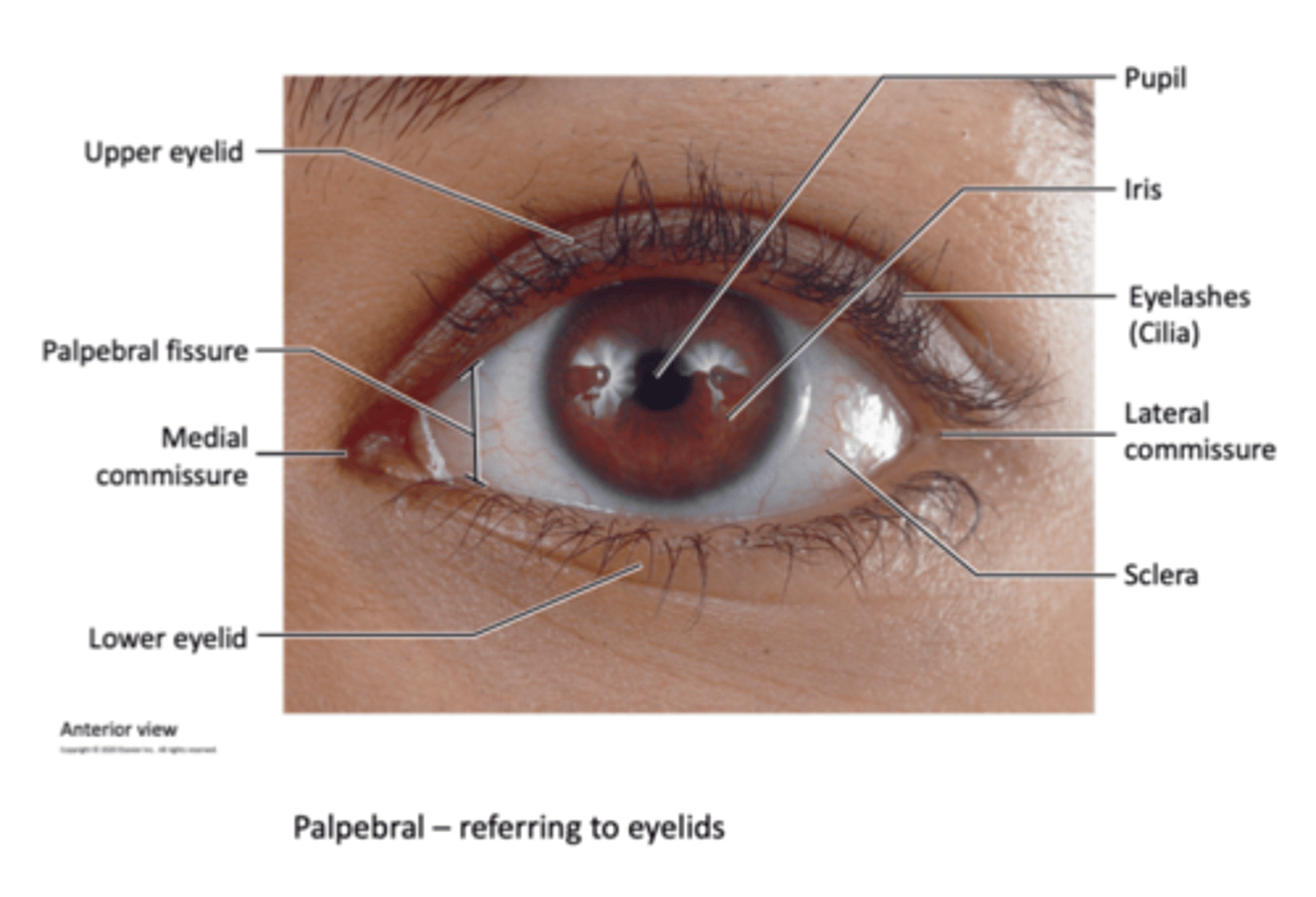
Eyelashes
They help protect our eyes from foreign objects, sweat, and sunlight
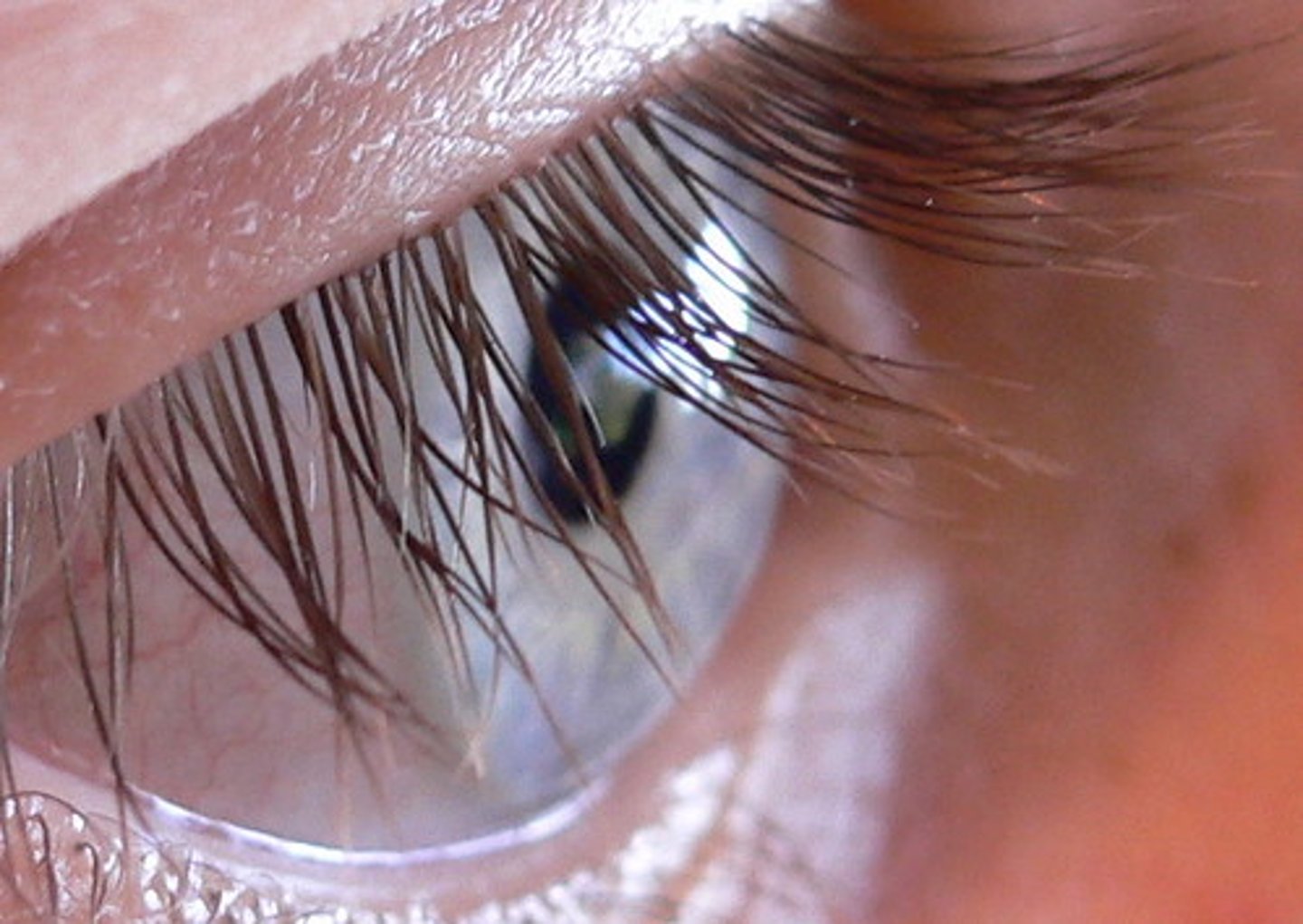

Conjunctive
Thin mucous membranes covering the inner wall of the eyelid and the anterior eye surface.
It keeps the front surface of the eyelids moist.
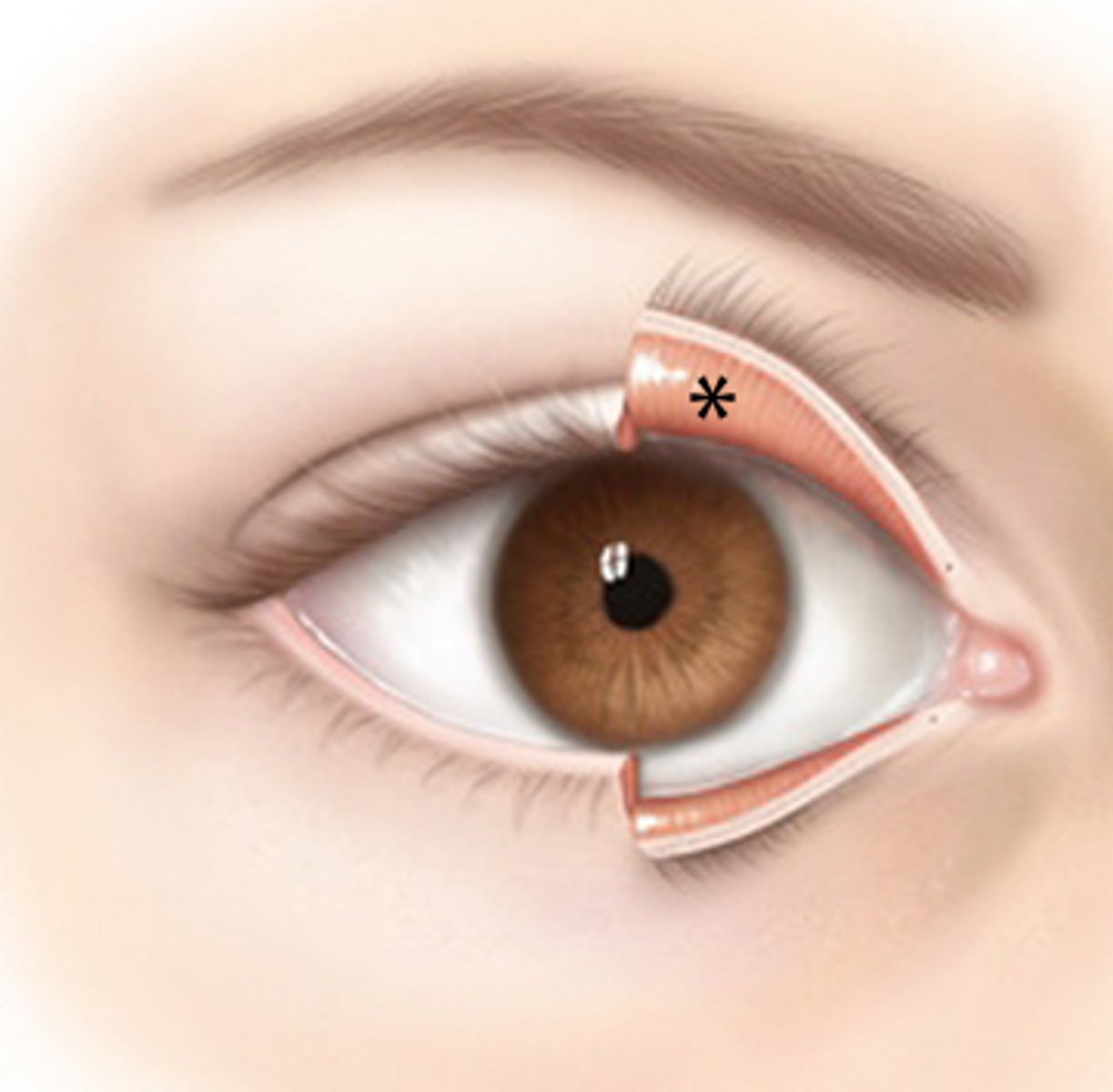
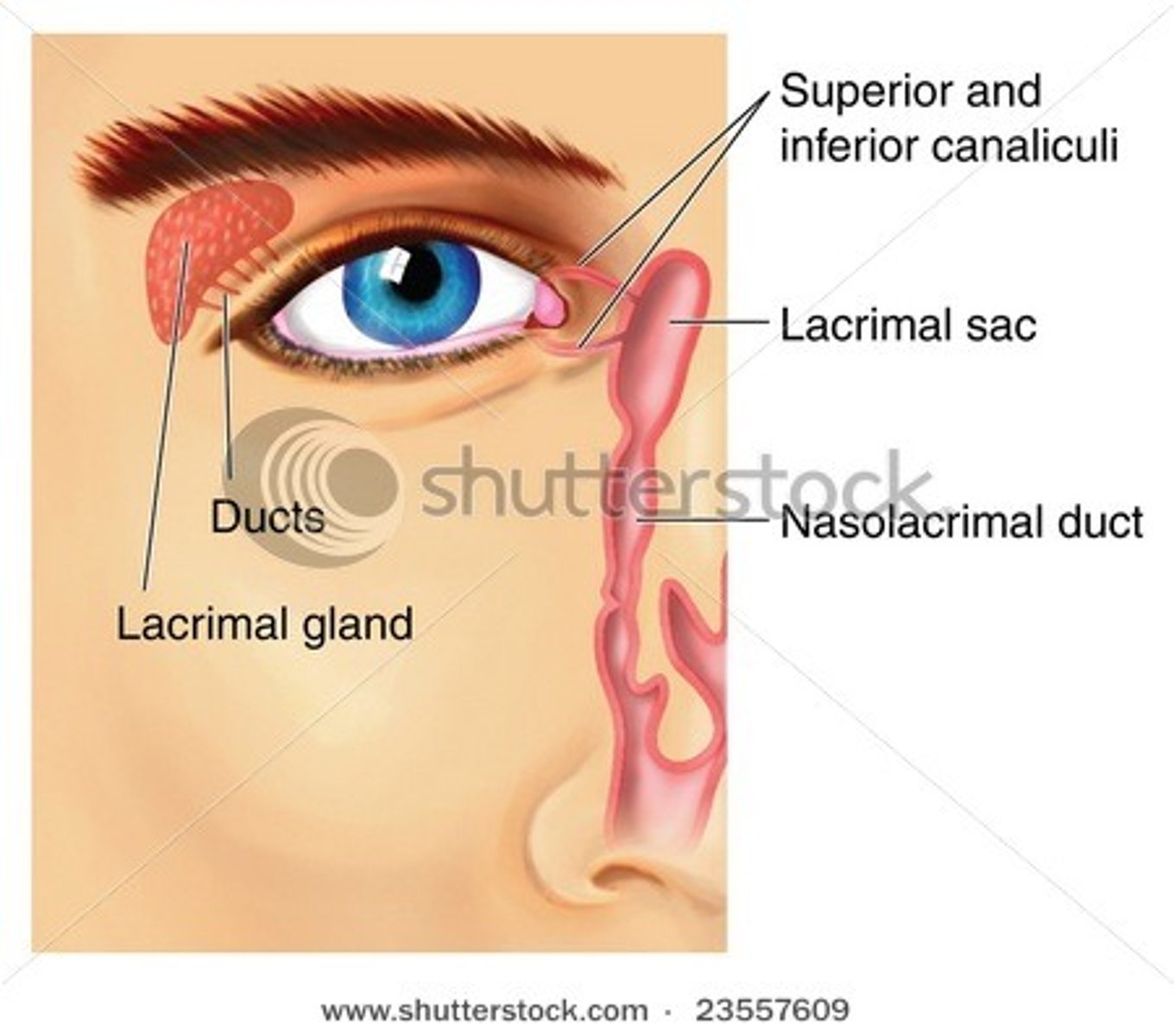
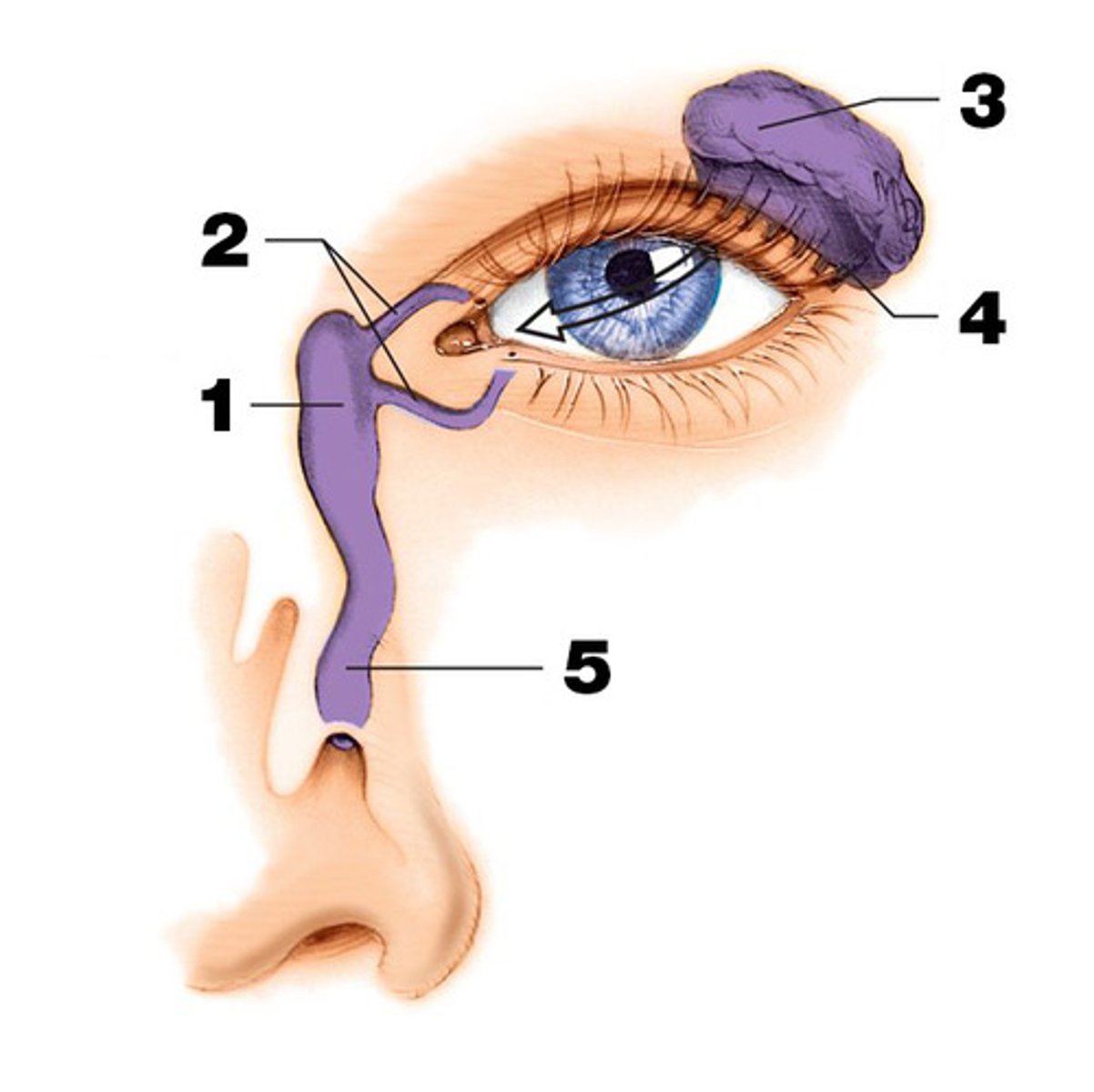
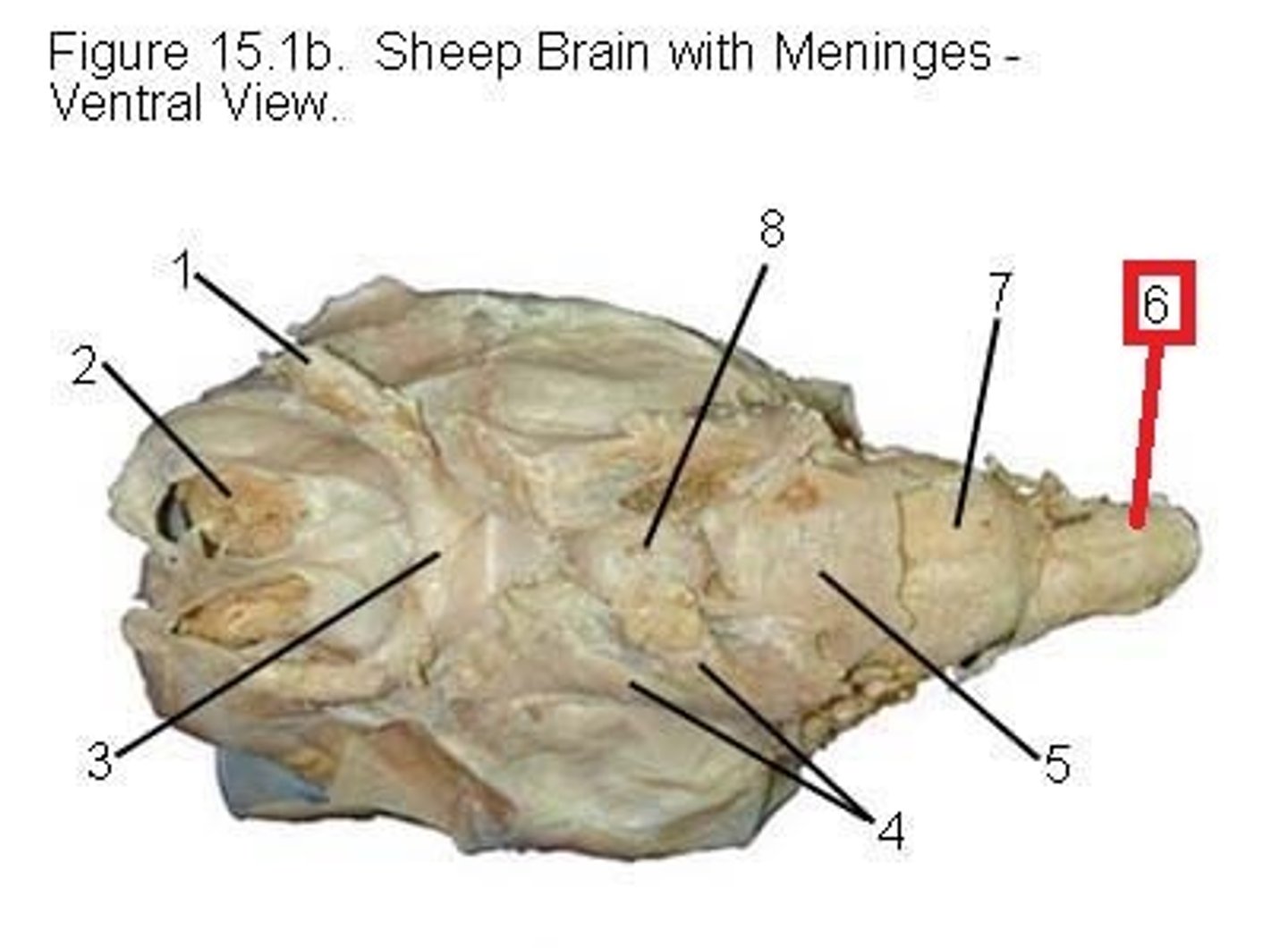
Lacrimal apparatus
produces and drains tears
-lacrimal gland
-lacrimal canals
-lacrimal sac
- nasolacrimal duct
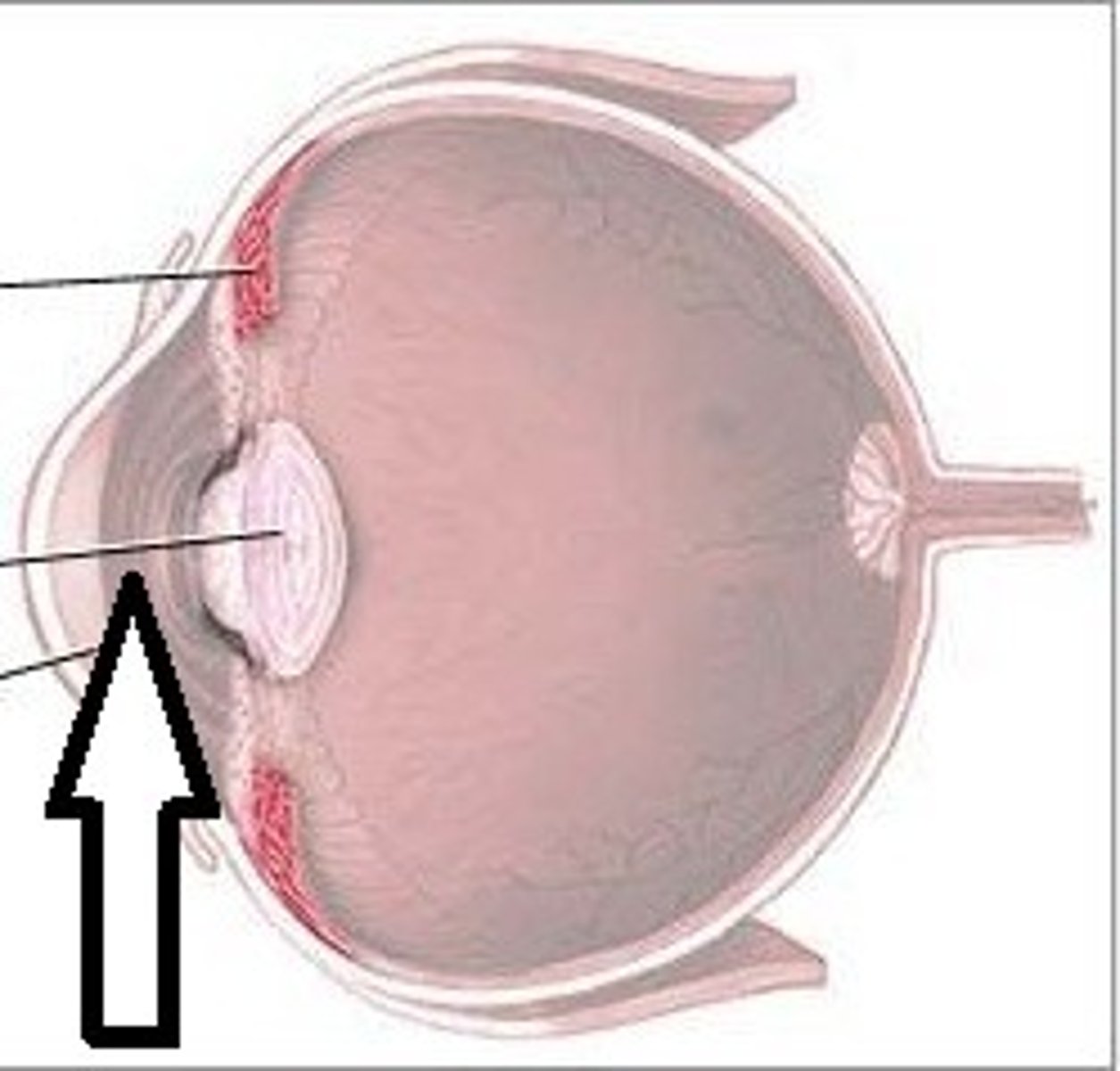
Lacrimal gland
produce and drain tears into the eye. (#3 on picture)
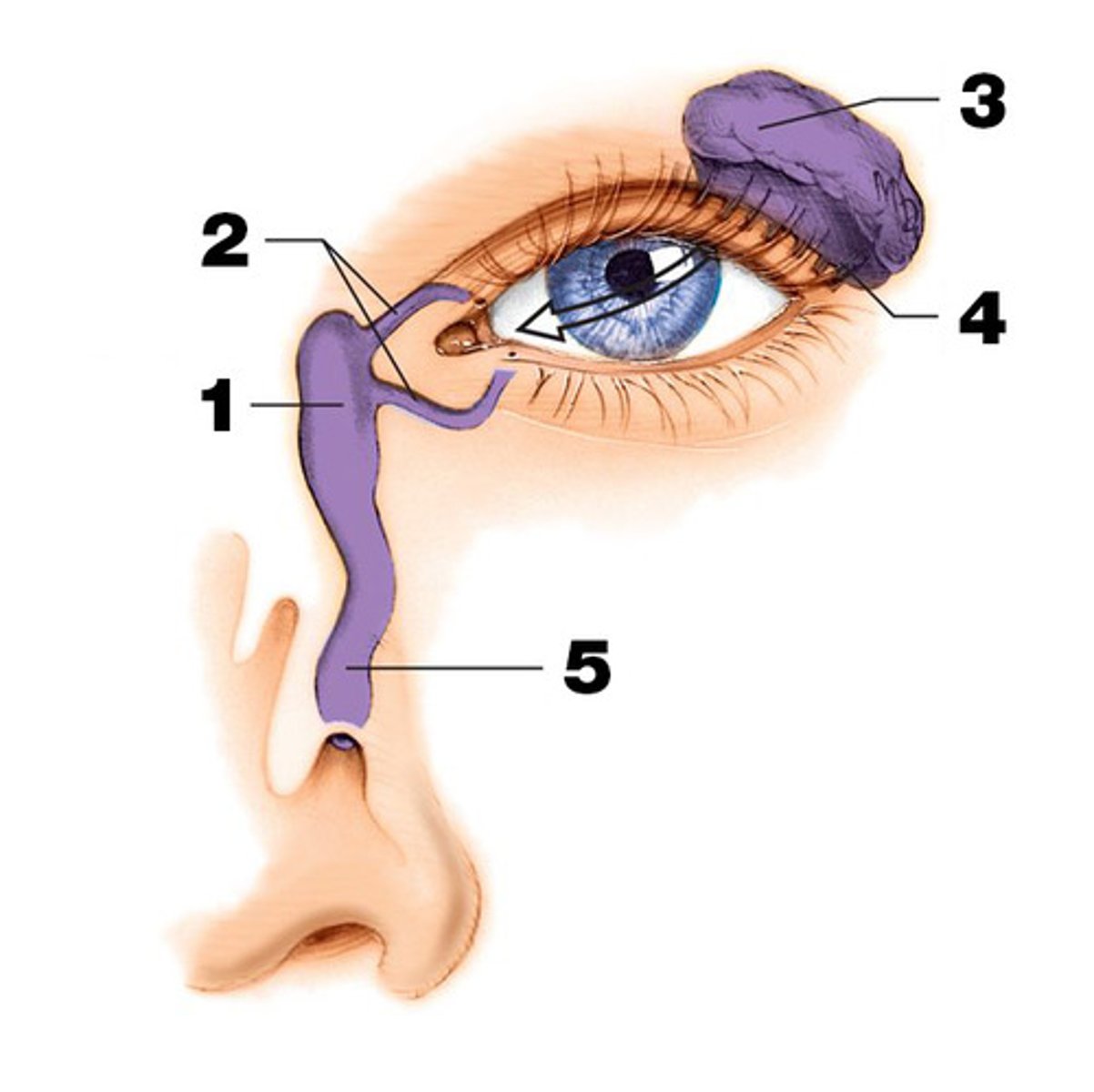
Lacrimal sac and lacrimal duct
drains into the eye. (#1 on picture)
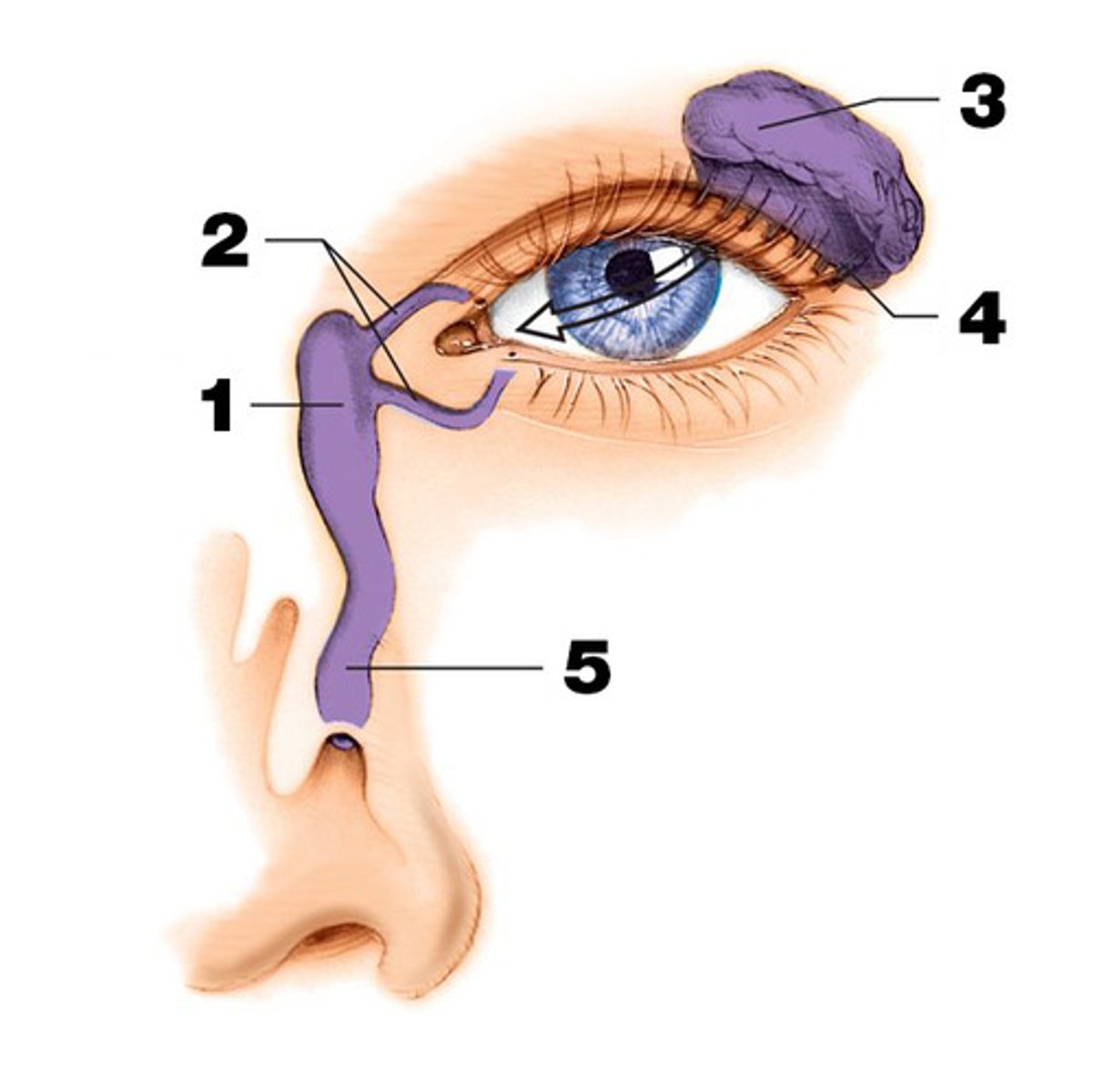
nasolacrimal duct
drains into the nasal cavity. (# 5 on picture)
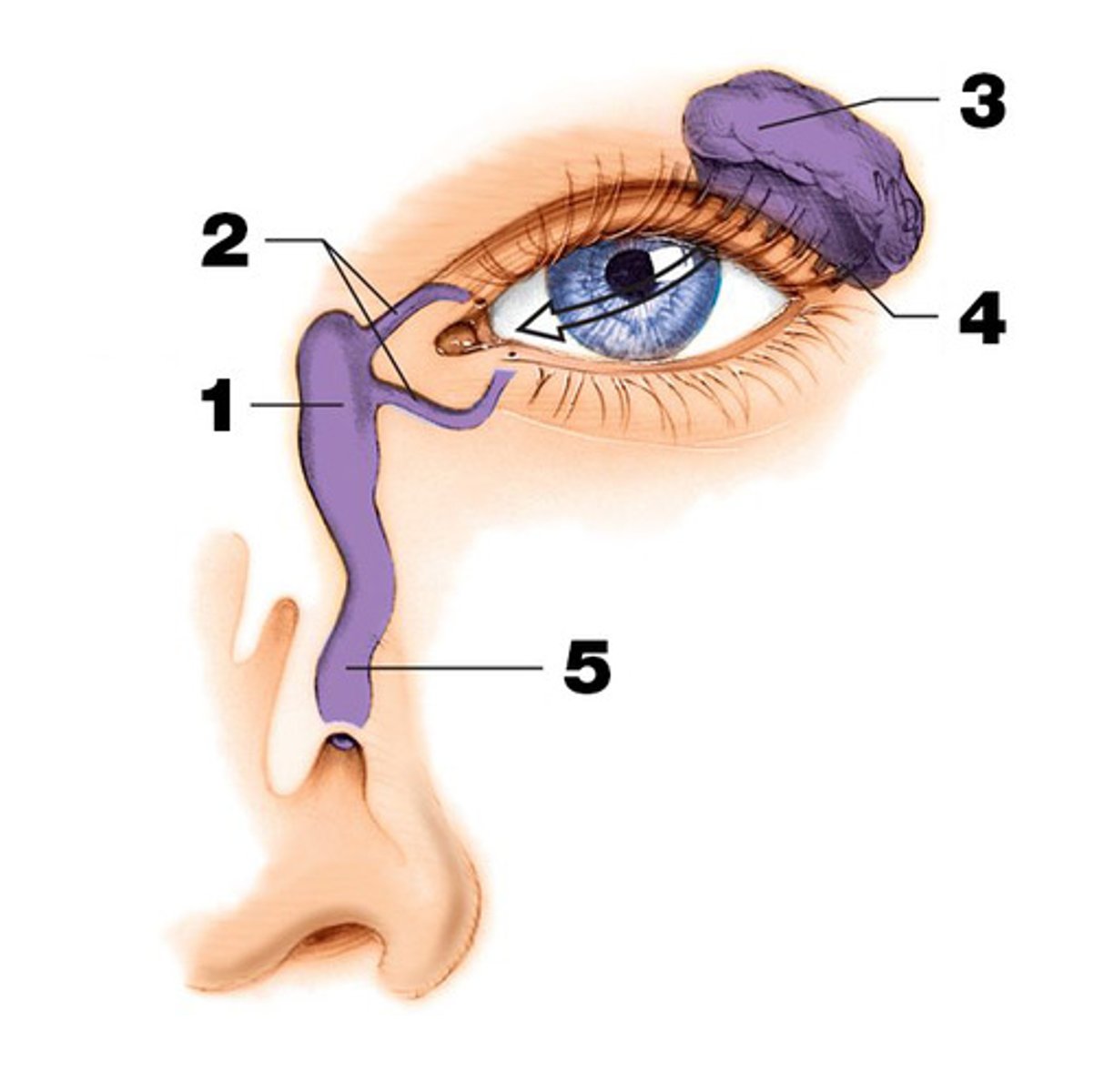
lacrimal canals (canaliculi)
Drain tears from at medial side of the eyes into the lacrimal sac. (#2 on the picture)
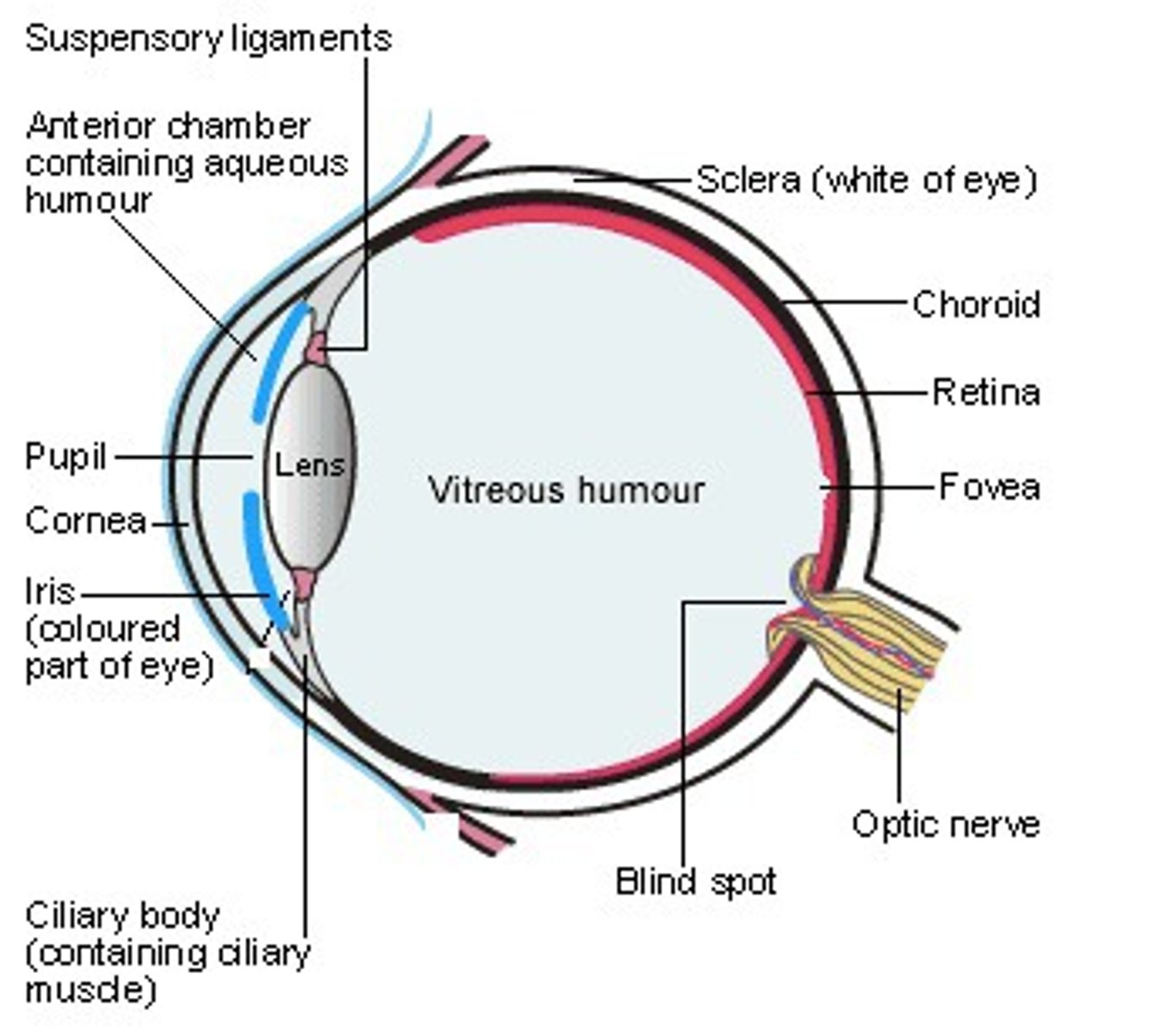
Sclera
The white of the eye. A coat of dense connective tissue that adds to the shape of the eye and provides protection of the internal eye structures.
Cornea
The anterior most portion of the sclera. It appears cloudy in preserved specimens. The cornea is the first portion of the eye to receive light.

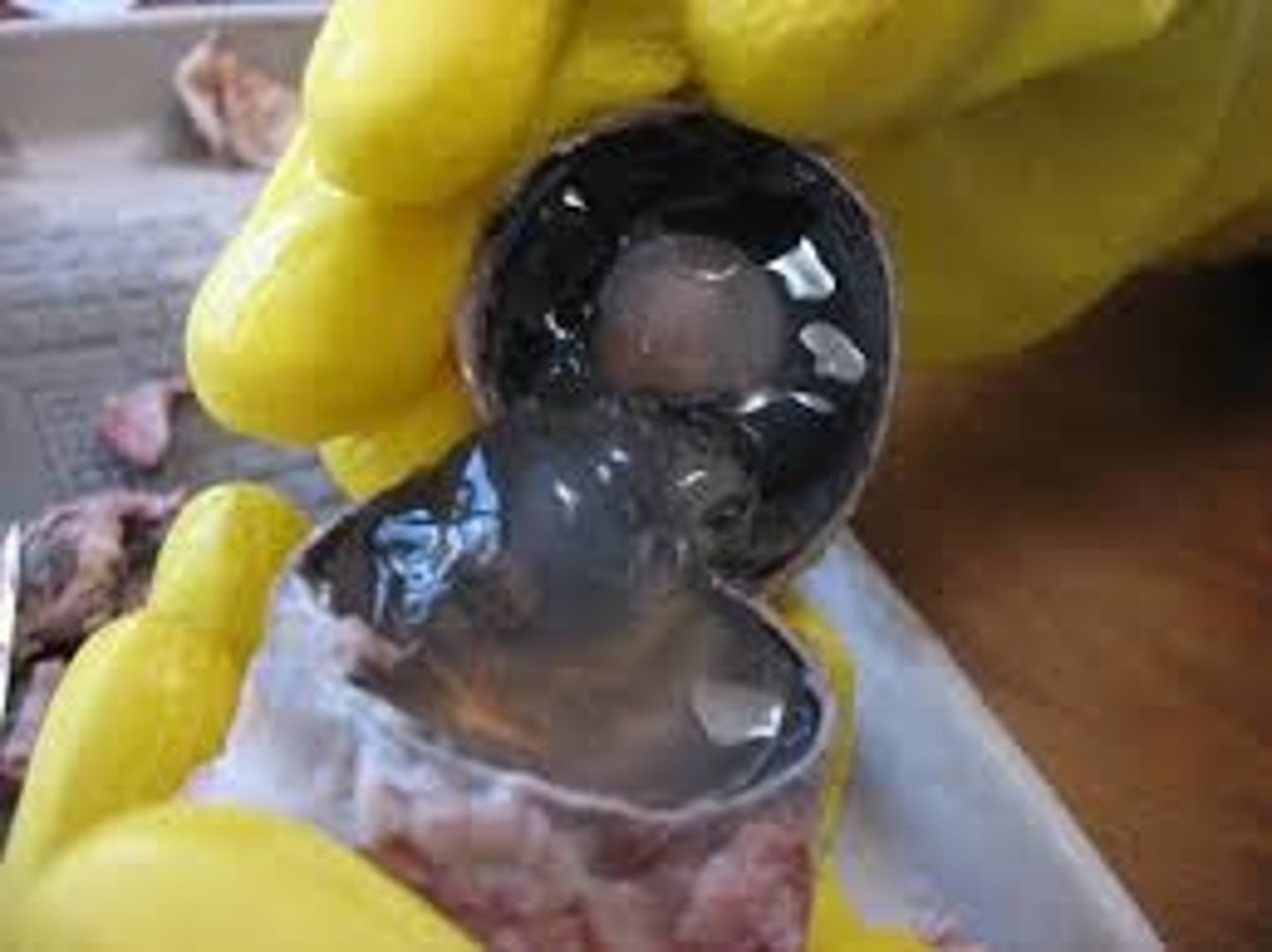
Optic nerve
Cranial nerve II can be seen exiting the back of the eye en route to the brain. This nerve carries information regarding visual stimuli to the occipital lobe.
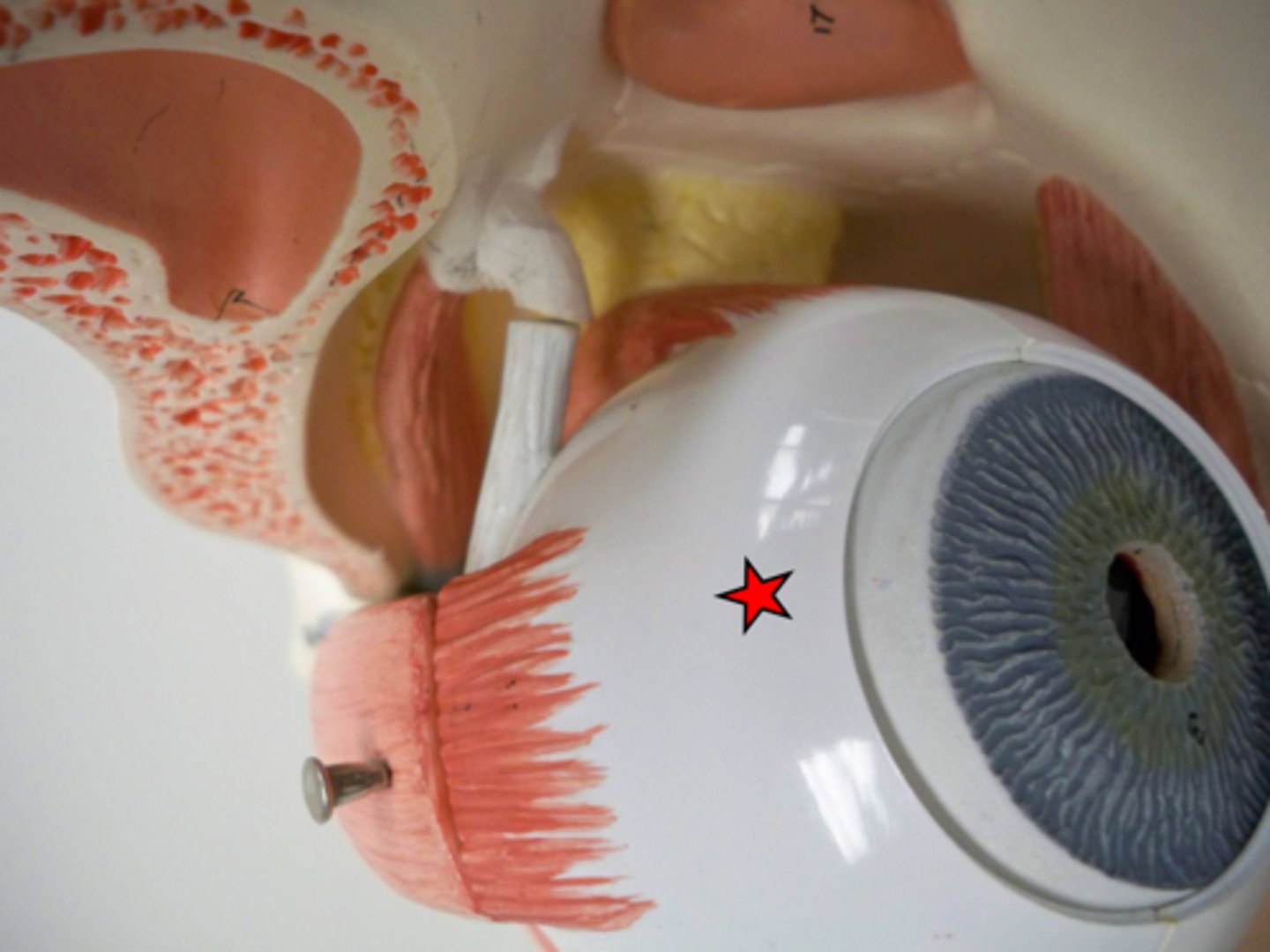
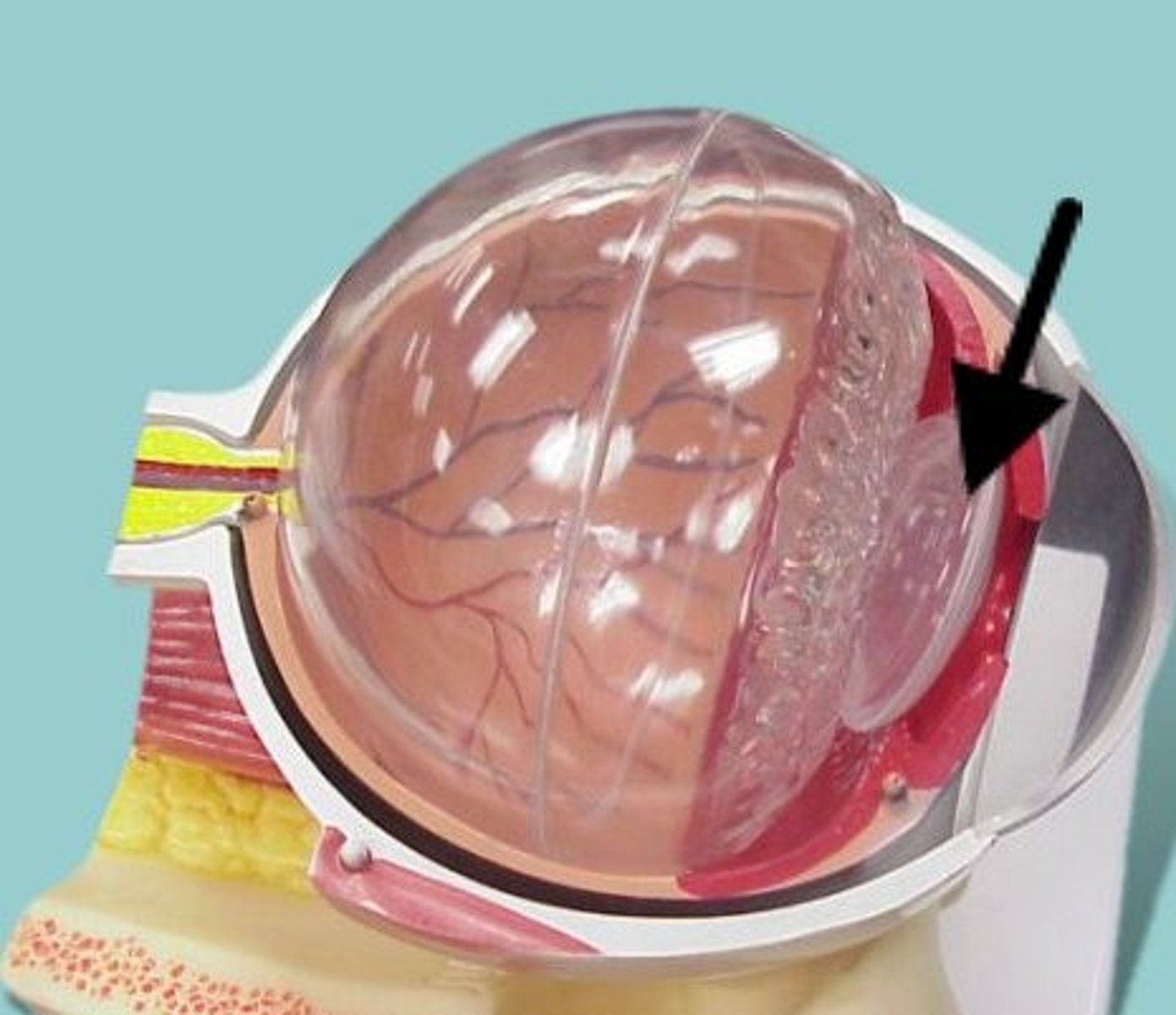
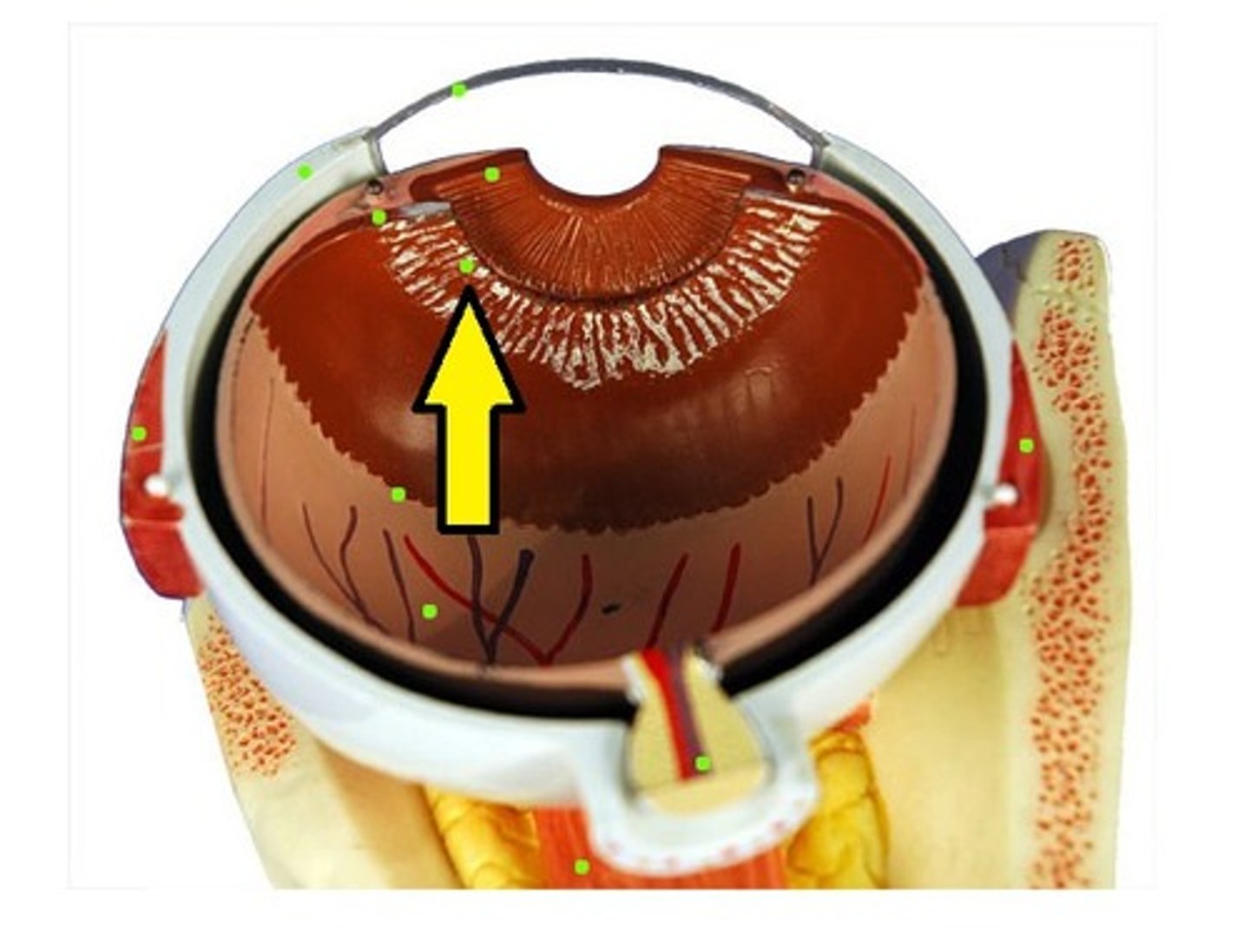
Ciliary body
A black pigmented body that appears as a halo encircling the lens. It consists of mostly muscle for controlling the tension of the suspensory ligaments. The ciliary body also secretes the aqueous humor that circulates in the anterior cavity of the eye.
Lens
A biconvex structure that is hard and opaque in preserved specimens. The shape of the lens determines where light will be focused on the retina.
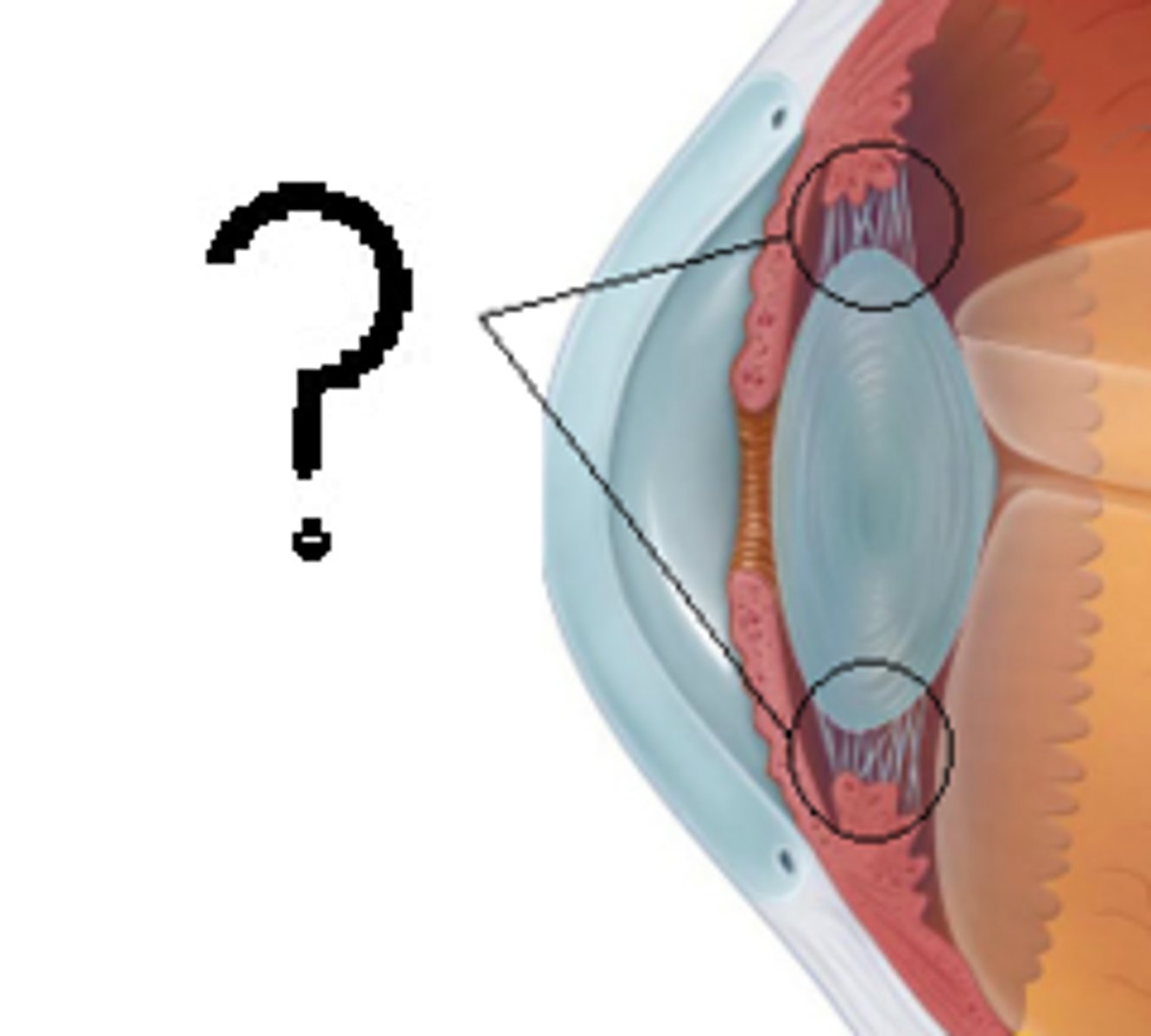
Suspensory ligaments
A halo of delicate fibers attaching the lens to the ciliary body. A change in the tension of the suspensory ligaments will alter the shape of the lens and affect the focusing of light on the retina.
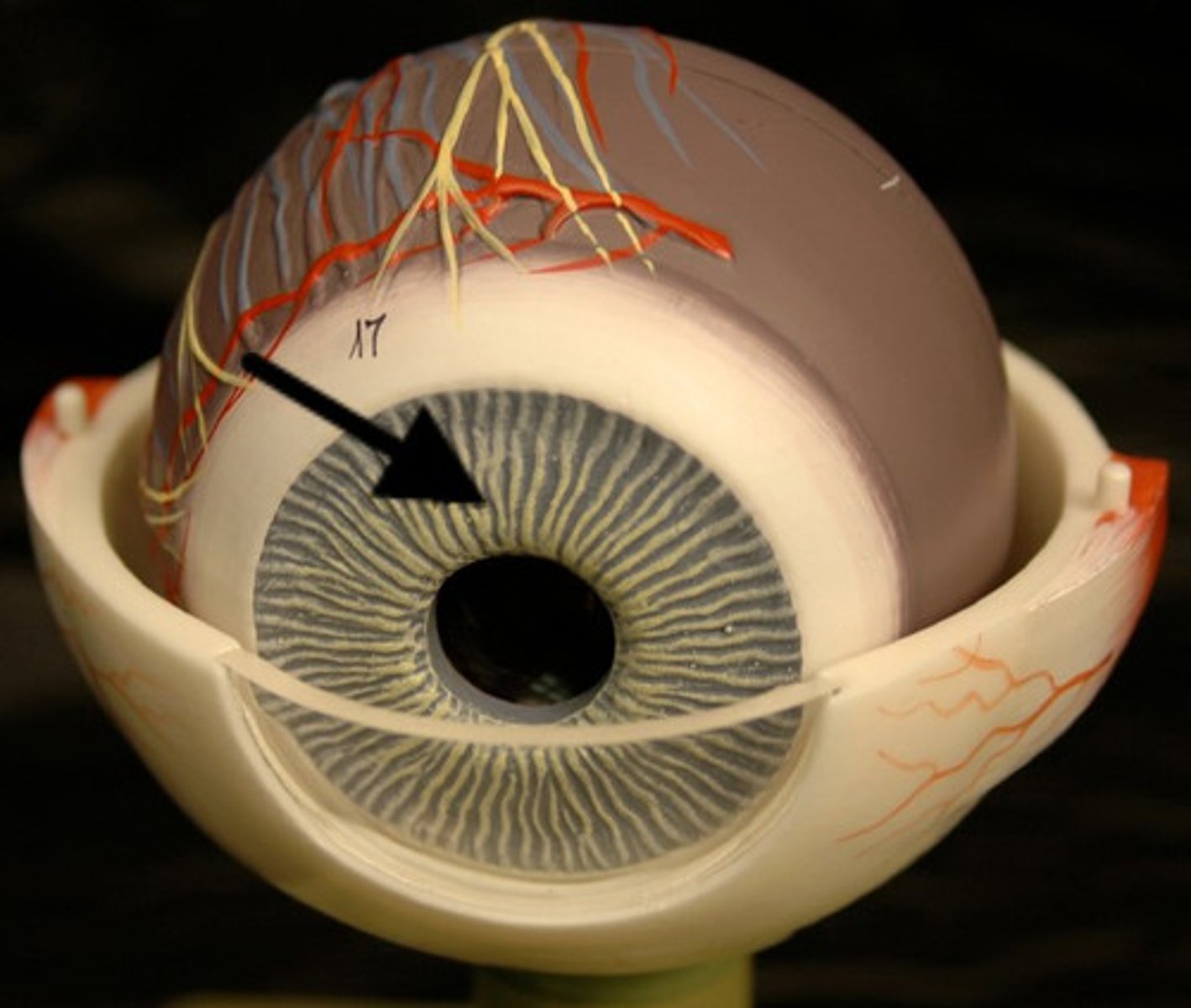
Iris
Anterior continuation of the ciliary body penetrated by the pupil. This portion of the eye gives the eye its color.
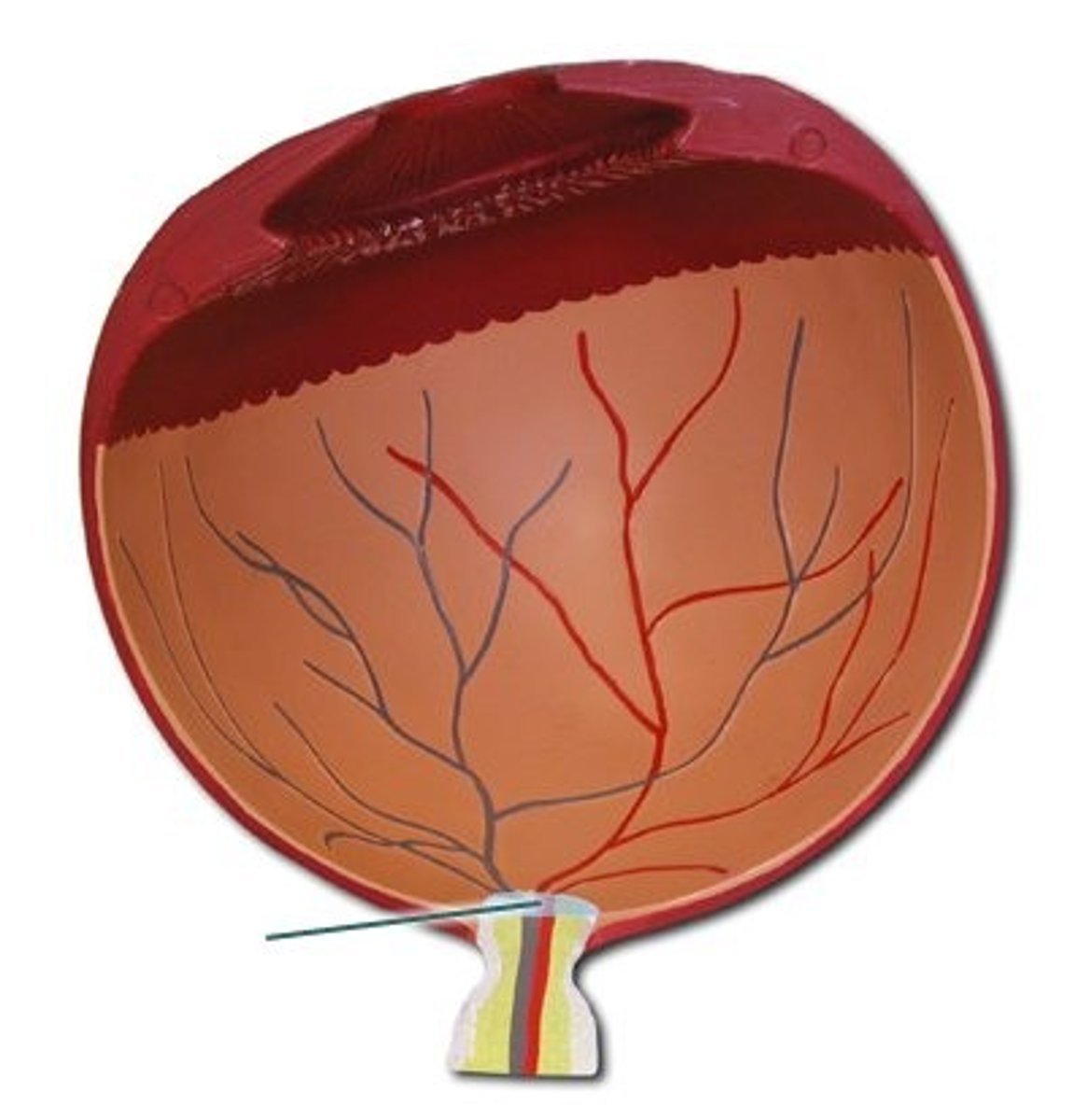
Choroid
Posterior continuation of the ciliary body. It appears brownish-black in humans, but is iridescent in nocturnal animals (tapetum lucidum).
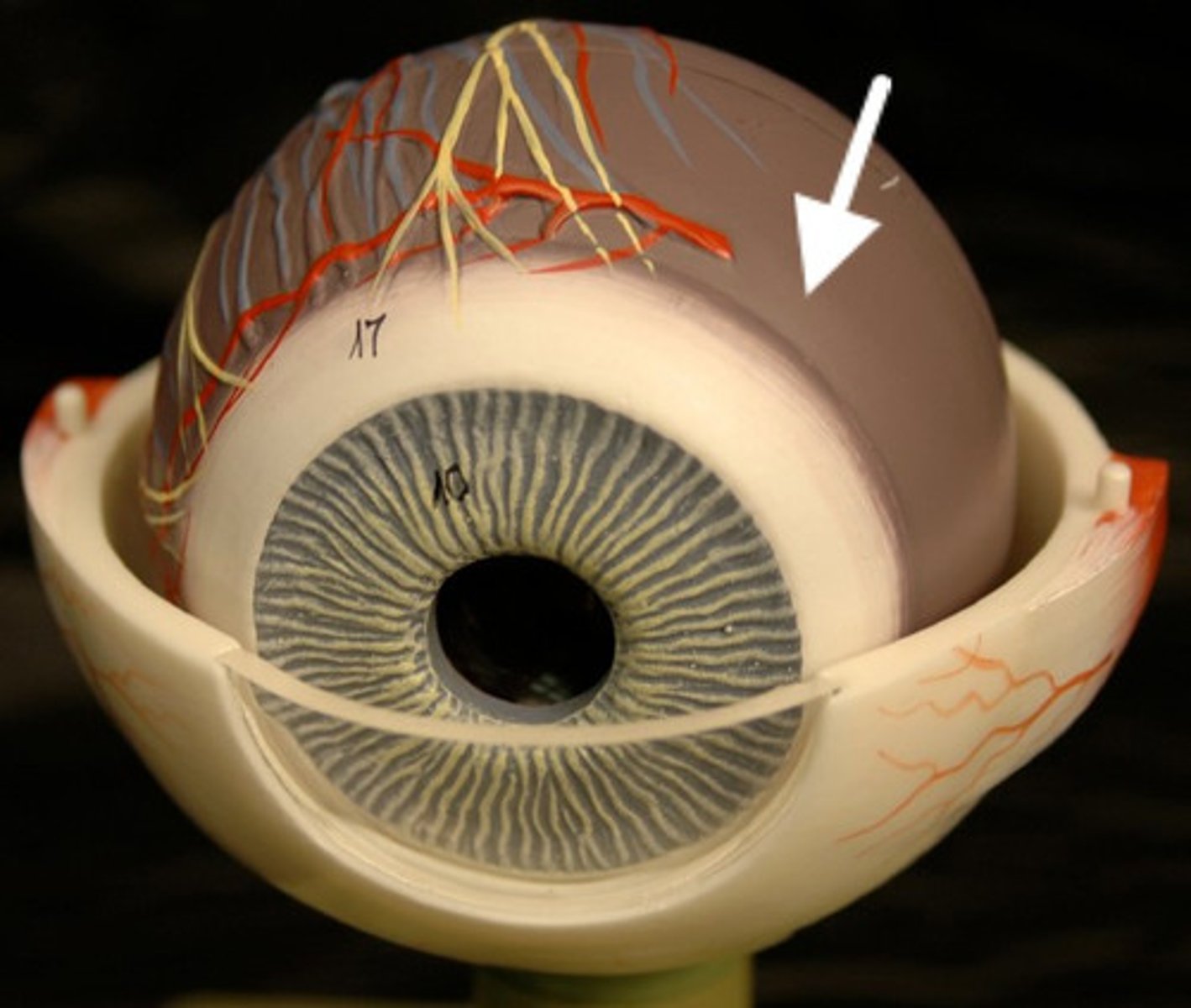
Retina
Delicate yellowish-white membrane that easily separates from the choroid layer during dissection. The retina contains the photoreceptors necessary for vision. Neurons from sensory cells in the retina exit the eye to form the optic nerve at the optic disc.
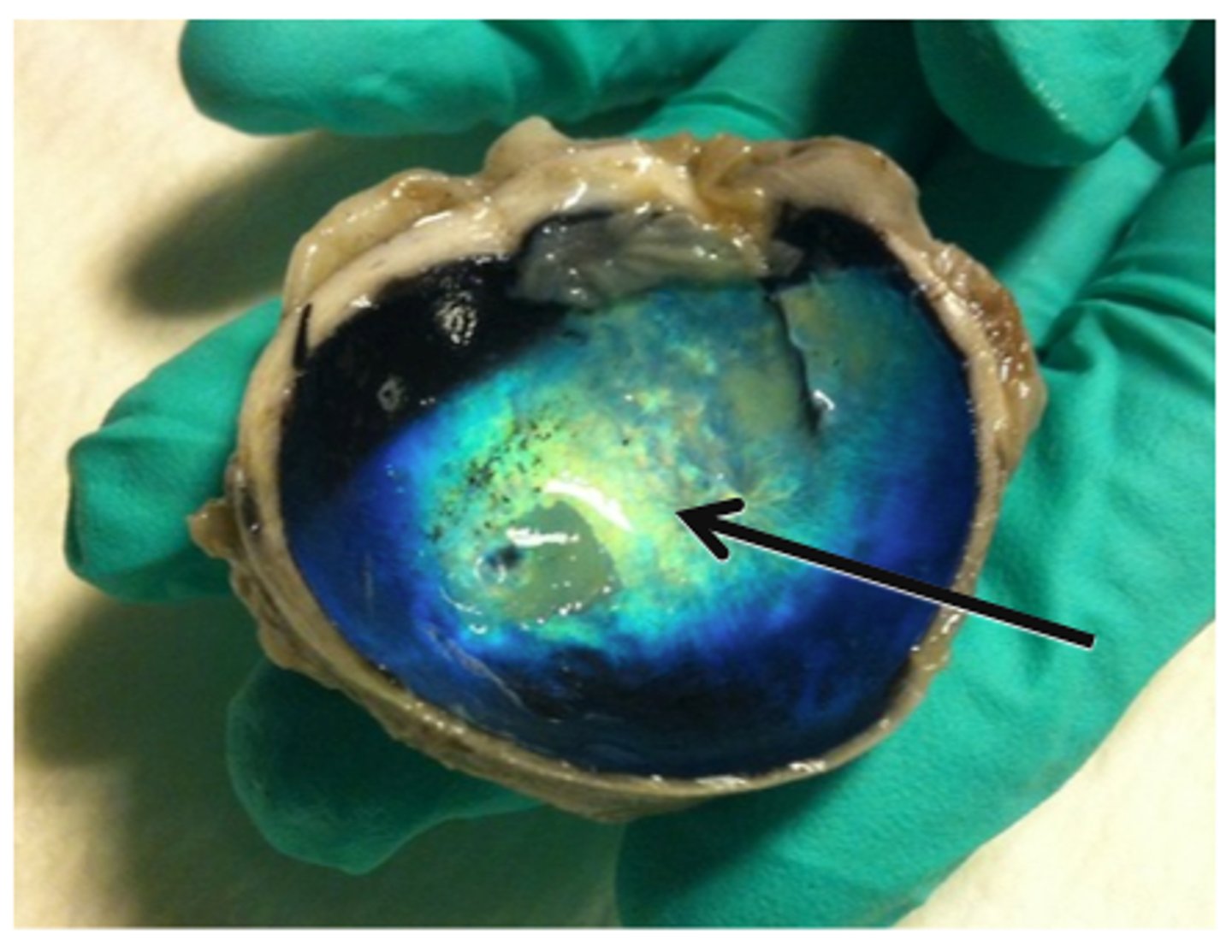
Tapetum lucidum (Choroid Coat)
Iridescent layer found in nocturnal animals for maximizing vision under low intensity light
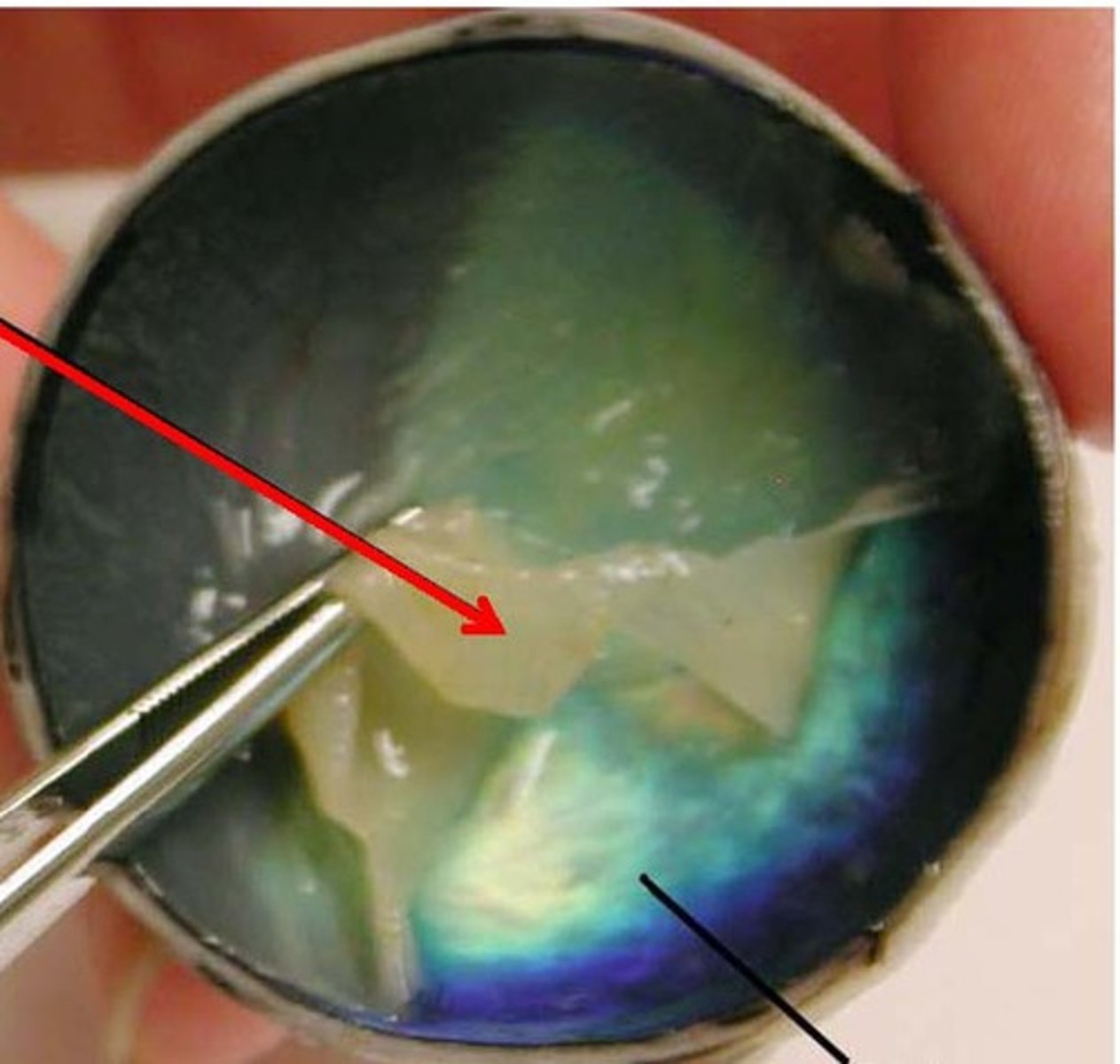
Aqueous humor
The watery liquid secreted by the ciliary body that circulates in the anterior cavity of the eye. The aqueous humor must be drained to avoid an increase in intraocular pressure (glaucoma results from a blockage in the aqueous humor drainage system).
Vitreous humor
A thick, gelatinous substance located in the posterior cavity of the eye behind the lens. This humor helps to maintain the position of the retina against the choroid layer of the eye.

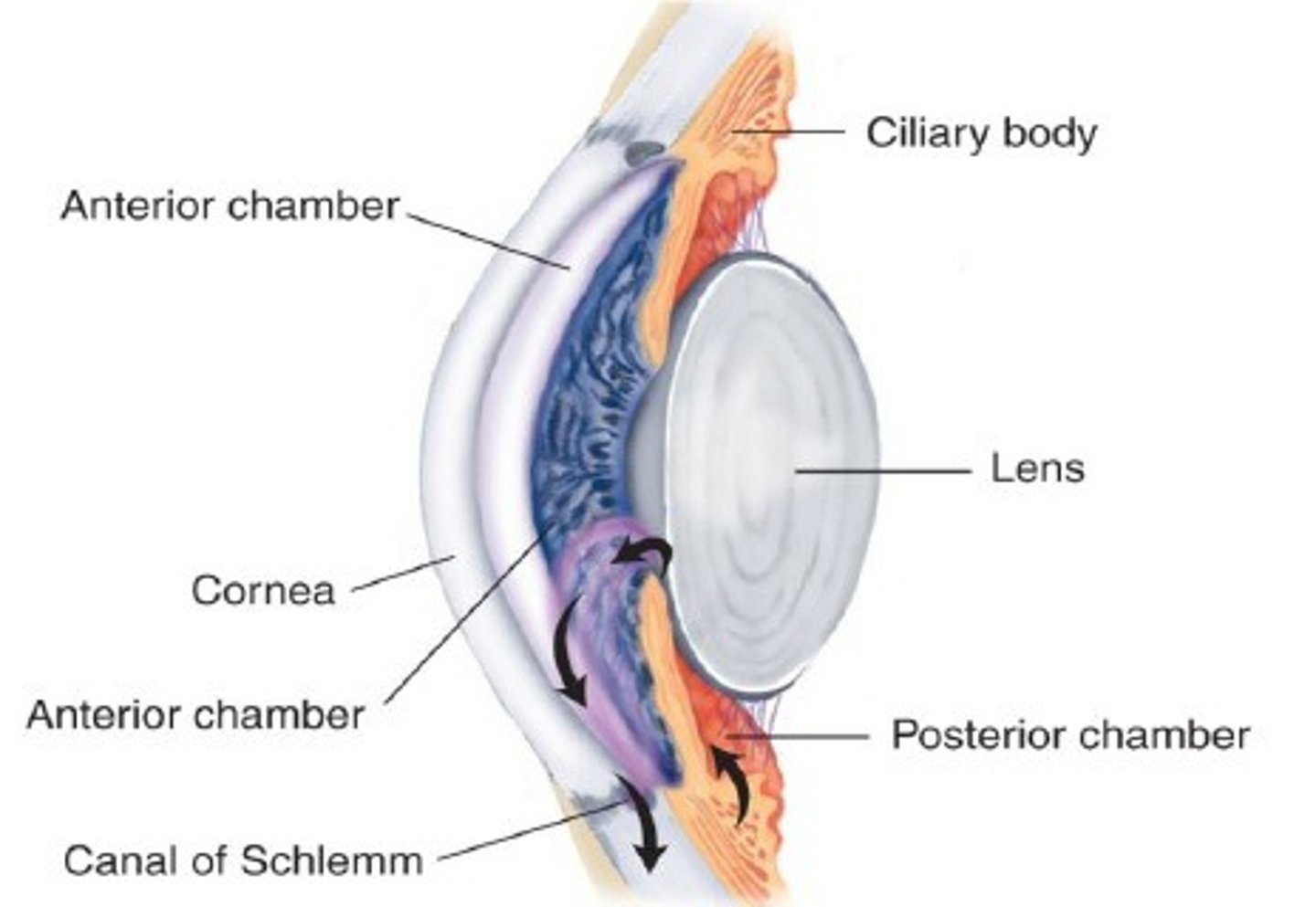
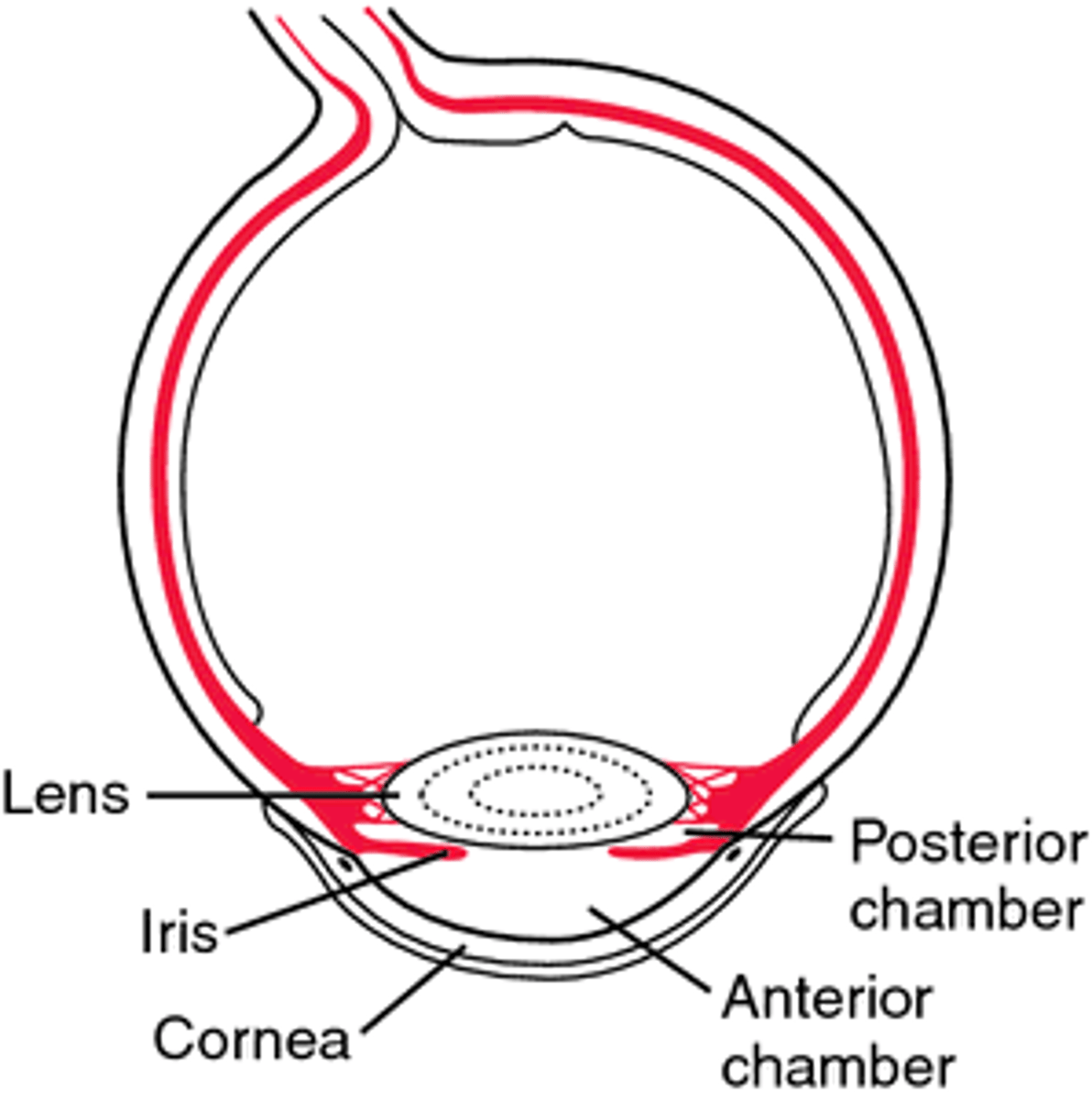
Anterior Cavity
The fluid-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Aqueous humor is the clear fluid that fills the anterior chamber.
Posterior chamber of the eye
filled with a watery fluid known as the aqueous humor, or aqueous. Produced by a structure alongside the lens called the ciliary body, the aqueous passes into the posterior chamber and then flows forward through the pupil into the anterior chamber of the eye.
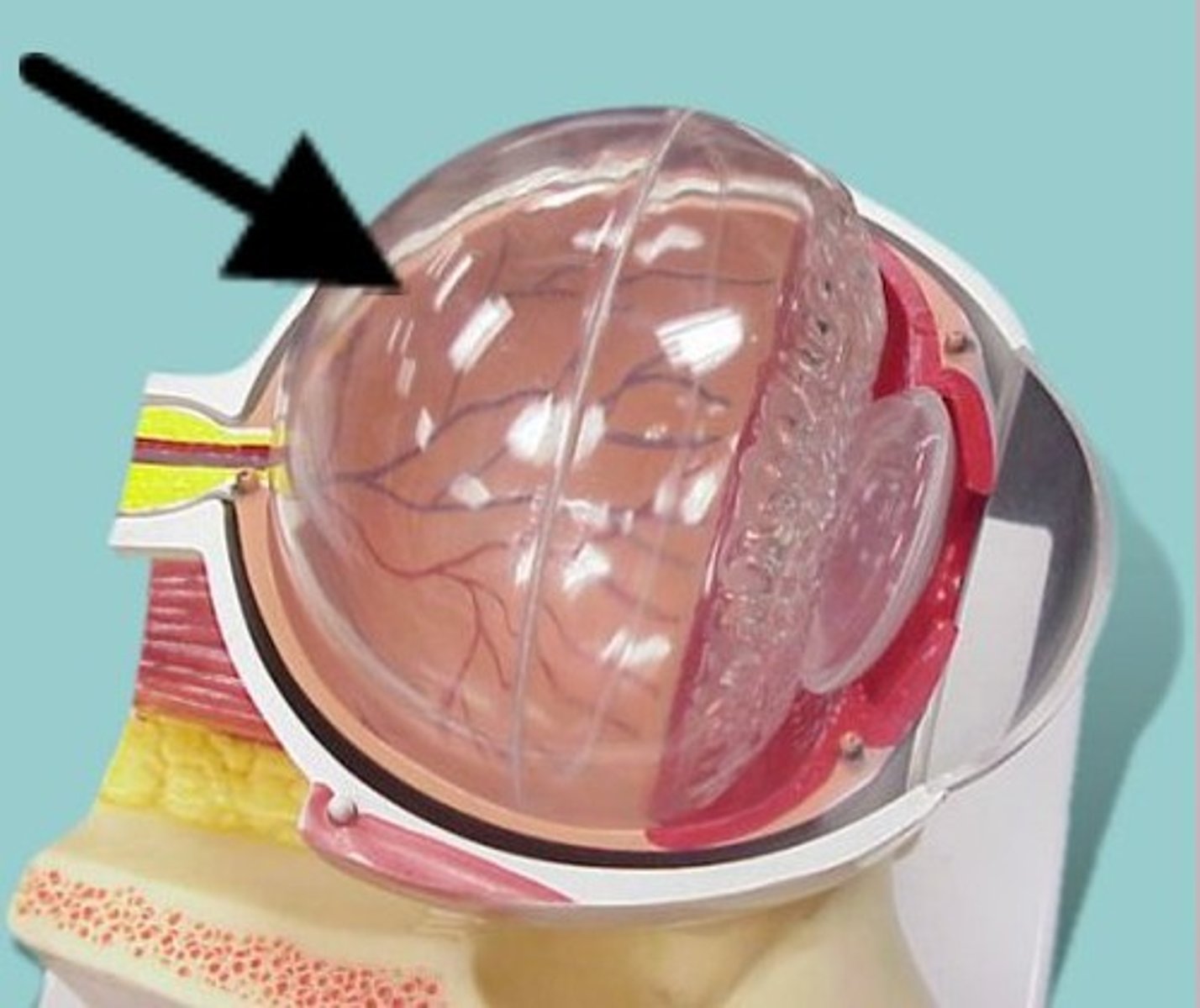
Vitreous Chamber
largest of the three chambers and is located behind the lens and in front of the optic nerve. This chamber is filled with a thick, clear gel-like substance called the vitreous humor (also vitreous body). The humor plays a crucial role in supporting the posterior side of the lens.
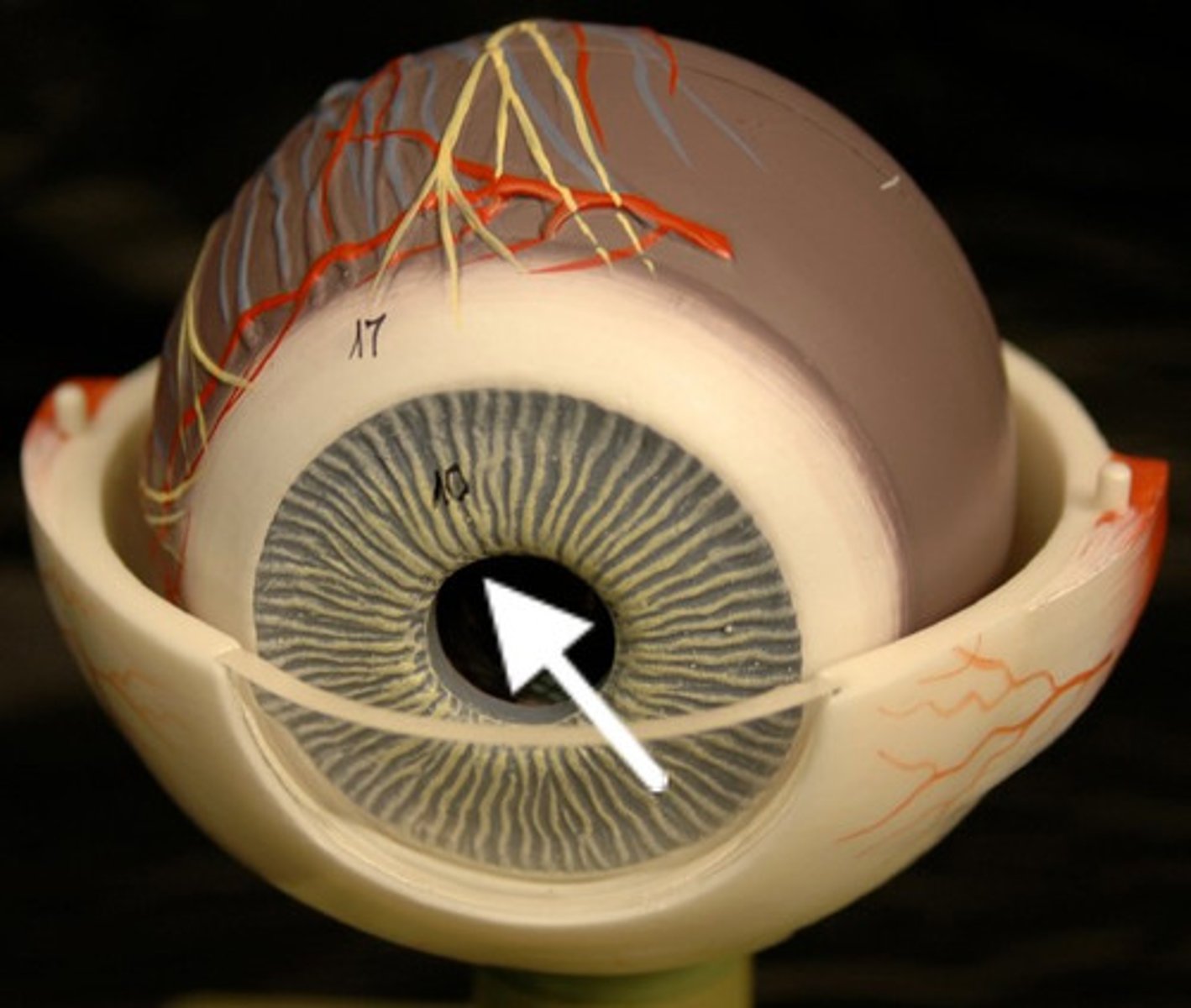
Pupil
a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to strike the retina. It appears black because light rays entering the pupil are either absorbed by the tissues inside the eye directly, or absorbed after diffuse reflections within the eye that mostly miss exiting the narrow pupil.
Optic Disc
the raised disk on the retina at the point of entry of the optic nerve, lacking visual receptors and so creating a blind spot.
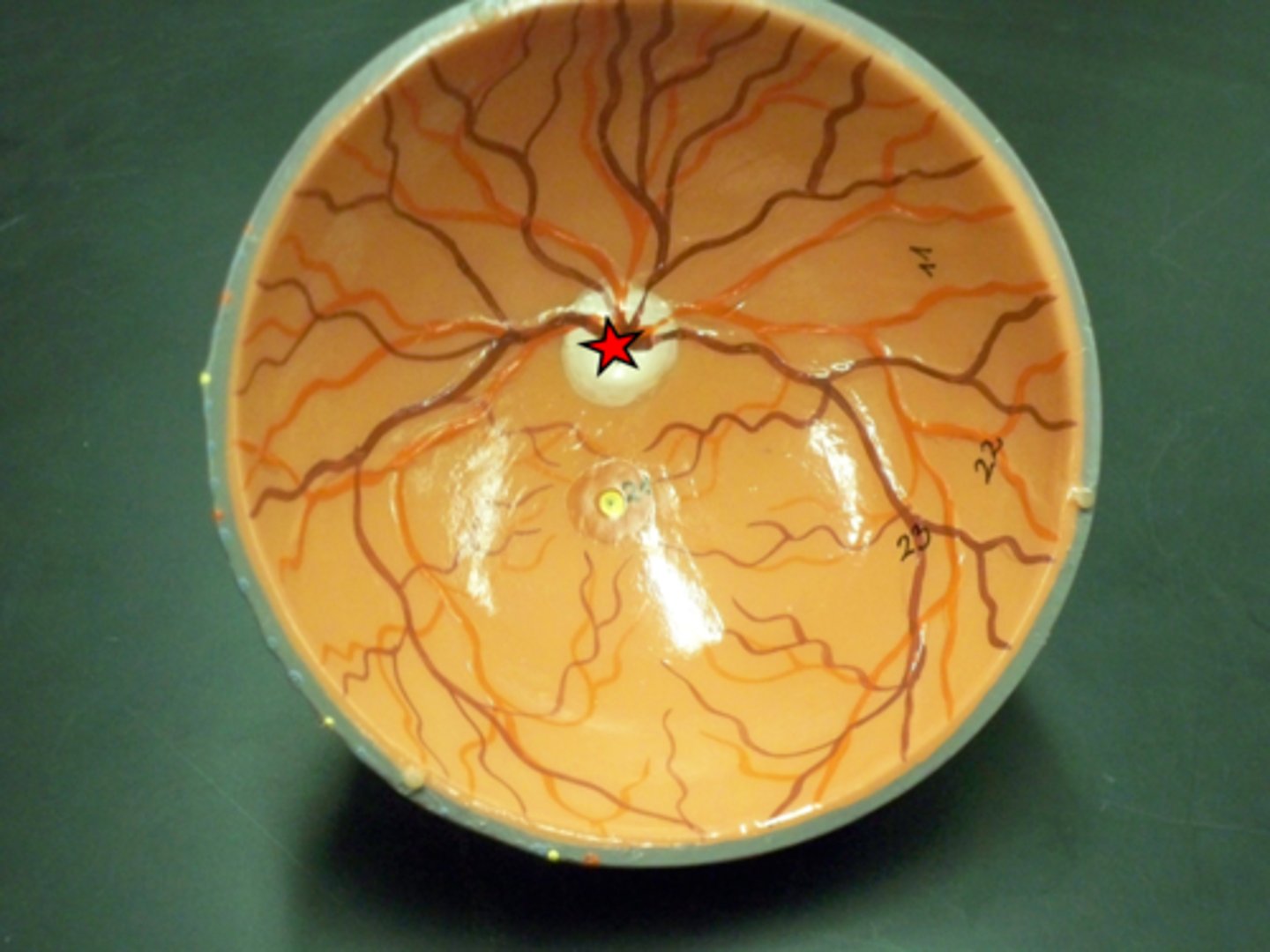
Fovea Centralis
a small depression in the retina of the eye where visual acuity is highest. The center of the field of vision is focused in this region, where retinal cones are particularly concentrated.
Macula Lutea
an oval yellowish area surrounding the fovea near the center of the retina in the eye, which is the region of keenest vision.
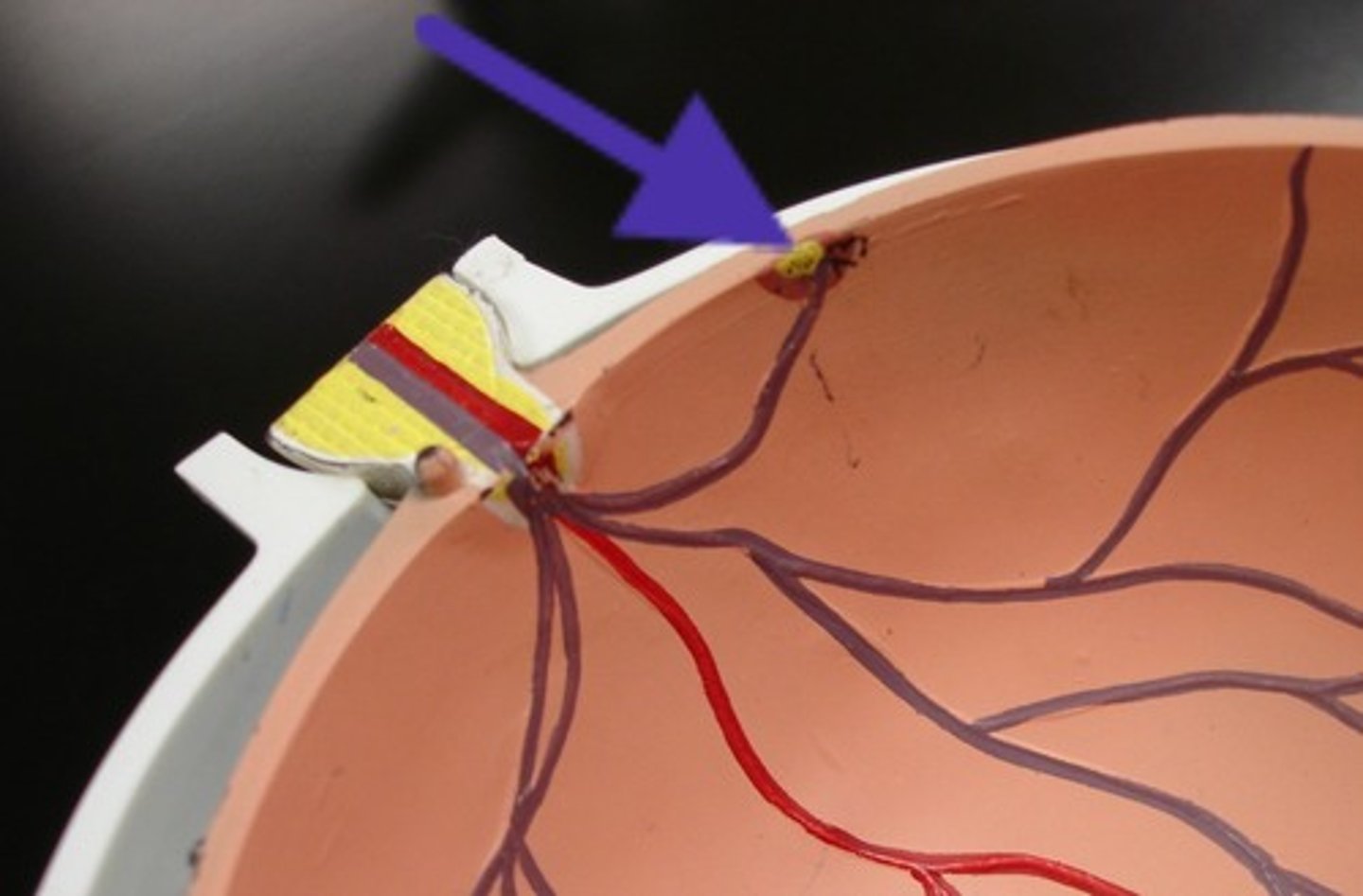
Suspensory ligaments of the eye
a series of fibers that connect the ciliary body of the eye with the lens, holding it in place.
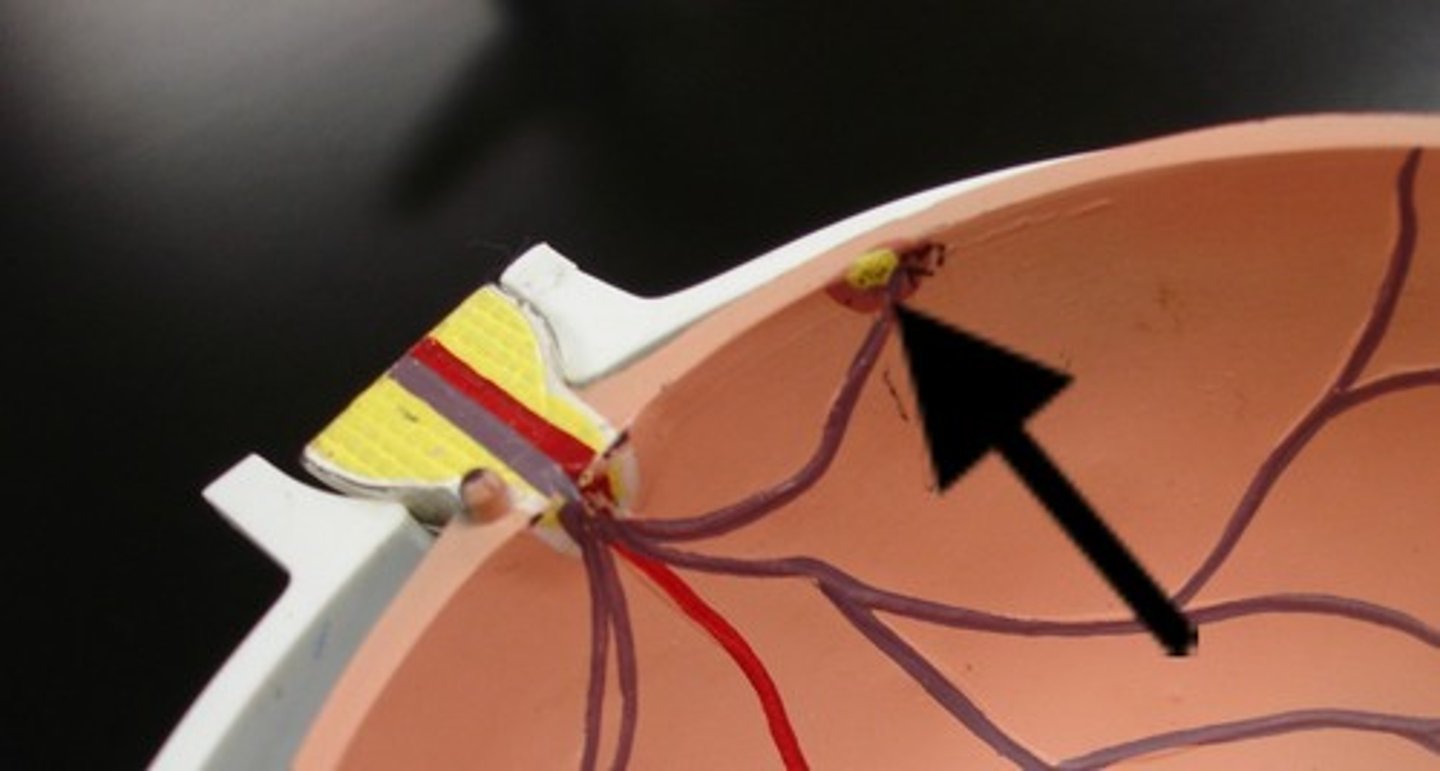
Ciliary Body
includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The vitreous humor is produced in the the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body.
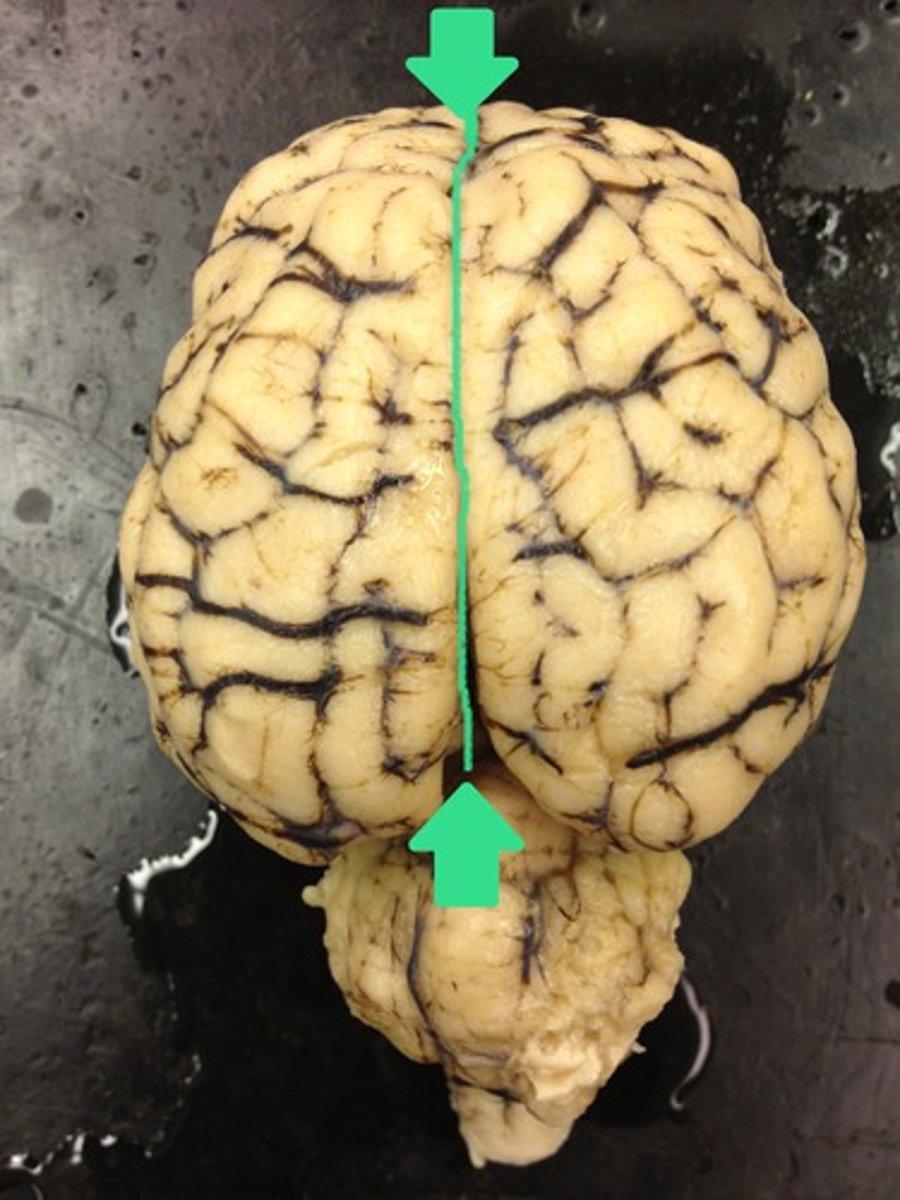
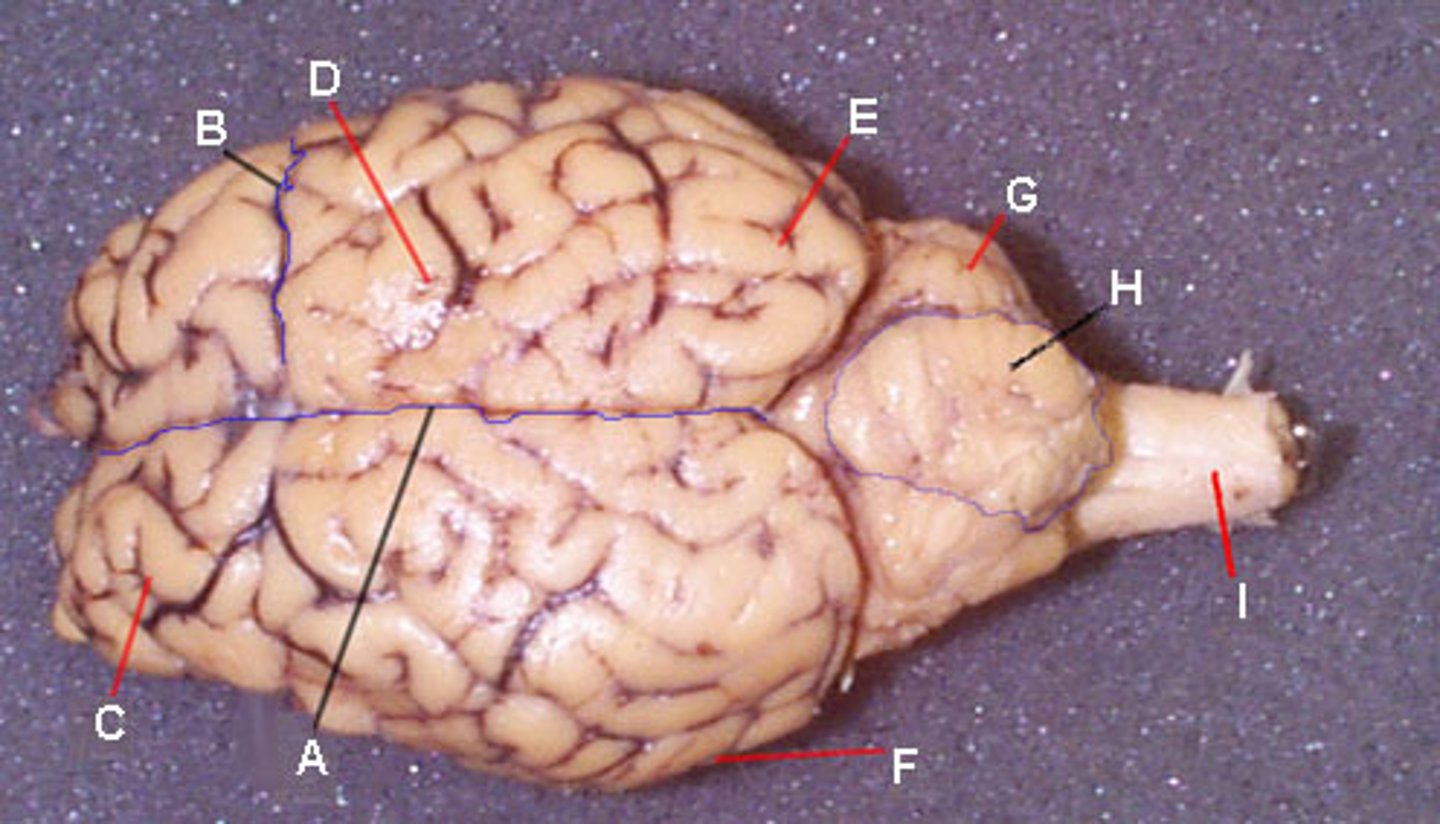
Longitudinal fissure
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
What are sulcus (sulci)?
grooves in the brain
what are gyrus (gyri)?
elevated ridges of the brain
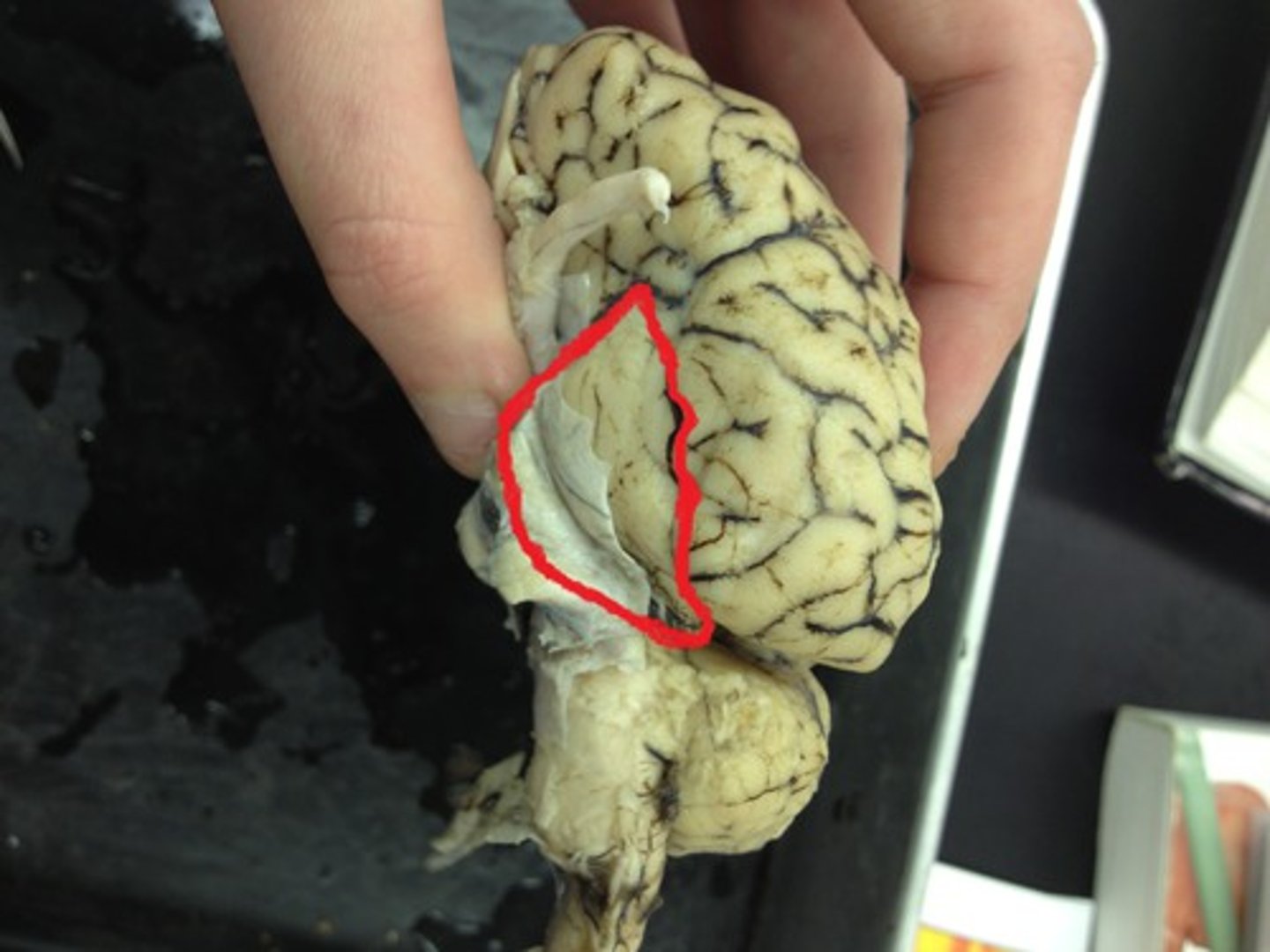
Arachnoid mater
Identify the membrane
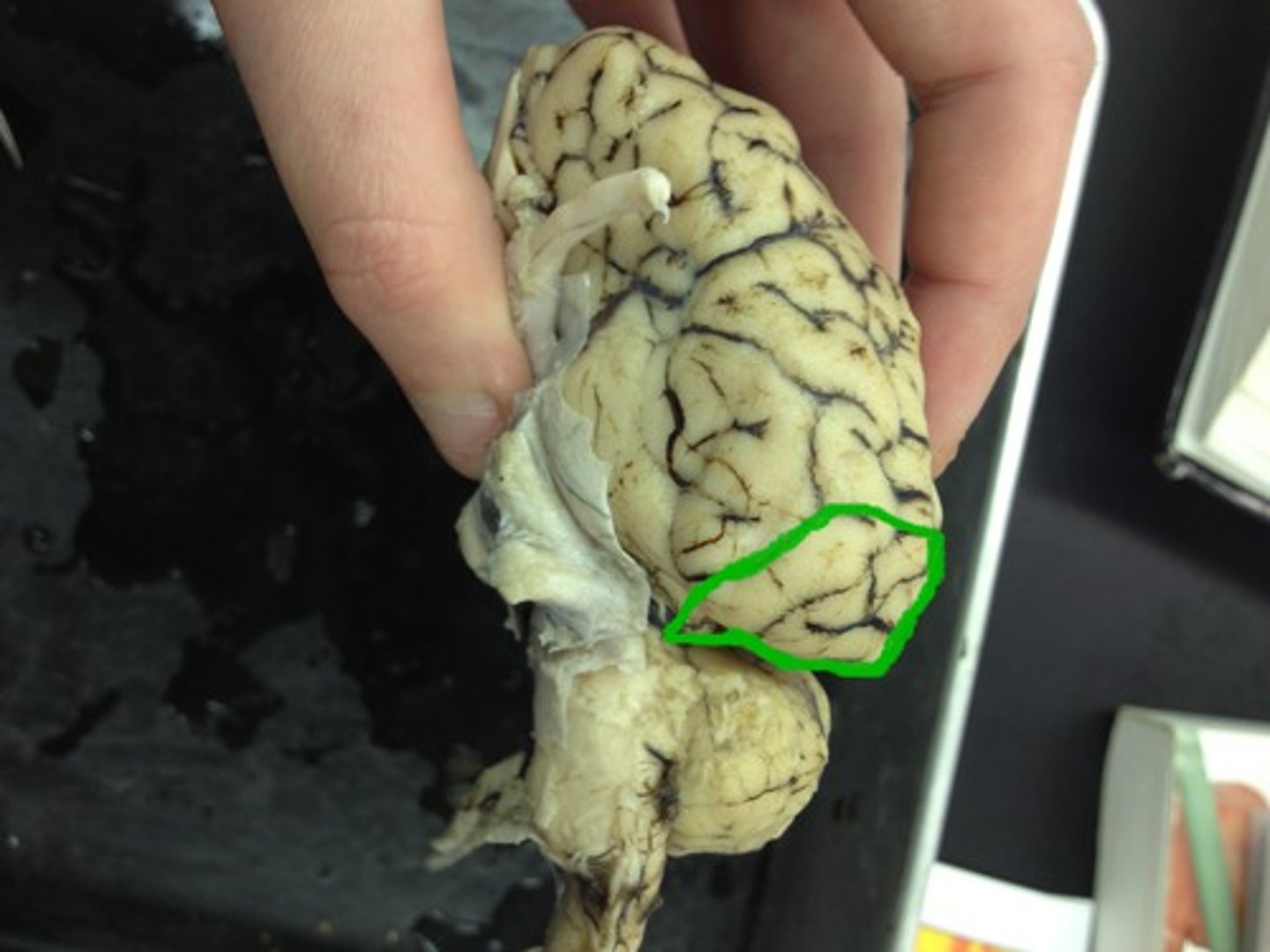
Cerebellar hemispheres
Identify the hemisphere G
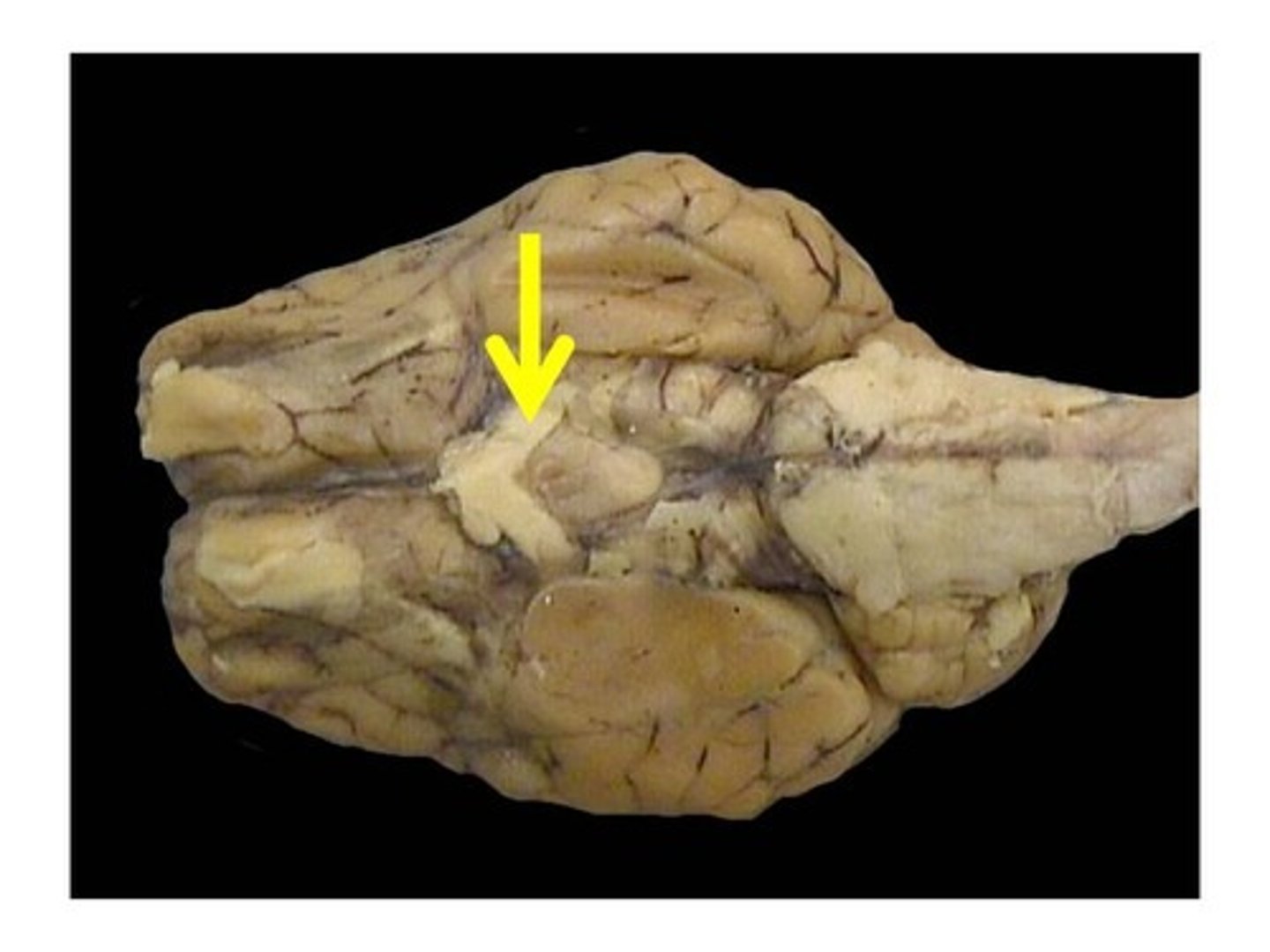
Superior Colliculi
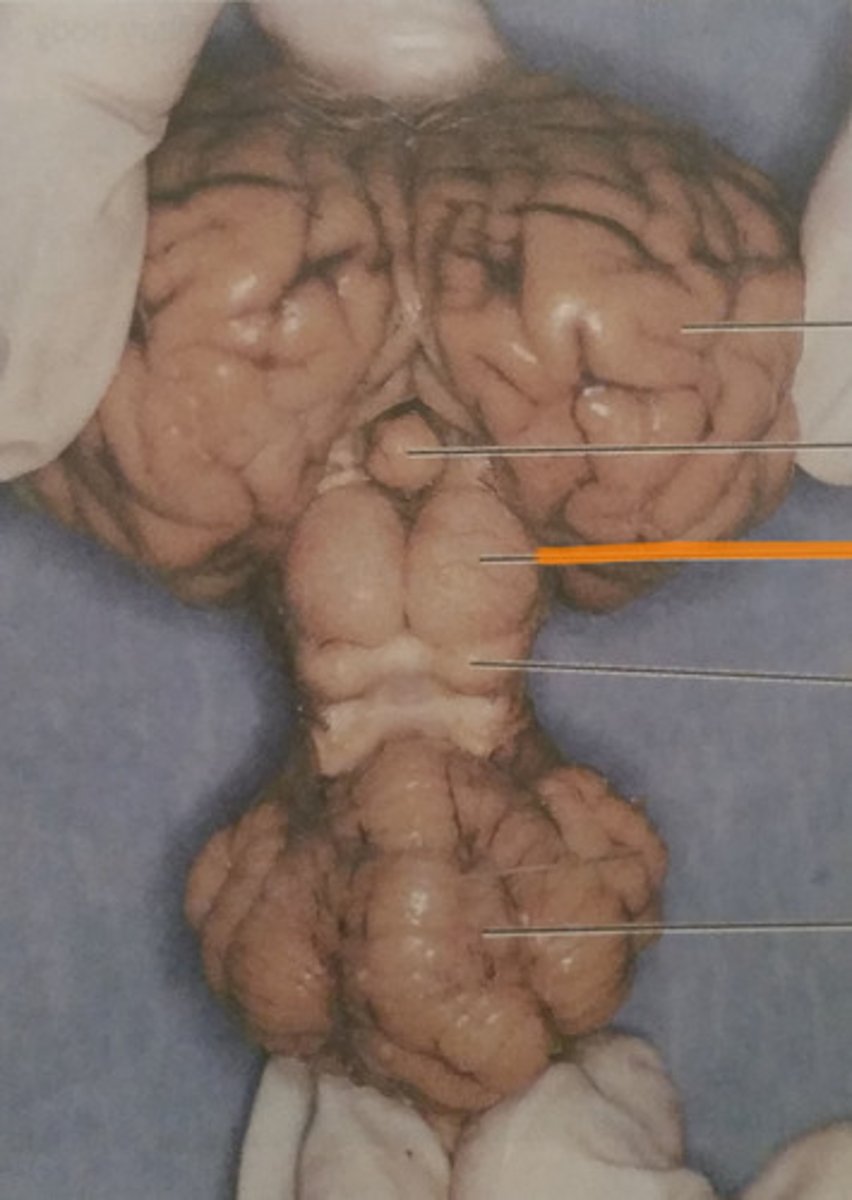
Inferior Colliculi
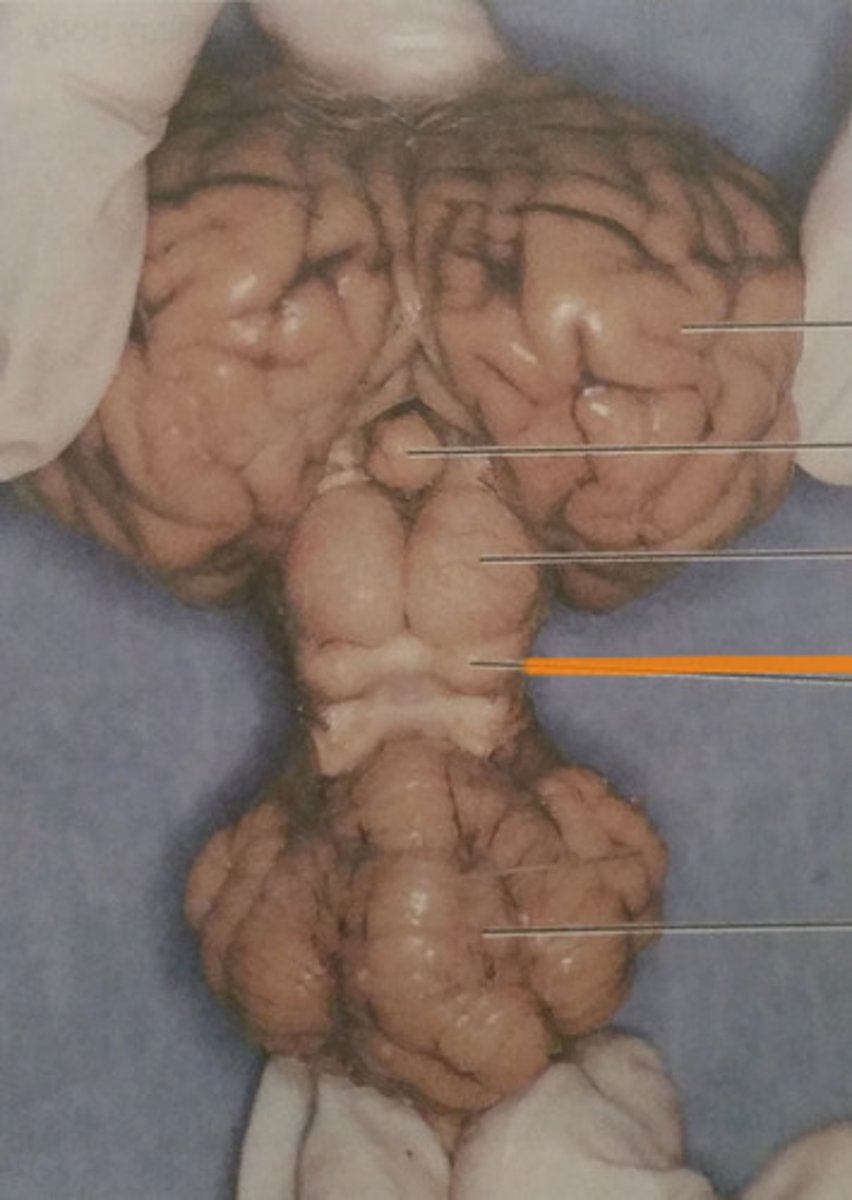
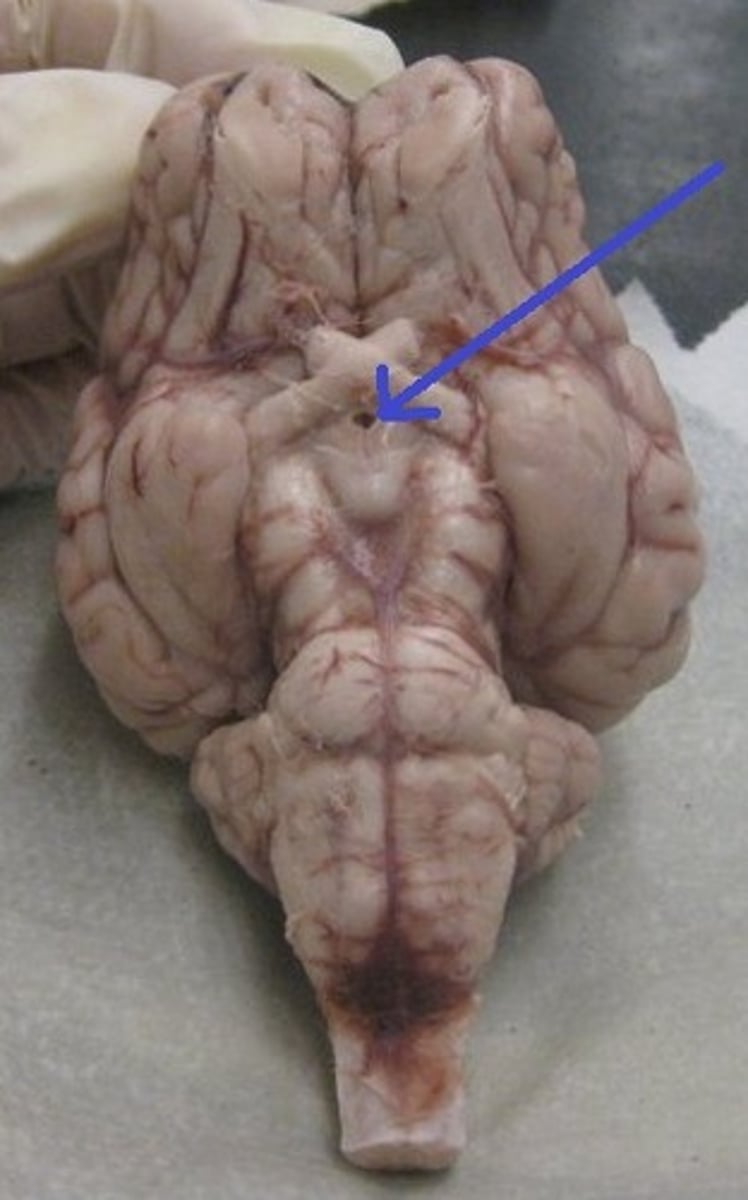
Olfactory bulbs
Optic nerves
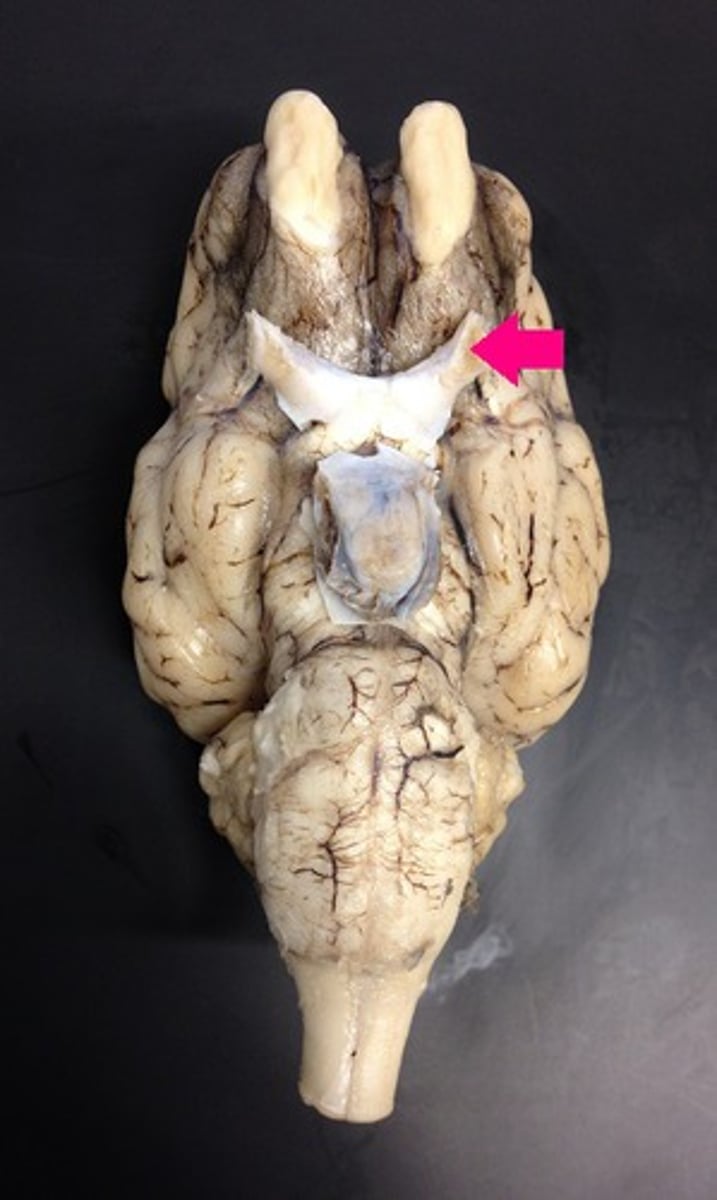
Optic chiasma
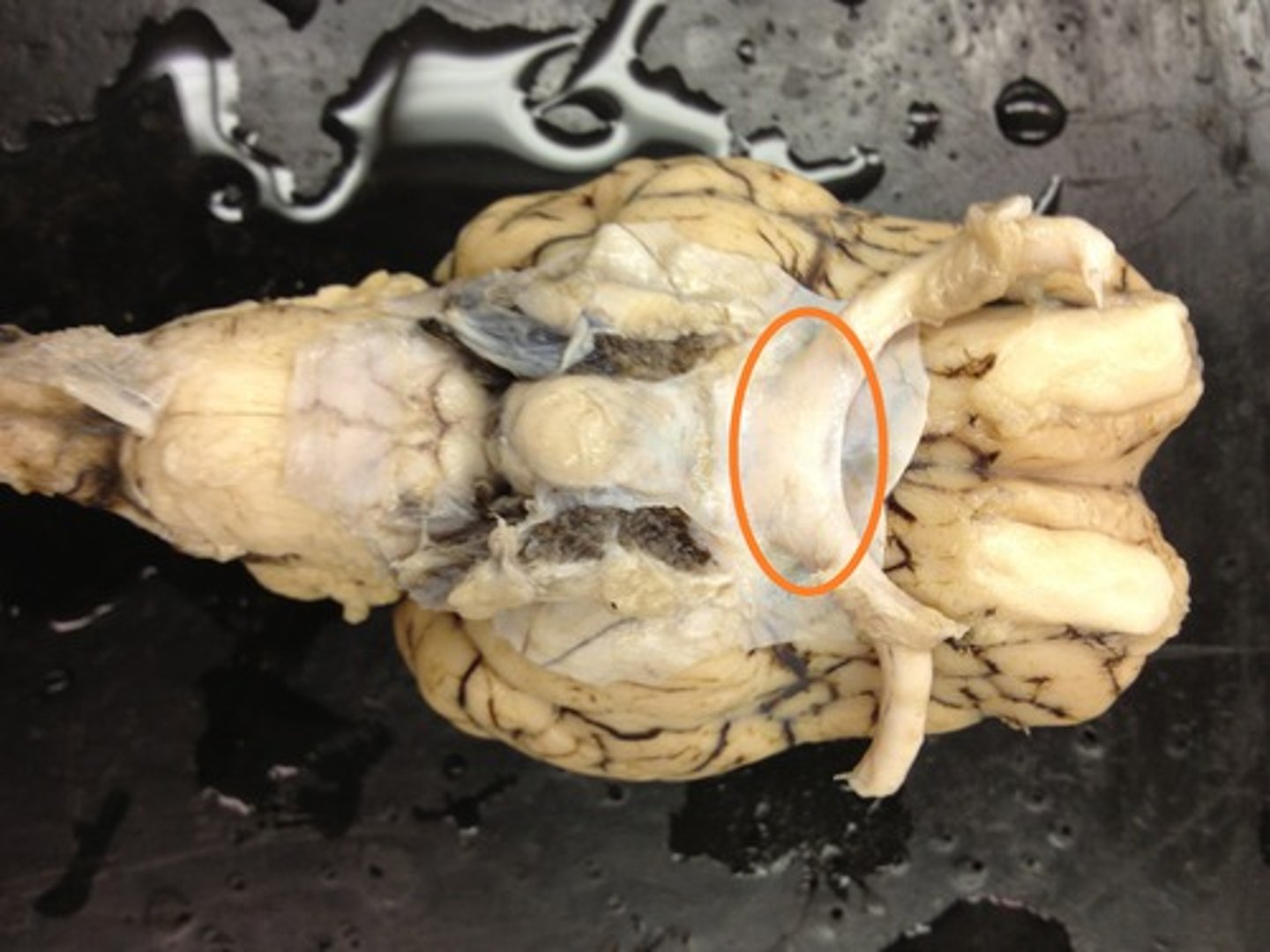
Optic tracts
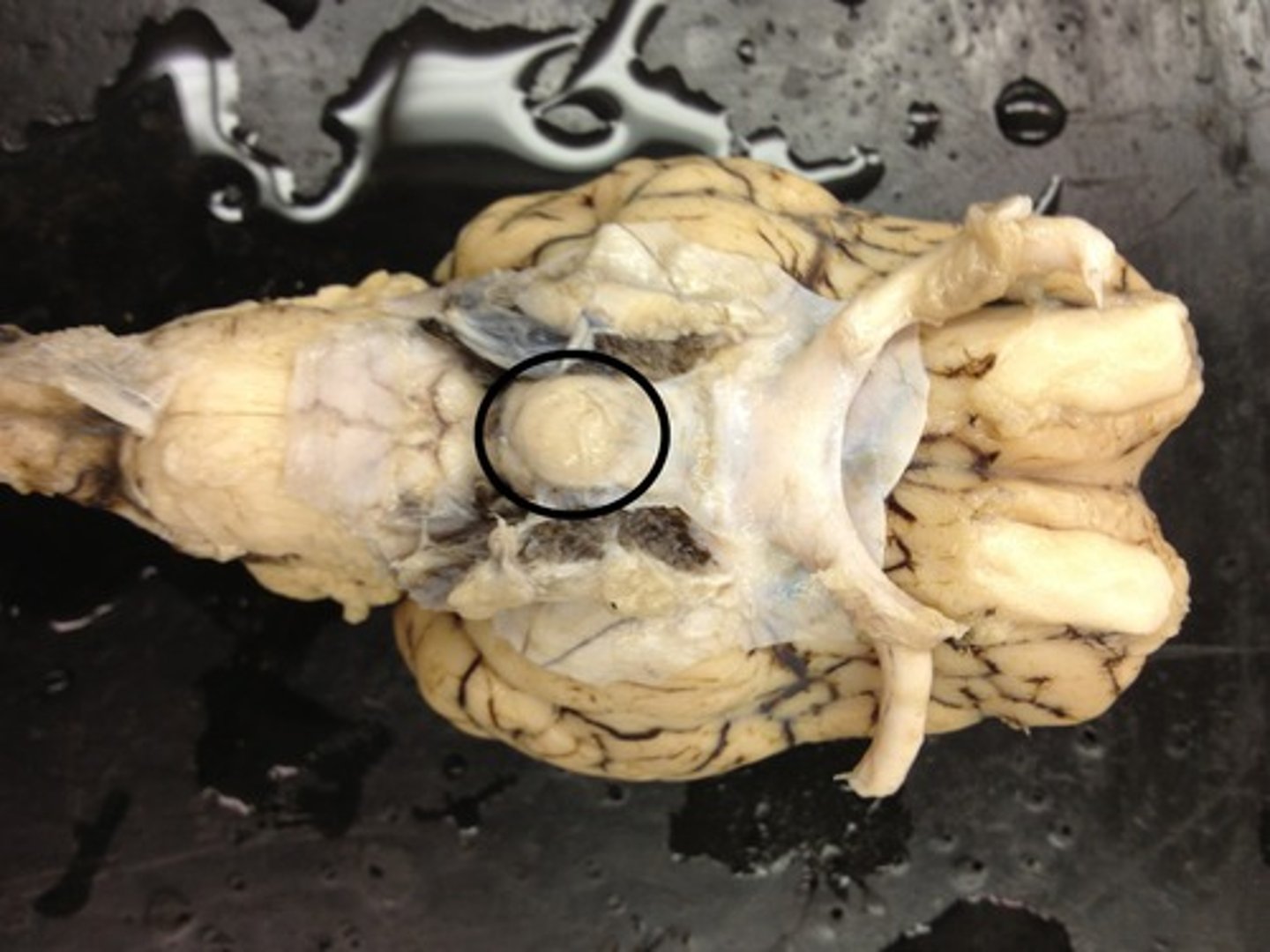
Infundibulum
Mammillary bodies
Midbrain
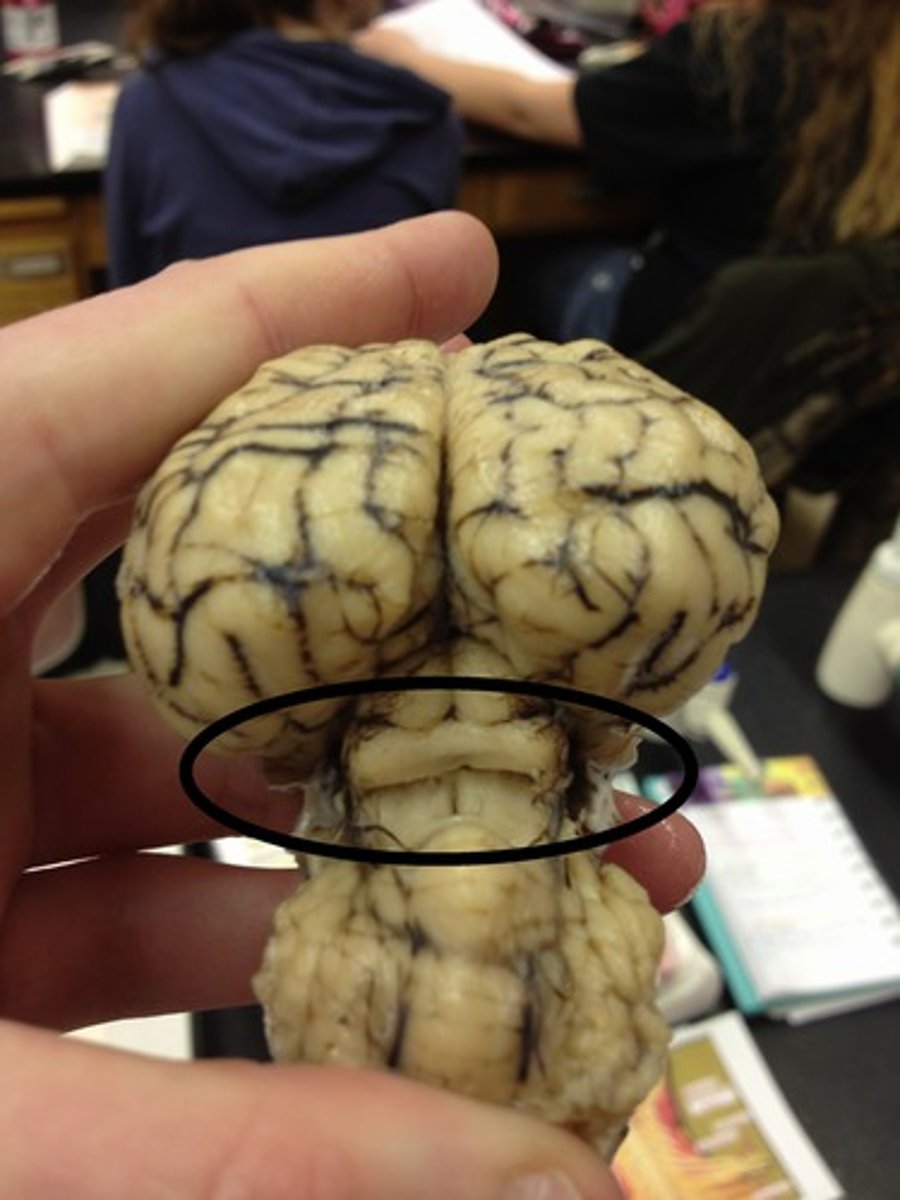
Cerebral peduncles
Pons
Medulla oblongata
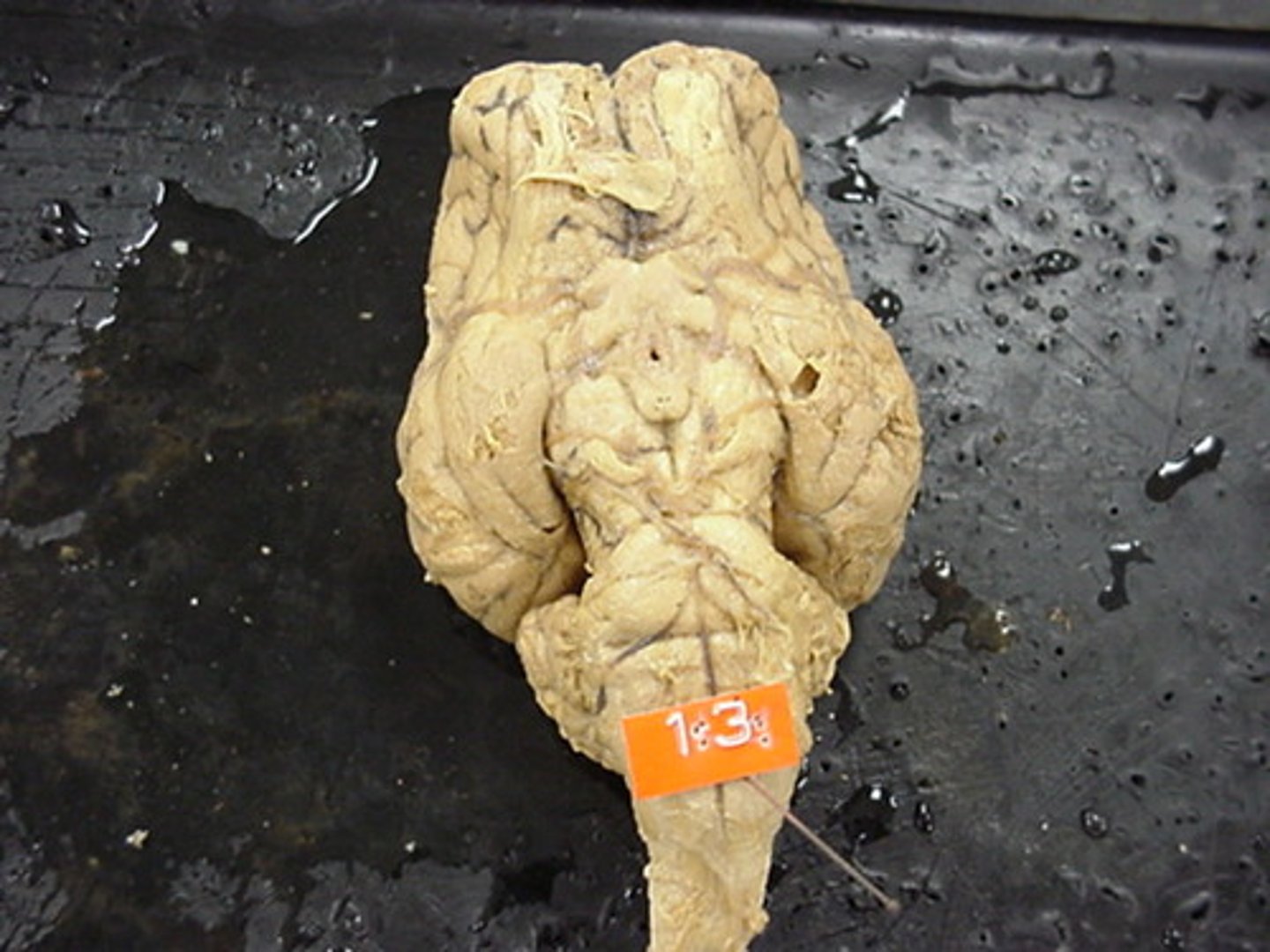

Spinal cord
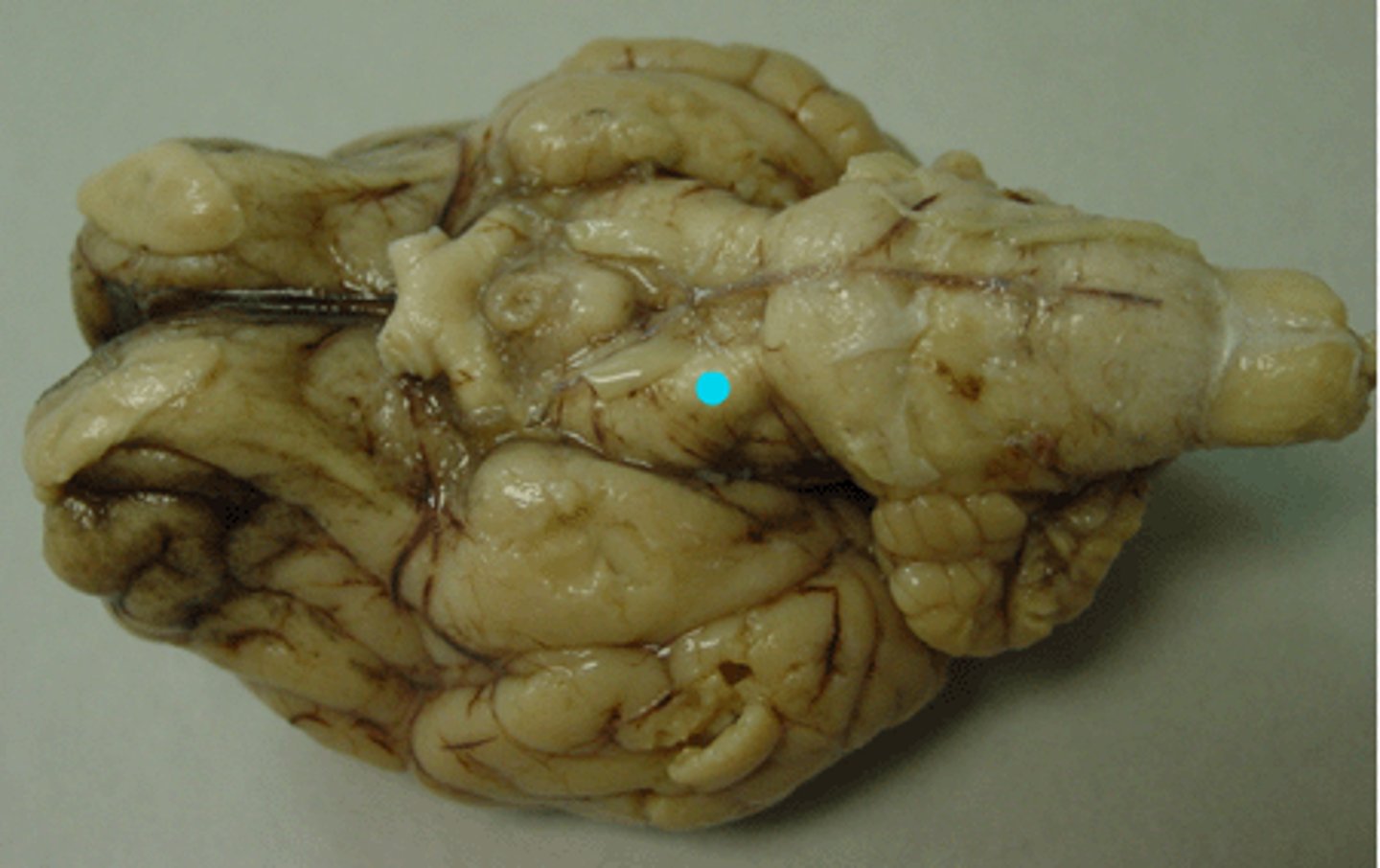
Lateral ventricle
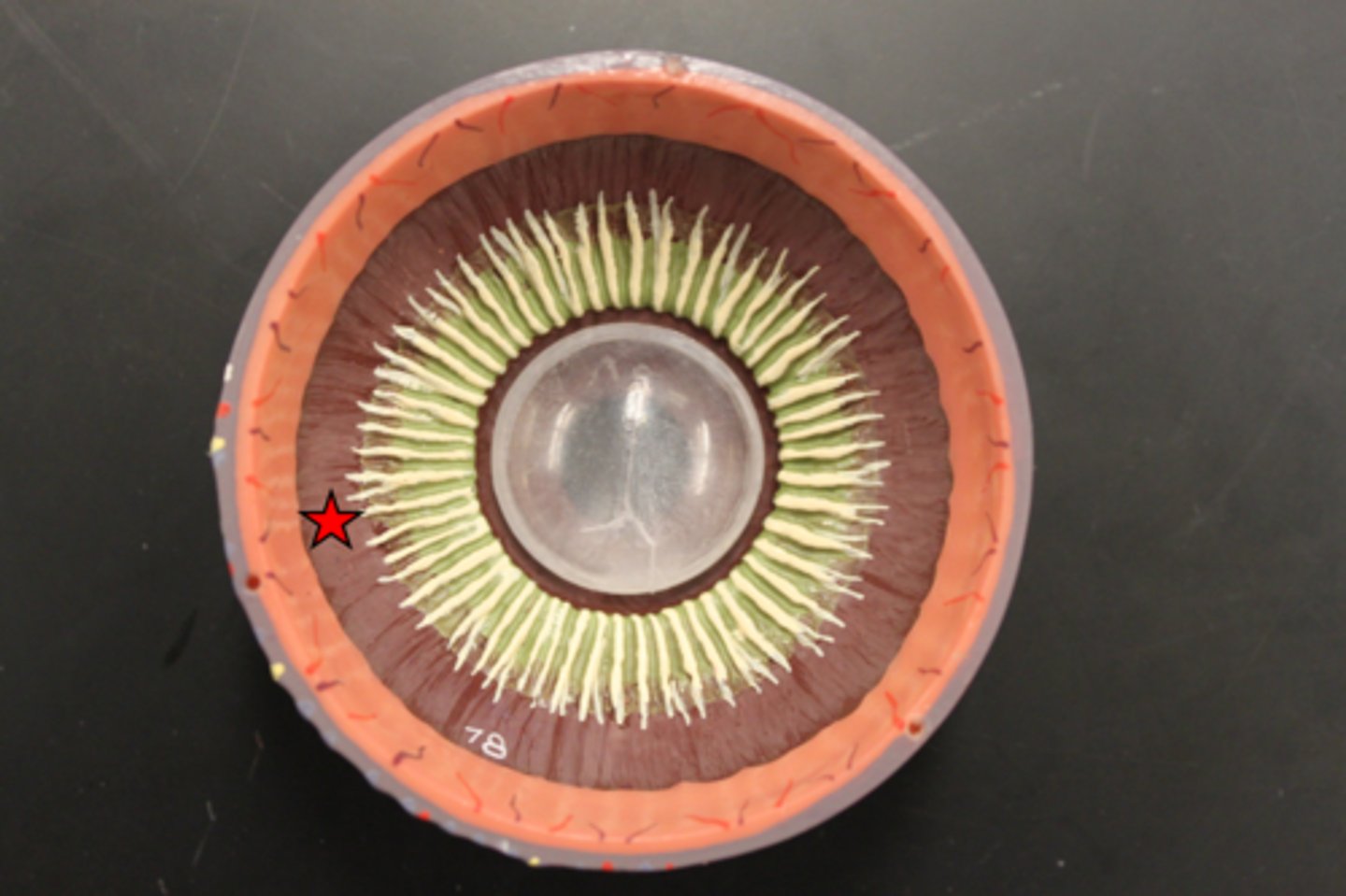
Identify the star
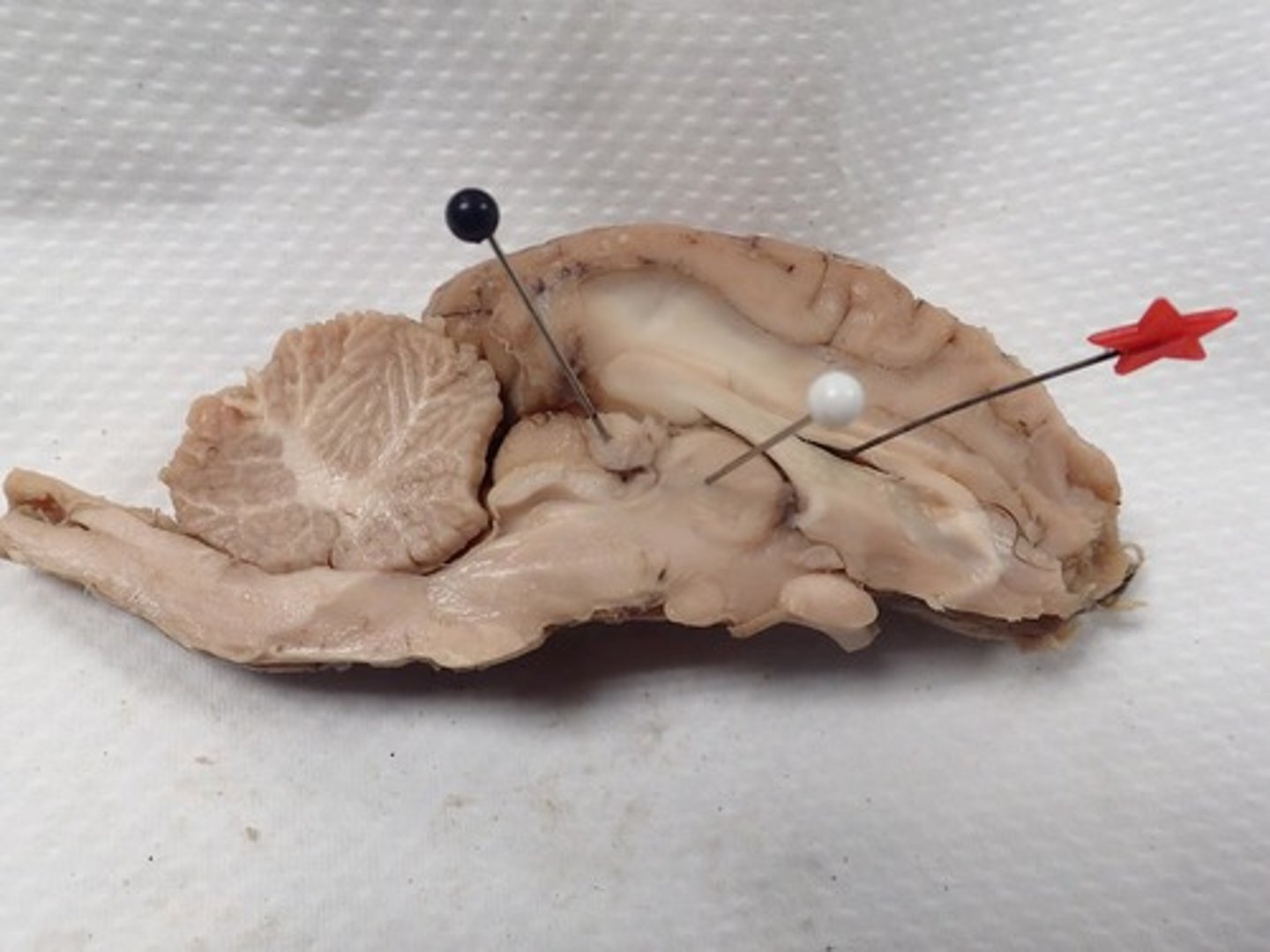
Choroid plexus
Fourth Ventricle
Cerebral Aqueduct
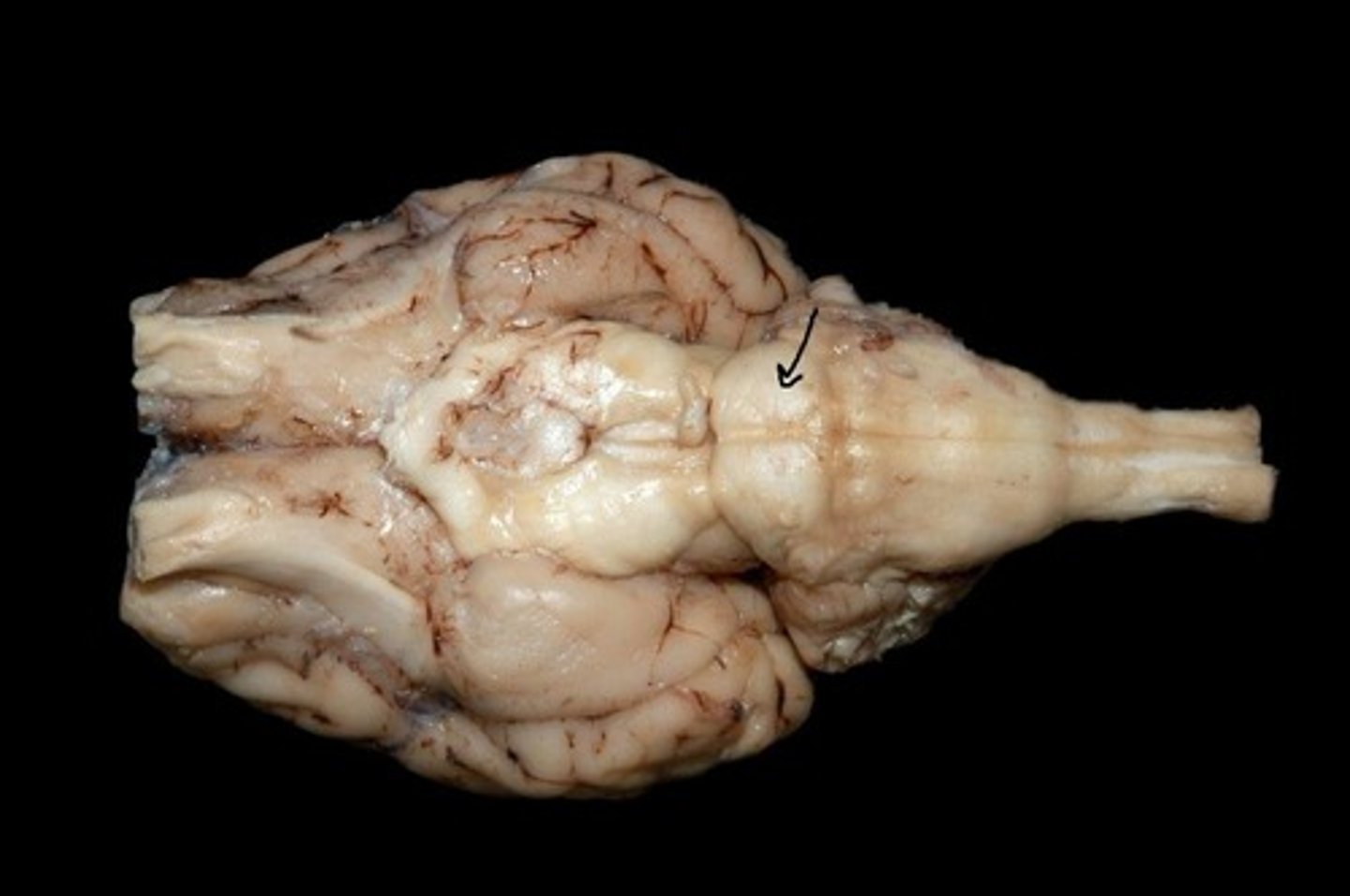
Cerebral peduncle
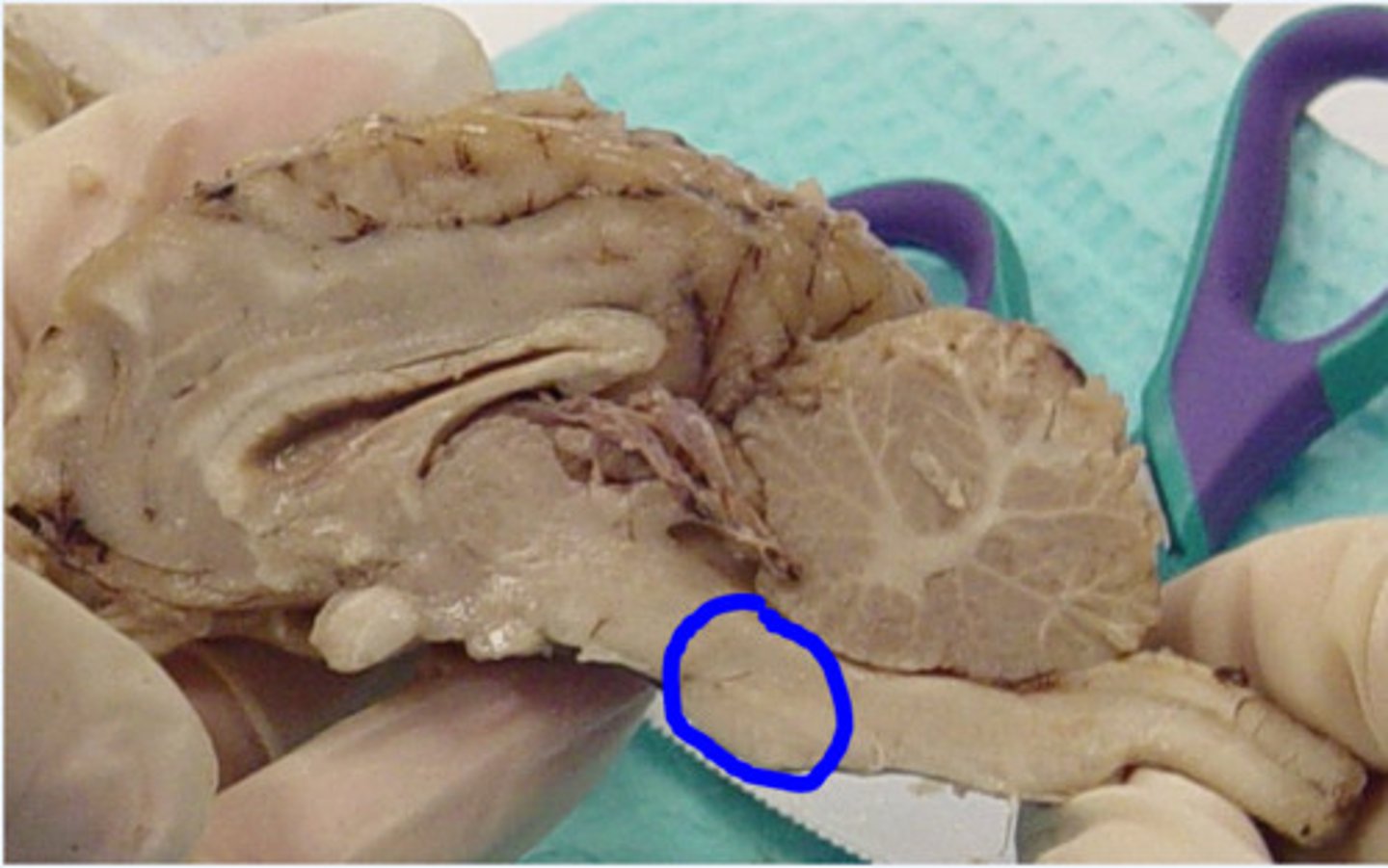
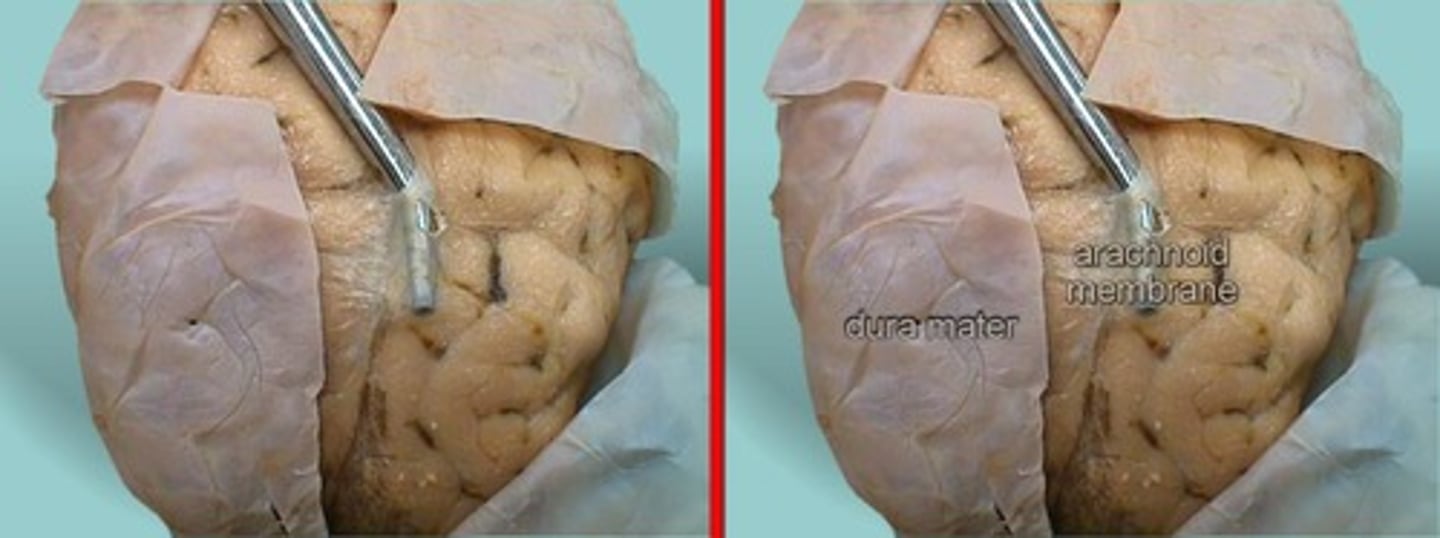
dura mater
Identify the covering.
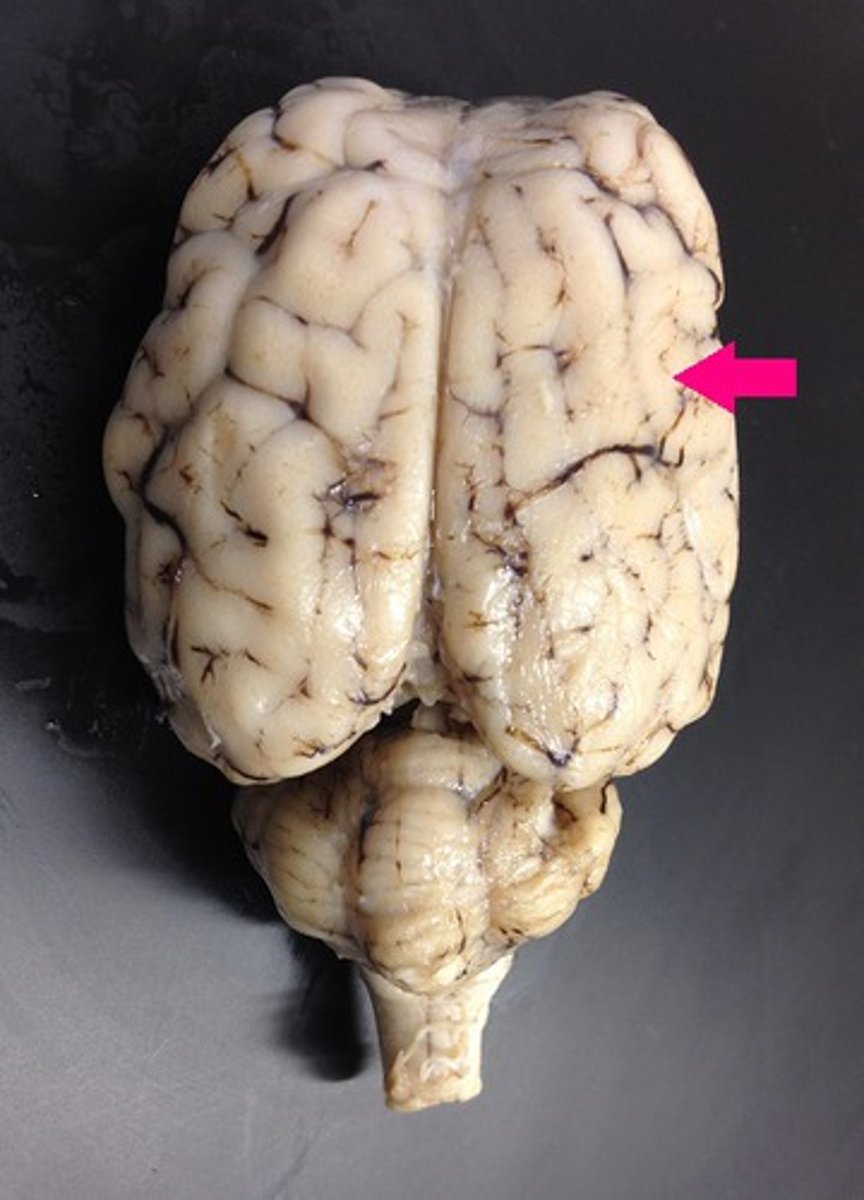
cerebrum
Identify the major brain region.
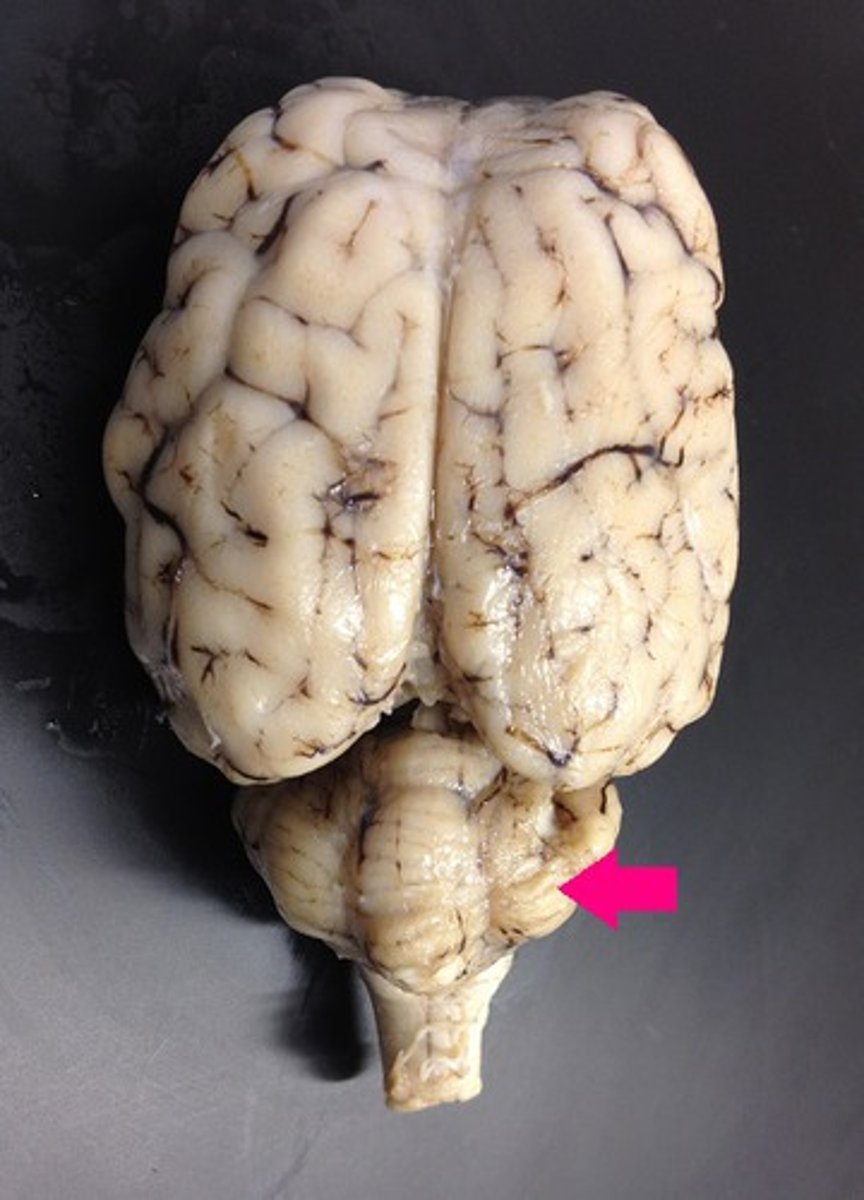
cerebellum
Identify the major brain region.
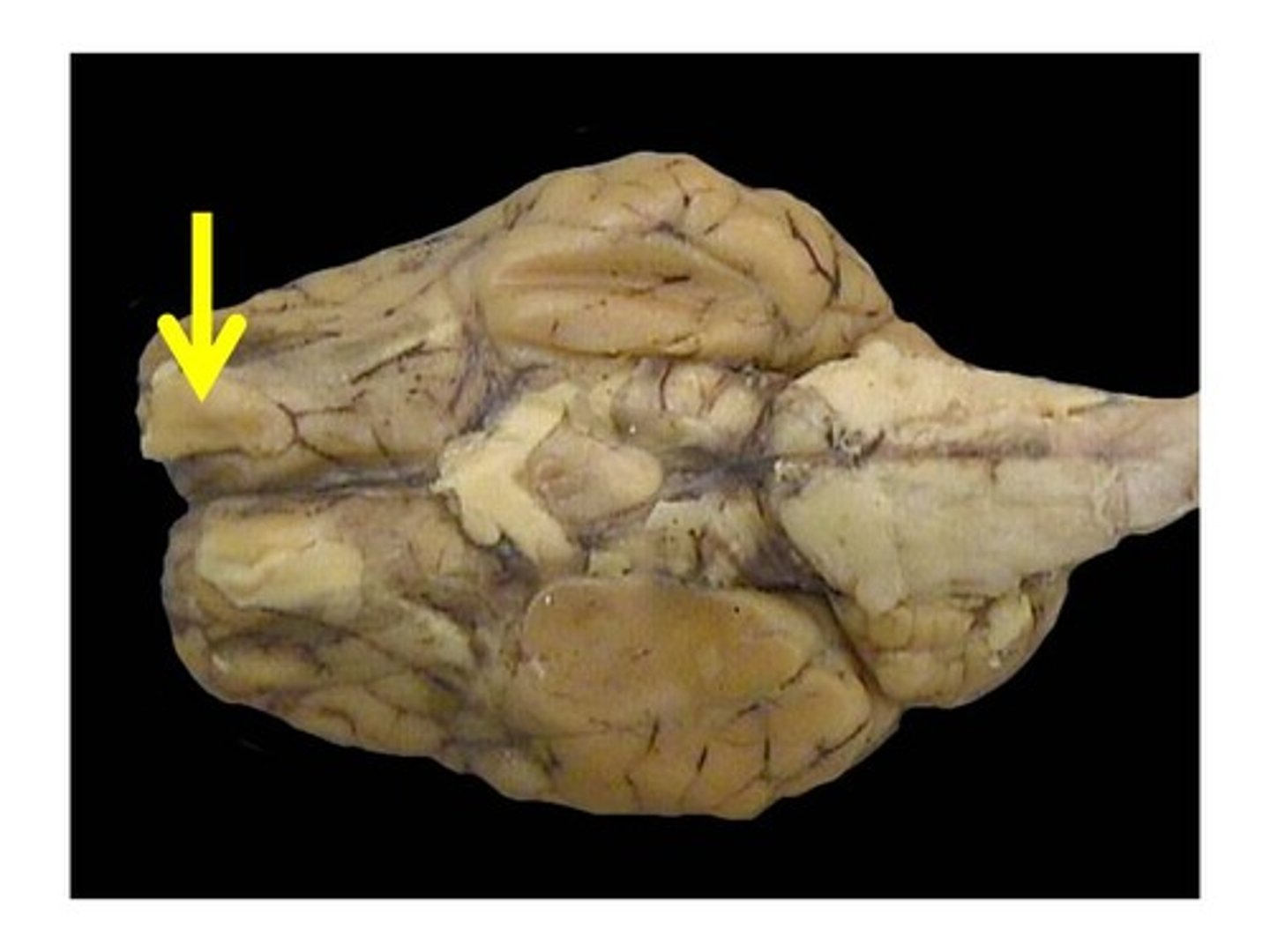
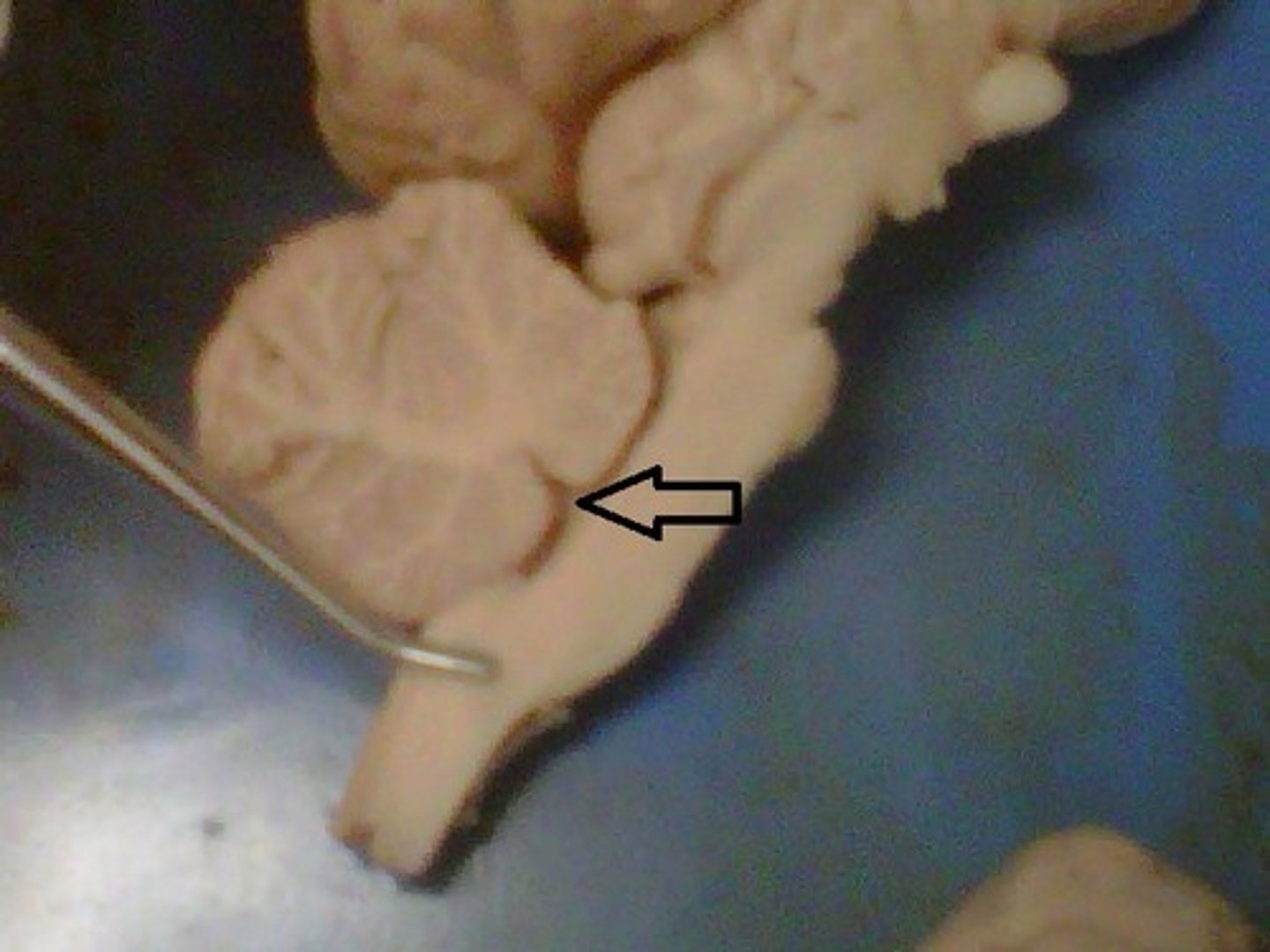
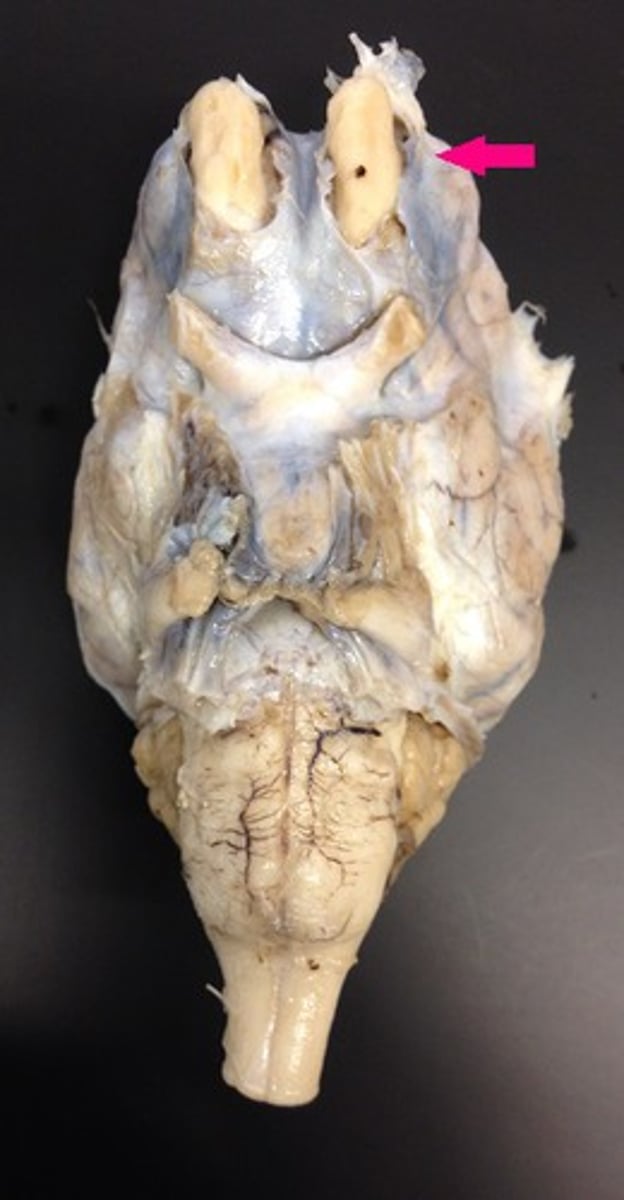
olfactory bulb
Identify the tip.
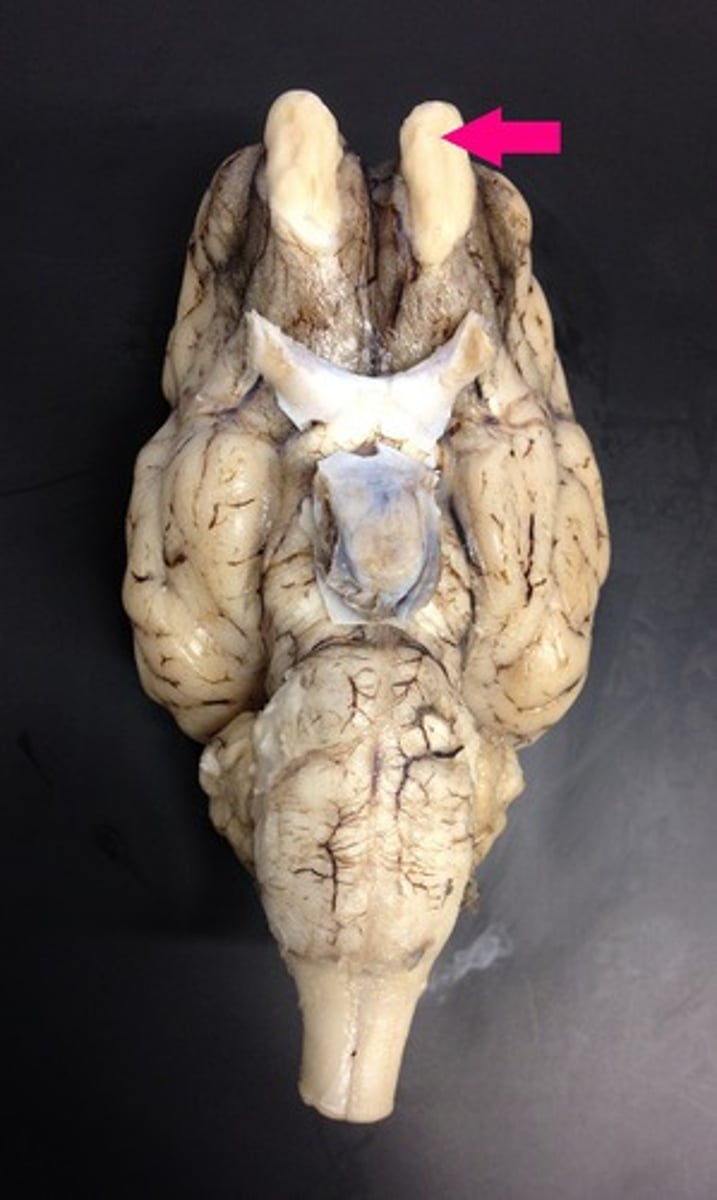
optic nerve
Identify the nerve by name.
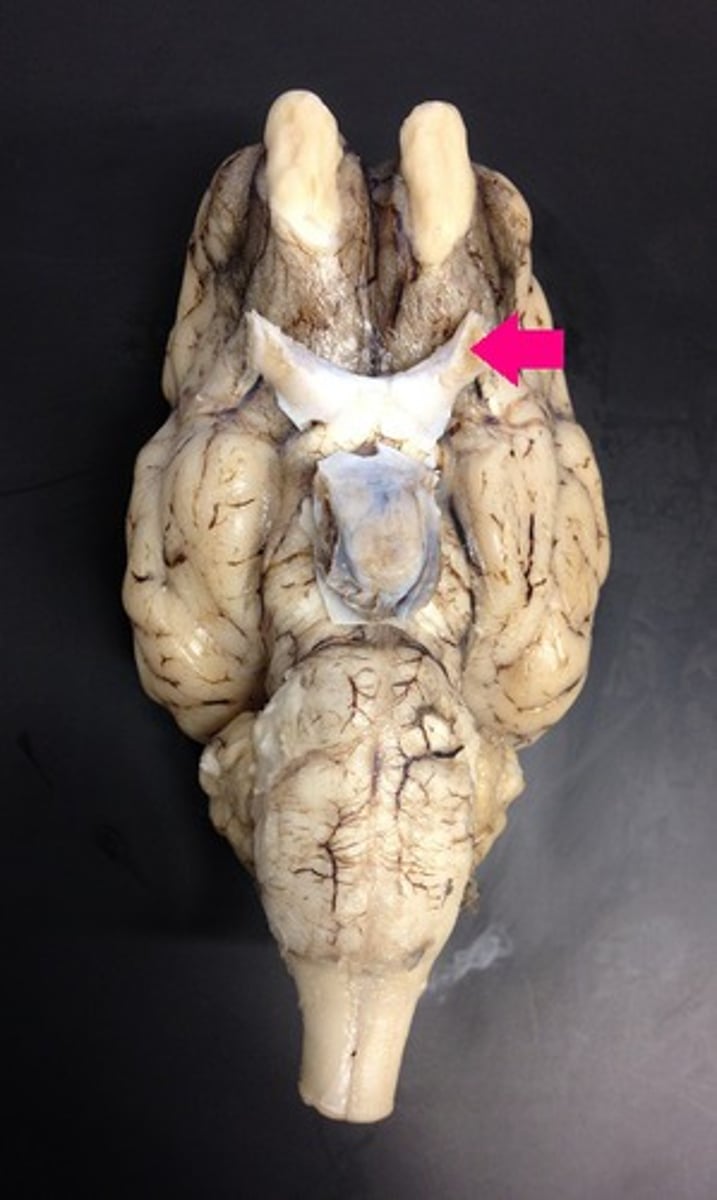
optic tract
Identify the structure.
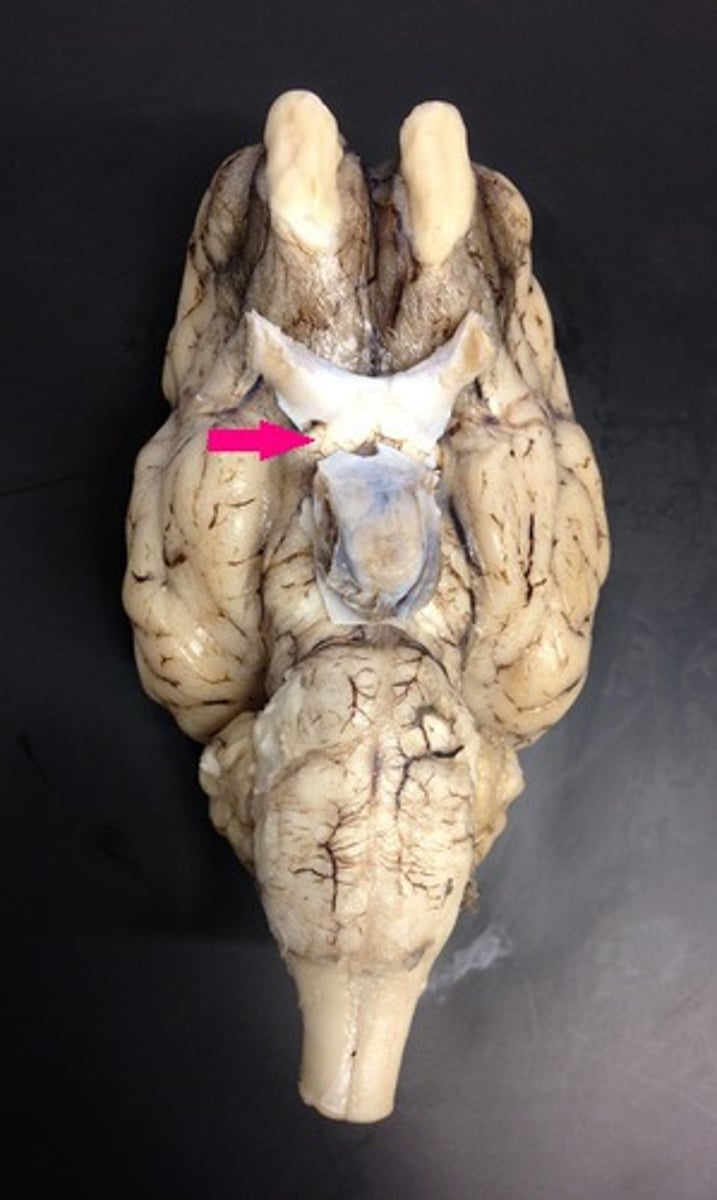
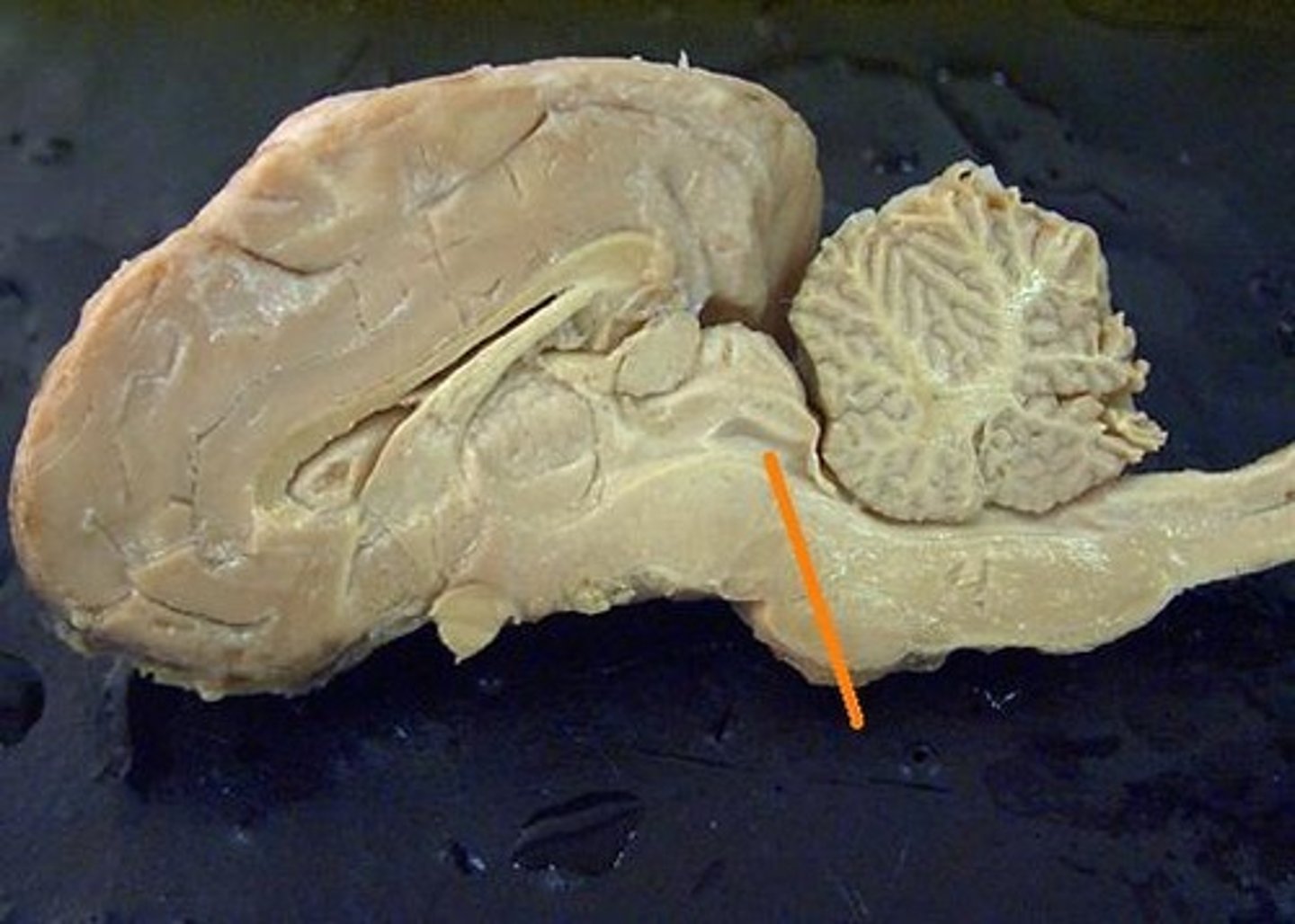
pituitary gland
Identify the structure.
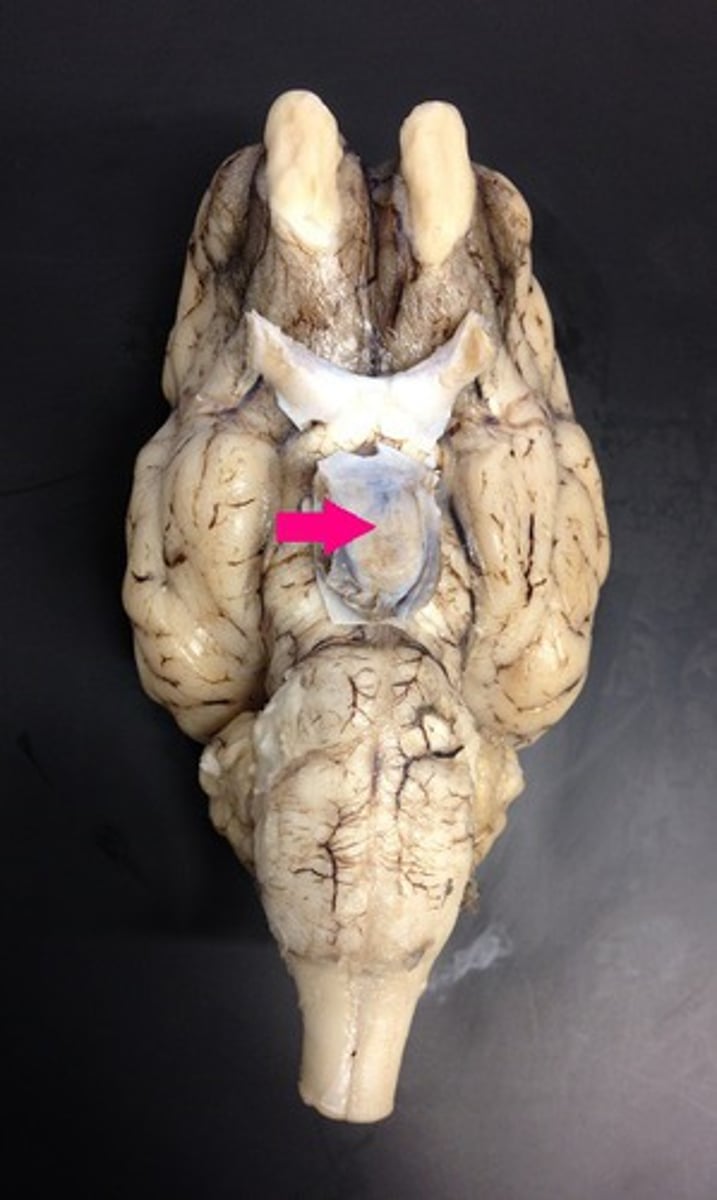
infundibulum
Identify the structure.
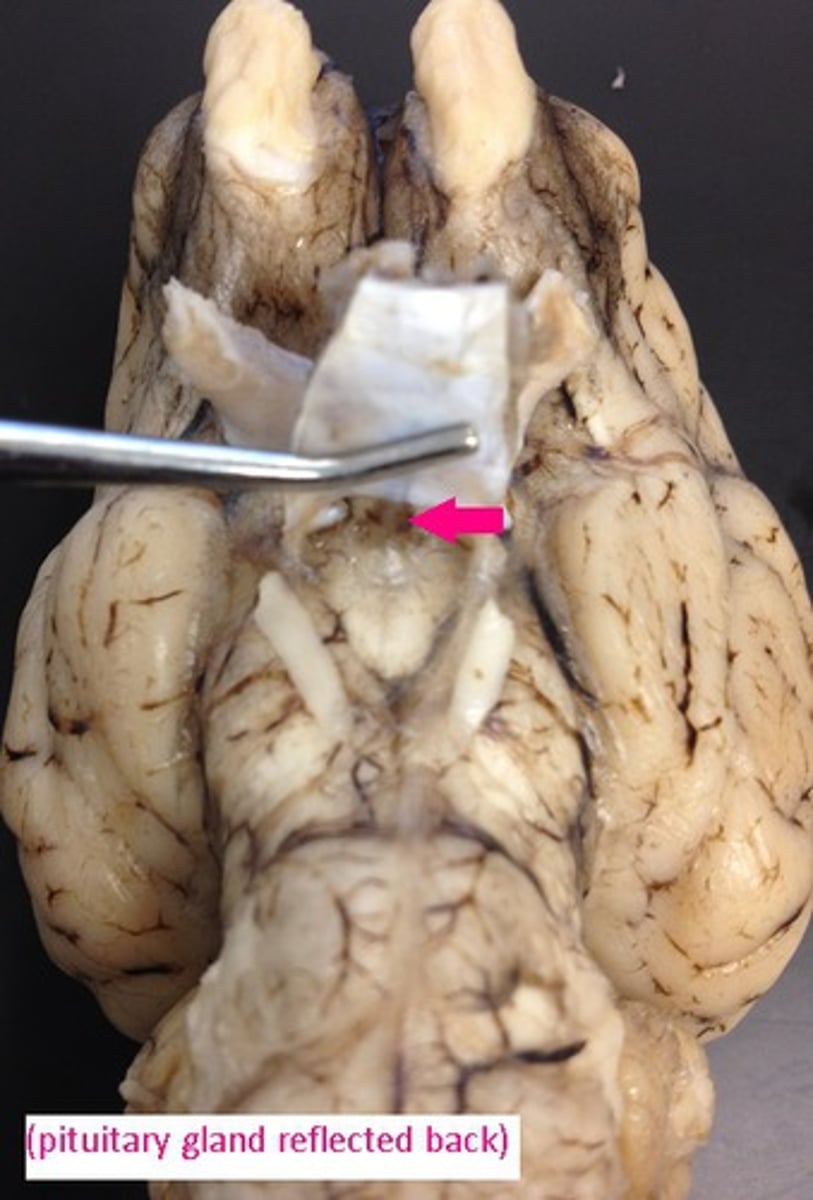
mammillary body
Identify the structure.
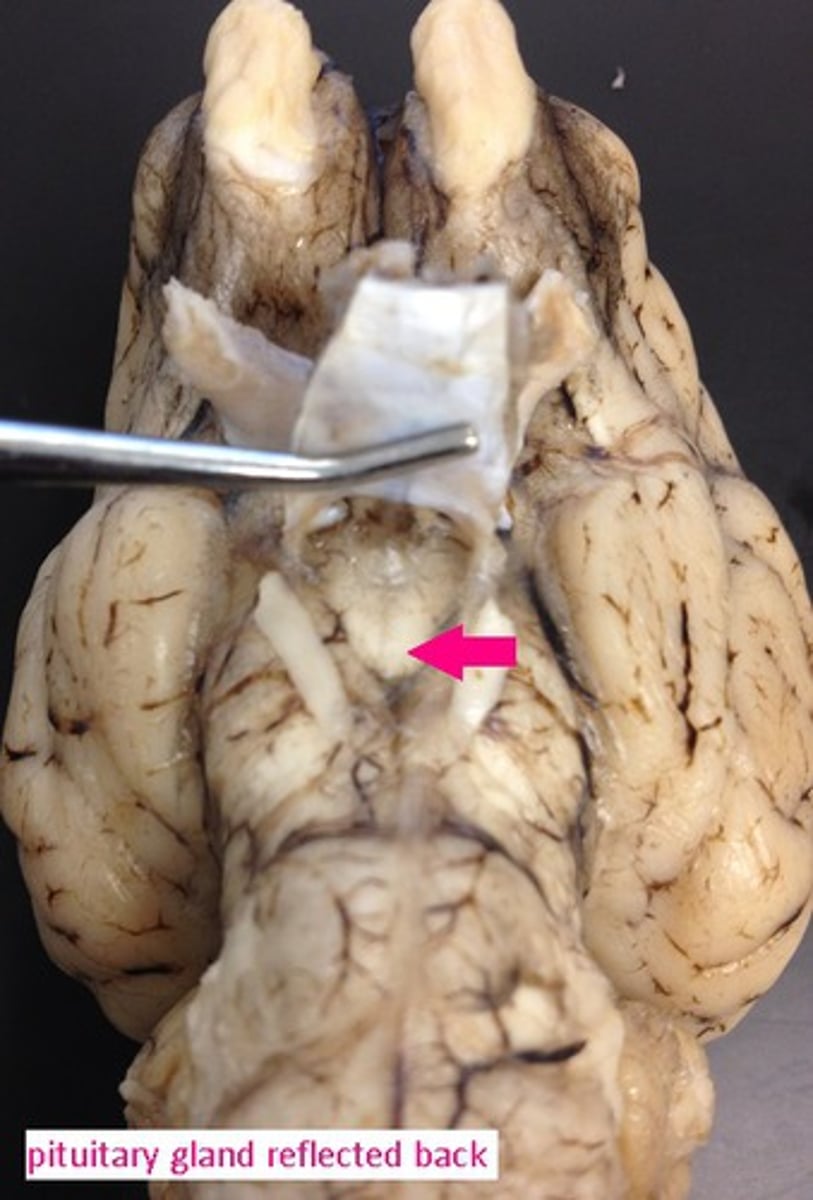
cerebral peduncle
Identify the structure.
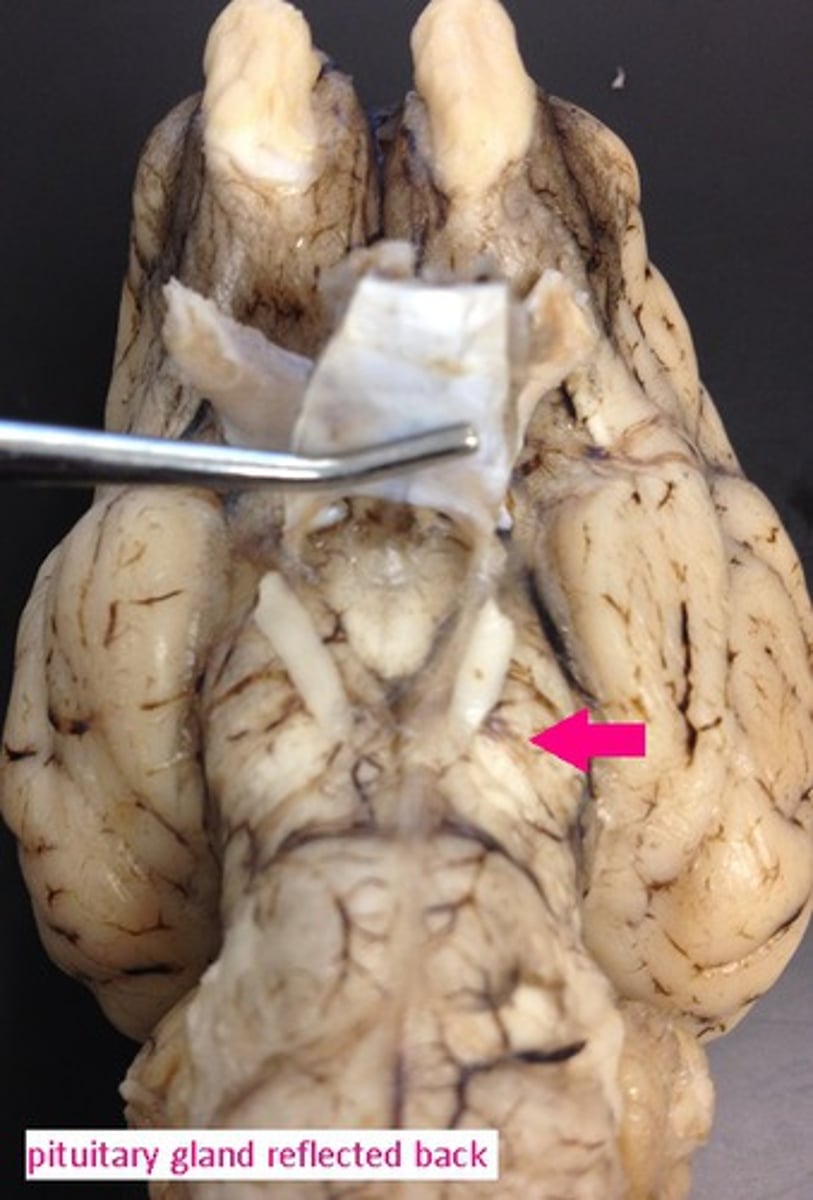
pons
Identify the structure.
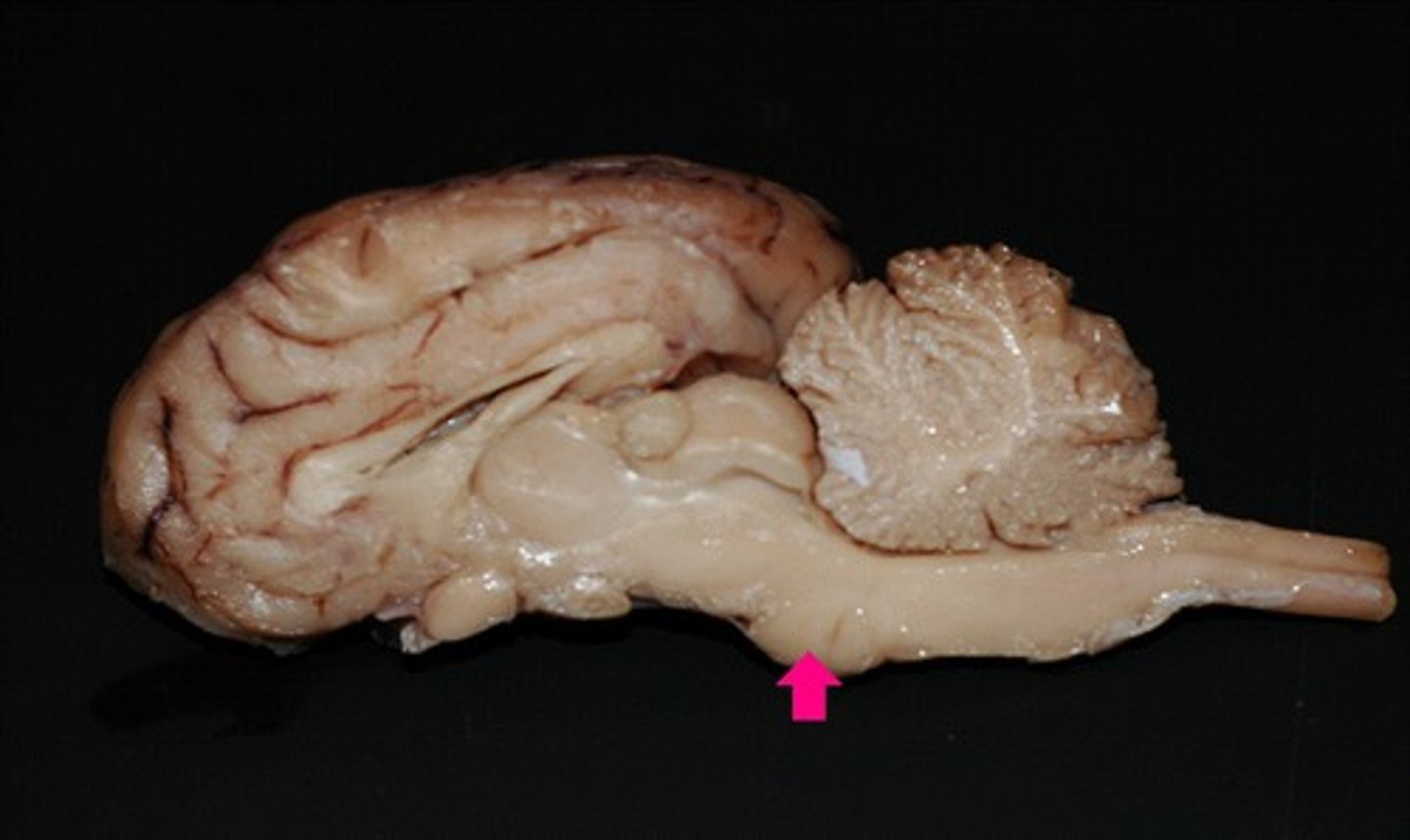
pons
Identify the structure.
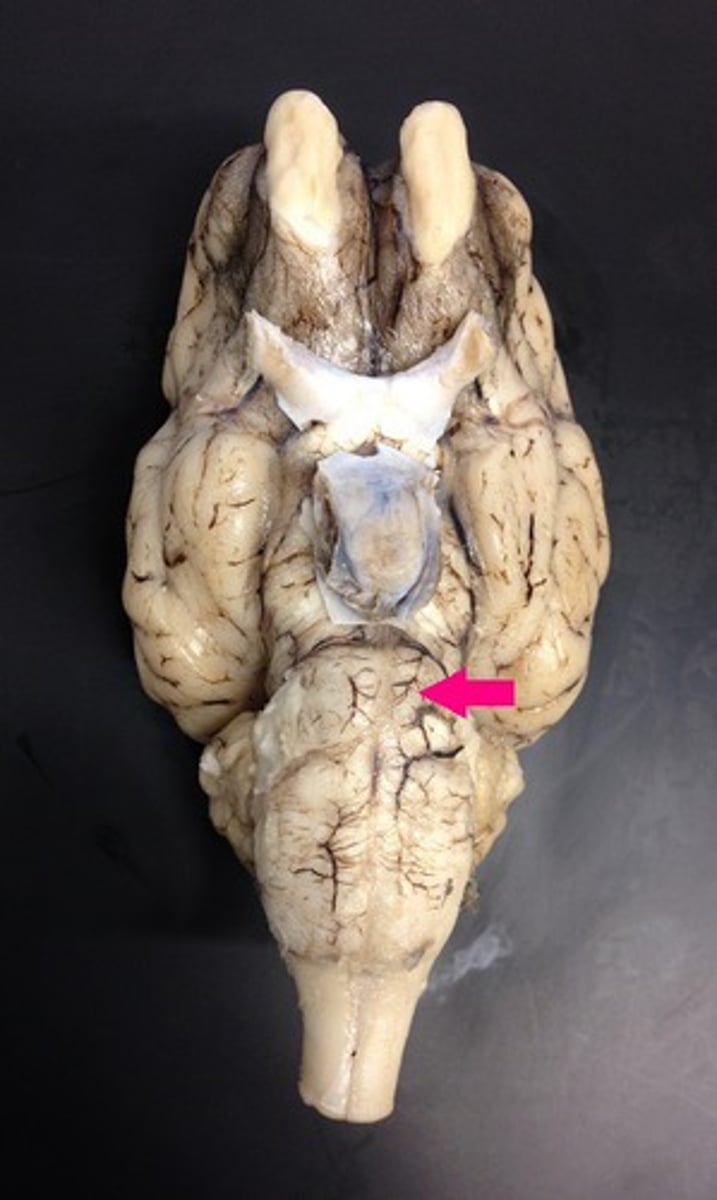
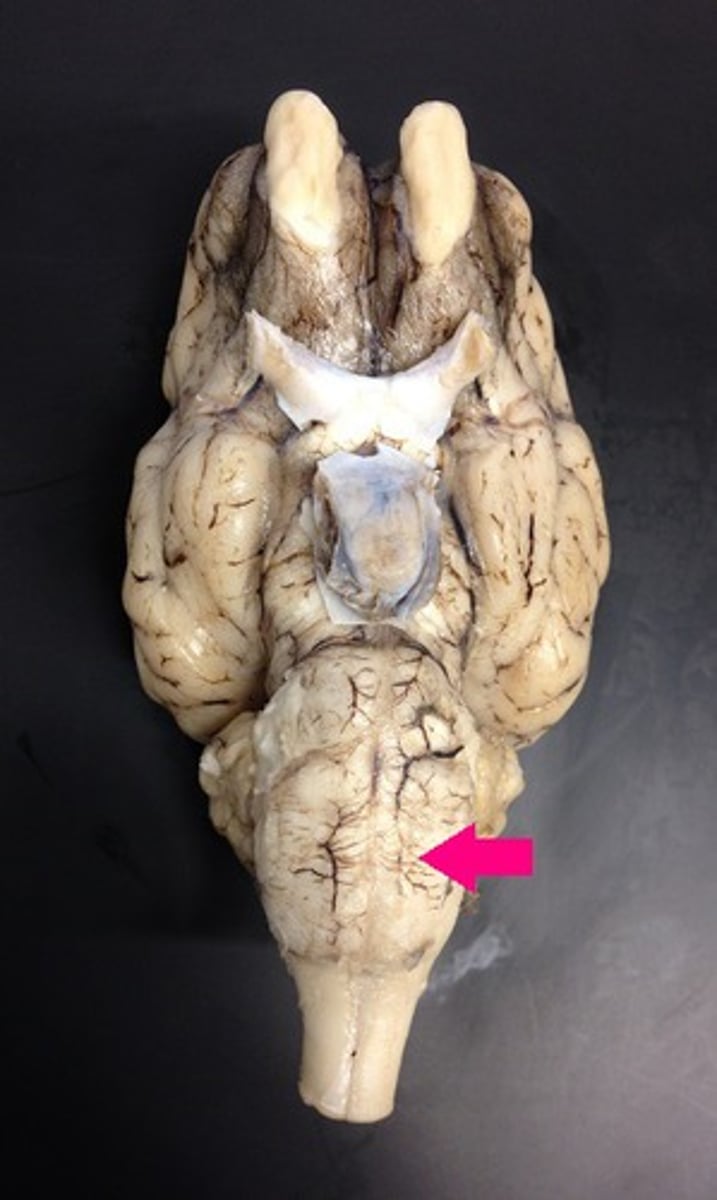
medulla oblongata
Identify the structure.
medulla oblongata
Identify the structure.
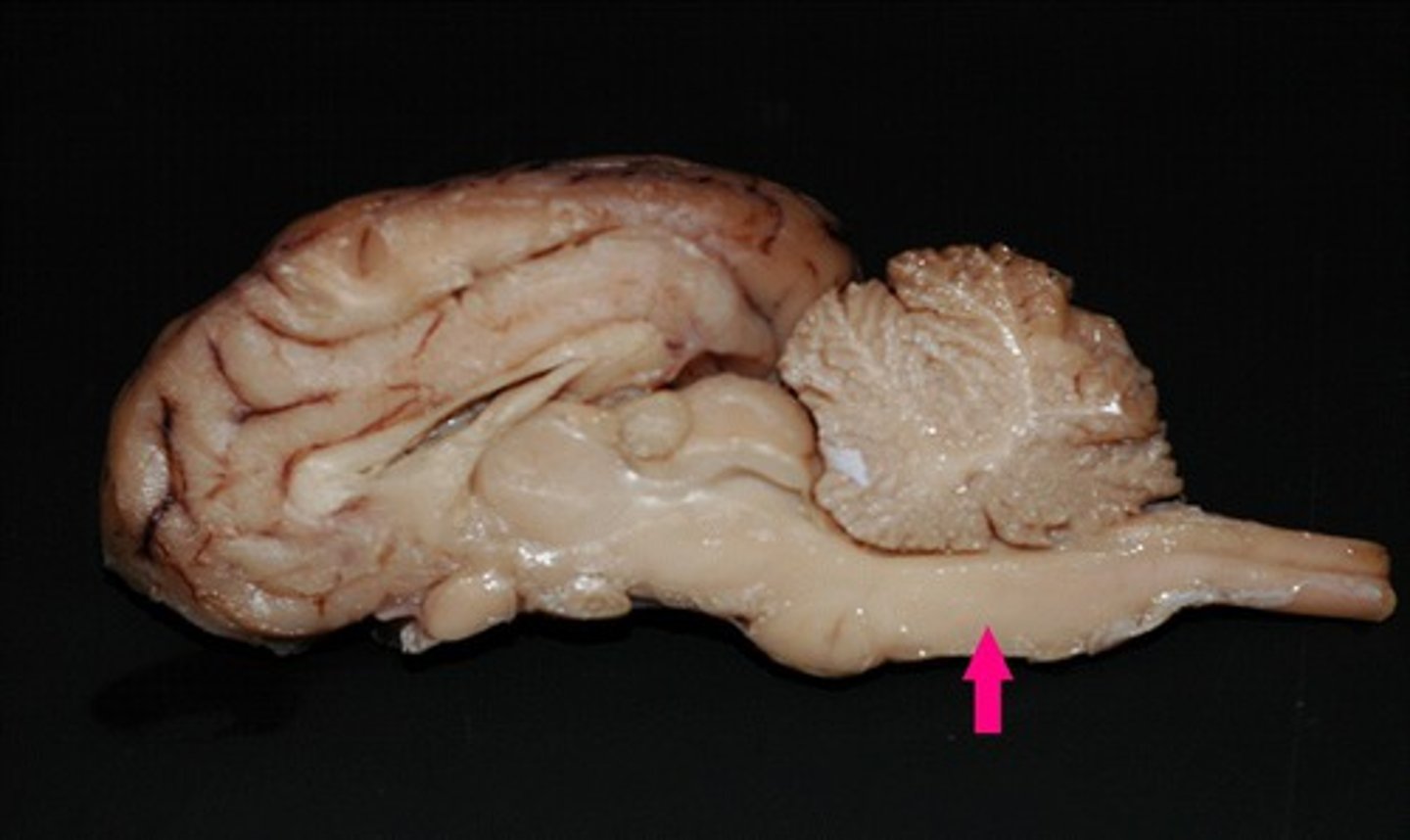
thalamus
Identify the structure.
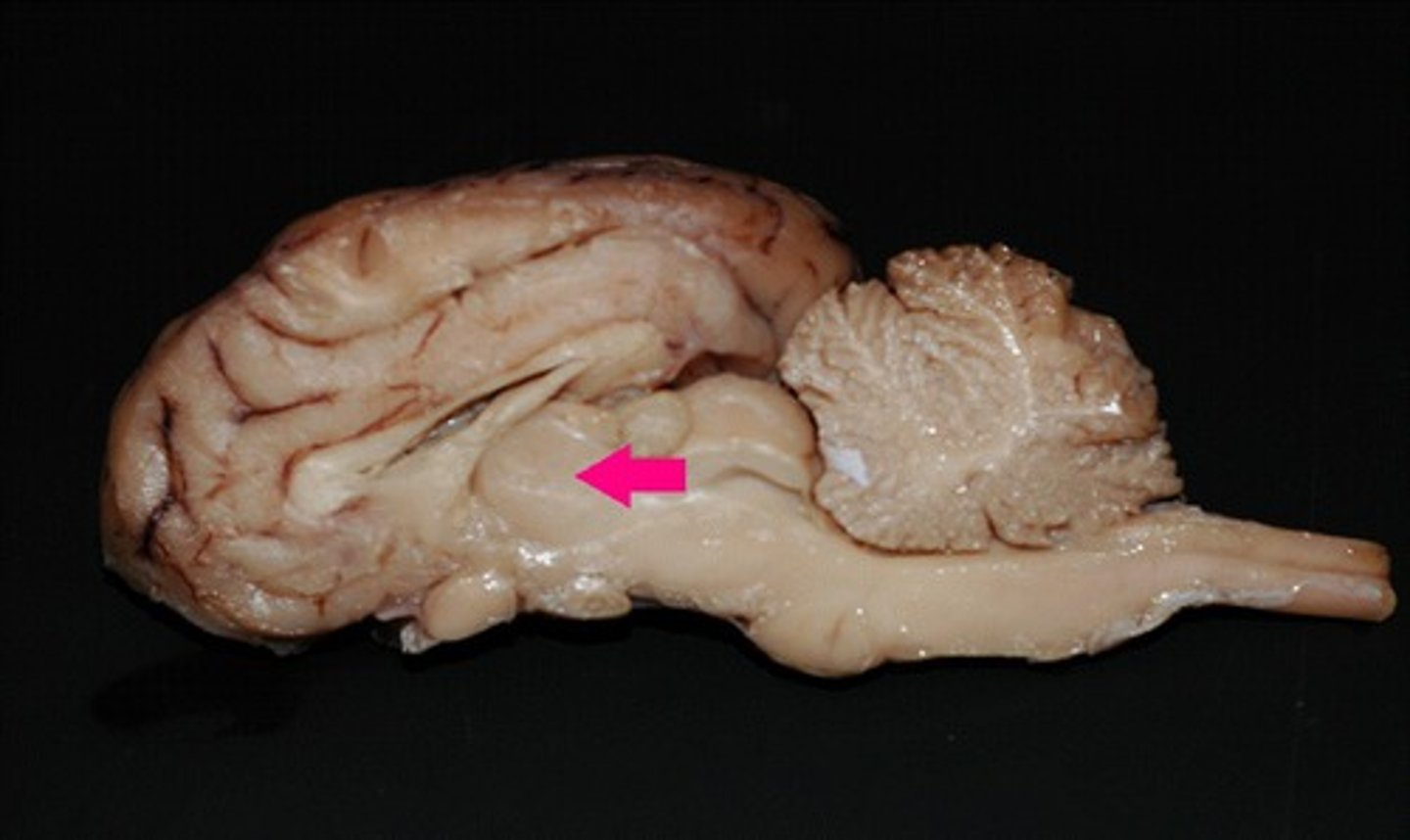
hypothalamus
Identify the structure.
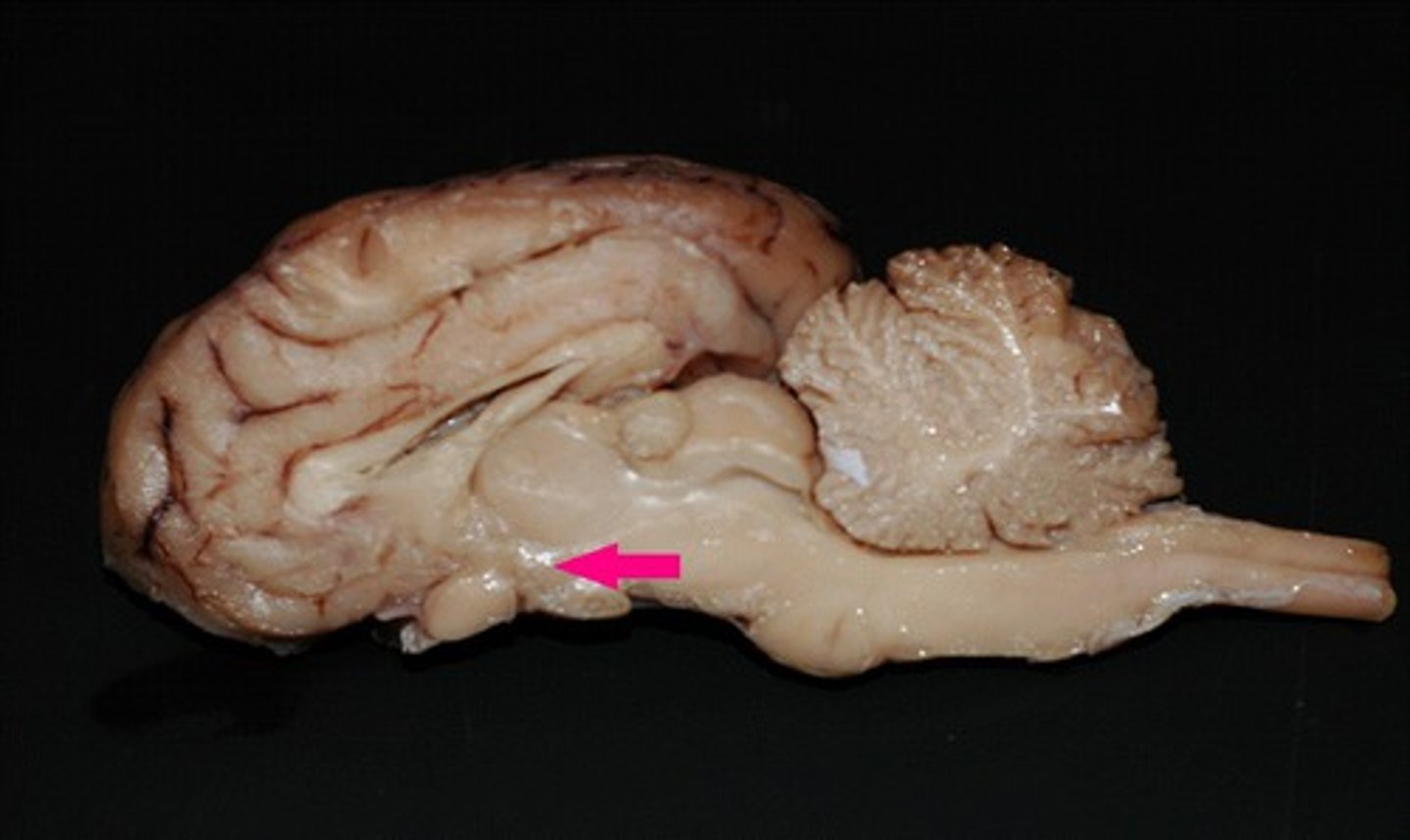
corpora quadrigemina
Identify the multi-part structure.
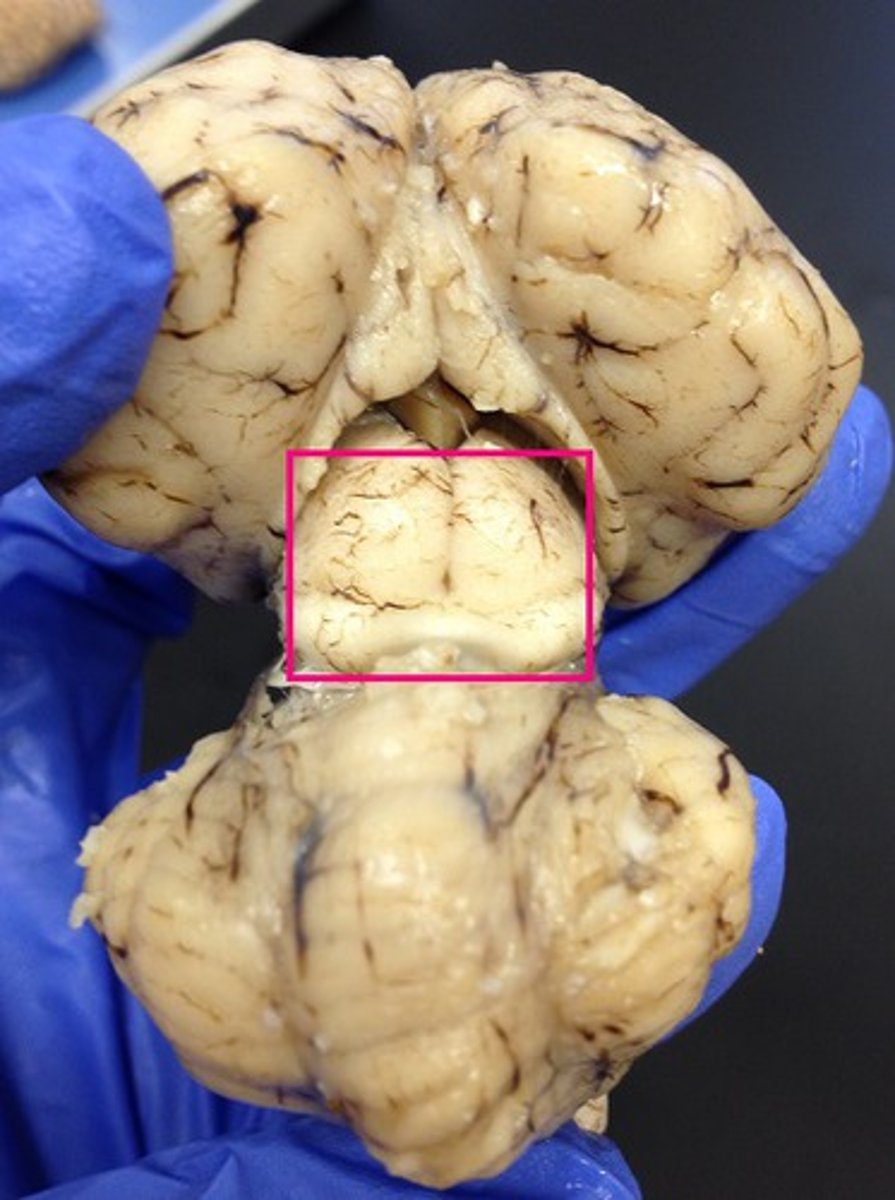
superior colliculus
Identify the structure (dorsal view of midbrain).
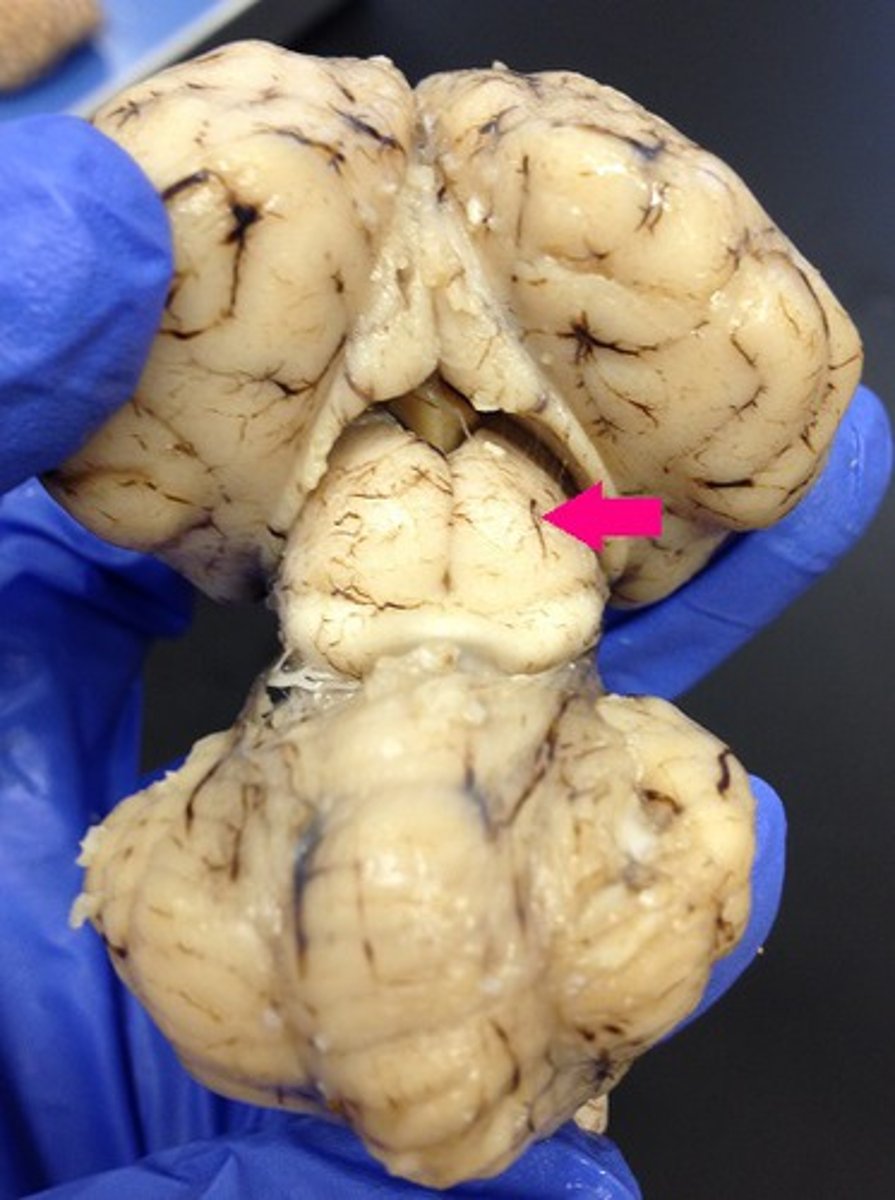
superior colliculus
Identify the structure.
inferior colliculus
Identify the structure (dorsal view of midbrain).
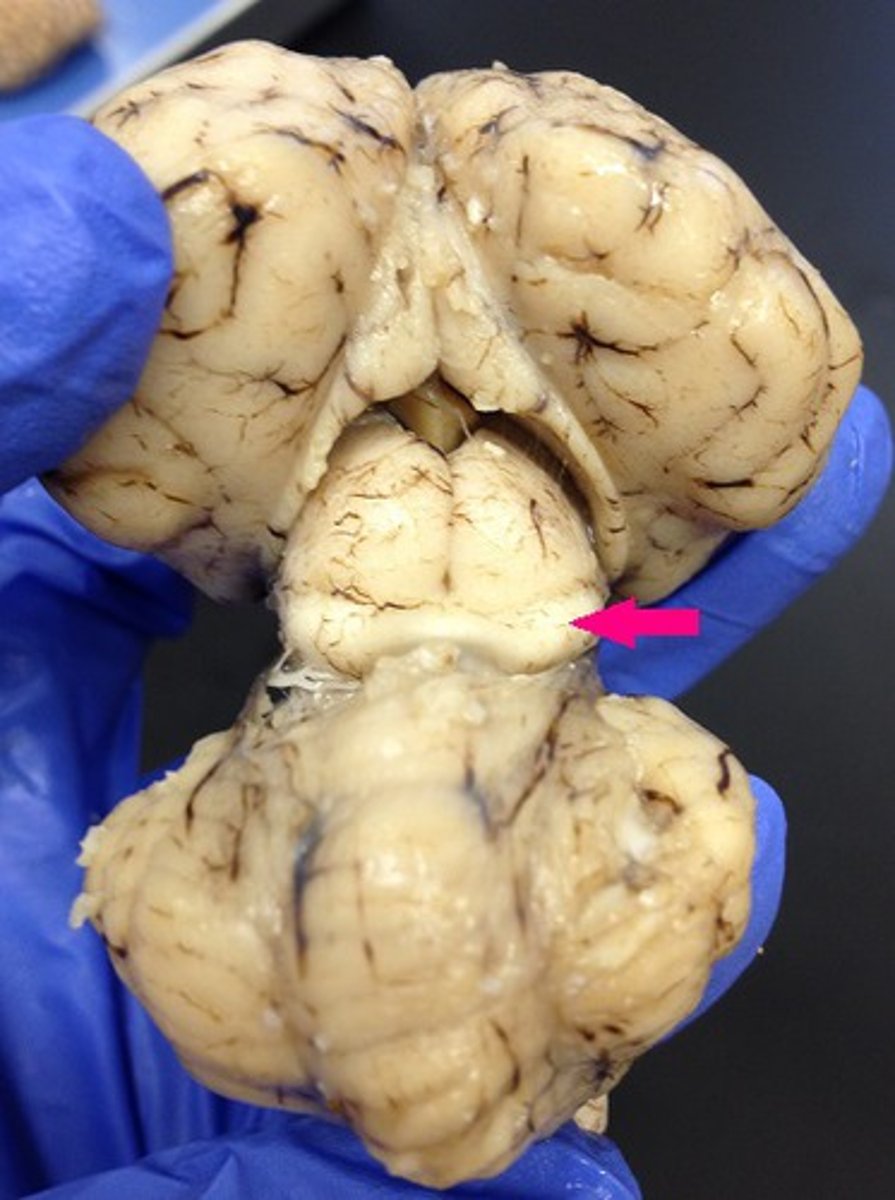
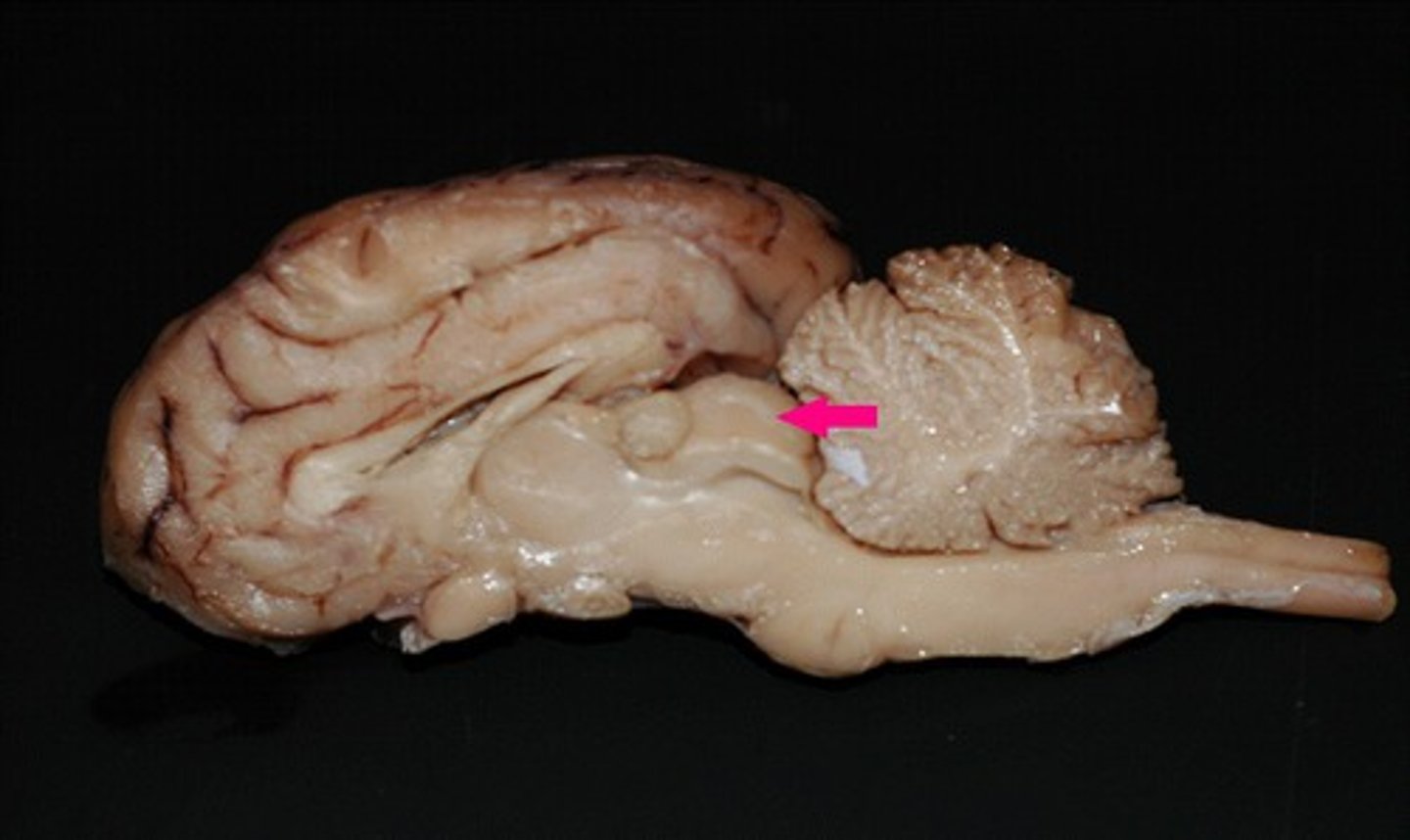
inferior colliculus
Identify the structure.
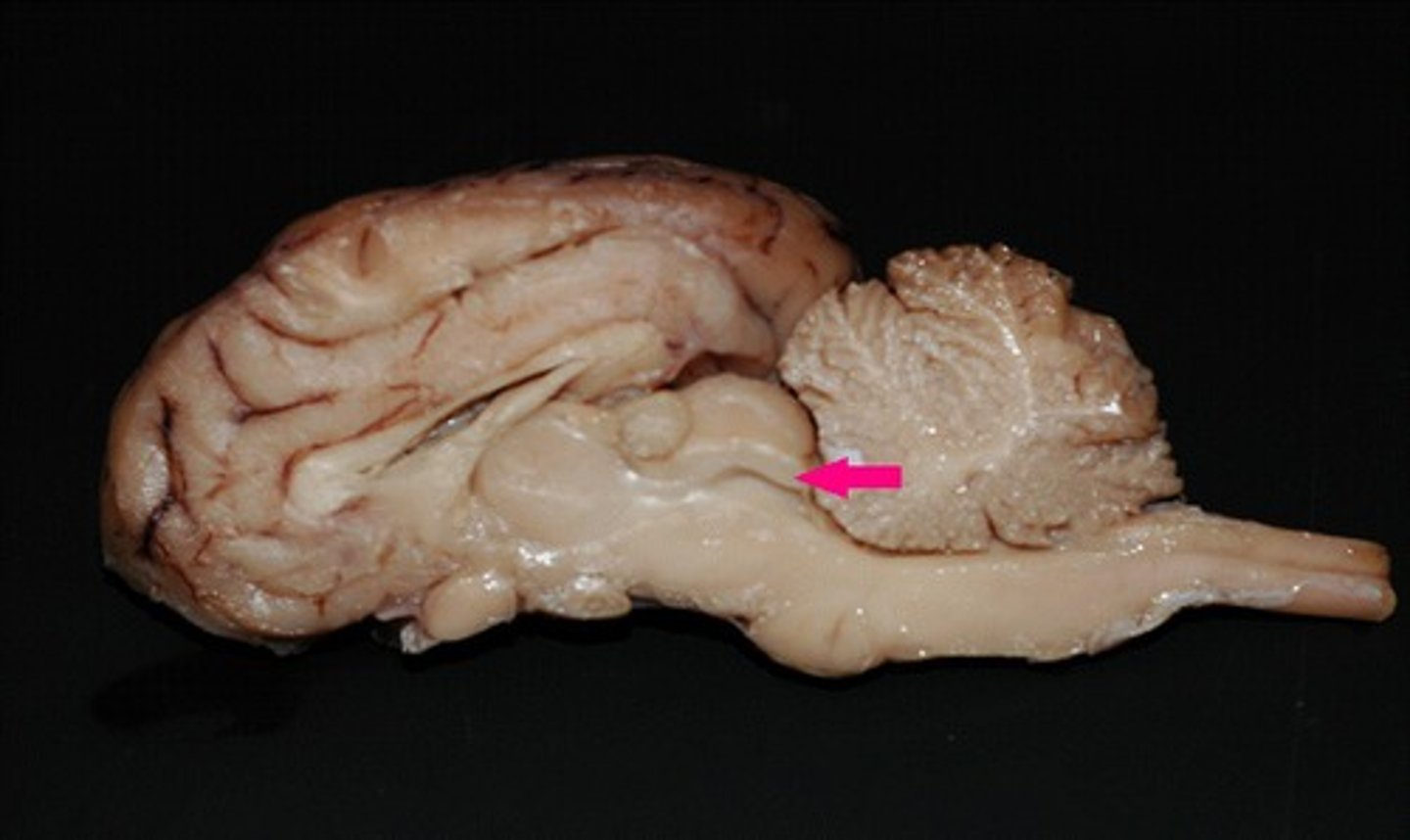
pineal gland
Identify the structure (dorsal view of midbrain).
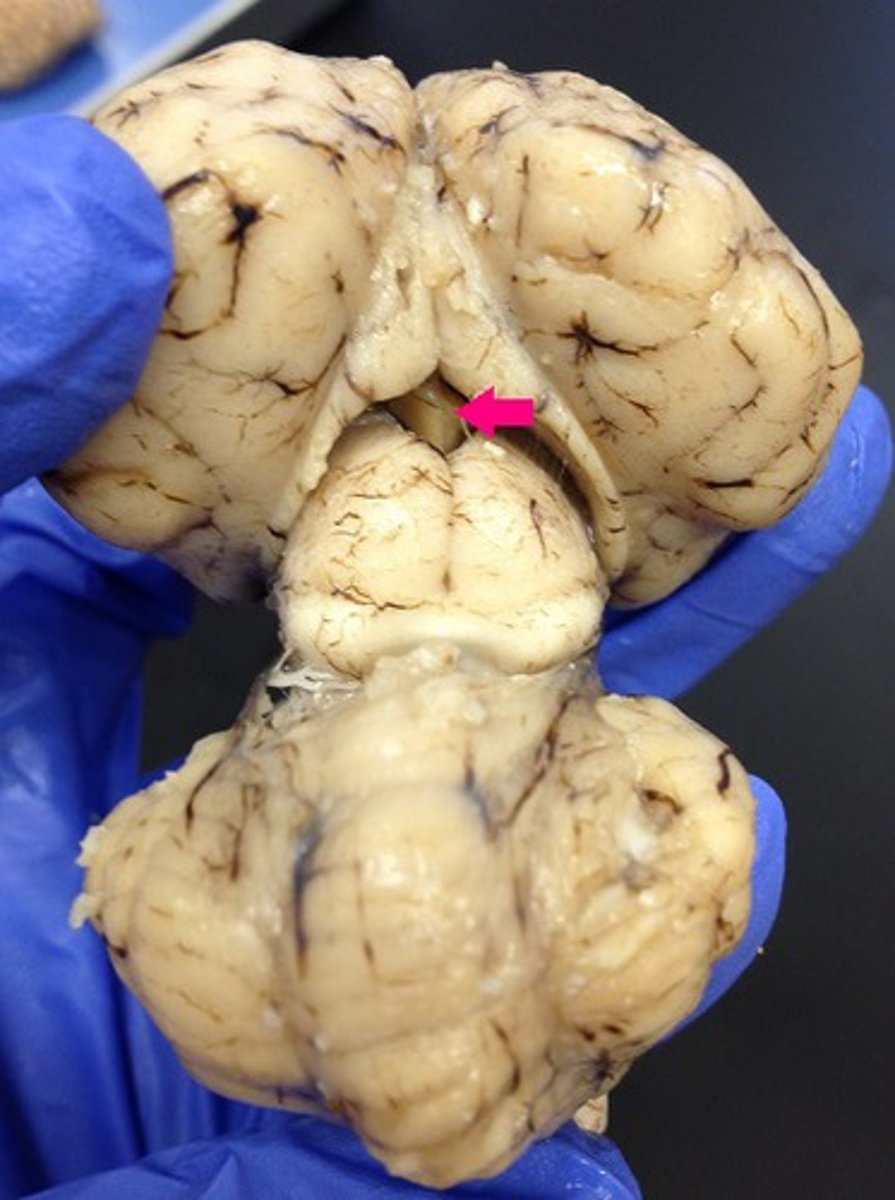
pineal gland
Identify the structure.
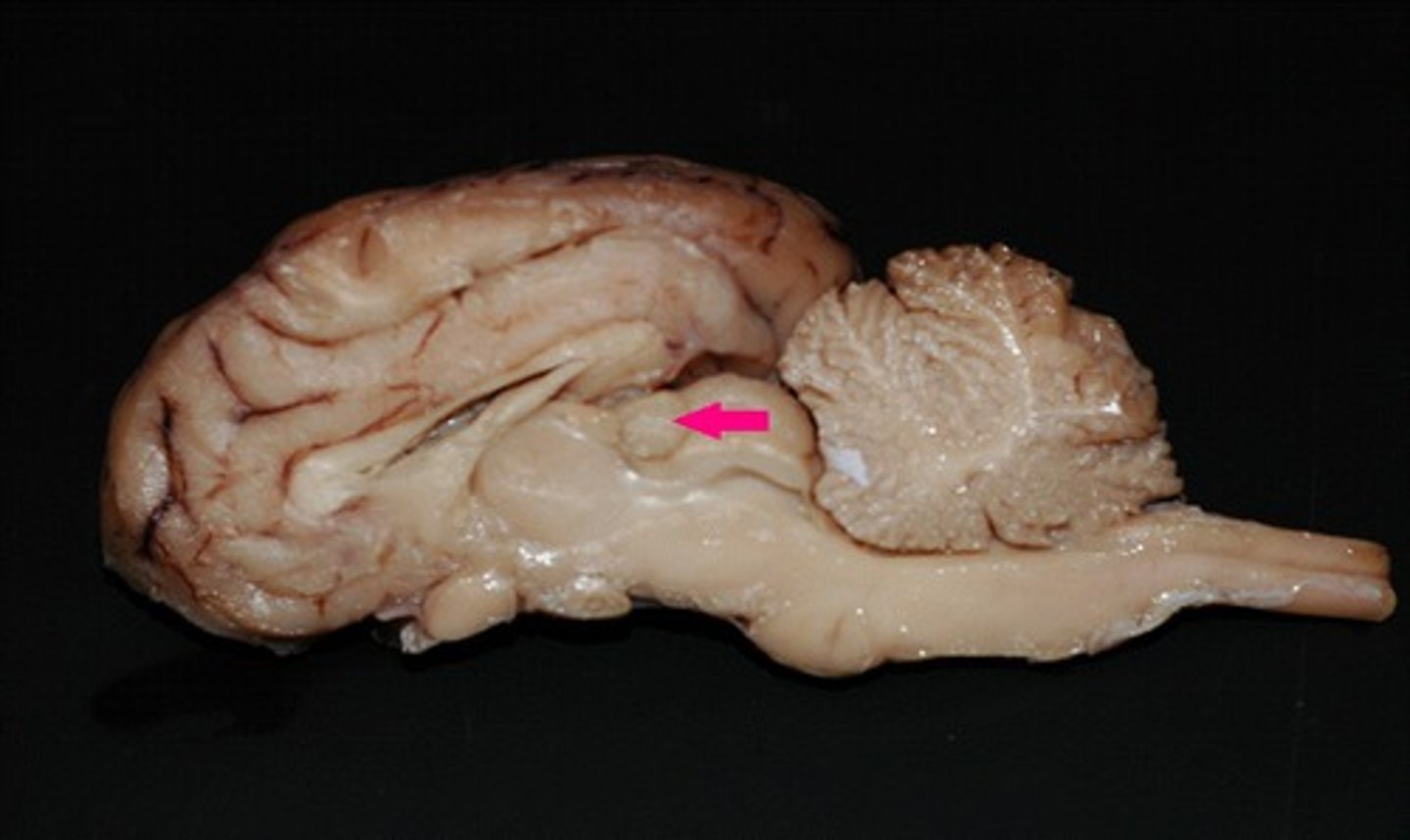
arbor vitae
Identify the branching structure.
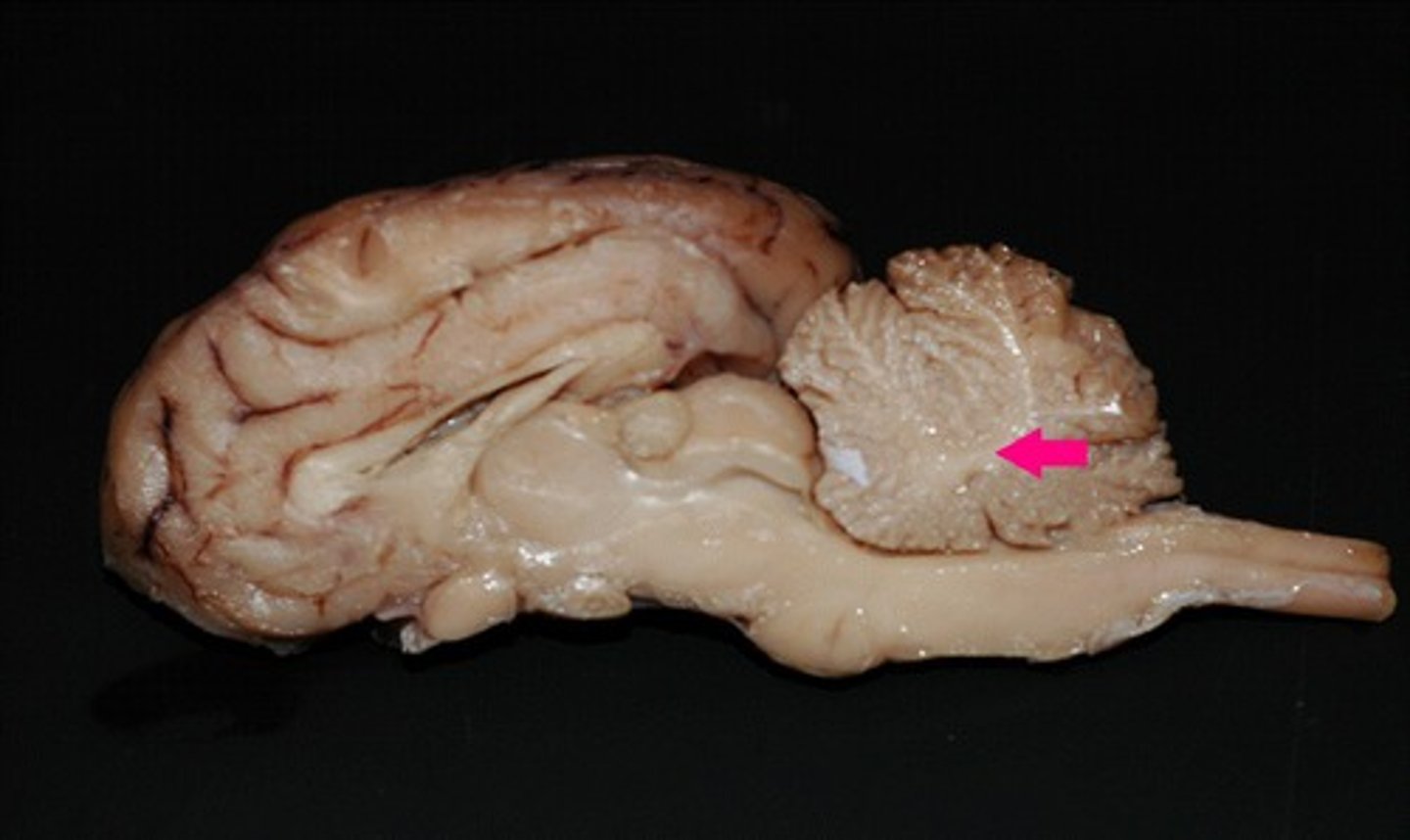
corpus collosum
Identify the structure.
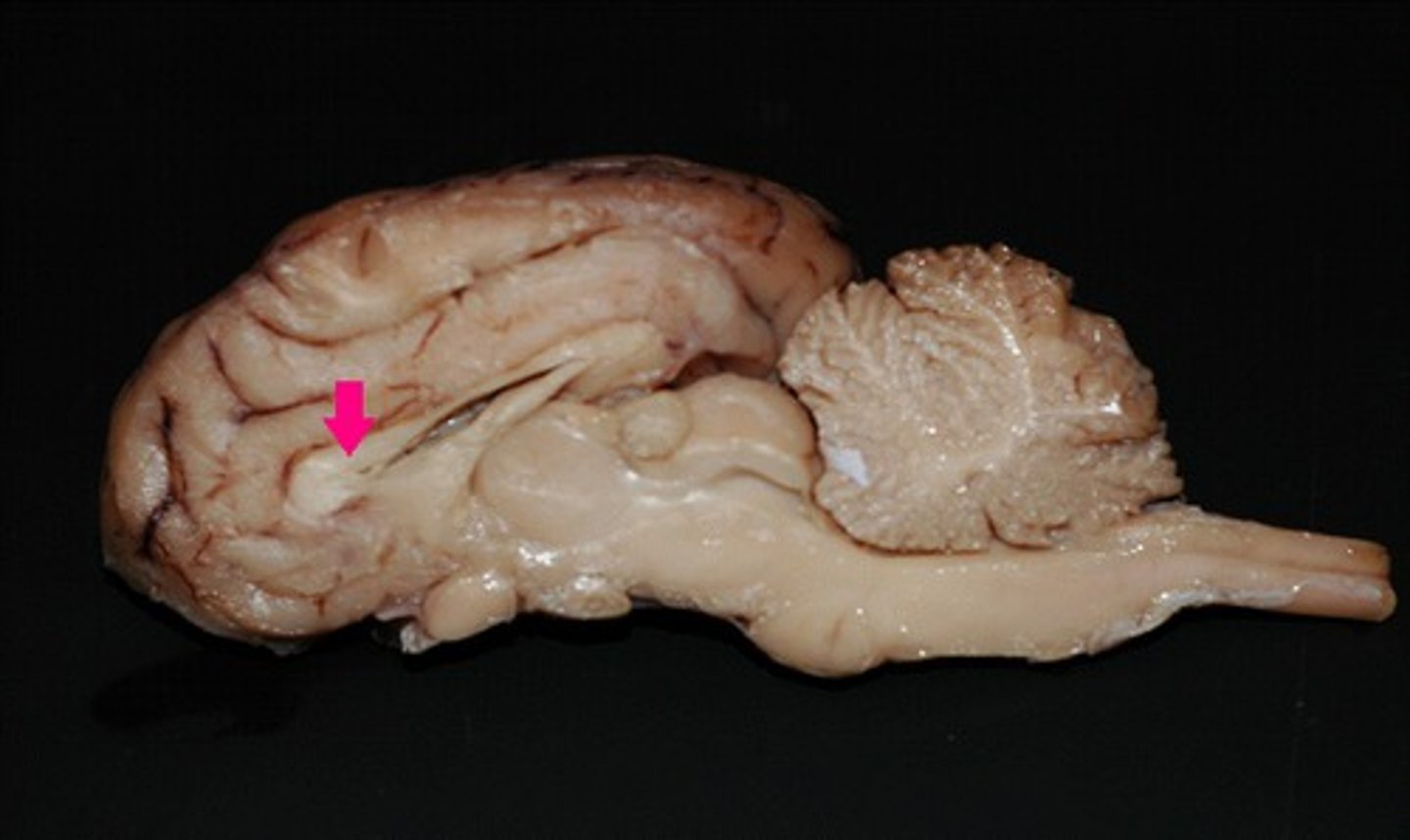
fornix
Identify the structure.
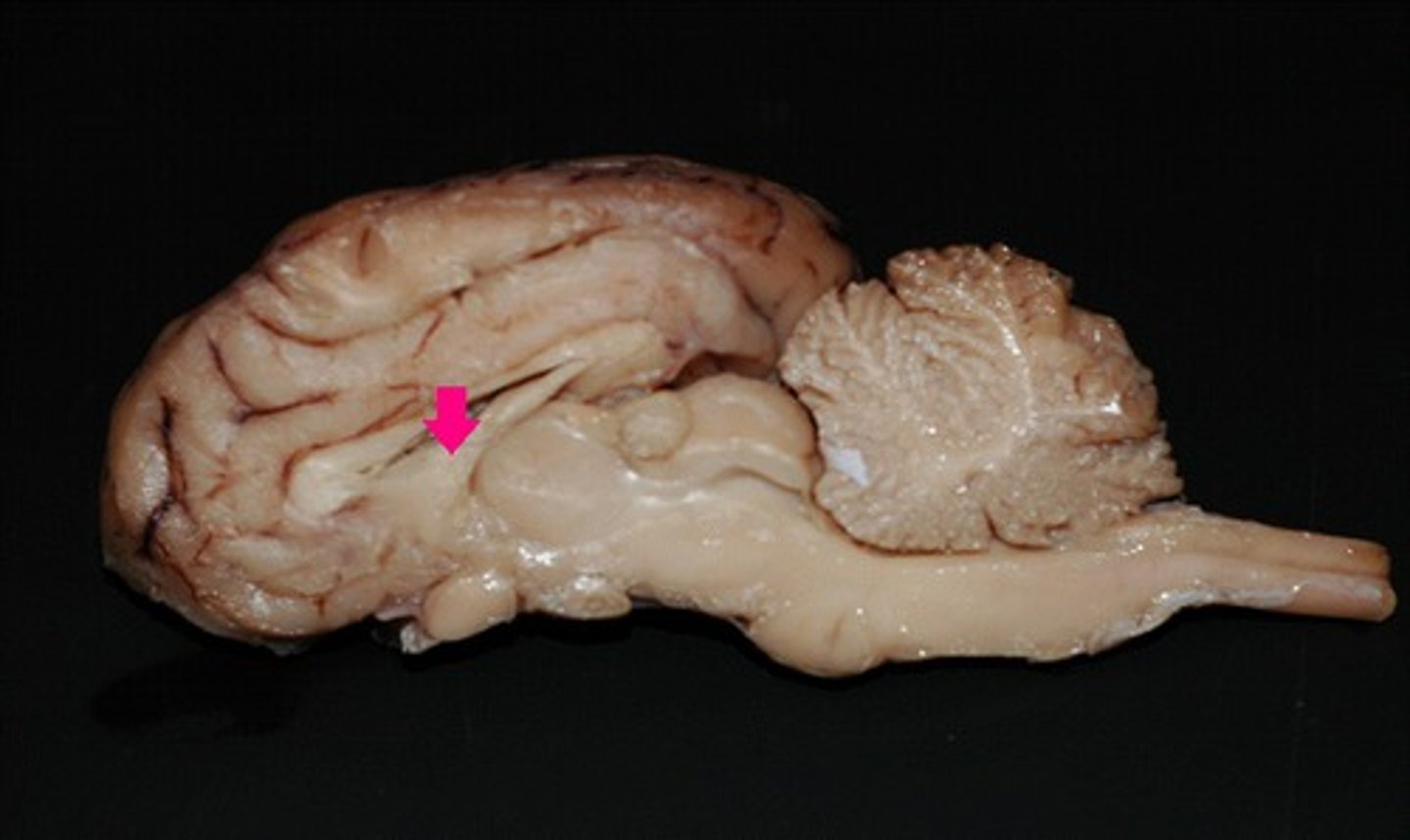
septum pellucidum
Identify the membrane.
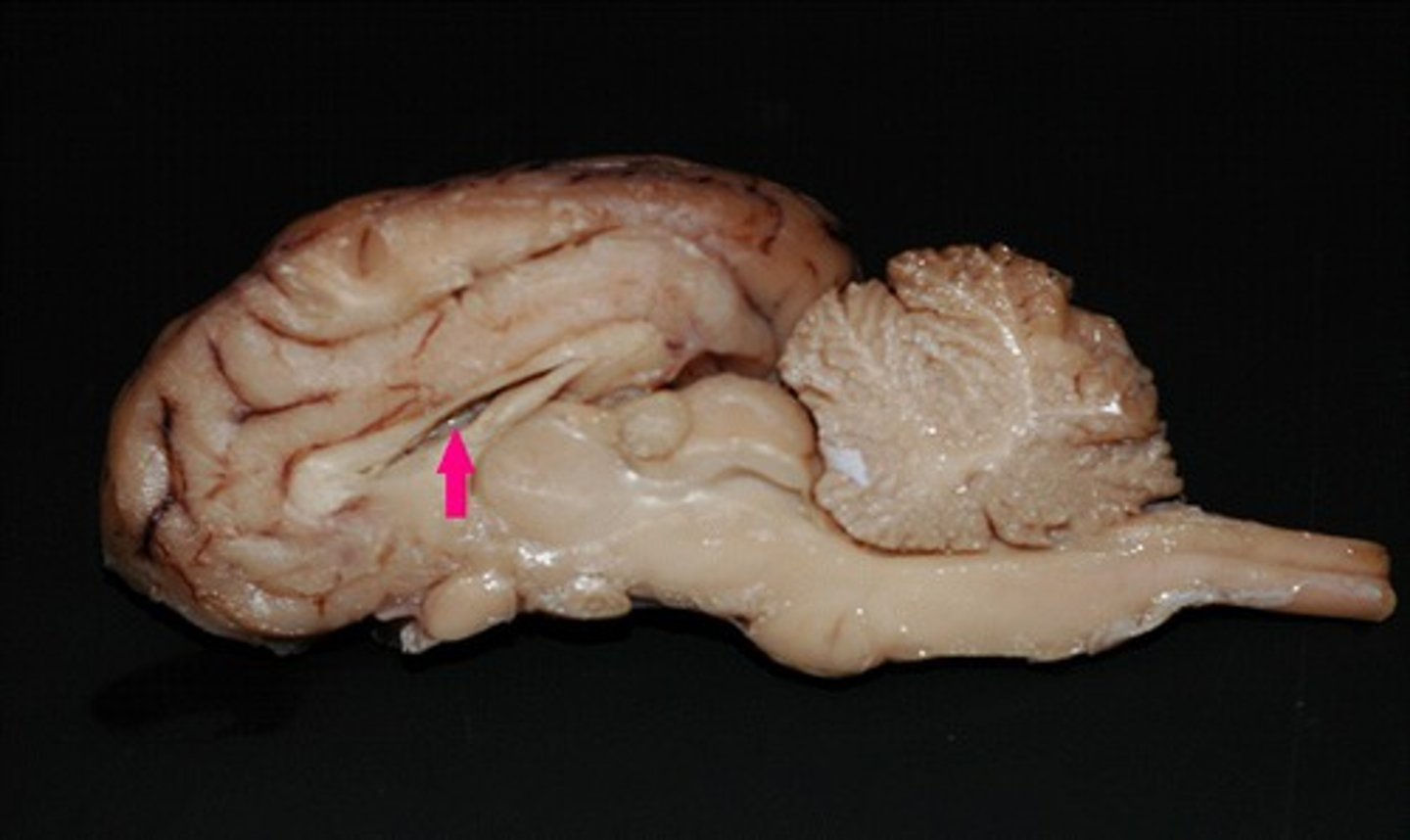
What is cranial nerve I?
olfactory nerve
What is cranial nerve II?
optic nerve
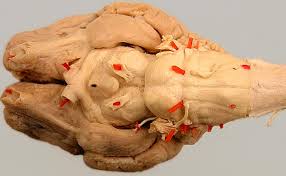
Identify as many cranial nerves as you can
Check for correction