Understanding the Hippocampus and Memory Formation
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
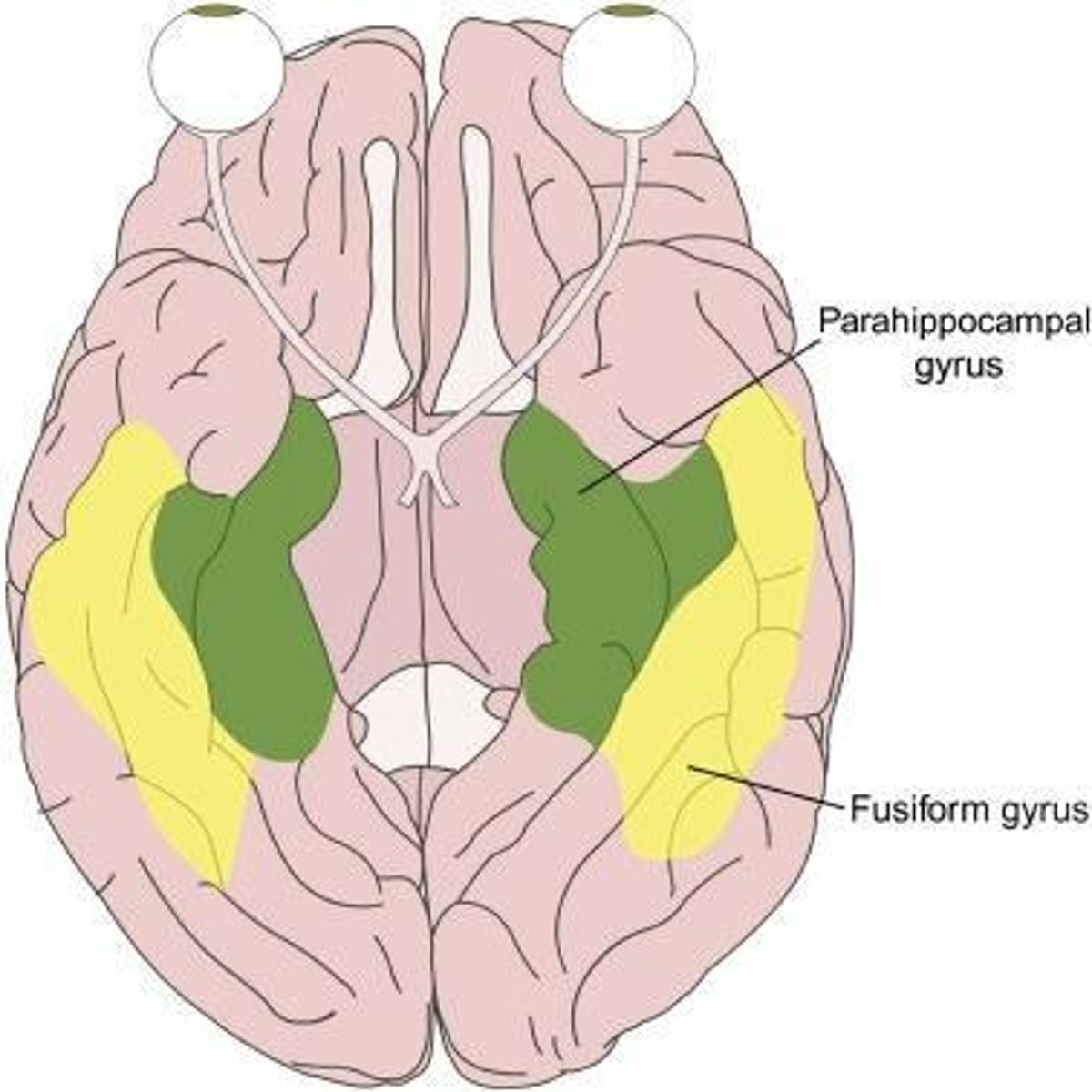
What is the significance of the parahippocampal gyrus?
It is a cortical layer surrounding the hippocampus, contains the entorhinal cortex, and is critical for hippocampal functions, including long-term and spatial memory.
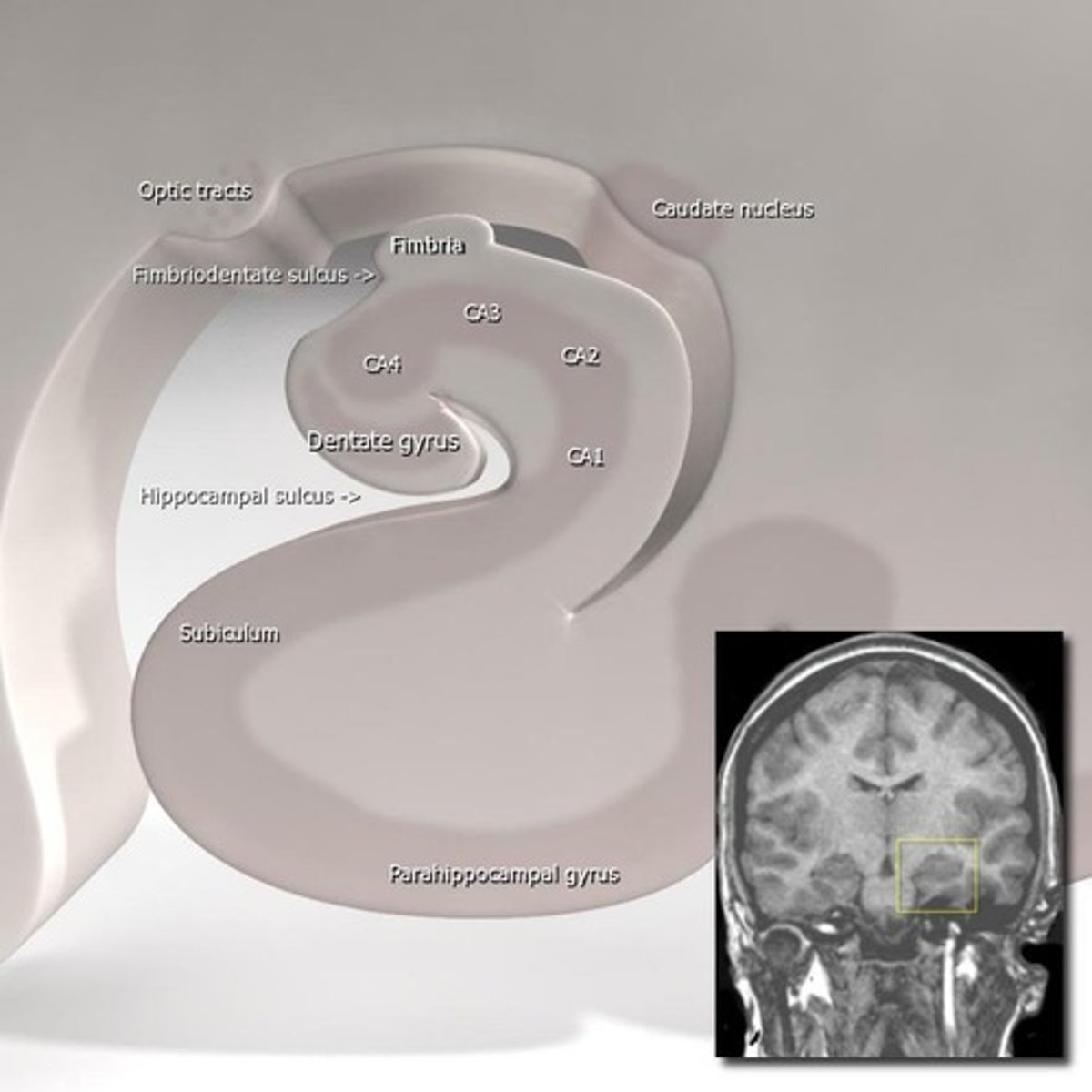
What is the dentate gyrus?
A structure tucked along the hippocampal sulcus that integrates cortical input, is important for episodic memory, and outputs to the hippocampus proper.
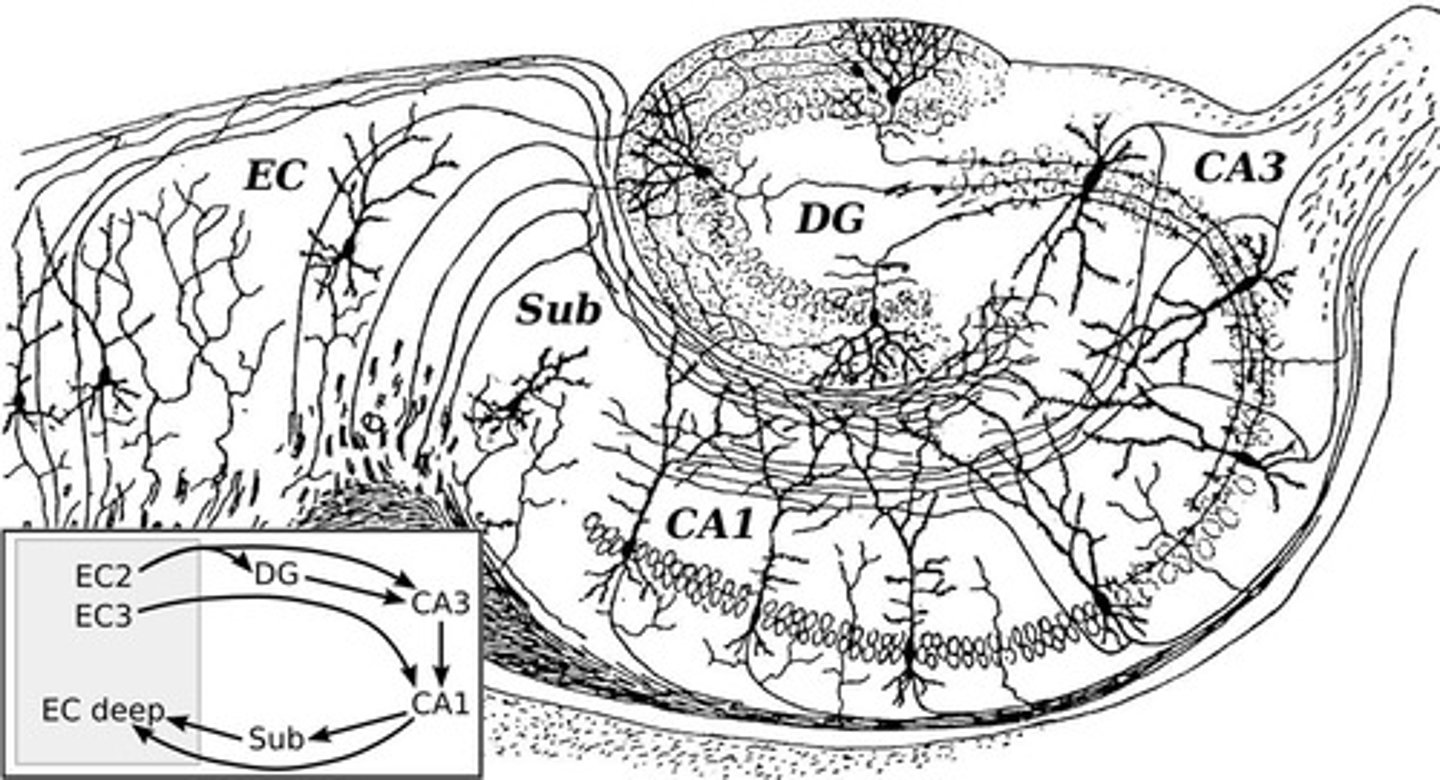
What are the major divisions of the hippocampal formation?
Hippocampus proper, dentate gyrus, subiculum, and parahippocampal gyrus.
What are hippocampal place and grid cells?
Specialized neurons in the hippocampus that help with spatial navigation and memory.
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
A neurodegenerative disease characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline, often associated with the hippocampus.
What is memory?
The cognitive processes involved in encoding, storing, and retrieving information, crucial for learning and personal identity.
What are the types of memory?
Sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What does the hippocampus proper refer to?
The main part of the hippocampal formation, involved in memory processing.
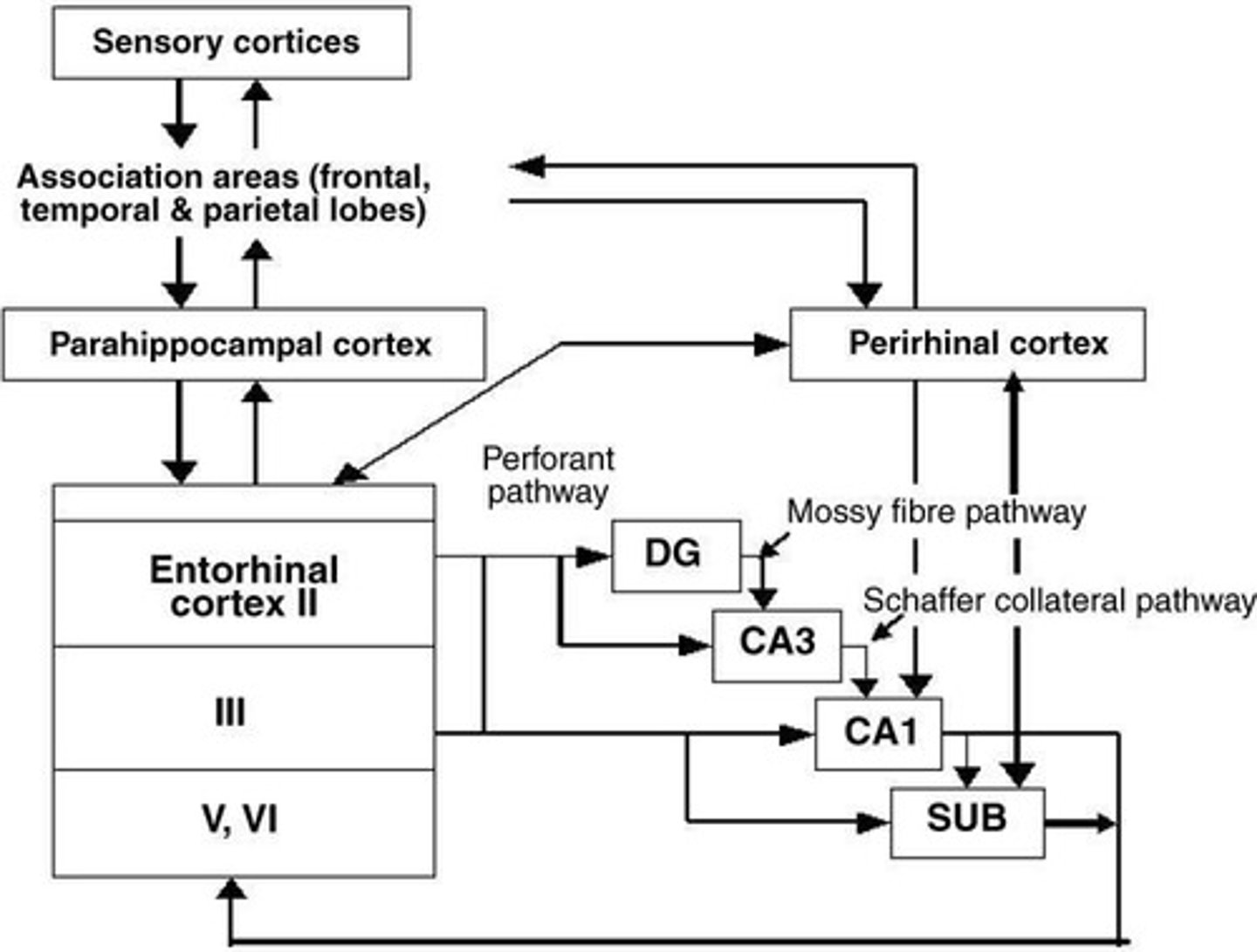
What is the role of the entorhinal cortex?
It provides major inputs to the dentate gyrus and is involved in memory and spatial navigation.
What is the function of the hippocampus in memory?
It plays a crucial role in the formation and retrieval of memories.
How does the hippocampus relate to episodic memory?
The hippocampus is critical for the formation and retrieval of episodic memories.
What is the relationship between the dentate gyrus and the hippocampus proper?
The dentate gyrus outputs to the hippocampus proper and integrates inputs primarily from the entorhinal cortex.
What is the primary function of the parahippocampal gyrus?
It is involved in long-term memory storage and spatial memory.
What is the role of the subiculum in the hippocampal formation?
The subiculum serves as a transitional area between the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex, involved in memory processing.
What cognitive processes are involved in memory formation?
Encoding, storing, and retrieving information.
What are the four subfields of CA designations mentioned in the 1740s?
Each subfield has its own distinct role in hippocampal function.
What is the primary input source for the hippocampus?
The dentate gyrus, with additional inputs from the entorhinal cortex.
Describe the general flow of information in the hippocampus.
The flow is EC → DG → CA3 → CA1 → EC.
What type of projections are found in the hippocampus?
All glutamatergic projections, which can lead to a feedforward loop resulting in seizures.
What does the hippocampus primarily output to?
The entorhinal cortex and the subiculum.
What was the significance of lesion studies in neuroscience?
They moved neuroscience from pure anatomical description towards modern computational neuroscience.
What is a lesion?
A physical injury to the brain, either by accident or surgery.
Who is Phineas Gage and why is he significant in neuroscience?
His case study in 1948 demonstrated profound personality changes due to frontal lobe lesions.
What discovery in the 1900s advanced the understanding of brain function?
The discovery that electrical stimulation of the brain can produce movements.
What hypothesis emerged regarding seizures in the early 1900s?
Seizures are considered 'cortical irritations' that can be surgically removed.
Who was Dr. William Scoville and what was his contribution to neurosurgery?
He was an early neurosurgeon who practiced lobotomies and pioneered medial temporal lobe resections.
What happened to patient H.M. after his treatment?
He could no longer form new memories or recall anything from the previous 3 to 11 years.
What did H.M.'s case spur in the field of neuroscience?
Decade-spanning debates about the nature of memory and its functions.
What are the types of memory described by encoding type?
Sensory memory, semantic memory, procedural memory, and spatial memory.
What are the types of memory categorized by duration?
Immediate (sensory), short-term (minutes to hours), and long-term (years or a lifetime).
What is sensory memory?
A millisecond awareness of sensory input, largely not a conscious process.
How does visual sensory memory function?
It rapidly fades and is not to be confused with larger memories.
What is echoic memory?
Acoustic memories that fade rapidly but are important for language acquisition.
How do olfactory memories relate to the hippocampus?
Smells processed near the hippocampus can strongly induce memory recall.
What types of smells can evoke memories?
Water smells, food smells, familiar smells, perfumes, favorite meals, and seasonal scents.
What is gustatory memory?
Gustatory memory refers to the ability to recall taste, which is integrated similarly to other types of memory.
What is semantic memory?
Semantic memory is the ability to recall words, concepts, and numbers, critical for communication.
What is episodic memory?
Episodic memory is the ability to recall specific events that happened personally, such as experiences like apple picking.
What are procedural memories?
Procedural memories are unconscious long-term memories that help complete tasks, such as tying shoes or playing piano.
Which brain structures are involved in procedural memory?
Procedural memory likely involves the cerebellum and basal ganglia, in addition to the hippocampus.
What is the duration of sensory memories?
Sensory memories last seconds or fractions of seconds.
What is the capacity of short-term memory according to Miller's classic paper?
Short-term memory can hold 7 +/- 2 units of information.
How can chunking improve memory recall?
Chunking allows for grouping information into larger units, making it easier to remember, e.g., turning 8459023 into 845-9023.
What is the maximum duration of short-term memory before transfer to long-term memory?
Short-term memory can last for minutes before information is transferred to long-term memory.
What is the capacity and duration of long-term memory?
Long-term memory is seemingly limitless in both capacity and duration, assuming successful transfer of information.
How can rehearsal facilitate memory storage and recall?
Rehearsal involves repeating information, making new connections, and engaging more of the brain.
What role does sleep play in memory storage?
Sleep triggers parallel activity from the hippocampus to the outer cortices, aiding in memory consolidation.
What is the Morris water maze used for?
The Morris water maze is a method used to study hippocampal function.
What are memory engrams?
Memory engrams are the physical units of memory, a concept coined by Richard Semon.
What are hippocampal place cells?
Hippocampal place cells are neurons that help identify familiar objects in space.
What are grid cells in the hippocampus?
Grid cells are organized cells that increase activity based on spatial navigation, relating to where one has been.
What is the prevalence of Alzheimer's Disease in older adults?
1 in 9 people over 65 and 1 in 8 over 80 are affected by Alzheimer's Disease.
What is the highest risk factor for Alzheimer's Disease?
The highest risk factor for Alzheimer's Disease is age.
What are some treatments for Alzheimer's Disease?
Treatments include Memantine, Aricept, and Aducanumab.
What are the common symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease?
Symptoms include memory loss, impairments in short and long-term memory, and inability to navigate.
What is the current status of Alzheimer's Disease?
Alzheimer's Disease is currently incurable and progresses slowly until incapacitation and death.
What are the end-stage symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease?
End-stage symptoms include hypo-frontality, risk-taking behaviors, and loss of the ability to swallow.
What is addiction?
Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain.
What is a neuropsychological symptom of addiction?
A pervasive and intense urge to engage in maladaptive behaviors providing immediate sensory rewards, despite harmful consequences.
What are some signs of addiction?
Compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, preoccupation with rewarding stimuli, continued use, and immediate gratification.
What percentage of people who use illicit drugs suffer from addiction?
Over 25%.
How many people in the USA drink alcohol, and what percentage suffer from addiction?
140 million people drink alcohol, with over 20% suffering from addiction.
What is the annual cost of drug and alcohol addiction in the US?
$700 billion.
What is the relationship between drug addiction and mental illness?
Drug addiction is comorbid with a diagnosed mental illness over 50% of the time.
List some risk factors for drug addiction.
Childhood aggressive behavior, community economic status, impulsivity, youth intake, mental illness, epigenetics, and trauma.
What are the three stages in the cycle of drug addiction?
1. Binge/intoxication 2. Withdrawal/negative affect 3. Preoccupation/anticipation.
What brain pathway is involved in binge/intoxication?
The mesolimbic pathway and basal ganglia.
What is the role of dopamine (DA) in binge/intoxication?
All addictive substances produce feelings of pleasure through direct and/or indirect DA activation.
What brain structures are involved in withdrawal/negative affect?
The amygdala and extended amygdala.
What does the corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) relate to in addiction?
It is associated with 'flight or fight' response, HPA axis activation, stress, appetite, and negative affect.
What is the allostasis theory of addiction?
The process of maintaining apparent reward function stability by changes in brain reward mechanisms.
How does constant dopamine release affect habit formation?
It can lead to increases in habit formation by altering the basal ganglia.
What brain circuitry is involved in preoccupation/anticipation?
Executive control circuitry, including the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus.
What are the effects of low doses of alcohol?
Euphoria, analgesic effects, and increased sociability.
What are the effects of high doses of alcohol?
Loss of coordination, memory loss, unconsciousness, and death.
What are common routes of alcohol administration?
Oral consumption.
What are the withdrawal symptoms of alcohol?
Nausea/vomiting, negative affect, hallucinations, and delirium tremens.
What are benzodiazepines and their common effects?
Depressants that act as GABAA agonists, usually short-acting, causing sedation and anxiety relief.
What is marijuana classified as, and what are its effects?
A psychoactive drug that can act as a depressant, hallucinogen, or stimulant, causing relaxation, eye reddening, and hunger.
What is cocaine and how does it affect the brain?
A stimulant that blocks the DAT transporter in the mesolimbic pathway, producing intense euphoria and increased heart rate.
What is crack cocaine?
A freebase form of cocaine that can be smoked, providing higher bioavailability and similar stimulant effects.
What are the effects of amphetamines?
Increased alertness, energy, focus, and cognitive enhancement.
What are the effects of opiates?
Analgesic effects, euphoria, dry mouth, respiratory depression, constipation, and warm flush.
What is the historical significance of opiates?
Used since ancient times, with significant developments in their use and regulation throughout history, including the marketing of heroin and oxycontin.
What are the effects and routes of administration for heroin?
Intense euphoria, respiratory depression, alertness and drowsiness, with routes including IV, inhalation, and smoking.
What is addiction?
A neuropsychological symptom defining a pervasive and intense urge to engage in maladaptive behaviors providing immediate sensory rewards, despite their harmful consequences.
What are the signs of addiction?
Compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, preoccupation with rewarding stimuli, continued use, and immediate gratification.
What percentage of illicit drug users suffer from addiction?
Over 25%.
What percentage of alcohol drinkers in the USA suffer from addiction?
Over 20%.
What are the annual costs of drug addiction in the US?
$700 billion.
How often is drug addiction comorbid with diagnosed mental illness?
Over 50% of the time.
What are some risk factors for drug addiction?
Childhood aggressive behavior, community economic status, impulsivity, youth intake, mental illness, epigenetics, and trauma.
What brain pathways are involved in binge/intoxication?
Mesolimbic pathway and basal ganglia.
What brain structures are involved in withdrawal/negative affect?
Limbic circuitry, including the amygdala and extended amygdala.
What is the function of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) in addiction?
It is involved in the 'fight or flight' response and is linked to stress and negative affect.
What is allostasis theory of addiction?
The process of maintaining apparent reward function stability by changes in brain reward mechanisms.
What brain regions are involved in preoccupation/anticipation?
Prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus.
What is the effect of diminished PFC function in addicts?
It affects the 'go and stop' system and incentive salience.
What is alcohol and how is it produced?
Alcohol is produced by the fermentation of grains, fruits, and sugar.
What are the common routes of alcohol administration?
Oral consumption.