
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what is business marketing
the marketing of goods and services to individuals and organizations for purposes other than personal consumption
business product
-the key is intended use
-are used to manufacture other products
-become part of another product
-aid the normal operations of an organization
relationship marketing
-loyal customers are more profitable than price-sensitive customers with little brand loyalty
-long-term relationships build competitive advantage
relationship marketing diagram
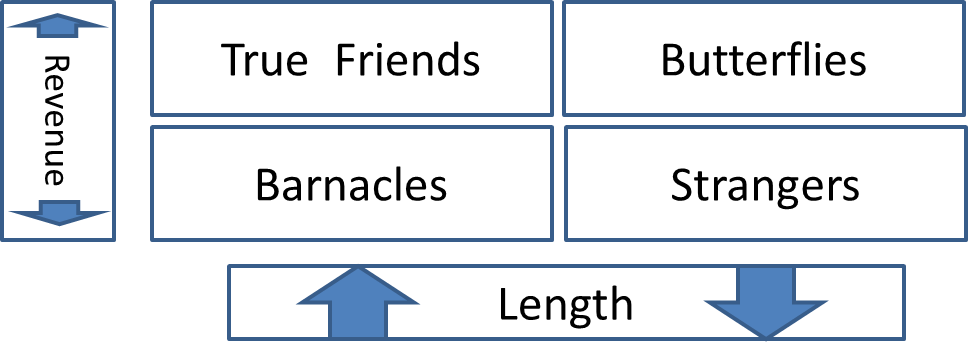
butterflies benefit the most; long term and profitable
major categories of business customers
producers: OEMS
resellers: wholesalers, retailers
governments: federal, state, local
institutions: schools, churches, hospitals
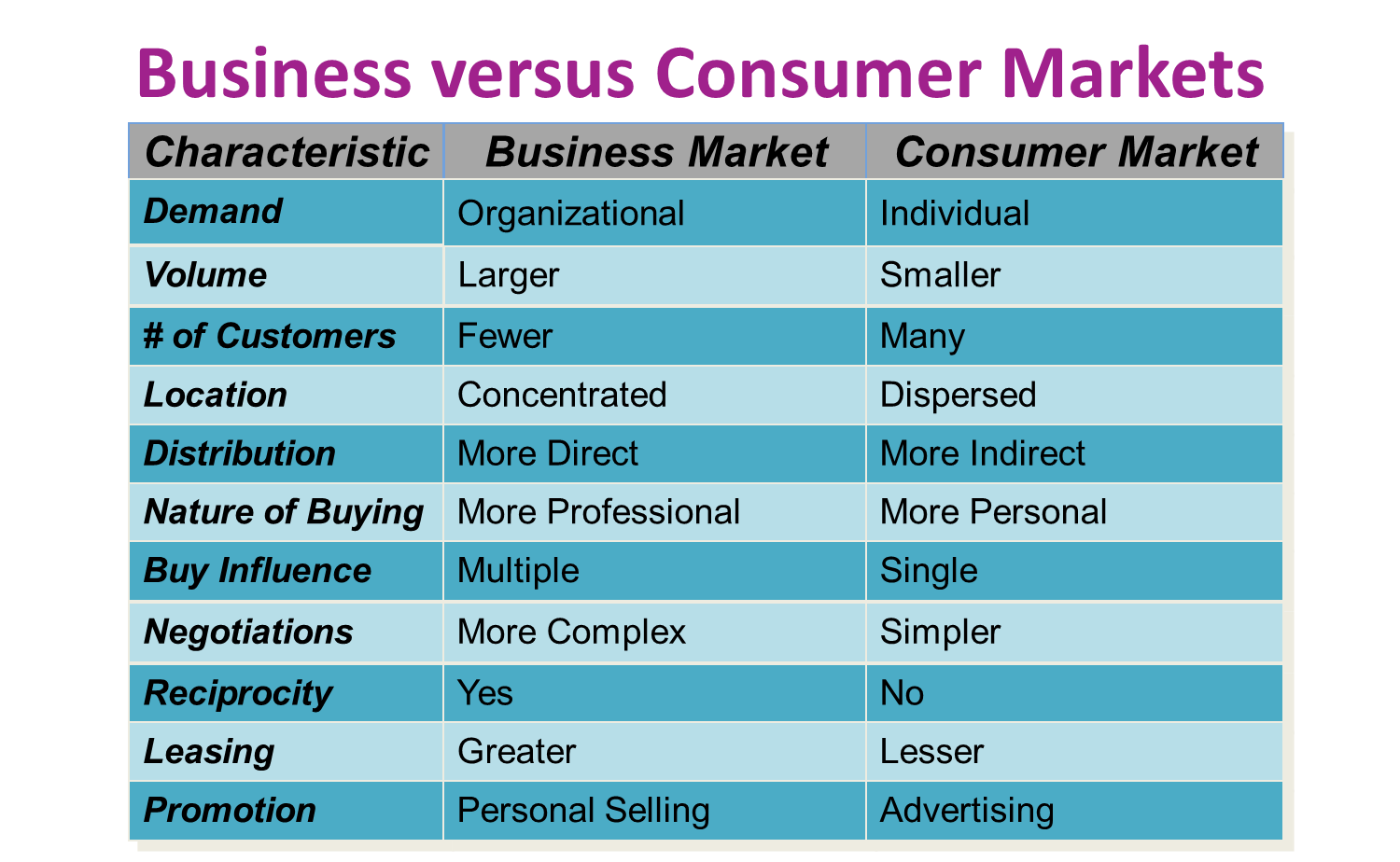
business vs consumer markets
roles in buying centers 1.Initiator
The person who suggests the purchase.
roles in buying centers 2.Influencers/Evaluators:
Help define specifications and provide information for evaluating options.
roles in buying centers 3.Gatekeepers
Group members who regulate the flow of information, often the purchasing agent.
roles in buying centers 4.Decider:
The person with the power to choose or approve the selection.
roles in buying centers 5.Purchaser:
The person who negotiates the purchase.
roles in buying centers 6.Users:
Members of the organization who actually use the product.
buying situations 1. new buy
A situation requiring the purchase of a product for the first time
buying situations 2. modified rebuy
A situation where the purchaser wants some change in the original good or service.
buying situations 3. straight rebuy
A situation in which the purchaser reorders the same goods or services without looking for new information or investigating other suppliers.
characteristics of a market
-They are composed of people or organizations.
-These people or organizations have wants and needs that can be satisfied by particular product categories.
-They have the ability to buy the products they seek.
-They are willing to exchange their resources, usually money or credit, for desired products.
market segmentation 1. market
People or organizations with needs or wants and the ability and willingness to buy.
market segmentation 2. market segment
A subgroup of people or organizations sharing one or more characteristics that cause them to have similar product needs
market segmentation 3. market segmentation
The process of dividing a market into meaningful, relatively similar, identifiable segments or groups.
importance of market segmentation
-Plays a key role in the marketing strategy of successful organizations
-Powerful marketing tool
-Helps marketers define customer needs and wants precisely
-Helps decision makers define objectives and allocate resources more accurately
substantiality
Segment must be large enough to warrant a special marketing mix
identifiability
Segments must be identifiable and their size measurable
accessibility
Members of targeted segments must be reachable with marketing mix.
responsiveness
Unless segment responds to a marketing mix differently, no separate treatment is needed.
geographic segmentation
-region of the country or world
-market size
-market density
-climate
benefits of regional segmentation
-New ways to generate sales in sluggish and competitive markets
-Scanner data allow assessment of best selling brands in region
-Regional brands appeal to local preferences
-Quicker reaction to competition
demographic segmentation
-age
-gender
-income
-ethnic background
-family life cycle
income segmentation
-Income level influences consumers’ wants and determines their buying power.
-Retailers can appeal to: Low-income, High-income, Both
bases for psychographic segmentation
-psychographic segmentation: segmenting markets on the basis of: personality, motives, lifestyles, geodemographics
-Geodemographic segmentation: segmenting potential customers into neighborhood lifestyle categories
lifestyle segmentation
-How time is spent
-Importance of things around them
-Beliefs
-Socioeconomic characteristics
benefit segmentation 1. benefit segmentation
the process of grouping customers into market segments according to the benefits they seek from the product
benefit segmentation 2. usage-rate segmentation
dividing a market by the amount of product bought or consumed
benefit segmentation 3. 80/20 principle
a principle holding that 20 percent of all customers generate 80 percent of the demand
satisfices
Business customers who place an order with the first familiar supplier to satisfy product and delivery requirements.
optimizers
Business customers who consider numerous suppliers, both familiar and unfamiliar, solicit bids, and study all proposals carefully before selecting one.
target market
a group of people or organizations for which an organization designs, implements, and maintains a marketing mix intended to meet the needs of that group, resulting in mutually satisfying exchanges
undifferentiated targeting strategy
a marketing approach that views the market as one big market with no individuals segments and thus uses a single marketing mix
advantage: potential savings on production and marketing costs
disadvantage: unimaginative products, company more susceptible to competition
concentrated targeting strategy
A strategy used to select one segment of a market for targeting marketing efforts.
-niche one segment of marketing
advantage: Concentration of resources, Meets narrowly defined segment, Small firms can compete, Strong positioning
disadvantage: segments too small or changing, large competitors may market to niche segment
multisegmented targeting strategy
a strategy that chooses 2 or more well-defined market segments and develops a distinct marketing mix for each
-Advantage: Greater financial success, Economies of scale
-Disadvantages: Higher costs, Cannibalization
costs of multisegmented targeting strategy
Product design costs
Production costs
Promotion costs
Inventory costs
Marketing research costs
Management costs
Cannibalization
positioning
Developing a specific marketing mix to influence potential customers’ overall perception or a brand, product line, or organization in general
effective positioning
-Assess the positions occupied by competing products
-Determine the dimensions underlying these positions
-Choose a market position where marketing efforts will have the greatest impact
what is a product
Everything, both favorable and unfavorable, that a person receives in an exchange.
-Tangible Good
-Service
-Idea
convivence product
A relatively inexpensive item that merits little shopping effort
shopping product
A product that requires comparison shopping, because it is usually more expensive and found in fewer stores
specialty product
A particular item for which consumers search extensively and are reluctant to accept substitutes
unsought product
A product unknown to the potential buyer or a known product that the buyer does not actively seek (dash cam)
product item
A specific version of a product that can be designated as a distinct offering among an organization’s products.
product line
A group of closely-related product items
product mix
All products that an organization sells.
width of product mix
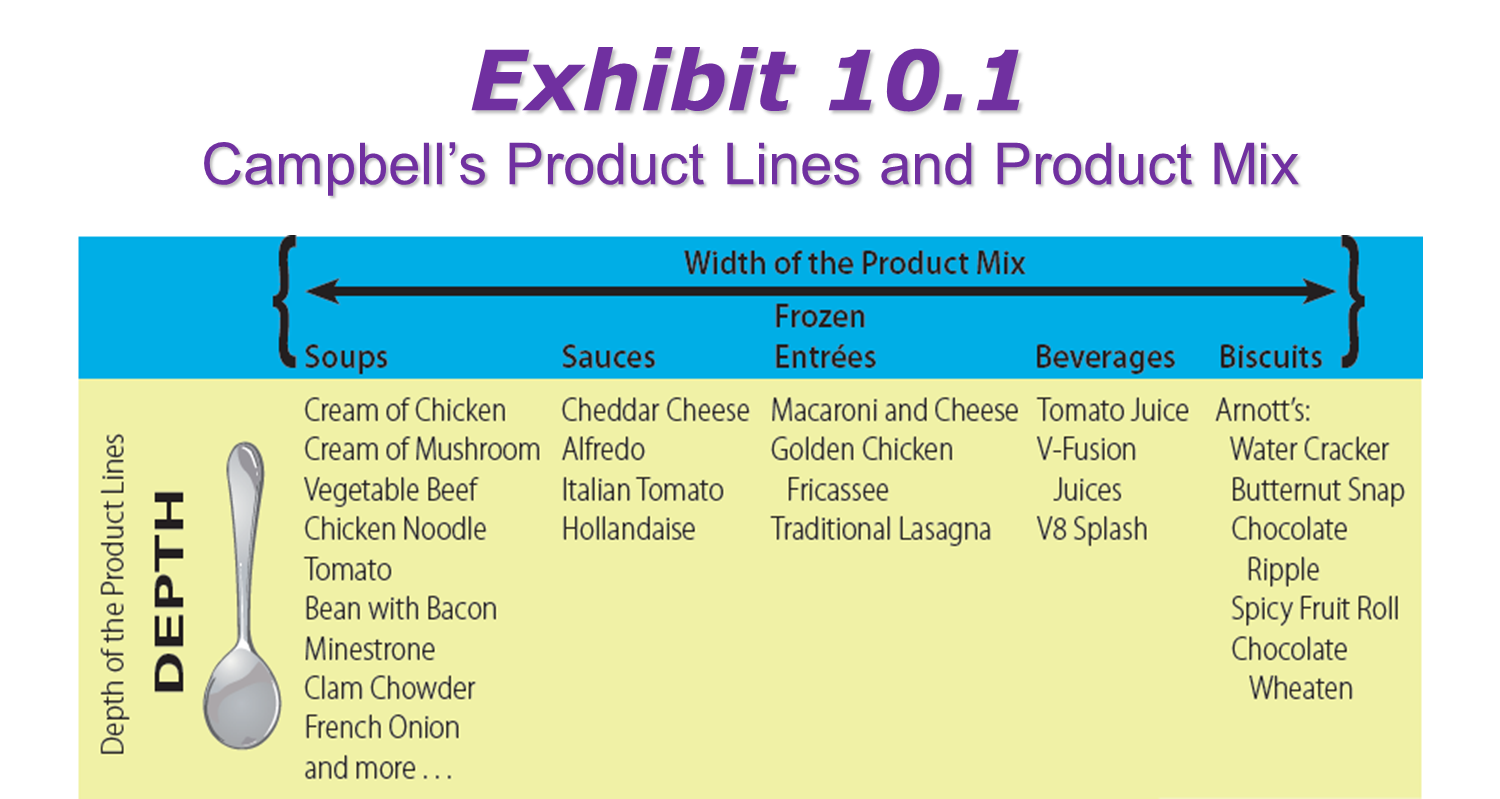
benefits of product lines
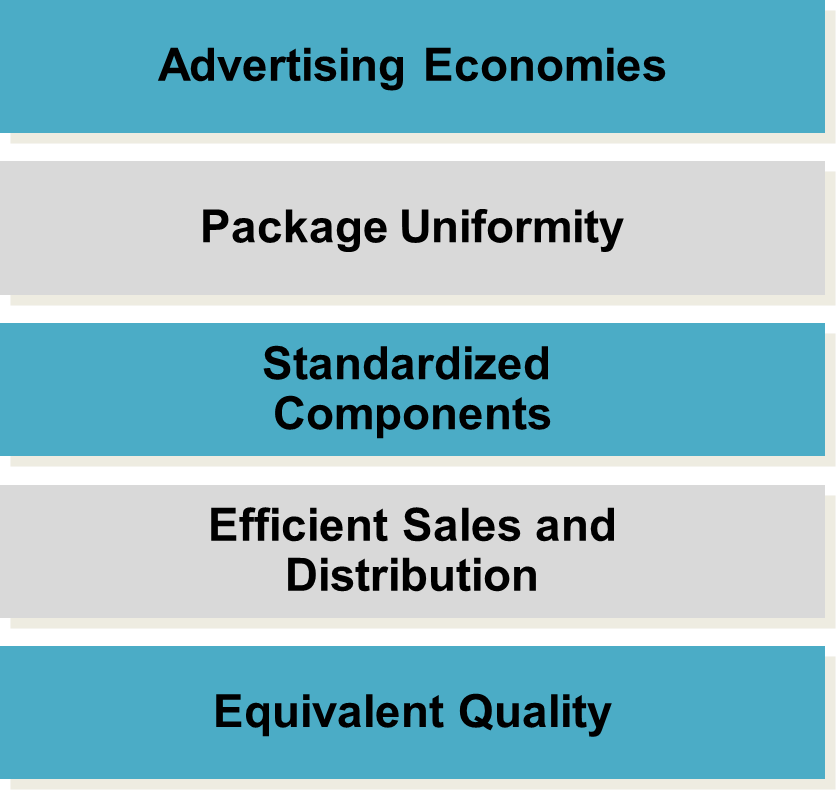
types of product modifications
functional modification, style modification and quality modification
-Planned Obsolescence: The practice of modifying products so those that have already been sold become obsolete before they actually need replacement.
product line extension
adding additional products to an existing product line in order to compete more broadly in the industry
-symptoms of overextension: Some products have low sales or cannibalize sales of other items and Items have become obsolete because of new product entries
brand name
That part of a brand that can be spoken, including letters, words, and numbers
brand mark
The elements of a brand that cannot be spoken (e.g., Nike’s “Swoosh”)
brand equity
The value of company and brand names
global brand
A brand where at least a third of the earnings come from outside its home country
benefits of branding
product identification, repeat sales, new product sales
manufacture brand
the brand name of a manufacturer (Tylenol, Dasani water)
private brand
A brand name owned by a wholesaler or a retailer. Also known as a private label, store brand or generic brand (e.g, Acetaminophen tablets from Walmart, CVS, etc; Kirkland water from Costco).
advantages of manufacturers’ brands
-Heavy consumer ads by manufacturers
-Attract new customers
-Enhance dealer’s prestige
-Rapid delivery, carry less inventory
-If dealer carries poor quality brand, customer may simply switch brands and remain loyal to dealer
advantages of private brands
-Earn higher profits on own brand
-Less pressure to mark down price
-Manufacturer can become a direct competitor or drop a brand/reseller
-Ties customer to wholesaler or retailer
-Wholesalers and retailers have no control over the intensity of distribution of manufacturers’ brands
cobranding
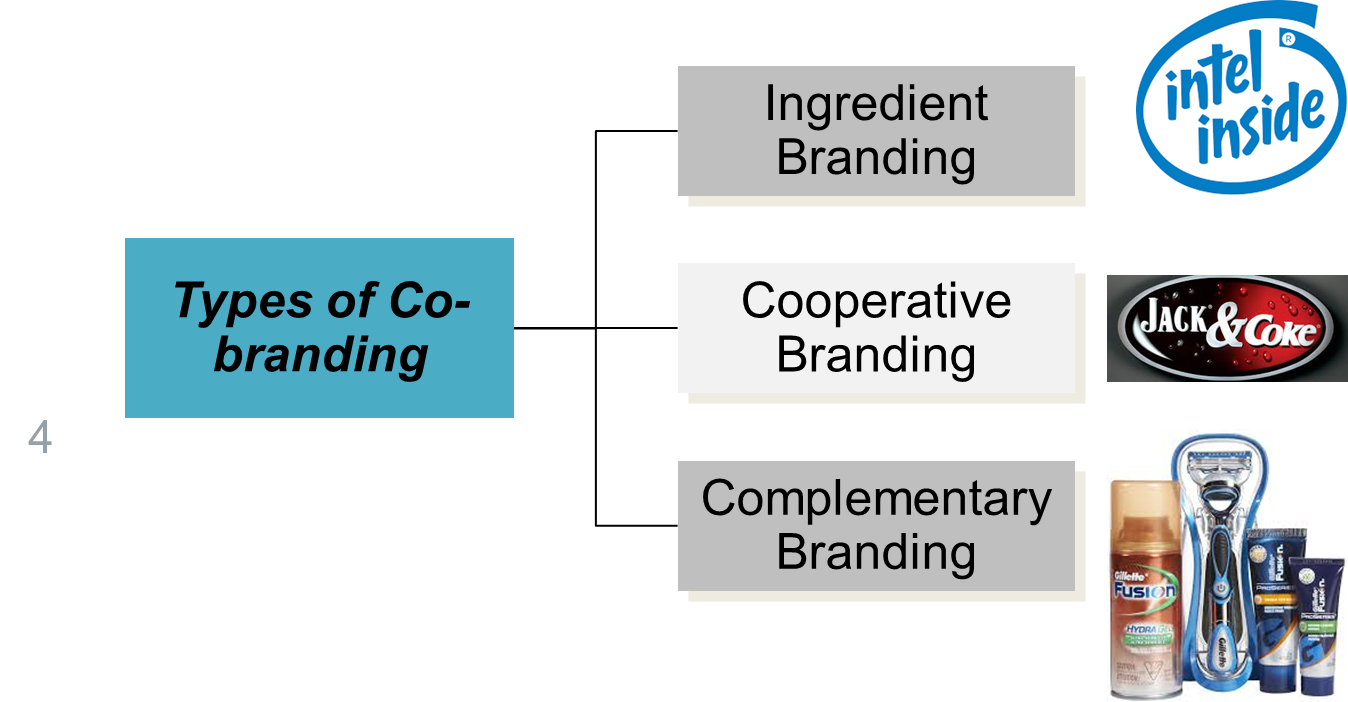
trademark
exclusive right to use a brand. a service mark performs the same function for services
-Many parts of a brand and associated symbols qualify for trademark protection.
-Trademark right comes from use rather than registration.
-The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) explicitly applies trademark law to the digital world.
-Companies that fail to protect their trademarks face the possibility that their product names will become generic.
categories of a new product
-new to the world
-new product lines
-product line additions (brand extension)
-improvements
-repositioned products
-lower-priced products
new product success factor
-long term commitment
-company-specific approach
-capitalize on experience
-establish an environment
brainstorming
The process of getting a group to think of unlimited ways to vary a product or solve a problem.
focus group
The objective of focus group interviews is to stimulate insightful comments through group interaction.

screening
The first filter in the product development process, which eliminates ideas that are inconsistent with the organization’s new-product strategy or are inappropriate for some other reason.
concept test
A test to evaluate a new-product idea, usually before any prototype has been created. Often successful for line extensions.
considerations on business analysis stage
-demand
-cost
-sales
-profitability
development
-Create of a prototype
-Sketch a marketing strategy
-Decide on packaging, branding, and labeling
-Map out promotion, price, and distribution strategy
-Examine manufacturing feasibility
test marketing
The limited introduction of a product and a marketing program to determine the reactions of potential customers in a market situation.
costs of test marketing
-Often takes one year or more
-Can cost over $1 million
-Exposes new product to competitors
-Competitors can “jam” testing programs with their own promotions
commercialization

product failure
-Despite the amount of time and money spent on developing and testing new products, a large proportion of new product introductions fail.
-The most important factor in successful new-product introduction is a good match between the product and market
new-product success factor
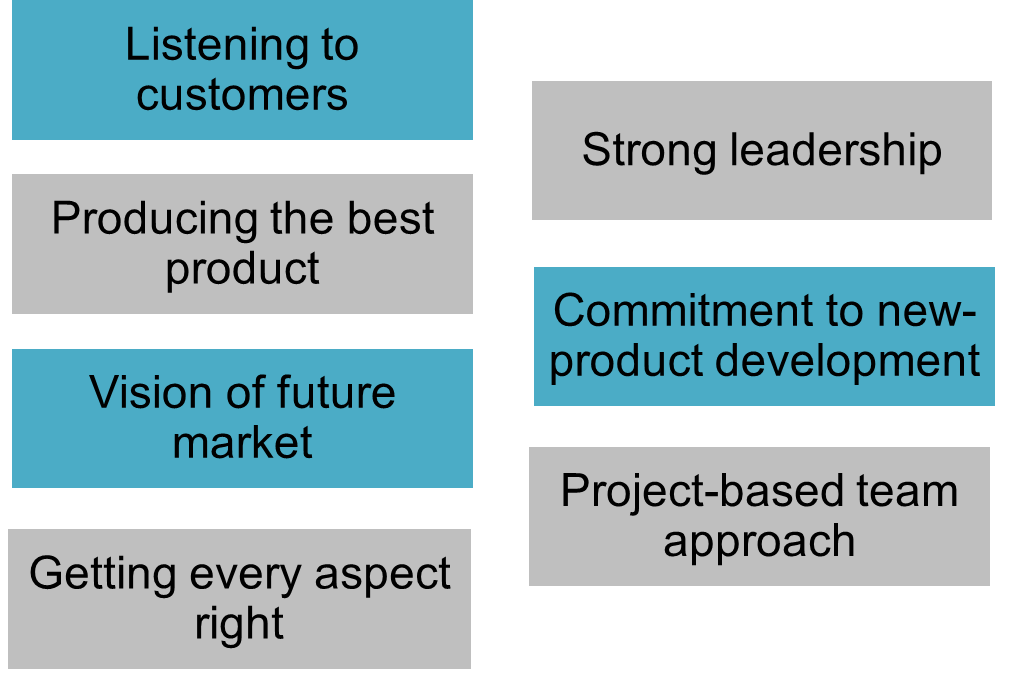
diffusion
the process by which the adoption of an innovation spread
categories of adopters
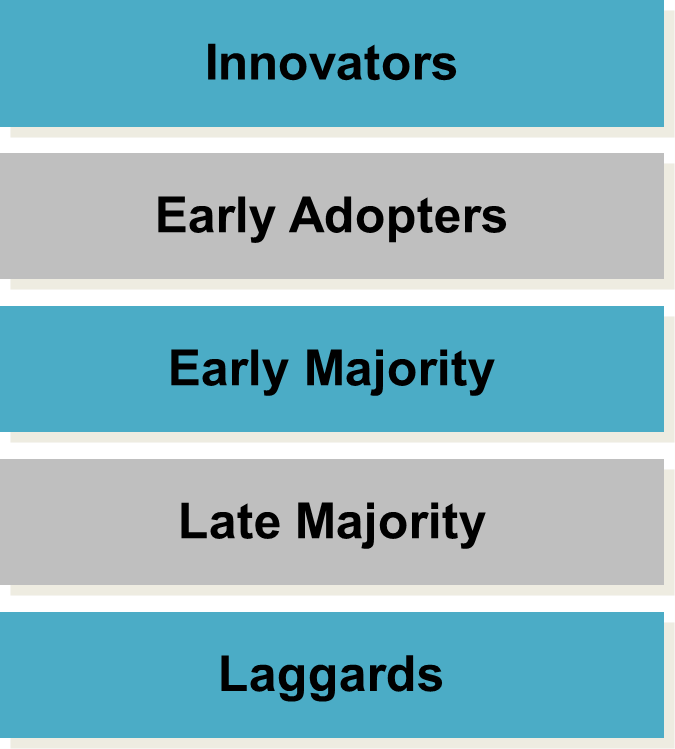
product lifecycle
A concept that provides a way to trace the stages of a product’s acceptance, from its introduction (birth) to its decline (death).
introductory stage
-High failure rates
-Little competition
-Frequent product modification
-Limited distribution
growth stage
-Increasing rate of sales
-Entrance of competitors
-Initial healthy profits
-Aggressive advertising of the differences between brands
-Wider distribution
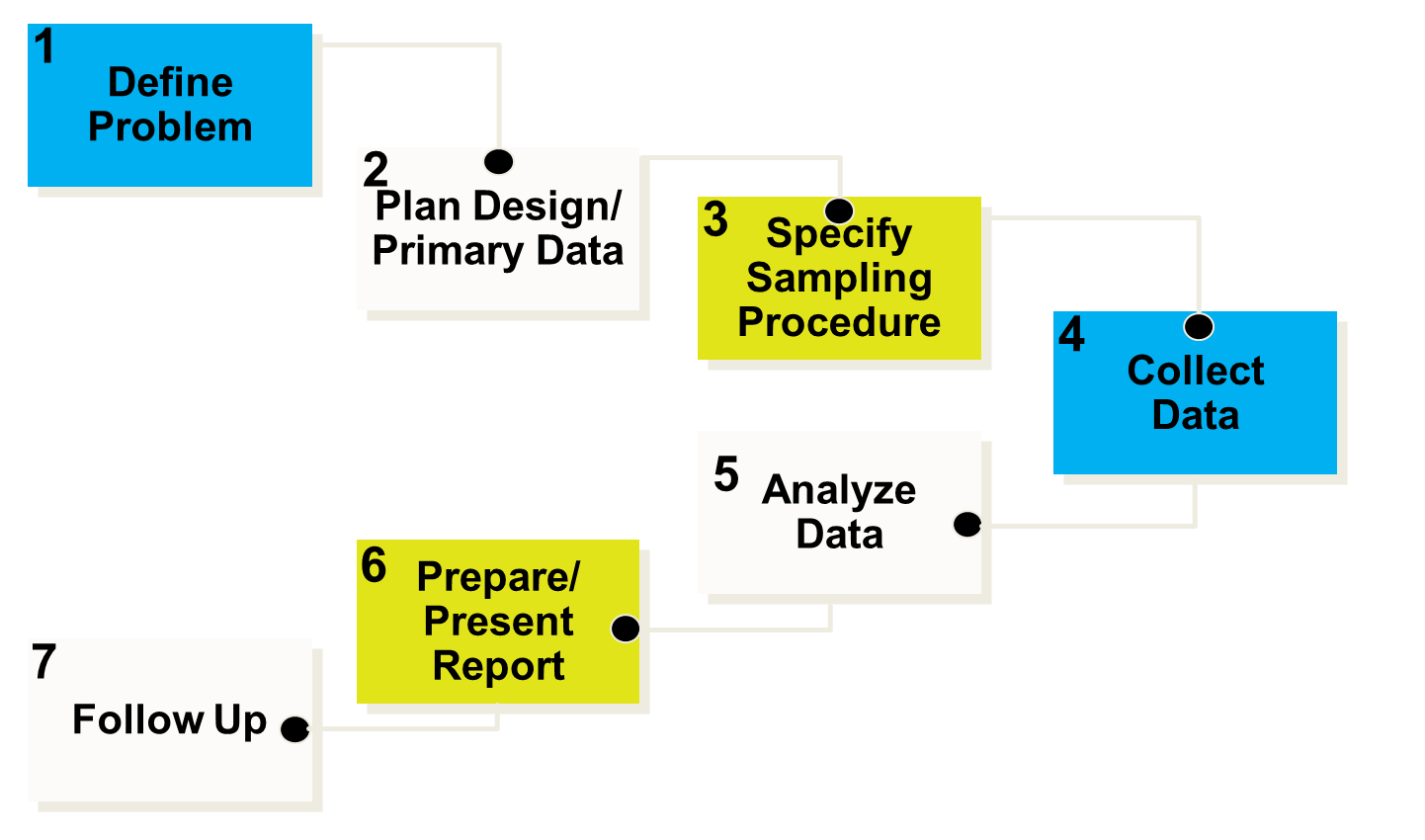
role of marketing research
Marketing research is the process of planning, collecting and analyzing data relevant to a marketing decision
management uses of marketing research
-It improves the quality of decision making
-It helps managers trace problems
-It can help managers serve their customers accurately and efficiently
-It helps managers gauge the perceived value of their goods and services, as well as the level of customer satisfaction
steps in a marketing research project
secondary data
previously collected for any purpose other than the one at hand
primary data
information that is collected for the first time; used for solving the particular problem under investigation
sources of secondary data
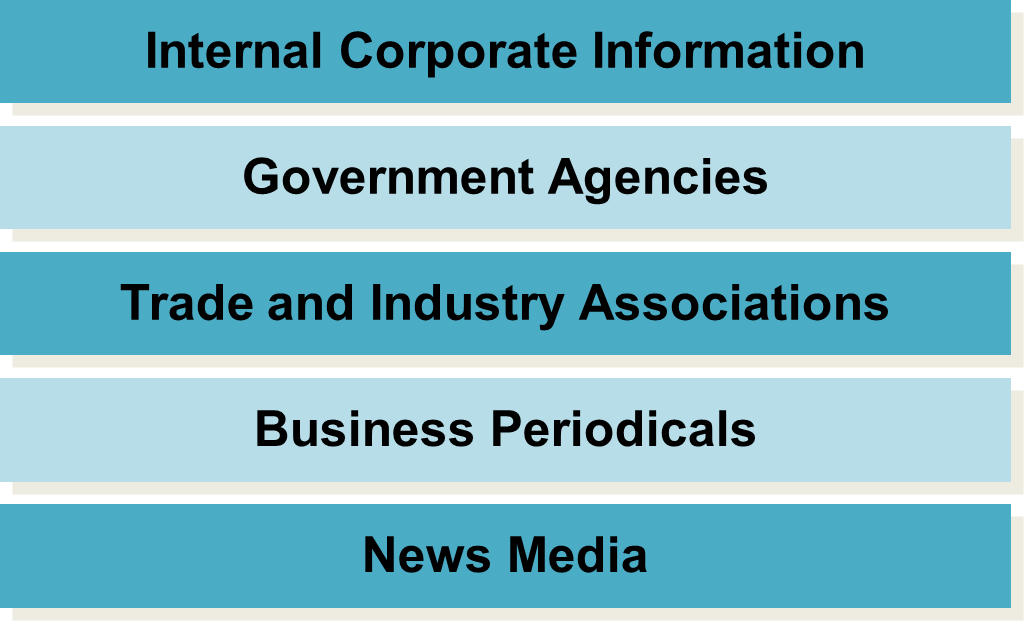
disadvantages of secondary data
-may not give adequate information
-may not be on target with the research problem
-quality and accuracy of data may pose a problem
primary data advantages
-Answers a specific research question
-Data are current
-Source of data is known
-secrecy can be maintained
disadvantages of primary data
Primary data can be very expensive
Disadvantages are usually offset by the advantages of primary data.
forms of survey research
-in home interviews
-mall intercept interviews
-telephone interviews
-mail surveys
-executive interviews
-focus groups
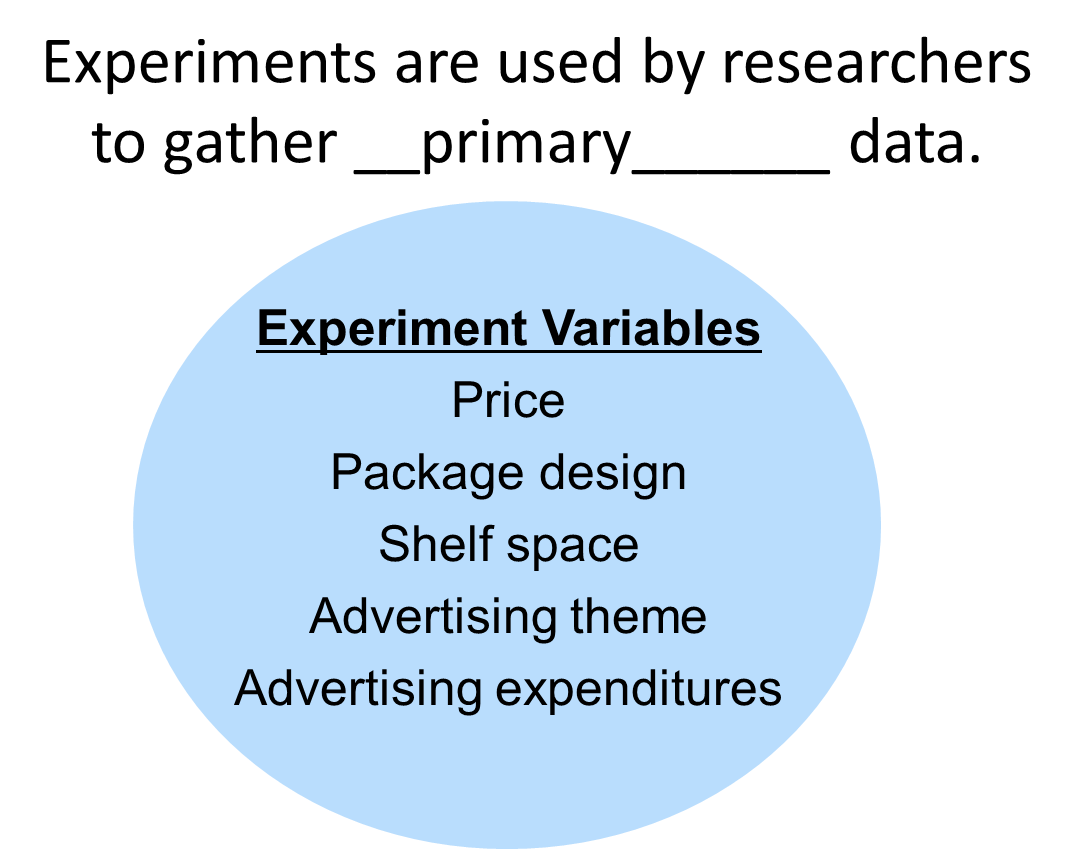
experiments
-used by researcher to gather primary data
supply chain
: the connected chain of all of the business entities, both internal and external to the company, that perform or support the logistics function