2.2.1-2.2.2 Study Guide
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
What does MRI stand for?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2
New cards
Define an MRI (use definition in my.pltw)
A medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to take pictures of the soft tissues of the body
3
New cards
What is mitosis?
Mitosis involves the doubling and separation of genetic material and results in the formation of two new nuclei
4
New cards
Why is mitosis important? 3
Mitosis is important because cells need to reproduce for a variety of reasons including
1. replacing a cell that dies
2. healing a wound
3. when the body goes through a growth spurt
1. replacing a cell that dies
2. healing a wound
3. when the body goes through a growth spurt
5
New cards
What are the 5 stages of mitosis? (IPMAT+)
1. Interphase
2. Prophase
3. Metaphase
4. Anaphase
5. Telophase + cytokinesis
6
New cards
In what phase of mitosis does DNA condense into chromosomes?
Prophase
7
New cards
In what stage(s) of mitosis are there two new cells?
Telophase + cytokinesis
8
New cards
How are tumors connected to mitosis?
Mitosis is a highly regulated event, but there are times when this process goes unchecked and leads to uncontrolled cell division. This uncontrollable cell division can cause the formation of tumors.
9
New cards
What is cancer?
A disease caused when cells divide uncontrollably and spread into other tissues
10
New cards
Tumors are examined by *_.* This helps to determine if the tumor can be classified as _ or _. If it’s cancerous it will be considered _ . The cancer invades other tissues or parts of the body through _.
Tumors are examined by __BIOPSY__. This helps to determine if the tumor can be classified as __BENIGN__ or __MALIGNANT__. If it's cancerous it will be considered __MALIGNANT__. The cancer invades other tissues or parts of the body through __METASTASIS__.
11
New cards
What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues from a patient’s body using a needle, scalpel, or other tools to study them more closely using a microscope
12
New cards
What are mutations?
Changes to a DNA sequence
13
New cards
How do mutations affect DNA?
Mutations affect DNA because it causes a change in the sequence which causes a change to the amino acids used to make proteins. This can cause something different to be made.
14
New cards
Proteins are the building blocks of _
Life
15
New cards
What does protein synthesis do?
Protein synthesis creates new proteins
16
New cards
What are the two steps of protein synthesis?
1. Transcription
2. Translation
17
New cards
Describe what happens during transcription
During transcription DNA is copied into RNA
18
New cards
Describe what happens during translation
During translation RNA is read (in groups of 3 called codons) and specific amino acids are used to make proteins
19
New cards
RNA is read in groups of _
Three
20
New cards
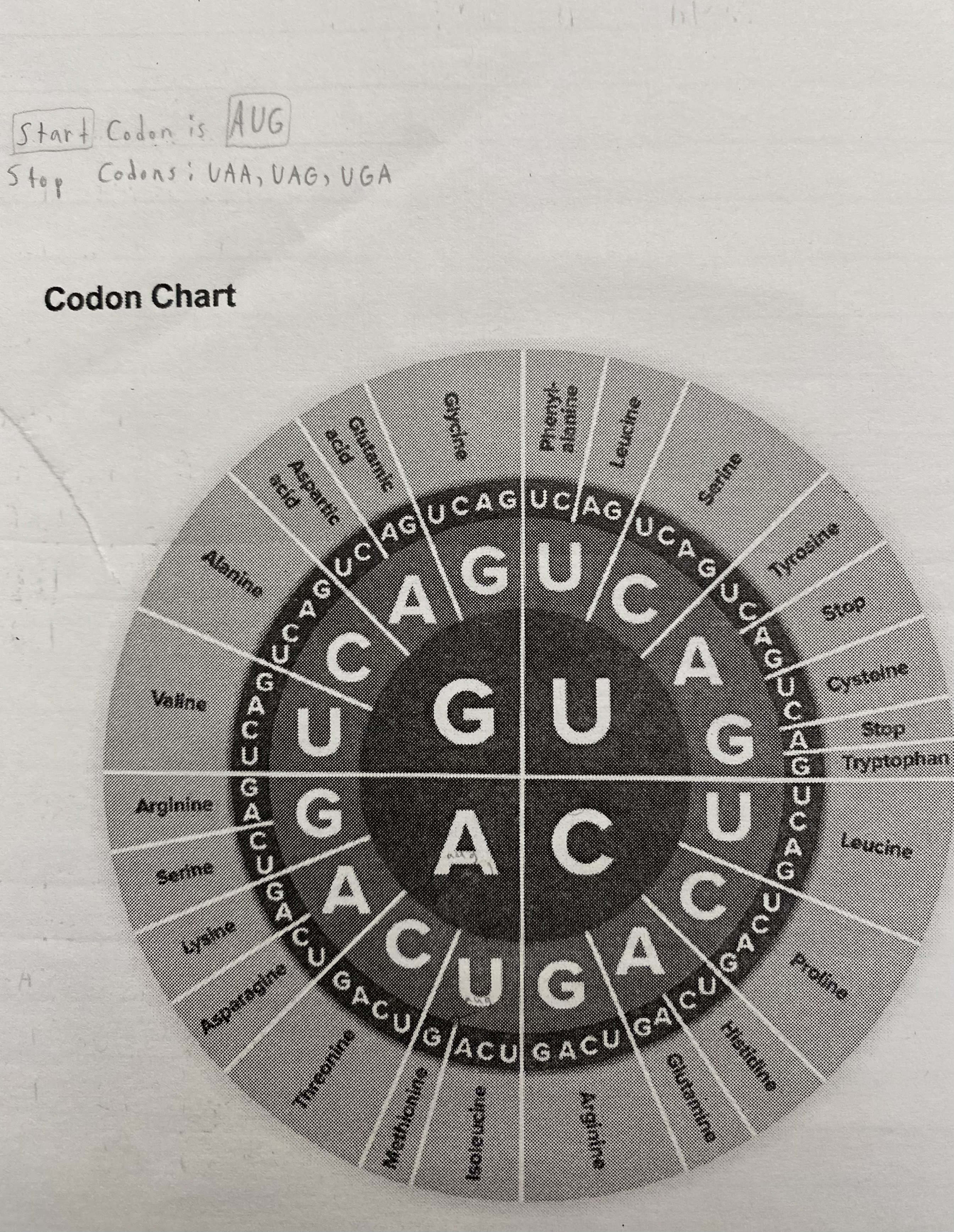
There are *_* and _ codons. These are codes that start and stop translation/the creation of a protein.
There are __START__ and __STOP__ codons. These are codes that start and stop translation/ the creation of a protein.
21
New cards
DNA: G A C C G A T A C C A T T C G G C G C A T A C T T C C, transcribe the DNA into RNA.
RNA: C U G G C U __A U G__ __G U A__ __A G C__ __C G C__ __G U A__ __U G A__ A G G
22
New cards
RNA: C U G G C U __A U G__ __G U A__ __A G C__ __C G C__ __G U A__ __U G A__ A G G, translate the RNA using your codon chart.
Amino Acids: methionine, valine, serine, arginine, valine, STOP
23
New cards
What will happen to the protein if there is a change to the DNA sequence? 4
1. No longer function
2. Have reduced function
3. Have increased function
4. Be different and have a different function
24
New cards
What are the 3 types of mutations in DNA?
1. Insertion
2. Deletion
3. Substitution
25
New cards
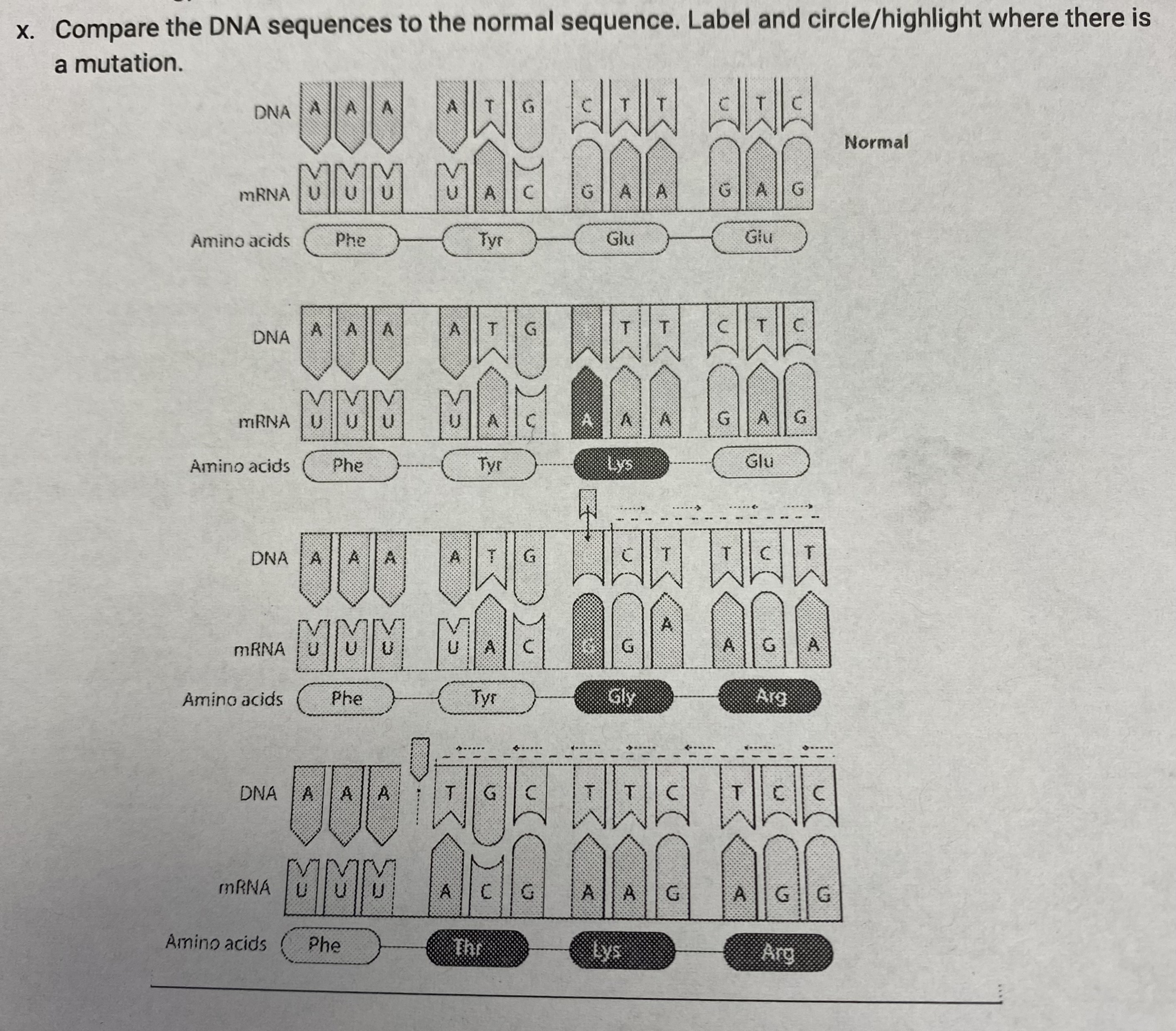
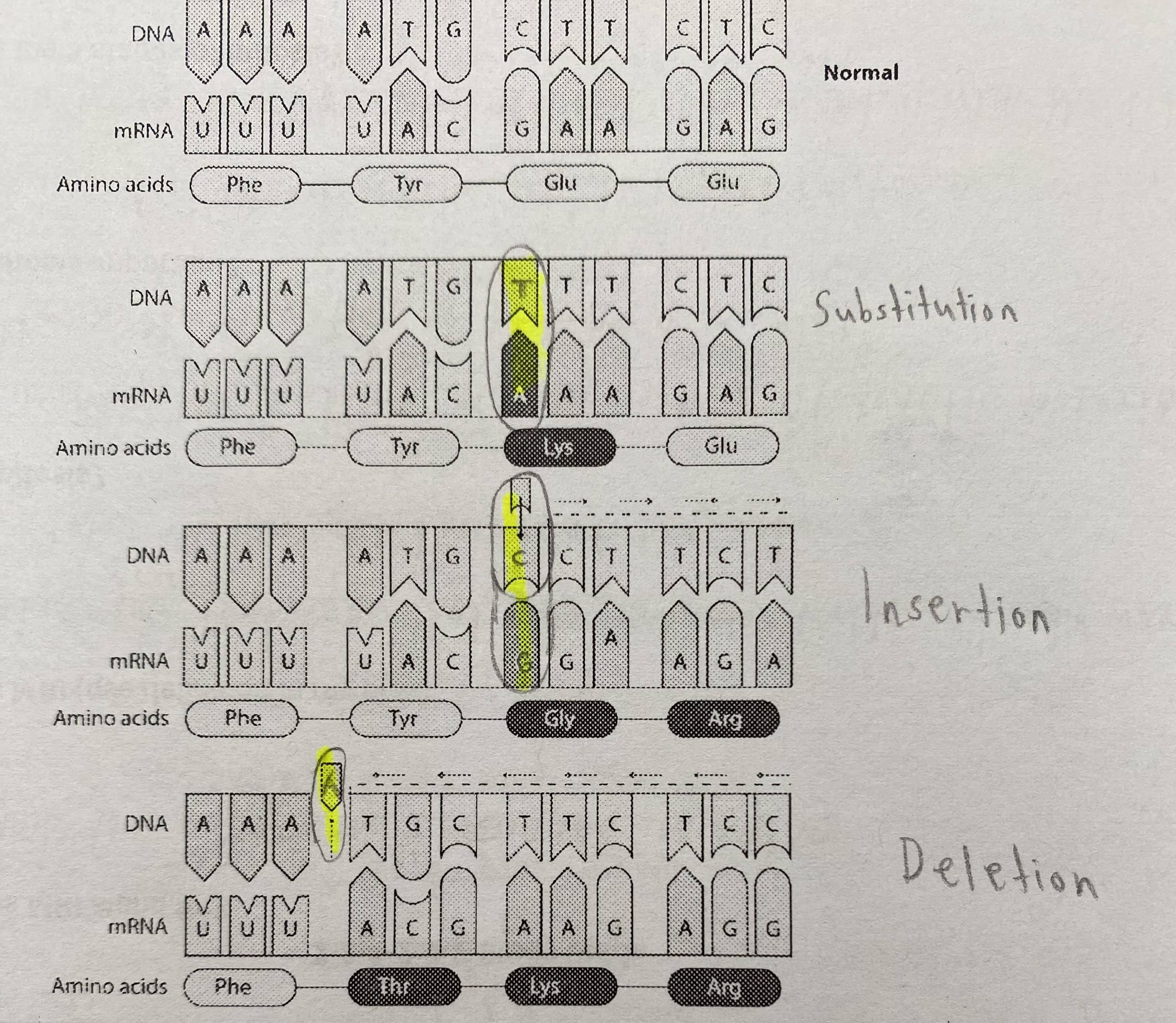
Compare the DNA sequences to the normal sequence. Label and circle/highlight where there is a mutation.
Substitution (C→T), Insertion (+C), Deletion (-A)
26
New cards
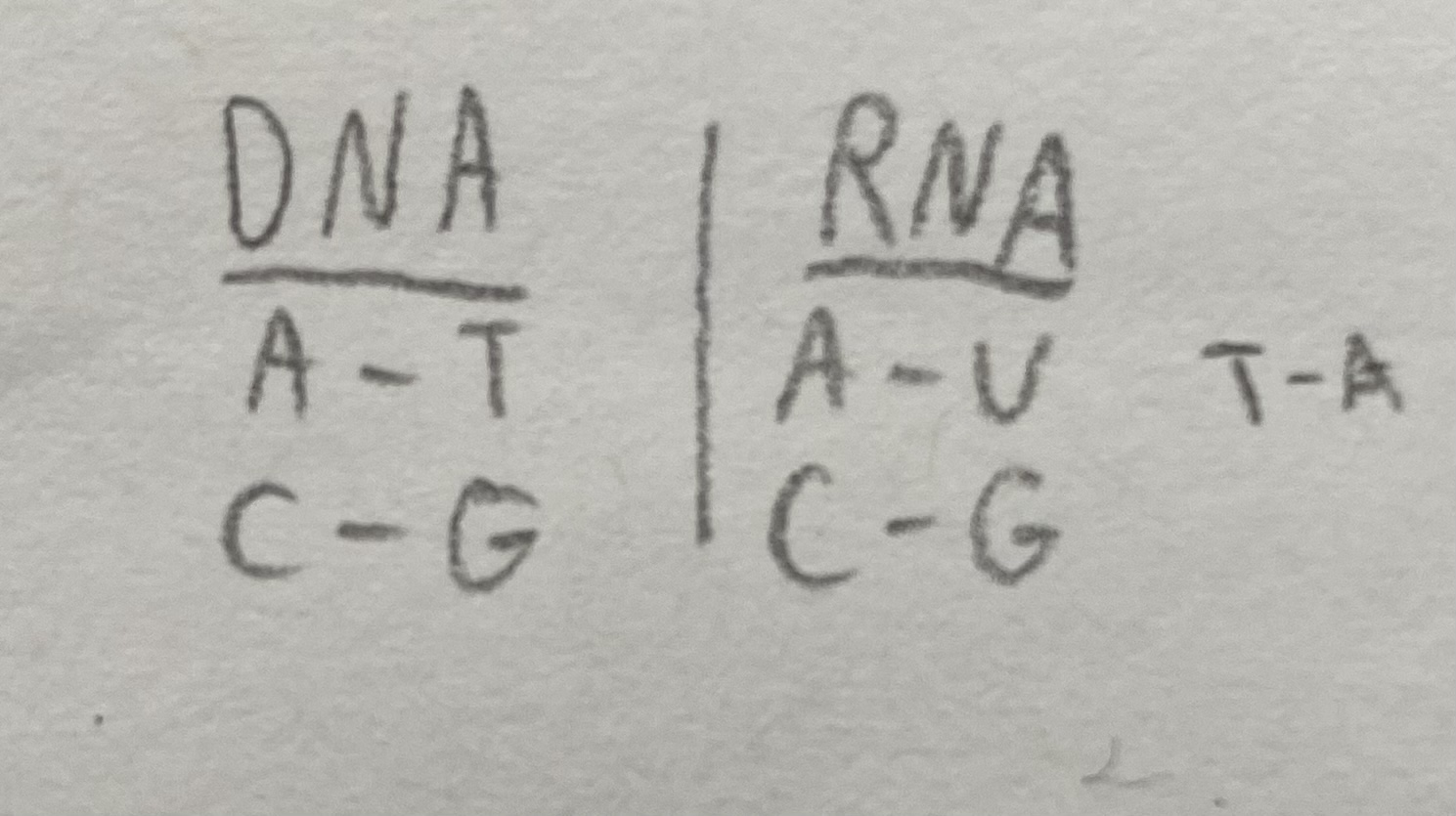
Transcribe the DNA sequences:
a. TAC TAT GCC TTA
b. TAC TTC AAA ATC
a. TAC TAT GCC TTA
b. TAC TTC AAA ATC
a. TAC TAT GCC TTA → RNA: AUG AUA CGG AAU
b. TAC TTC AAA ATC → RNA: AUG AAG UUU UAG
b. TAC TTC AAA ATC → RNA: AUG AAG UUU UAG
27
New cards
Make a mutation of your choice to the original DNA sequence. Label and highlight where the mutation is.
**ORIGINAL**
DNA: TAC TAT G==**C**==C TTA → RNA: AUG AUA CGG AAU
TRANSLATION: methionine, isoleucine, arginine, asparagine
\
**MUTATED (insertion of the letter T)**
DNA: TAC TAT G==**T**==C CTT A → RNA: AUG AUA CAG GAA U
TRANSLATION: methionine, isoleucine, *glutamine, glutamic acid*
DNA: TAC TAT G==**C**==C TTA → RNA: AUG AUA CGG AAU
TRANSLATION: methionine, isoleucine, arginine, asparagine
\
**MUTATED (insertion of the letter T)**
DNA: TAC TAT G==**T**==C CTT A → RNA: AUG AUA CAG GAA U
TRANSLATION: methionine, isoleucine, *glutamine, glutamic acid*
28
New cards
Describe the change that was made and the effect it had on the protein.
The letter T was INSERTED into the sequence. This caused all the letters after the mutation to slide over. This caused new codons to be made. The sequence now has glutamine and glutamic acid instead of arginine and asparagine. This mutation caused new amino acids to be used in the making of this protein which can cause a different protein to be made all together.
29
New cards
Translate the RNA sequences:
\
a. RNA: AUG AUA CGG AAU
b. RNA: AUG AAG UUU UAG
\
a. RNA: AUG AUA CGG AAU
b. RNA: AUG AAG UUU UAG
a. methionine, isoleucine, arginine, asparagine
b. methionine, lysine, phenyl-alanine, STOP
b. methionine, lysine, phenyl-alanine, STOP