BCH261 - Module 3 - Nucleic Acids
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
2 types of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Where were nucleic acids found
in nuclei of WBC
Monomer, oligomer, and polymer of nucleic acids
Monomer: Nucleotides
Oligomer: Oligonucleotides
Polymer: Polynucleotides (nucleic acids)
Nucleotide functions (monomer)
1. energy for metabolism (ATP)
2. enzyme cofactors (NAD+)
3. Signal transduction (cAMP)
Nucleic acid functions (polymer)
1. storage of genetic info (DNA)
2. transmission of genetic info (mRNA)
3. protein synthesis (tRNA and rRNA)
4. Processing of genetic info (ribozymes)
Difference in structure between DNA and RNA. Draw the structure RN!
DNA:
- Has H on 2' end of pentose sugar
- Has thymine instead of uracil in nitrogenous base
- beta-2'-deoxy-D-ribofuranose in DNA
RNA:
- Has OH on 2' end of pentose sugar
- Has uracil instead of thymine in nitrogenous base
-beta-D-ribofuranose in RNA
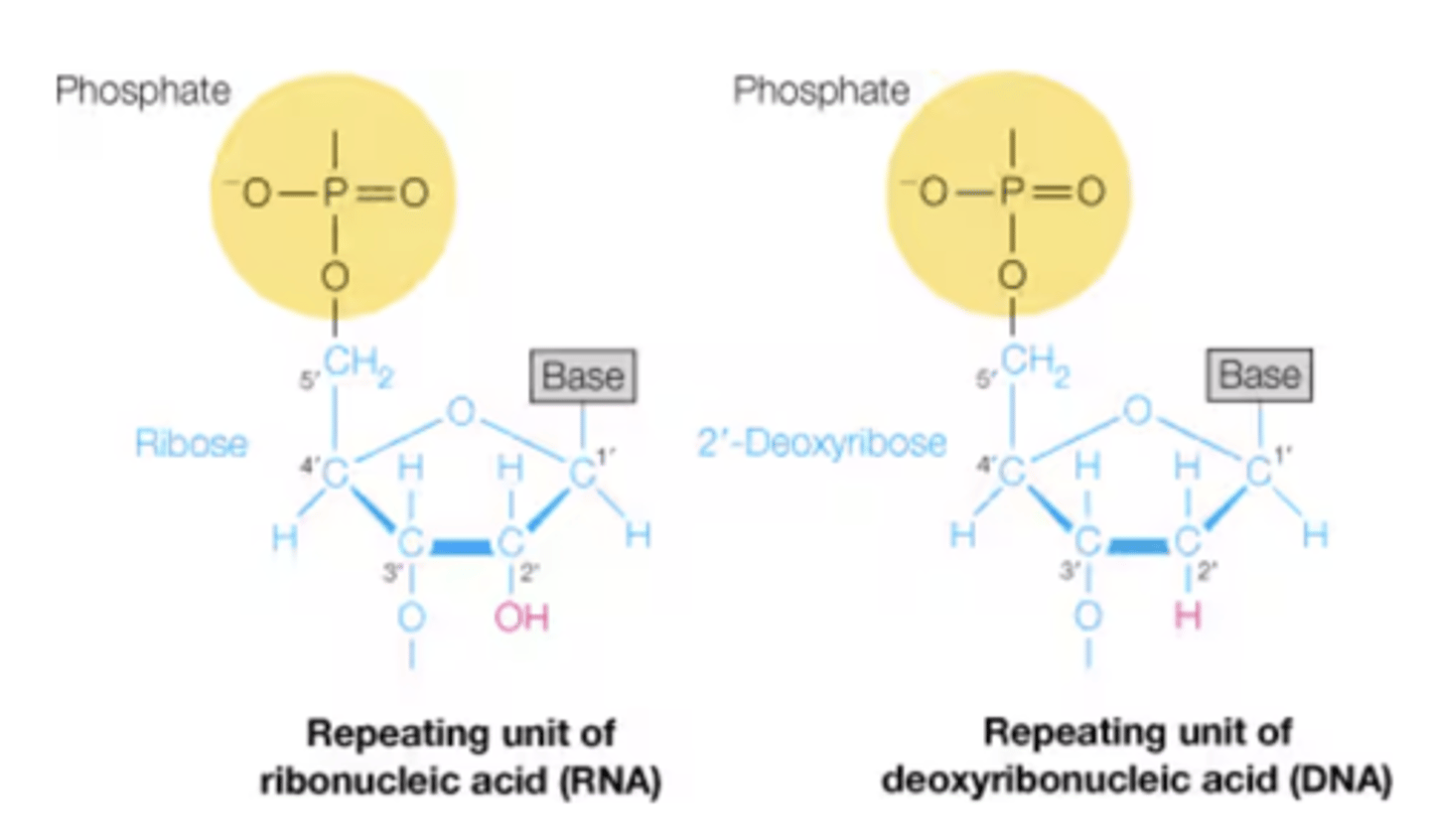
Similarity in structure between DNA and RNA
- Both have guanine and cytosine
- Both have pentose sugar, organic nitrogenous base, and phosphate
How are monomers connected
Covalently by phosphodiester link between the phosphate group attached to the hydroxyl on C5' of one unit and the hydroxyl on C3' on the other unit (therefore, phosphodiester is between two sugar residues)
Is DNA and RNA acidic or basic? Why?
ACIDIC! Phosphate groups are strong acids with a pKA of around 1
What forms the backbone of the nucleic acid molecule?
The phosphodiester-linked sugar residues
Explain nucleic acid synthesis (the monomer, what gets cleaved, what new monomer gets added to the chain, the specific carbons)
Monomer: (d)NTPs (deoxynucleotide triphosphates)
- PPi gets cleaved from NTP (NTP->NMP)
- then, (d)NMP gets added to chain
- new nucleotides are added to 3' C of the previous nucleotide
- Forms phosphodiester bond which releases PPi
Do nucleic acids have branching?
No branching
In what direction is nucleic acid sequence read?
5' to 3'
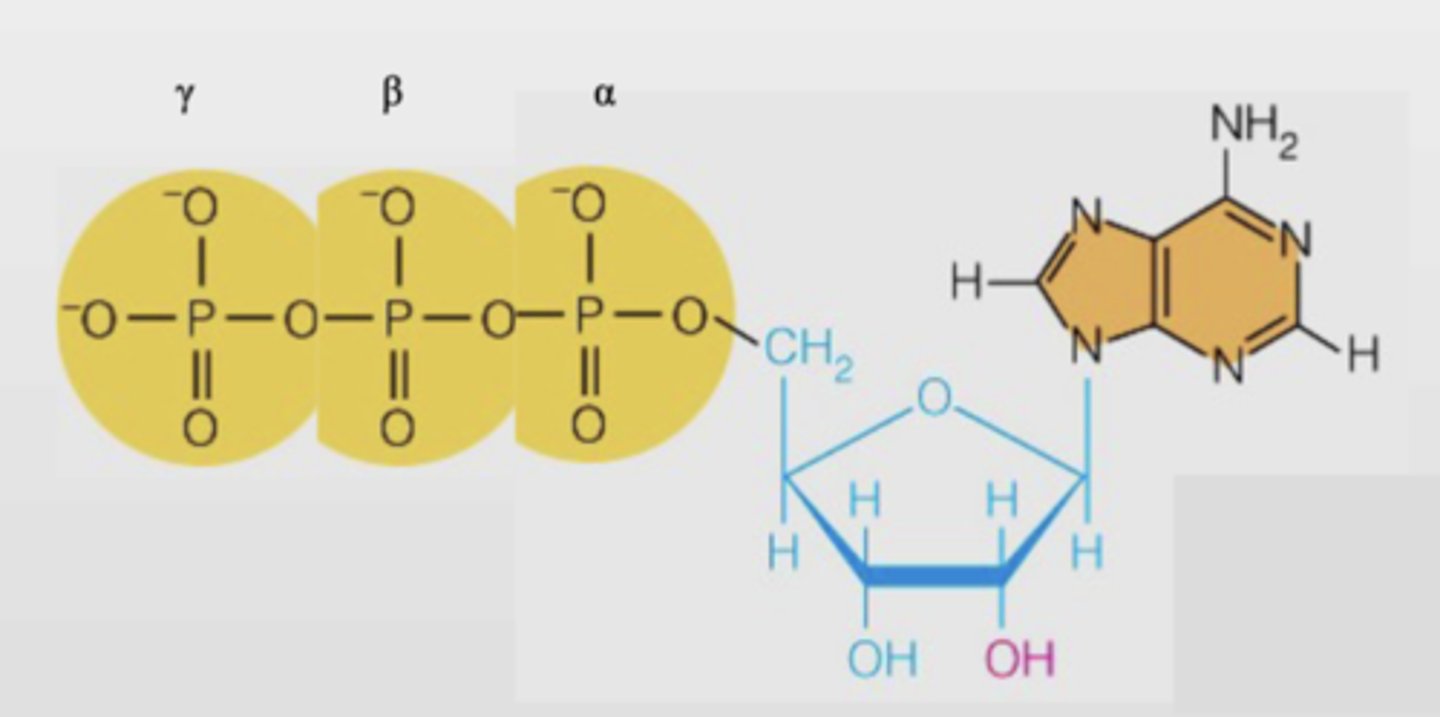
What is the structure of Nucleoside triphosphate?
How is a phosphodiester bond formed?
5' phosphate binds with 3' OH of next nucleotide. condensation reaction, so water molecule is released between each pair of monomers (delta G=+25 kJ/mol - endergonic)
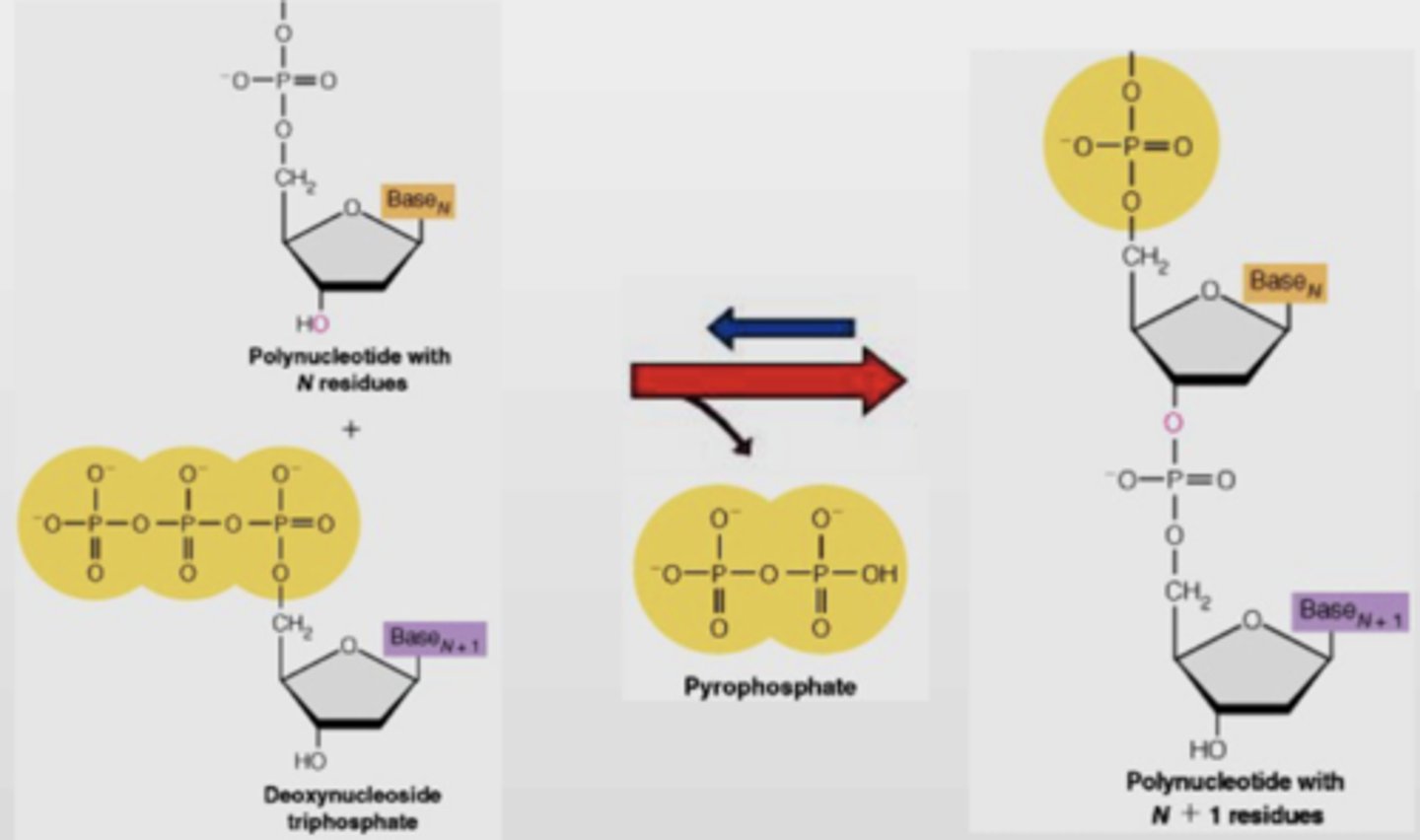
What does the formation of a phosphodiester bond release?
Water and pyrophosphate (PPi)
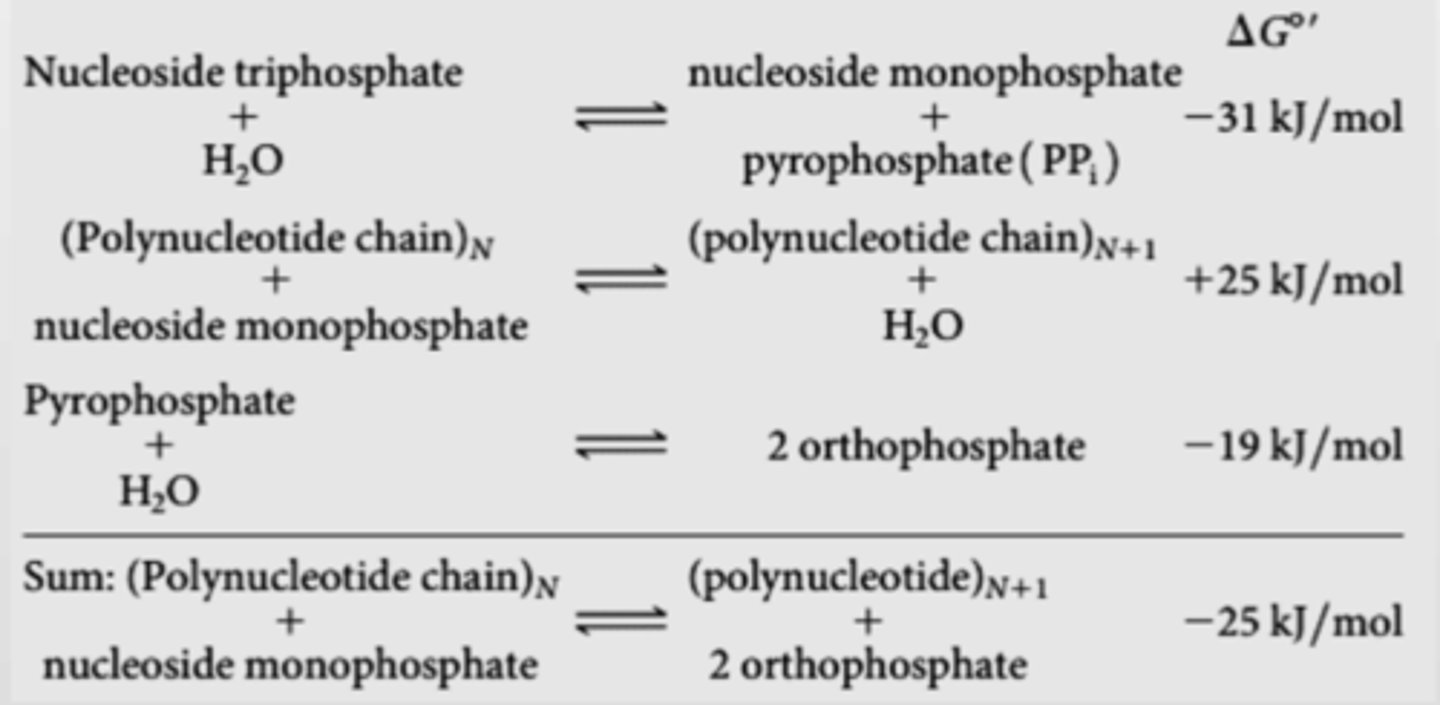
Since phosphodiester bond is endergonic, what reaction is it coupled with so it can be favourable?
Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphate into nucleoside monophosphate + PPi (-31 kJ/mol)
also pyrophosphate + water into 2 orthophosphate (-19 kJ/mol)
Nucleobases are also called
Heterocyclic bases
What are nucleobases?
Base ALWAYS linked to C1' of sugar
- Purine (A Giant)
- Pyrimidine (CUTy Py)
Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules with planar ring structure (either double or single ringed)
How much UV light do nucleobases absorb? What is absorption used for?
- around 250-270 nm
- used to measure nucleic acid concentration
What happens to excited states of common nucleobases?
Decay rapidly via radiation-less transitions
Why is the speed of decay important for nucleobases?
1. effective photoprotection of genetic material
2. no fluorescence from nucleic acids
How does the absorbance of UV light differ in nucleotides vs aromatic amino acids
Nucleotides absorb 250-270nm (260 is prime)
Aromatic amino acids absorb around 260-290nm (280 is prime)
How can a 280:260 ratio be used to measure purity of DNA?
Why do nucleobases and their derivatives (nucleic acids, nucleotides, nucleosides) strongly absorb light in UV range?
Due to conjugated double-bond systems
- depends kinda on pH too, due to ionization reactions in the bases
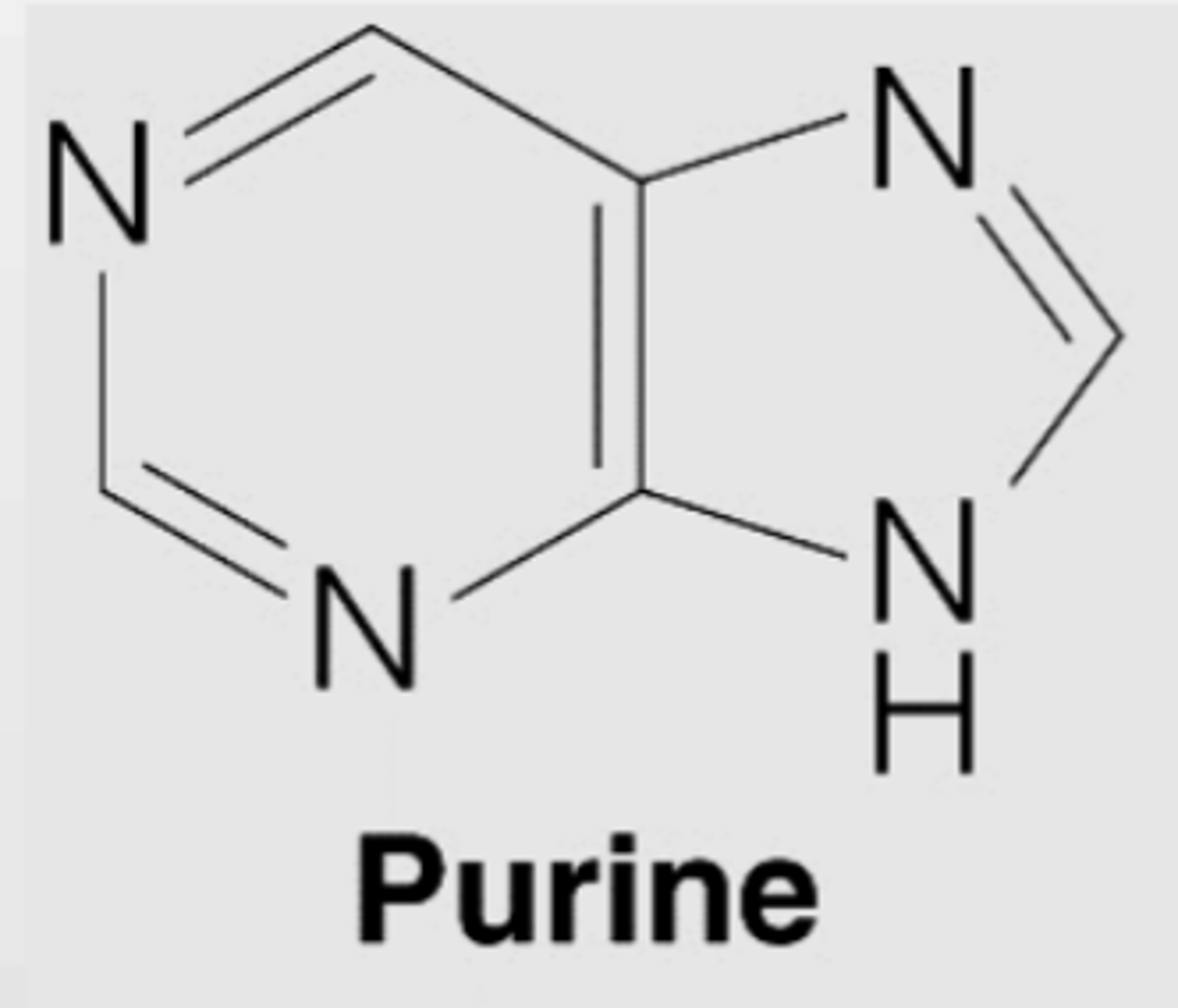
Purine
double ringed
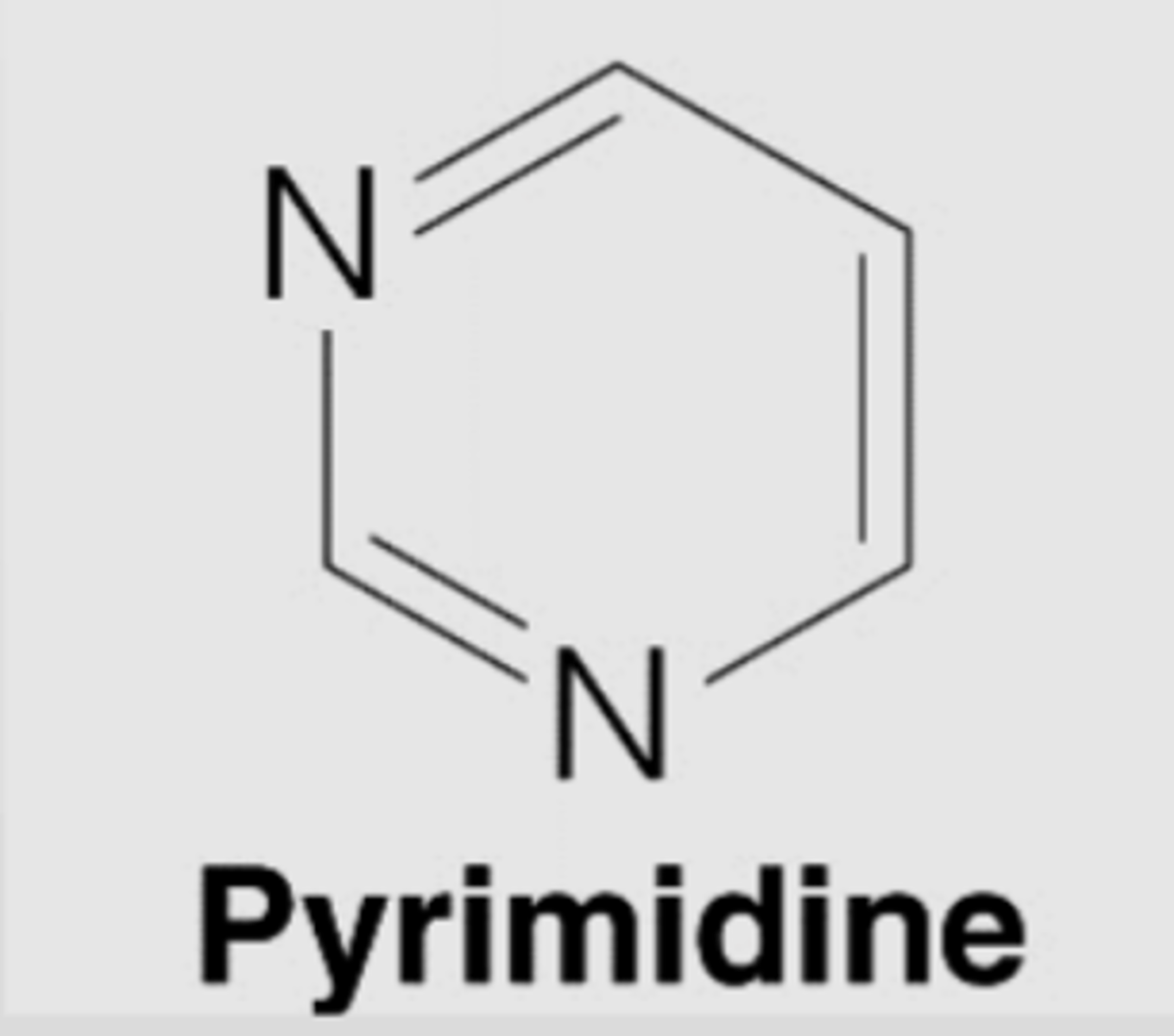
Pyrimidine
single ringed
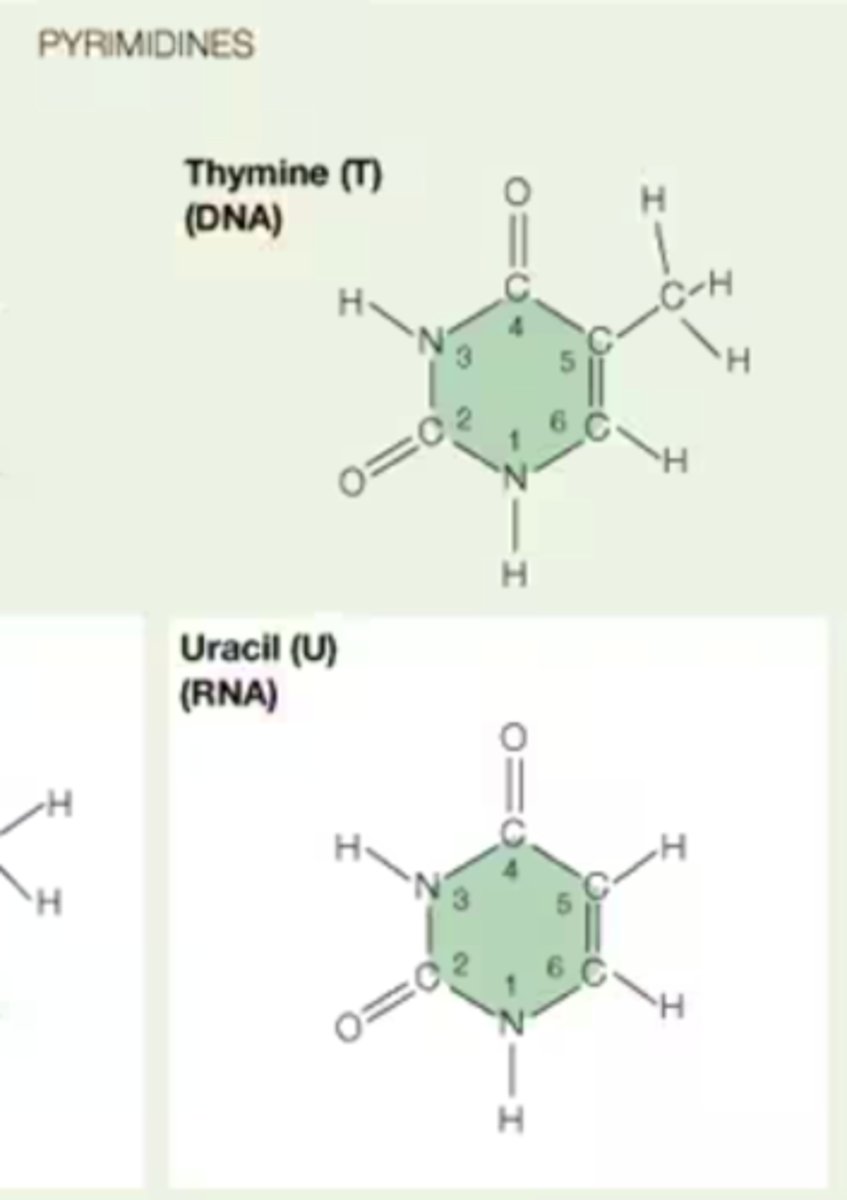
Difference in structure between thymine and uracil
Thymine is a 5-methyluracil (uracil with an added methyl group on C5')
How many nucleobases do DNA and RNA have?
DNA has 2 purine bases (A and G) and 2 pyrimidines (C and T)
RNA has 2 purine bases (A and G) and 2 pyrimidines (C and U)
What attaches the pentose sugar and base nitrogen (nucleobase) within a monomer?
Beta-N-Glycosidic bond between C1' of sugar and nitrogen in purine (N9') or pyrimidine (N1')
In pentose sugar, what configuration is the anomeric carbon in?
Beta, which is why the glycosidic bond is called beta-N-
Does beta-N-glycosidic bond allow for free or limited rotation?
Free rotation in FREE nucleotides
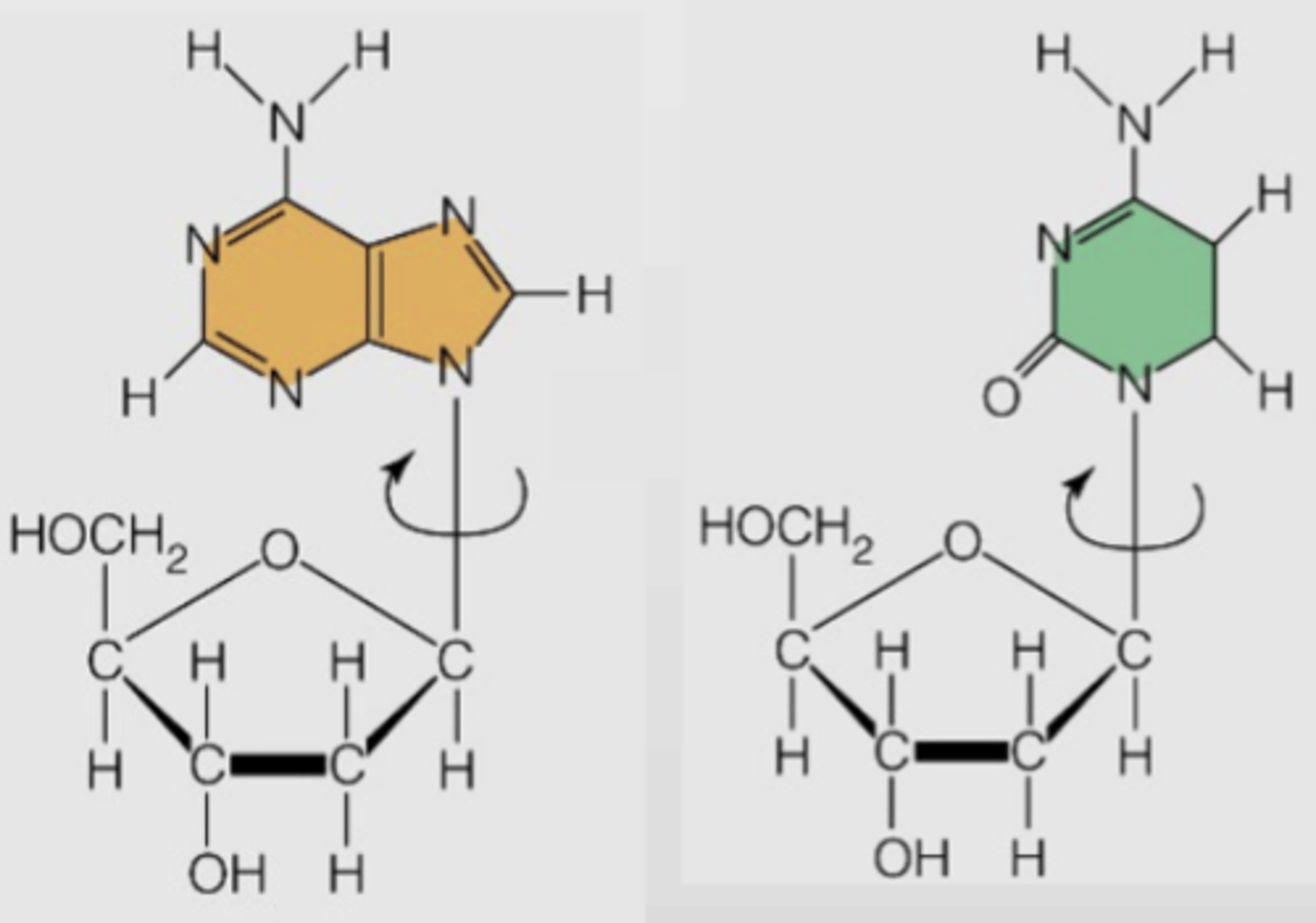
How does beta-N-glycosidic bond impact stability?
makes it stable, but can be hydrolyzed by acid
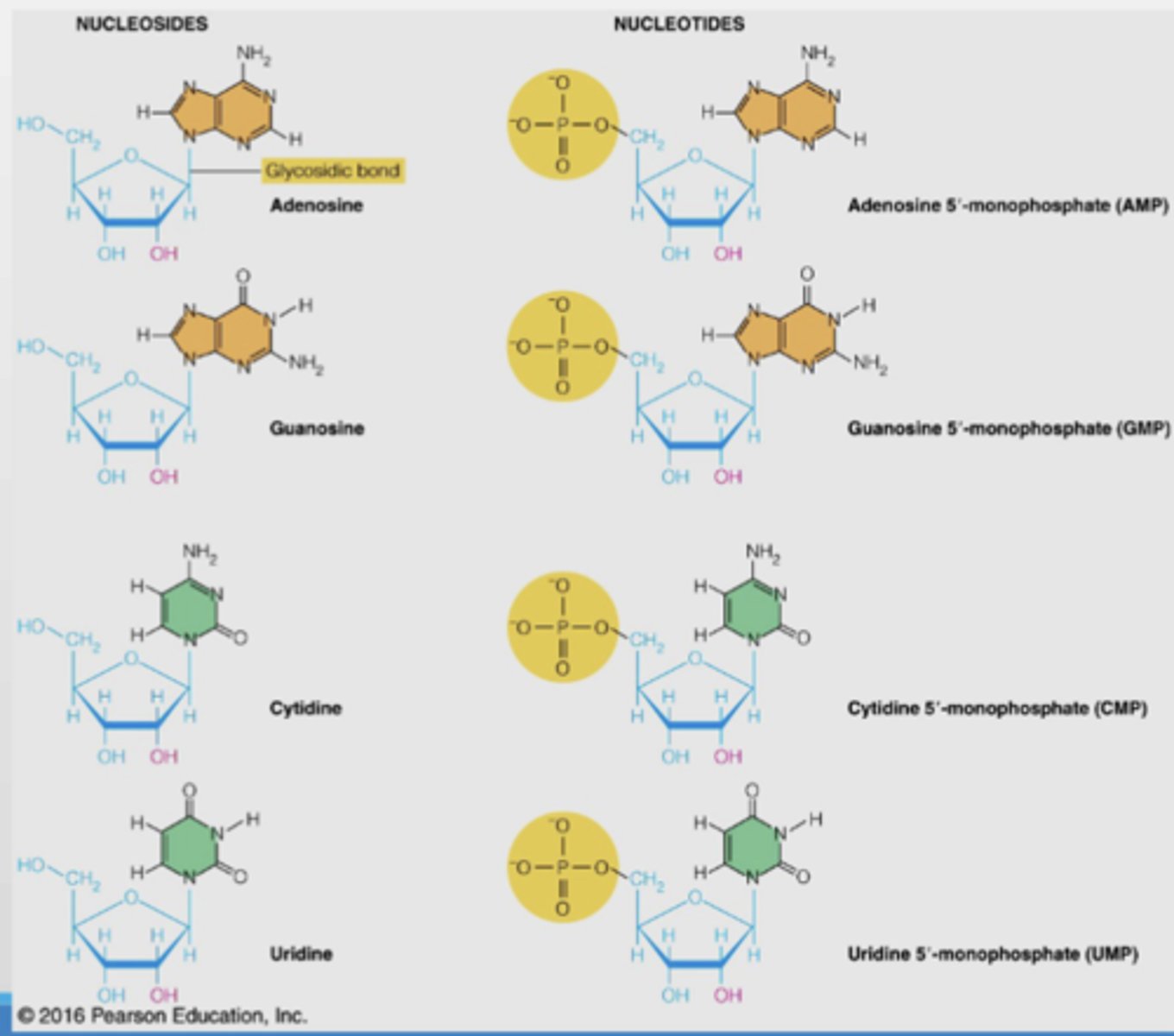
Nucleosides vs nucleotides structure
Nucleotides are the 5'-monophosphates of the nucleosides (add one phosphate group to C5')
Nucleotides are monomers of nucleic acids
Tautomers
Bases are capable of conversion between tautomeric forms
Tautomers: structural isomers differing only in the location of their hydrogen atoms and double bonds
In terms of tautomerization, what conversion guanine and thymine undergo?
Guanine and Thymine can undergo conversion between keto (H on N in ring) and enol (H on O outside of ring) (tautomeric) forms
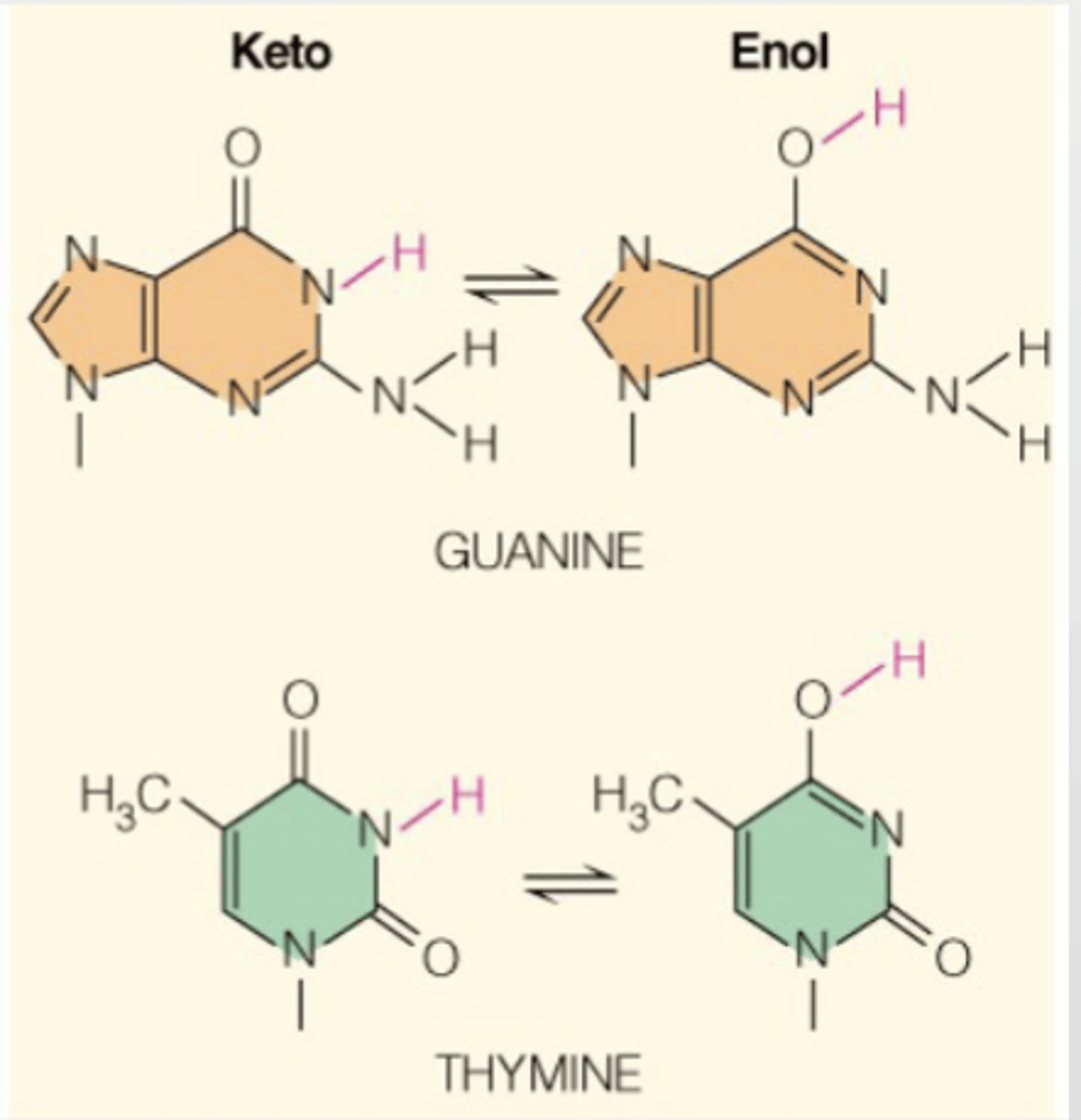
Which tautomeric forms are more common for A, C, T, G?
Amino for A and C
Keto for T and G