ap psych unit 5 pt. 2 - intelligence and creativity
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
intelligence
the ability to **acquire** **knowledge**, **learn** from **experience**, and use reasoning to **adapt** in different **environments**
2
New cards
aptitude test
predicts **future** performance in an ability; assesses specific types of mental abilities and the **ability** to learn; for ex: ACT, SAT
3
New cards
achievement test
measure a person’s **mastery** and **knowledge** (info. already learned); for ex: AP psych test
4
New cards
standardization
uniform procedures used in administration and scoring of a test; for ex: all students aren’t allowed calculators on portions of the PSAT to ensure every student has an equal chance of scoring well
5
New cards
norms
provide **meaning** to scores and information about where a score on a psychological test ranks in **relation** to other scores; for ex: norming ap psych exam scores to the scale 1-5 grading scale
6
New cards
percentile
indicates the percent of people in the testing population who score **at** or **below** your score
7
New cards
reliability
**consistency** of scores
8
New cards
test-retest reliability
measuring the stability/correlation of a test overtime; **same** test to **same** person at a **different** time; **same** test to **different groups**
9
New cards
alternate form reliability
using **parallel** measurements comparing their correlation; **different** test (same context and difficulty) to the **same** person
10
New cards
split-half reliability
measures the extent to which all parts of the test contribute equally (correlate) to what is being measured; looking within **1 test** given at **1 time**
11
New cards
inter-rater reliability
the degree to which (correlation) **different** raters give consistent measurements; high = agreement between raters; low = different opinions
12
New cards
validity
asks does the measurement tool assess what it’s designed for?
13
New cards
content validity
does the measurement tool full assess **all components** of the behavior/topic/theory being studied?
14
New cards
criterion-related validity
does a **specific component** of the measurement tool truly assess the behavior/topic/theory being studied? ; for ex: using rubrics, how coaches assess a skill during tryouts
15
New cards
construct validity
does the measurement tool accurately assess the **theory** being tested?
16
New cards
predictive validity
does the measurement tool accurately **predict future** outcomes?
17
New cards
galton
first to study mental ability; believed it was hereditary
18
New cards
binet
created the first test in France to study special education services for students; the test was designed to compare “mental age” with “chronological age”; “age graded test”
19
New cards
terman + stanford binet
terman brought the stanford-binet test to the U.S.; introduced IQ score
20
New cards
intelligence quotient (IQ) (terman)
IQ = mental age/chronological age x 100
21
New cards
WISC
weschler intelligence scale for children
22
New cards
WAIS
weschler adult intelligence scale
23
New cards
verbal performance scales
vocabulary, arithmetic reasoning, similarities, general information, and memory
24
New cards
performance scales
picture completion, digit substitution, and object assembly
25
New cards
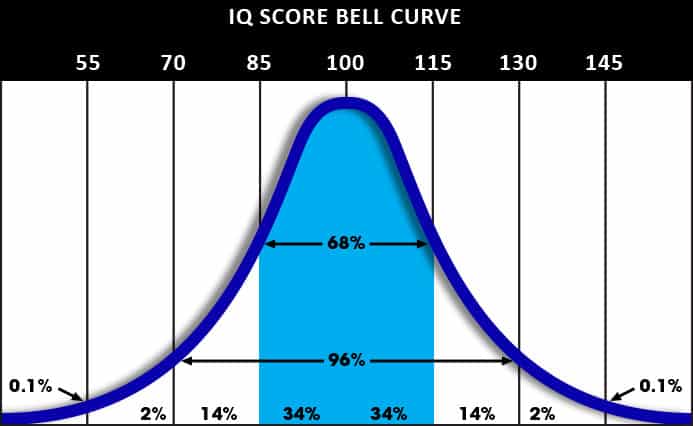
normal distribution and IQ score
the bell curve; mean, median, and mode are all the same; IQ mean is 100; standard deviation is 15
26
New cards
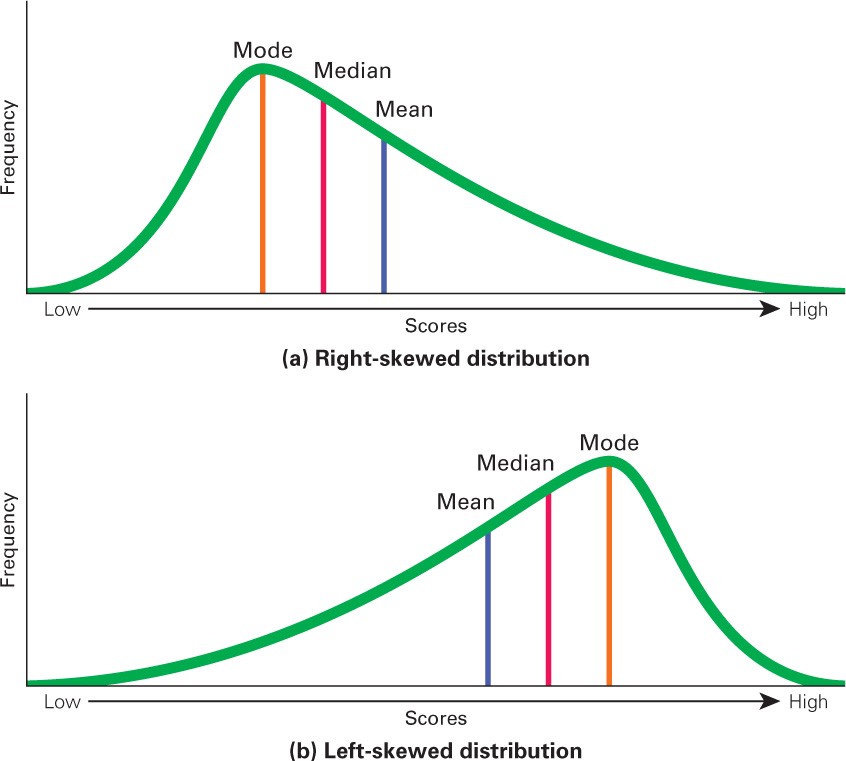
skewed distribution
frequency data is not spread evenly; data that is positively skewed has a long tail that extends to the right; data that is negatively skewed have a long tail that extends to the left.
27
New cards
factor analysis
statistical technique used to identify clusters of related information
28
New cards
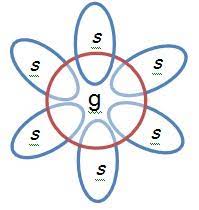
g-factor (spearman)
general intelligence, problem solving, and reasoning
29
New cards
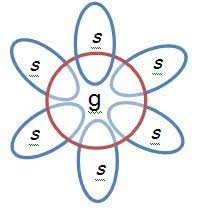
s-factor (spearman)
specific information and skills needed for particular tasks
30
New cards
fluid intelligence (cattell)
reasoning and problem solving, memory, and info-processing speed
31
New cards
crystallized intelligence (cattell)
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; we used fluid for crystallized intelligence
32
New cards
7 primary mental abilities (thurstone)
there are 7 relatively **independent** primary mental abilities: numerical ability, reasoning, verbal fluency, spatial visualization, perceptual ability, memory, and verbal comprehension
33
New cards
how reliable is intelligence testing over a lifetime?
reliable after 7 years old
34
New cards
is intelligence testing valid?
yes
35
New cards
how do crystallized and fluid intelligence change over a lifetime?
crystallized intelligence increases and fluid decreases (in mid/late adulthood)
36
New cards
are IQ tests widely used in other cultures?
IQ tests are mainly used in western cultures and in individualist cultures
37
New cards
intellectual disability
IQ < 70; deficiencies in adaptive skills; cognitively impaired
38
New cards
metacognition
awareness and understanding of one’s own thought processes; those with intellectual disabilities are deficient in metacognition
39
New cards
learning disabilities
measured intelligence ≠ academic performance; intelligence usually ***≥*** average intelligence
40
New cards
giftedness
IQ > 130
41
New cards
what do twin studies and adoption studies say about intelligence?
identical twins have the highest correlation; genetics play a large role
42
New cards
heritability ratio
proportion determined by heredity (nature)
43
New cards
how do environmental deprivation and enrichment affect intelligence?
nurture plays a role; especially at an early age
44
New cards
flynn effect
IQ scores have been **rising** steadily over time
45
New cards
reaction range
genetically determined **limits** on IQ (or other traits); for ex: heredity sets limits/ranges, while environment determines where in the range
46
New cards
stereotype threat
when worry about **conforming** to a **negative stereotype** leads to **underperformance** on a test/other task by a member of the stereotyped group
47
New cards
sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence: analytic intelligence
abstract reasoning, logic, and problem solving
48
New cards
sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence: practical intelligence
“street smart”; deal with **everyday problems**; the ability to adapt and strategize
49
New cards
sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence: creative intelligence
novel solutions and ideas
50
New cards
gardner’s multiple intelligences
linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, body-kinesthetic, nature, interpersonal, and intrapersonal
51
New cards
convergent thinking
when you attempt to narrow down a list of alternative to find a **single, correct answer** to a problem
52
New cards
divergent thinking
when you attempt to expand the **range of possible alternatives by generating many possible solutions**
53
New cards
creativity
generation of ideas that are original and useful
54
New cards
what are the necessary components of creativity?
expertise, persistence, risk willingness, divergent thinking, and intrinsic motivation