Expressive language and grammar impairment
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:56 PM on 1/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Characteristics of Expressive language and grammar impairment
Poor at learning new vocab - effecting auditory memory, phonological perceptions, word reteival
Cannot use syntactic inference
Comprehension defecits
Need more examples and repetitions for new words
Morphological (plurals) dev is late
Grammatical markers are later - auxiliaries, questions forms
Cannot use syntactic inference
Comprehension defecits
Need more examples and repetitions for new words
Morphological (plurals) dev is late
Grammatical markers are later - auxiliaries, questions forms
2
New cards
Intervention
Providing optimal envirnments
Directly develop skills in a specifc way
Directly develop skills in a specifc way
3
New cards
Mapping defecits
Arise from phonological memory deficit
Inability o effectively use imitation to store grammatical forms
Inability o effectively use imitation to store grammatical forms
4
New cards
Syntactic bootstrapping
Inferring meaning of a word from syntactic and Sentence information
5
New cards
Morphological dveelopment difficulties
Past tenses
3rd person singular
Auxiliary do
Copula be
Subject/verb agreement
Tense related syntactic knowledge morphemes
3rd person singular
Auxiliary do
Copula be
Subject/verb agreement
Tense related syntactic knowledge morphemes
6
New cards
Appropriate assessments
Pre school language scales - comprehension and expression
Early grammatical impairment- morphological markers production
CELF
Non standardised- RAPT, STASS
Early grammatical impairment- morphological markers production
CELF
Non standardised- RAPT, STASS
7
New cards
Appropriate therapy approaches
Grammatical techniques
- elicited imitation
- modelling
- recasting
- focused stimulation
Metalinguistic techniques
- colourful semantics
- shape coding
- narrative therapy
- elicited imitation
- modelling
- recasting
- focused stimulation
Metalinguistic techniques
- colourful semantics
- shape coding
- narrative therapy
8
New cards
Grammatical facilitation strategies
Aim to increase frequency of target Norms
- and awareness of the function of target norms
Achieved through repetition
- and awareness of the function of target norms
Achieved through repetition
9
New cards
Elicited imitation approach
Presenting non-verbal stimulus alongside a verbal request to respond
A stimulus form to be imitated (the target form)
Reinforcement contingent on correct target form being produced
Adult chooses target form, acceptable response and stimulus materials (verbal and non-verbal)
• Intensive production practice provided
- can involve shaping
- is based on operant learning theory
A stimulus form to be imitated (the target form)
Reinforcement contingent on correct target form being produced
Adult chooses target form, acceptable response and stimulus materials (verbal and non-verbal)
• Intensive production practice provided
- can involve shaping
- is based on operant learning theory
10
New cards
Imitative modelling
Adult produces target in responses to stimulus and child listens
Childs asked to respond to stimuli- same or different
Aims to enhance their recognition of grammatical similarities/ differences
- by confining request to produce utterance to initial position child has uninterrupted productions - reduced cognitive demands
Childs asked to respond to stimuli- same or different
Aims to enhance their recognition of grammatical similarities/ differences
- by confining request to produce utterance to initial position child has uninterrupted productions - reduced cognitive demands
11
New cards
Sentence recasting process
modifying a child's sentence while maintaining the meaning
- Immediate adult response that mirrors child's utterance (major lexical items, meaning) BUT modifies 1+ sentence constituent or changes sentence modality e.g. statement to question
- gives child opportunity to compare their production with adult model
- focuses on child's attention on specific grammatical features
- has low interactional demands
- Immediate adult response that mirrors child's utterance (major lexical items, meaning) BUT modifies 1+ sentence constituent or changes sentence modality e.g. statement to question
- gives child opportunity to compare their production with adult model
- focuses on child's attention on specific grammatical features
- has low interactional demands
12
New cards
Focused stimulation weismer and Robertson 2006 study
Simplified condition\= clinicians produced target words in 1-2 phrases
Expanded condition\= clinician produced target words in naturalistic speech
Results- more vocab was acquired in simplified it still acquired in both
- more expressive lang in expanded
Expanded condition\= clinician produced target words in naturalistic speech
Results- more vocab was acquired in simplified it still acquired in both
- more expressive lang in expanded
13
New cards
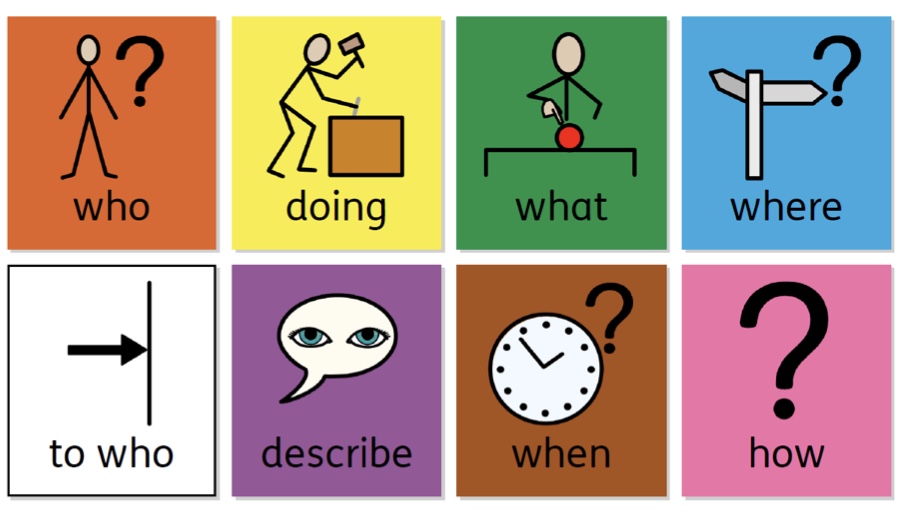
Colourful semantics- functional level
Semantic relationship between form and meaning
Major nouns and verbs are chosen and semantic relationship between them is assigned
What doing
What
Who
Where
What like
Major nouns and verbs are chosen and semantic relationship between them is assigned
What doing
What
Who
Where
What like
14
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 1
Putting together agent and verb
Reception age +
Reception age +
15
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 2
Introduce theme - the what
SVO pictures with agent verb and heme
SVO pictures with agent verb and heme
16
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 3
Interlude location- the where
Introduce copula in verb role
Introduce copula in verb role
17
New cards
Copula
A linking verb between subject and complement
18
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 4
Develop a sentence with a verb and all 3 thematic roles
19
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 5
Introduce an inanimate object in the role of agent
- doesn't answer who
- doesn't answer who
20
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 6
Introduce complement role
- answering Q what's it like
- answering Q what's it like
21
New cards
Colourful semantics stage 7
Introducing a coordination role
22
New cards
Shape coding
Used after colourful semantics
Supports literacy comprehension and expression and teach auxiliary and modals
Aimed for teenagers age range
Includes verb morphology- tensest shown by arrows
Supports literacy comprehension and expression and teach auxiliary and modals
Aimed for teenagers age range
Includes verb morphology- tensest shown by arrows
23
New cards
Shape coding builds on Colourful semantics through including colours
Red- Noun/pronoun
Pink- Det/possessive pronouns
Yellow- Verb
Green- Adjective
Blue- Preposition
Purple- Coordinating conjunction
Orange- Subordinating conjunction
Pink- Det/possessive pronouns
Yellow- Verb
Green- Adjective
Blue- Preposition
Purple- Coordinating conjunction
Orange- Subordinating conjunction
24
New cards
Shapes are used for coding phrases-
Noun phrase - subject \= oval - who, what
Object \= rectangle- who what
Verb phrase - hexagon- what doing
Prepositional phrase - semicircle Adjective phrase - cloud- what like, how feel
Object \= rectangle- who what
Verb phrase - hexagon- what doing
Prepositional phrase - semicircle Adjective phrase - cloud- what like, how feel
25
New cards
Narrative therapy- Becky shanks 2011
For expressive and receptive lang difficulties
Taught to use. Story framework through colour coding, symbol and sign
Is easily adaptable for differing levels of ability
Story components are broken to: who where when what happened
Taught to use. Story framework through colour coding, symbol and sign
Is easily adaptable for differing levels of ability
Story components are broken to: who where when what happened