health - pharmacology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
wegovy effects
weight-loss drug — increase feelings of satiety, reduces energy intake, affects hypothalamus & brainstem + reduction of blood glucose (treats diabetes)
wegovy chemistry
semaglutide similar to glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue & GLP-1 receptor agonist
pharmacokinetics
what does the human body do with the drug
pharmacodynamics
what does the drug do with the human body
proper definition of pharmacokinetics
study of the interactions that determine the speed of onset, intensity and duration of drug action
steps in pharmacokinetics
absorption, distribution, metabolism, & elimination
absorption step
into the body and into the cells — molecule in blood stream & almost always have to cross membranes to work
how are drugs absorbed?
passive diffusion (depends on lipid solubility, area of absorption, magnitude of concentration gradient), carrier-mediated transport, endo/exocytosis, diffusion through aqueous & intracellular pores
distribution step
drug is transferred from the bloodstream (plasma) to tissues (interstitial fluid & cells)
metabolism step
when the drug is broken down and inactivated, or sometimes transformed into an active form
elimination step
excretion from the body (urine, faeces, exhalation)
factors that impact rate & degree of distribution
blood flow, capillary permeability, protein binding, & accumulation in + redistribution to other sites
protein binding in drug distribution
no pharmacological effect (e.g. albumin which buffers the effect of drugs)
apparent volume of distribution
measure for the amount of substance located outside circulation = total amount of drug in body / drug blood plasma concentration
pH partitioning
when the neutral form of the drug is absorbed then drug entrapment b/c acid ionized in basic environment, and vice versa
thiopentol effect
anaesthetic effect is terminated by redistribution of drug into adipose tissue & not through metabolism
biomagnification
increase in concentration of a substance as you go higher in the food chain
propofol characteristics
works quick, highly protein bound -- pretty well buffered in body, clinical effect very short b/c of distribution in fatty tissues
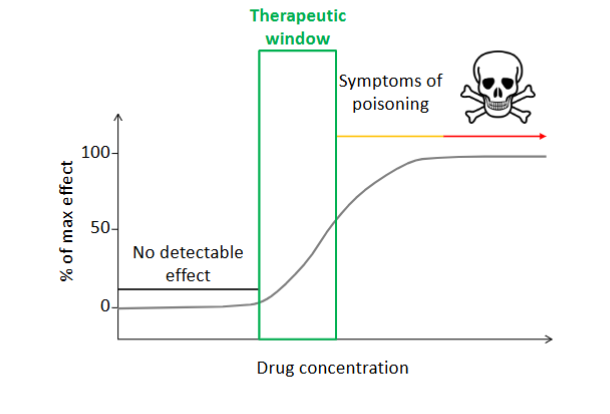
therapeutic window
range of drug dosage in which there is a positive effect AND there are no indications of poisoning
liver
major site for metabolism of drugs
outcomes of drug metabolism
production of metabolites that are less potent, more potent + persist longer, conversion from inactive pro-drug to active, toxic metabolites, or inactive metabolites that are water soluble
phase I of drug metabolism
oxidation (most important), reduction, hydrolysis (often performed by Cyt. P450)
phase II of drug metabolism
conjugation, glutathion/glucuronate, acetylation — makes drugs water soluble which make them easier to excrete
morphine
respiratory depressant
morphine side effects
hypoventilation, congestion, addiction
morphine biological half life
around 2 to 3 hours (quite long so easy to overdose)
synthetic opioid (remifentanil) side effect
hypoventilation
synthetic opioid biological half life
around 4 minutes
synthetic opioid breakdown
easily targeted by enzymes in our bodies & broken down in liver
isoenzyme of Cyt. P450
CYP3A4
CYP3A4 function
responsible for 50% of drug oxidation
blood-brain barrier
tight apposition of endothelial cells that hinders the crossing of charged molecules from the blood to cells of the brain (and the other way around)
ramipril
prodrug - converted in the liver by de-esterification into its active form ramiprilat
ramiprilat
ACE inhibitors — decreases blood pressure
ACE enzyme
in pathway that causes vasoconstriction which leads to increased blood pressure
ion trapping = weak base will accumulate in compartments with relatively ___ pH
low
ion trapping = weak acid will accumulate in compartments with relatively ___ pH
high