3.3 Revenues, Costs and Profits
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What type of demand exists in perfect competition?
Perfectly elastic demand
What does perfectly elastic demand look like?
A horizontal line
Where does the AR line go in relation to MR in most graphs?
AR is to the right of MR
When is a cost curve short run?
When at least one factor of production is fixed and cannot be change
When is a cost curve long term?
When all factors of production become variable
Draw a Long Run Average Cost Curve
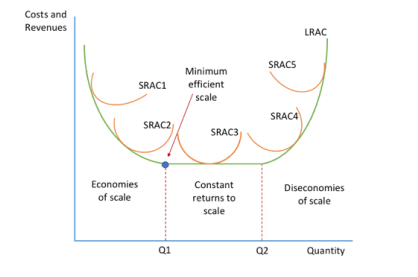
Why does LRAC decrease at the start?
increasing economies of scale as the firm grows
Why does LRAC increase at the end of an LRAC curve
Diseconomies of scale as firm gets too large
What types of internal economies of scale are there? 5
Technical economies (specialisation, balanced teams of machines, increased dimensions, indivisibility of capital, R&D)
Financial economies (more assets, so less likely to be forced out of business quickly)
Risk bearing economies (eggs in different baskets)
Managerial economies (specialist managers can be appointed, leading to higher efficiency)
Marketing and purchasing economies (Buying in bulk, specialised buyers are more efficient, distribution is cheaper)
What types external economies of scale are there? 4
Labour (specialised labour comes to that area e.g. silicon valley)
Local education and training providers are more likely to develop courses to prepare people to take up jobs in these businesses)
Firms can hire staff who have been trained in other firms
Support services (suppliers for large businesses naturally move to their area, reducing transport costs)
What are 5 diseconomies of scale?
Workers (people may work less hard in large businesses as they think it goes unnoticed)
Geography (firms may have to transport finished products huge distances, also leads to lack of control)
Change (can take longer for large firms to respond to changes)
Material prices (large business demand can result in price increases, however they gain monopsony power)
Management (coordination and control becomes harder, along with communication getting slower and less accurate)
What does normal profit mean?
Return that is sufficient to keep the factors of production committed to the business