Chapter 7 - Enzyme Kinematics
enzyme kinematics
the study of rates of reactions catalyzed
disappearance of substrate and appearance of product
the reaction rate (velocity) can be described what two ways?
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
enzyme kinematics
the study of rates of reactions catalyzed
disappearance of substrate and appearance of product
the reaction rate (velocity) can be described what two ways?
non-linear
many enzymes react with substrates in a (linear/non-linear) fashion?
hyperbolic
what is the shape of a Michael-Menten curve?
[ES] is difficult to measure
What is the problem with Michaelis - Menten Kinetics?
Michaelis - Menten
This plot describes enzyme - catalyzed reactions in terms of Km and Vmax
[ES] is constant
What is the first assumption with Michaelis - Menten Kinetics?
[S] is very high, so does not change
What is the second assumption of the Michaelis - Menten Kinetics?
Reaction does not proceed in the reverse direction
What is the third assumption regarding the Michaelis - Menten Kinetics?
measure of enzymes affinity for a substrate
What does Km stand for?
high
Low Km = _____ affinity
low
High Km = _____ affinity
catalytic rate constant
What does Kcat stand for?
catalytic efficiency
What does the formula Kcat/Km indicate?
Lineweaver Burke plot
what plot linearizes Michaelis - Menten kinetics data?
experimentally
Km and Vmax are determined _____________
Km/Vmax
the slope of lineweaver - burke plot represents what equation?
Reversible
Enzyme Inhibition:
Noncovalent bonding of small biomolecules or proteins to the enzyme subunit; Four classes - Competitive, Uncompetitive, Noncompetitive, and Mixed
Irreversible
Enzyme Inhibition:
Inhibitory molecule forms a covalent bond or very strong non-covalent bond with catalytic groups in the enzyme active site
“Kills” the enzyme by tight binding to the enzyme
Effectively reduces the entire enzyme concentration
Competitive
Type of Reversible Inhibitor where inhibitor binds only to enzyme in the active site, blocking the substrate from binding
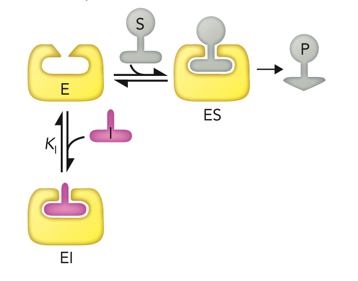
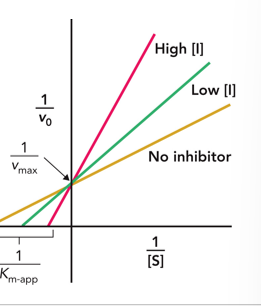
increases; no effect
In competitive inhibition, Km _________ and Vmax _____________
Competitive
This Lineweaver burke plot shows what type of Inhibition?
Uncompetitive
Type of Reversible Inhibitor where the inhibitor binds only to the enzyme substrate complex (ES) after it is formed
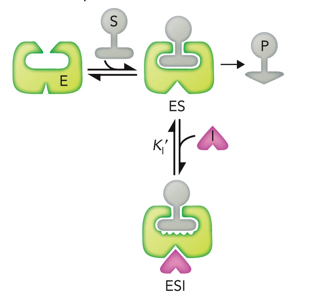
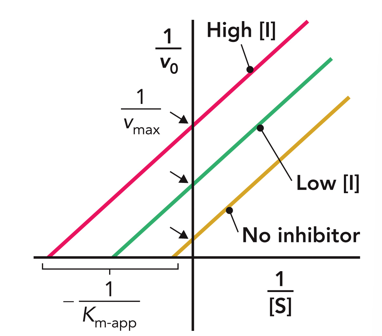
decreases; decreases
In uncompetitive inhibition, Km ________ and Vmax ____________
Uncompetitive
What inhibition does this Lineweaver Burke plot show?
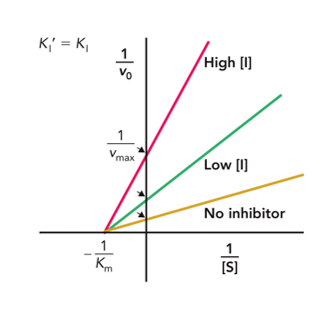
Noncompetitive
Type of Reversible Inhibitor where the inhibitor binds equally to E and ES complex; binds to allosteric site
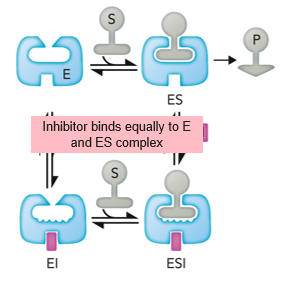
no effect; decreases
In noncompetitive Inhibition, Km ________ and Vmax ________
Noncompetitive
What type of inhibition does this Lineweaver - Burke plot show?
Mixed Inhibition
Type of Reversible Inhibition where binding is mixed unequally between both enzyme and enzyme substrate
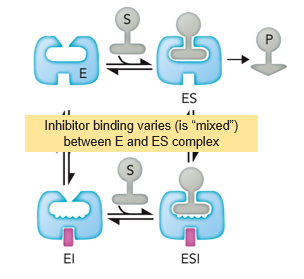
lowered
In mixed inhibition, the Km is ___________ if the inhibitor prefers the ES complex
increases
In miced inhibition, Km ____________ if the inhibitor prefers the enzyme
protease inhibitors and zymogens
If serine proteases exist in our body, why don’t we digest ourselves?
allosteric regulation
How are enzymes controlled?