Proteins
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key area 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the 6 types of protein function?
Structural Proteins
Haemoglobin
Hormones
Antibodies
Receptors
Enzymes
What are enzymes made up of?
All living Cell
Enzymes are describes as?
Being biological catalysts
What are some of the properties of enzymes?
.It speeds up chemical reactions within a cell
. Remains unchanged after the reaction
.Lower the energy required for a reaction
What is the definition of an enzymes?
Enzymes speeds up chemical reactions and remains unchanged at the end of the reactions
One enzyme only joins to what?
One type of substrate
Why does enzymes only join to one type of substrate
The enzymes and substrate are complementary to one another
What is Degradation?
Where ONE larger substrate is Brocken down into MANY smaller products
What is Synthesis?
Where MANY smaller substrates are synthesised/made up into ONE larger product
Examples of Degradtion?
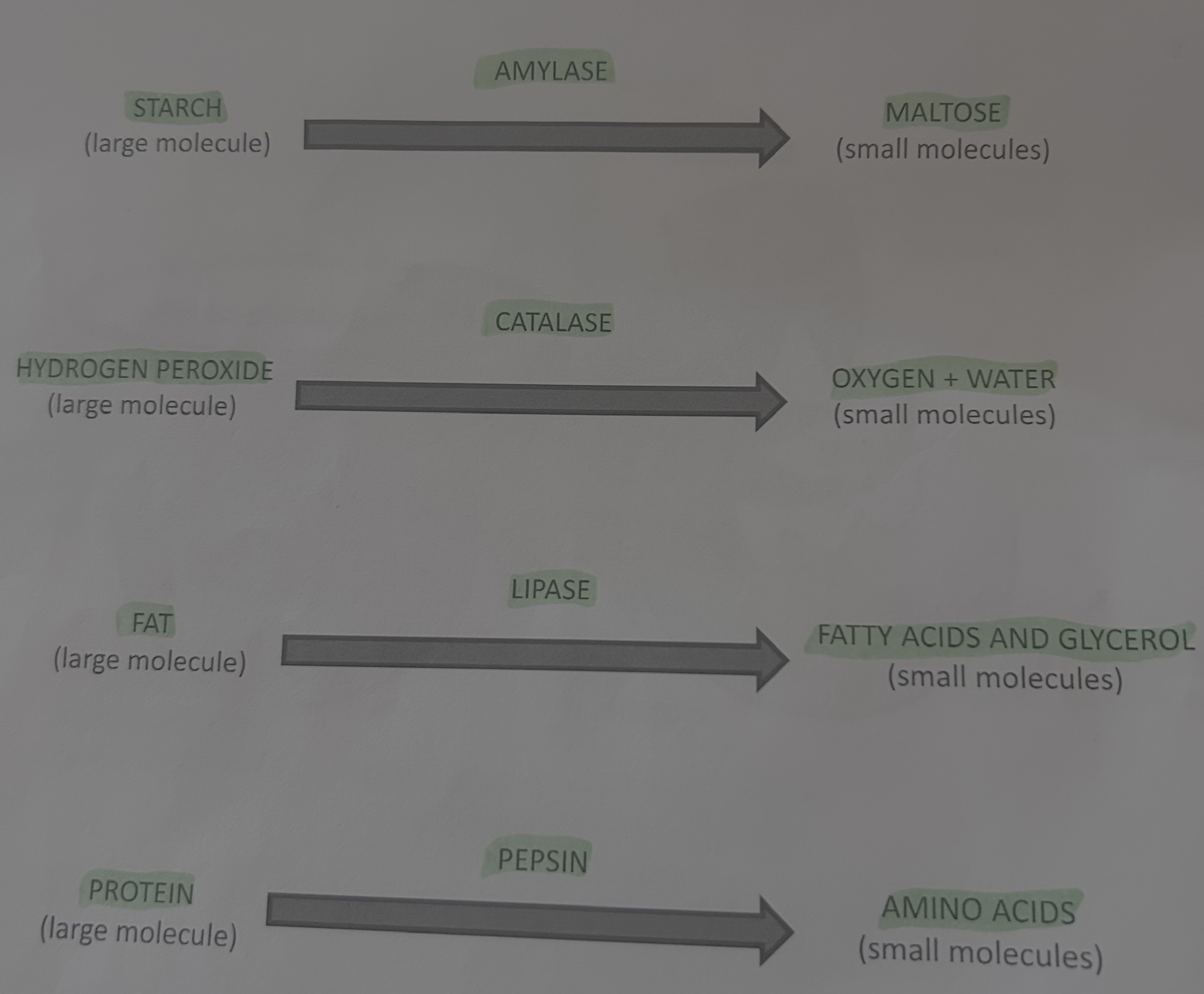
Examples is synthesis?

What is optimum condition?
There are conditions at which enzymes activity is at its most active
What are the 2 factors which affects enzymes?
Temperature and pH
If enzymes is high the rate of reaction will also be?
High
What is denatured mean?
It means that the ACTIVE site has CHANGED SHAPE due to HIGH temperatures or extremes of pH
What happens when the optimum is below enzymes activity?
Begins to decrease
What happens when the optimum is above enzymes activity?
Begins to decrease
What happens when enzymes are at a very high temperature?
The enzymes becomes denatured and can no longer bind to its substrate
Cellulase is an enzyme that speeds up the breakdown of a component of the plant cell wall
Name the component?
Cellulose
Name the substrate of which enzymes are made
Protein