Chemical Kinetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
rate of reaction equation
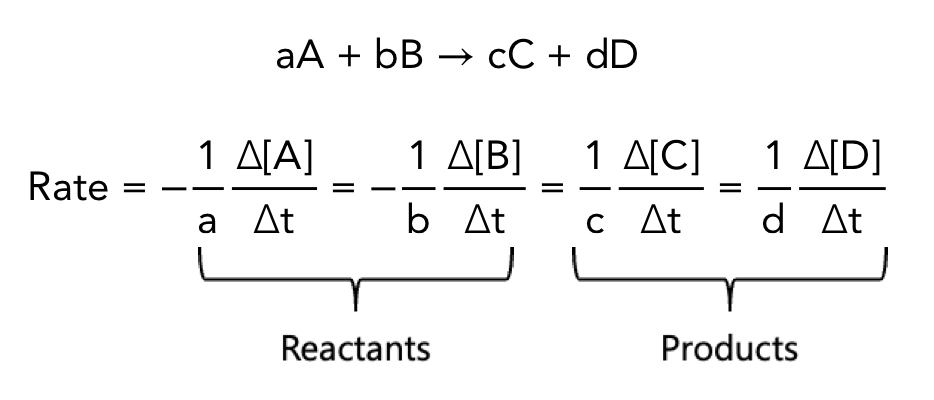
what is a rate law?
relates the rate of a reaction to the rate constant and the concentration of its reactants

what is a zero order reaction?
does not depend of the concentration of reactants
Rate= k[A]0
units of rate constant: M/s
![<ul><li><p>does not depend of the concentration of reactants </p></li><li><p>Rate= k[A]<sup>0</sup> </p></li><li><p>units of rate constant: M/s</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bcb65538-efd8-4580-b2c0-ff245dfcc10e.png)
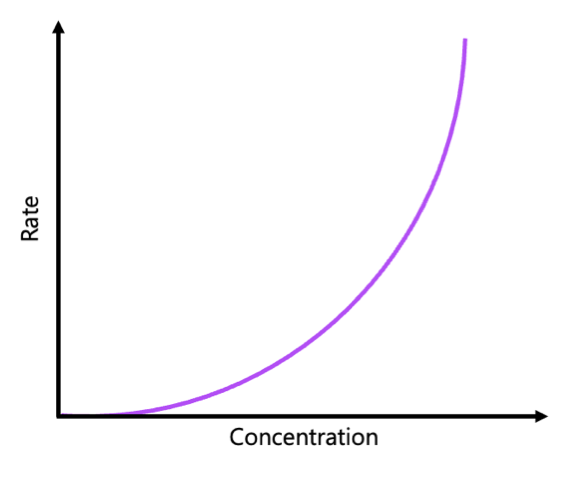
what is a first order reaction?
directly proportional to the concentration of reactants
rate= k[A]1
unit of rate constant: 1/s
![<ul><li><p>directly proportional to the concentration of reactants </p></li><li><p>rate= k[A]<sup>1</sup></p></li><li><p>unit of rate constant: 1/s</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e9eb24c9-056a-444d-972d-b27227c60675.png)
what is a second order reaction?
rate of reaction increases exponentially with the concentrations of reactants
rate= k[A]2 or k[A][B], k[A]2, k[B]2
unit of rate constant: 1/Ms
![<ul><li><p>rate of reaction increases exponentially with the concentrations of reactants</p></li><li><p>rate= k[A]<sup>2</sup> or k[A][B], k[A]<sup>2</sup>, k[B]<sup>2</sup> </p></li><li><p>unit of rate constant: 1/Ms</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8ddf951e-1e89-4219-a185-d6368a558adc.png)
unit of rate constant rule
M1-ns-1 where n=reaction order
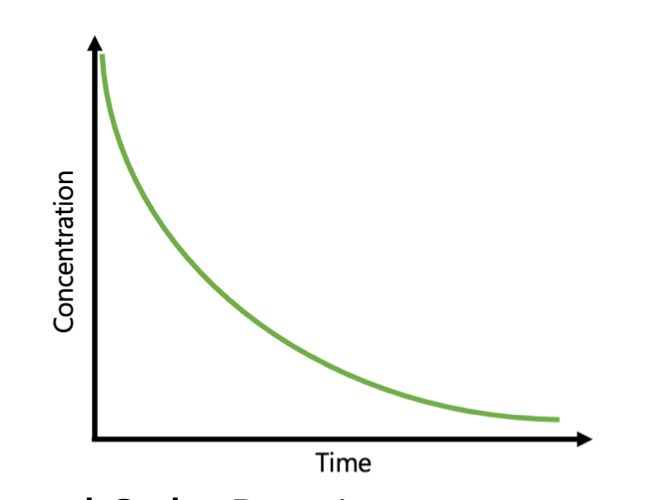
0th order concentration graph
concentrations of reactants decrease LINEARLY
1st order concentration graph
concentration of react decreases HYPERBOLICALLY
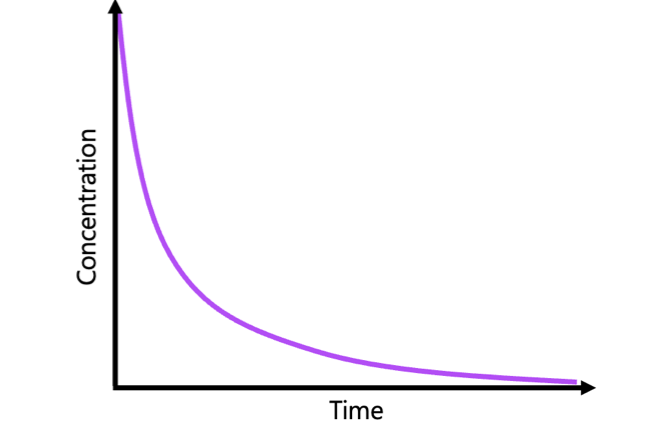
2nd order concentration graph
concentration decreases SHARPER HYPERBOLICALLY over time
determining the reaction order from dataset steps
For reactant A:
find the two trials where the concentrations of B are the same
divide the two concentrations of A for those trials
divide the two initial rates for those trials
write the divided concentrations to the power of x equals the divided initial rates
solve for x
what are integrated rate laws?
used to determine the amount of reactants or products present after a period of time
0th order integration law
[A]t=-kt+[A]0
unit of k= M/s
![<p>[A]<sub>t</sub>=-kt+[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>unit of k= M/s</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/eb15882a-2900-4cf1-96e6-c69a2ff23719.png)
1st order integration law
ln[A]t=-kt+ln[A]0
unit of k= 1/s
![<p>ln[A]<sub>t</sub>=-kt+ln[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>unit of k= 1/s</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/243dcc95-05f3-4c04-ae71-3097c1bfc36f.png)
2nd order integration law
1/[A]t=kt+1/[A]0
unit of k= 1/Ms
![<p>1/[A]<sub>t</sub>=kt+1/[A]<sub>0</sub></p><p>unit of k= 1/Ms</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dde5652a-cde3-4f7d-b04a-36d0523b763e.png)
what is the rate determining step
the slowest step of the reaction mechanism and determines the overall rate law of reaction
reactant coefficients of the RDS become the exponents of the OVERALL rate law
how to identify intermediates in a reaction mechanism?
intermediates will NOT be present as either reactants or products
how to identify catalysts in a reaction mechanism?
catalysts will be present as BOTH reactants or products
what are the 3 requirements in the collision theory that allow for a chemical reaction to occur?
molecules must collide
molecules must be in the correct orientation during collision
molecules must have enough energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
arrhenius equation
describes the relationship between temperature and reaction rates
A= frequency factor or the fraction of collisions that have enough energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
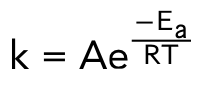
how does temperature affect activation energy?
no effect
half life time equations for varying order or reactions
0 order: t=[A]0/2k
1 order: t=0.693/k
2 order: 1/k[A]0
which order of reaction is radioactive decay?
1