Acquisition Quiz 2
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
The principal controlling factor of radiographic image receptor exposure is
A. mAs
B. focal spot size
C. kVp
D. tube angulation
A. mAs
Scatter radiation is mostly a result of the photoelectric interaction. True or false?
False, Compton
Size distortion in radiography can be ____ only.
A. Elongation
B. Foreshortening
C. Magnification
D. Minimization
C. Magnification
Size distortion is controlled by:
A. SID and OID
B. kVp
C. mAs
D. Patient motion
A. SID and OID
If an incident photon has an energy of 90 keV and undergoes a Compton interaction giving 20 keV to the ejected electron which had a binding energy of 2 keV, determine the energy of the scattered photon.
90-20--2=68KeV
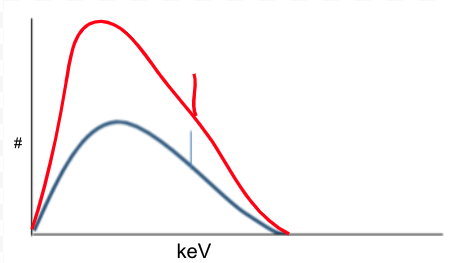
Consider the situation:
Change from 20mAs to 40mAs
How would the emission spectrum graph change?
Graph doubles in height
Poor SR is caused by an unacceptable amount of:
A. IR exposure
B. penumbra
C. umbra
D. contrast
b. penumbra
What factor influences the average E of the photons reaching the IR?
A. focal spot size
B. kVp
C. mA
D. mAs
B. kVp
Using the 15% rule changes:
A. Both IR exposure and the avg. E of the beam
B. Distortion
C. IR exposure
D. Avg. E of beam
A. Both IR exposure and the avg. E of the beam
Distortion can be a misrepresentation of:
A. Shape
B. Detail
C. Size
D. Size and shape
D. size and shape
As focal spot size increases, spatial resolution will _______.
A. Increase
B. Be unchanged
C. Decrease
C. Decrease
If 80kVp, 400mA, & 0.025sec produce a satisfactory radiograph, what mAs was used?
10mAs
Which of the following is NOT an interaction between x-ray photons and matter?
A. Coherent
B. Compton
C. Photoelectric
D. Brems
D. Brems
The unsharpness of an image is affected by all of the following except:
A. OID
B. Focal spot size
C. mAs
D. SOD
C. mAs
As mAs increases, IR exposure will _______.
A. Decrease
B. Increase
C. Be unchanged
B. Increase
IF the mA is set at 300 and the total mAs produced is 15mAs, the exposure time must be:
A. 0.5 sec
B. 0.2 sec
C. 0.05 sec
D. 20 sec
C. 0.05sec
15=300 x X
15/300= 0.05 seconds
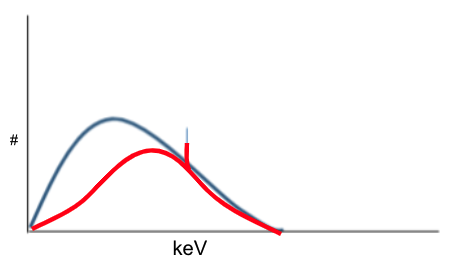
Consider the situation:
Change from 3mm Al filtration to 5mm Al filtration
How would the emission spectrum shift?
Spatial resolution is improved when:
A. SID decreases
B. OID decreases
C. SOD decreases
D. OID increases
B. OID decreases
The end product(s) of the photoelectric effect is/are:
A. One scattered photon only
B. One orbital vacancy only
C. One ejected electron and an orbital vacancy
D. One scattered photon, one ejected electron, and an orbital vacancy
C. One ejected electron and an orbital vacancy
If a 70kVp, 100mA, and 0.25sec produce a satisfactory radiograph, what mAs was used?
25mAs
100×0.25=25
With an SID of 40in, and an OID of 10in, what is the magnification factor?
A. 3X
B. 1.33X
C. 0.25X
D. 4X
B. 1.33X
SID/SOD
40-10=30
40/30=1.33
A change in kVp, as an exposure factor, affects
A. Beam intensity/quantity
B. The relative amount of scatter received on the IR
C. All answers are correct
D. Average beam energy
C. All answers are correct
Foreshortening is present if:
A. IR exposure is excessive
B. The image of the object is shorter than the object
C. The tube and IR are in alignment
D. The image of the object is longer than the object
B. the image of the object is shorter than the object
If a projected image measures 3in and the magnification factor is 1.1, what is the size of the actual object?
2.7in
If 10mAs at 120kVp is used for a radiograph and the kVp needs to be decreased 15%, determine the new technique to be used obtaining the same IR exposure.
102kVp @20mAs
120x.15= 18
120-18=102
Maintain the exposure by doubling mAs
As mAs increases, shape distortion will ________.
A. Be unchanged
B. Decrease
C. Increase
A. Be unchanged
The greatest amount of scatter is produced from the ______ interaction.
A. Compton
B. Characteristic
C. Brems
D. Coherent
A. Compton
Insufficent mAs is likely to contribute to ___ in the image.
A. quantum mottle
B. excessive OID
C. high SR
D. motion
A. quantum mottle
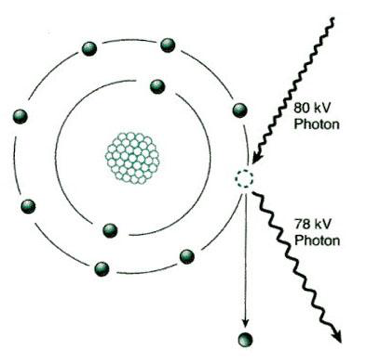
Name the interaction.
A. Characteristic
B. Brems
C. Compton
D. Unmodified scatter
C. Compton
Calculate the magnification factor when the SID is 40in and the OID is 5in
1.14X
40-5=3
40/35=1.14
As tube angle increases, shape distortion will:
A. Be unchanged
B. Decrease
C. Increase
C. Increase
An 80kV photon undergoes a coherent scattering interaction with an orbital electron having a BE of 8kV. What is the energy of the resulting scattered photon?
A. 8kV
B. 80kV
C. 88kV
D. 72kV
b. 80kV
Coherent doesn’t lose/gain E
If the signal is 16 and the noise is 4 on a hypothetical radiograph, what is the signal to noise ratio?
A. 0.25
B. 8
C. 4
D. 12
C. 4
As SID increases, spatial resolution will:
A. Increase
B. Be unchanged
C. Decrease
A. Increase
Calculate the magnification factor when the SID is 72in and the SOD is 25in
2.88x
72/25=2.88
Factor affecting spatial resolution include:
A. Scale of contrast
B. Focal spot size
C. kVp
D. mAs
B. Focal spot size
The brightness of the image on a viewing monitor is:
A. The result of density only
B. The result of IR exposure only
C. The result of the monitors brightness setting
D. The result of tissue thickness only
C. The result of the monitors brightness
The effect of mAs upon IR exposure is:
A. Dependent upon kVp
B. Inversely proportional
C. Inverse
D. Directly proportional
D. Directly proportional
Radiation that turns 180 degrees in direction after interacting with matter is called:
A. backscatter
B. coherent
C. brems
D. characteristic
A. backscatter
An increase in x-ray beam filtration:
A. increases magnification
B. decreases patient tissue density
C. increases the average photo E of the beam
D. increases the quantity of photons in the beam
C. increases avg. photon E of the beam
As filtration increases, IR exposure will:
A. be unchanged
B. decrease
C. increase
B. decrease
As OID increases, size distortion will:
A. be unchanged
B. increase
C. decrease
B. increase
What can negatively impact spatial resolution?
A. Using a small focal spot
B. A minimal OID
C. Small detectors/high resolving ability of digital IR
D. Patient motion
D. Patient motion
As kVp decreases, spatial resolution will:
A. Be unchanged
B. Decrease
C. Increase
A. Be unchanged
A radiograph of the elbow is produced using 4mAs at 70kVp. What kVp would be required to double the exposure
81kVp, 80.5kVp, 81kVp
70×0.15=10.5
70+10.5=80.5
An exposure with a technique of 100kVp and 10mAs was taken at a SID of 72in. If the SID were changed to 96in, adjust your technique to maintain the same exposure.
100kVp 18mAs
The partial absorption of the x-ray beam as it passes through the body is best referred as:
A. absorption
B. attenuation
C. brems
D. heterogeneity
B. attenuation
Electronic “snow” on a display monitor or TV monitor image is a form of:
A. Distortion
B. Scatter
C. Noise
D. IR exposure
C. Noise
Penumbra decreases as:
A. Focal spot decrease
B. SID increases
C. OID decreases
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
A radiograph with few shades of gray exhibits
A. High contrast
B. Low contrast
C. Long scale contrast
D. Medium contrast
A. High contrast
The ____ the SID, the ____ the magnification
A. Lesser, smaller
B. Greater, larger
C. SID has no effect on magnification
D. Greater; smaller
D. Greater, smaller
Which of the following is equivalent to low penumbra:
A. Low distortion
B. Low sharpness/SR
C. High sharpness/SR
D. High magnification
C. High sharpness/SR
The compton interaction is mainly responsible for radiographer dose. True or false?
True
If an incident x-ray photon ejects a k-shell electron during a photoelectric interaction with a binding energy of 37 keV, and the initial energy of the photon was 40 keV, the ejected electron leaves the atom with _____ keV of kinetic energy.
A. 3
B. 37
C. 40
D. 17
A. 3
If a radiograph using 40 mAs (400 mA at 0.10 sec.) produced a radiograph with satisfactory exposure, what new time should be used if mA is changed to 200?
0.2sec
40/200=0.2
The difference between two adjacent shades of gray is:
A. Spatial resolution
B. Distortion
C. Image contrast
D. Quantum mottle
C. Image contrast
If 20 mAs at 100 kVp is used and the IR exposure needs to be doubled without altering the kVp, determine the new technique that should be used.
100kVp 40mAs
A radiograph of the forearm is produced using 4 mAs at 65 kVp.
What kVp is required to double the exposure?
What kVp is required to halve the exposure?
74.75
55.25
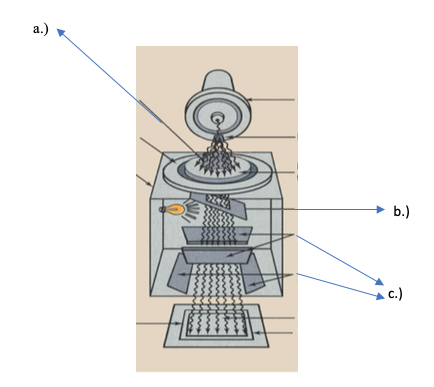
Label B. And C.
B. Mirror
C. Secondary shutters/second stage shutters
If 80mAs at 70kVp is used and the IR exposure needs to be doubled using kVp, determine the new technique that should be used.
80.5 kVp 80mAs
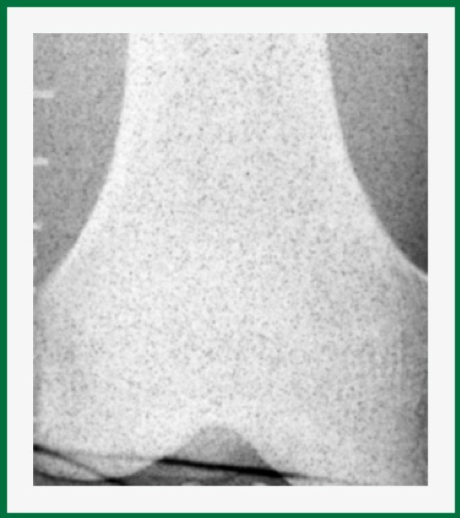
The term used to describe the “graininess” seen in the image is?
How might you adjust your technique to prevent it?
Quantum mottle
IR exposure too low- increase kVp or mAs