Understanding Loss, Grief, and Nursing Care
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Loss
Any situation in which a valued object is changed or is no longer accessible to the individual.
Actual loss
A type of loss where something valued is no longer available.
Perceived loss
A type of loss that is felt but may not be evident to others.
Physical loss
A type of loss involving the loss of a physical object or body part.
Psychological loss
A type of loss involving the loss of emotional or psychological well-being.
Anticipatory loss
A type of loss experienced in advance of the event, such as grieving before a loved one dies.
Sources of Loss
Factors that contribute to feelings of loss, including aspects of self, external objects, familiar environments, and loved ones.
Bereavement
The period of grief following a significant loss, especially the death of a person or pet.
Mourning
The period of time during which grief is expressed and is an adaptive response to loss.
Grief
A normal, natural, necessary, and adaptive response following a loss, essential for good mental and physical health.
Anticipatory grief
Grief experienced in advance of the event, often leading to abbreviated reactions when the actual loss occurs.
Disenfranchised grief
Grief when an individual is unable to acknowledge the loss to others, often due to socially unacceptable circumstances.
Factors affecting grief response
Elements that influence how an individual experiences and expresses grief.
Clinical symptoms of grief
Physical and emotional manifestations that indicate an individual is experiencing grief.
Measures to facilitate grieving process
Actions or interventions that help individuals cope with and process their grief.
Role of the nurse in grief
The responsibilities of nurses in supporting families or caregivers of dying clients.
Nursing measures after death
Actions taken by nurses for the care of the body after death.
Loss as Crisis
A situation where loss leads to anxiety and vulnerability, potentially resulting in a crisis.
Integrity of body image
The degree to which losses affect an individual, often related to how they perceive their physical self.
External objects loss
Loss of inanimate or animate objects that hold significance for the individual.
Familiar environment loss
Separation from environments and individuals that provide security, leading to feelings of loss.
Loved ones loss
The distress experienced from losing a valued individual through various means such as illness or death.
Unhealthy grief
Exists when the strategies to cope with the loss are maladaptive and out of proportion or inconsistent with cultural, religious, or age-appropriate norms.
Persistent complex bereavement disorder
Referred to by physicians as existing if the preoccupation lasts for more than 12 months and leads to reduced ability to function normally.
Inhibited grief
Many of the normal symptoms of grief are suppressed, and other effects, including physiologic, are experienced instead.
Unresolved or chronic grief
Same signs are expressed as with normal grief, but the bereaved may also have difficulty expressing the grief, may deny the loss, or may grieve beyond the expected time.
Delayed grief
Occurs when feelings are purposely or subconsciously suppressed until a much later time.
Exaggerated grief
A survivor who appears to be using dangerous activities as a method to lessen the pain of grieving may experience this.
Complicated grief
May be inferred from observations such as failing to grieve, avoiding memorial services, or developing persistent guilt and lowered self-esteem.
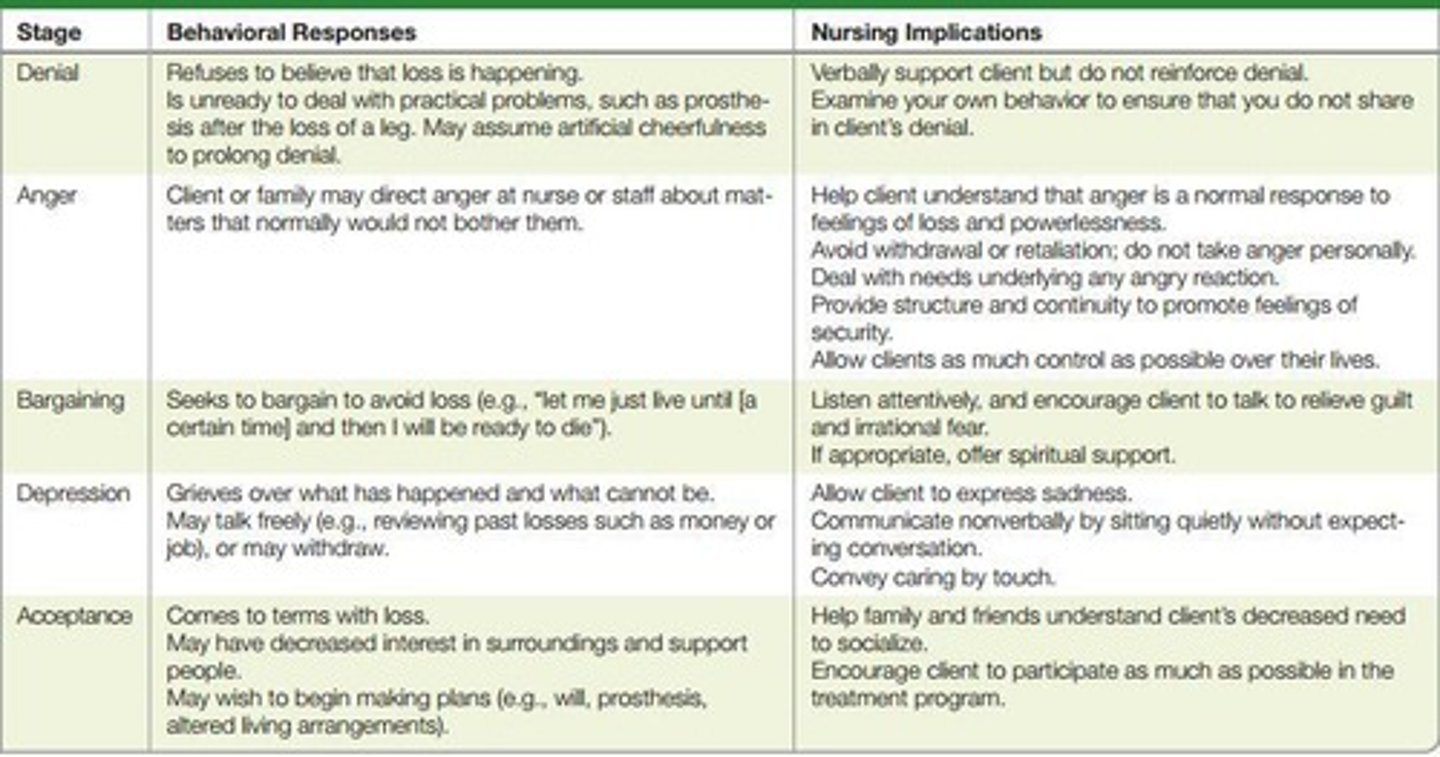
Stages of Grieving
Described stages or phases of grieving, most well known being Kübler-Ross (1969), who described five stages: Denial, Anger, Bargaining, Depression, Acceptance.
Factors Influencing Loss and Grief Responses
Include age, significance of the loss, culture, spiritual belief, gender, socioeconomic status, support system, and cause of death.
Patient-Centered Care: Grieving
Involves assessing knowledge, self-care abilities, current coping, manifestations of grief response, role expectations, and support people's availability and skills.
Community Assessment in Grieving
Involves assessing resources, availability, and familiarity with possible sources of assistance such as grief support groups and counseling services.
Live well and Die well
A phrase prompting reflection on what it means to the individual.
Responses to Dying and Death
Include changing the subject, offering false reassurance, and denying what is happening.
Nurses' discomfort with dying clients
Tends to impede clients' attempts to discuss dying and death.
Fatalistic remarks
Comments such as 'Everyone dies sooner or later' or 'What's meant to be, will be' that reflect a lack of engagement with the dying process.
Block discussion
Convey an attitude that stops further discussion of the subject.
Peaceful death preference
Individuals prefer a peaceful death at home rather than in the hospital.
Prognosis disclosure request
Members of certain ethnic groups may request that health professionals not reveal the prognosis to dying clients.
Family member diagnosis communication
Prefer that a family member (preferably a male in some cultures) be told the diagnosis so the client can be tactfully informed by a family member in gradual stages or not be told at all.
Preparation beliefs
Beliefs about preparation of the body, autopsy, organ donation, cremation, and prolonging life are closely allied to the client's religion.
Cremation beliefs
Cremation is discouraged, opposed, or prohibited by the Baha'i, Mormon, Eastern Orthodox, Islamic, and Roman Catholic faiths.
Hindu cremation practice
Indus, in contrast, prefer cremation and cast the ashes in holy rivers.
Autopsy opposition
Autopsy may be prohibited, opposed, or discouraged by Eastern Orthodox religions, Muslims, Jehovah's Witnesses, and Orthodox Jews.
Hindu autopsy opposition
Some groups, such as Hindus, may oppose autopsy based on not wanting non-Hindus to touch the body.
Body parts burial
Some religions prohibit the removal of body parts or dictate that all body parts be given appropriate burial.
Organ donation beliefs
Organ donation is prohibited by Jehovah's Witnesses, whereas Buddhists in America consider it an act of mercy and encourage it.
Prolonging life beliefs
Some religions, such as Christian Science, are unlikely to recommend medical means to prolong life, and the Jewish faith generally opposes prolonging life after irreversible brain damage.
Advance Healthcare Directives
Document describes preferences for future treatment, whether or not the client is currently unwell.
Do-Not-Resuscitate Orders
Also referred to as DNR, no code blue, no code, allow natural death (AND), refer to the documentation of the decision to refrain from cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) should the client's heart or breathing cease from an irreversible underlying condition.

Organ Donation approaches
Two main approaches to organ donation: presumed consent and explicit consent.
Euthanasia
Also known as physician-assisted death, end-of-life options, or death with dignity act.

Closed awareness
A type of awareness in nursing management.
Mutual pretense
A type of awareness in nursing management.
Open awareness
A type of awareness in nursing management.
Signs of impending clinical death
Indicators that clinical death is approaching.
Planning for Home Care
Maintaining physiologic and psychologic comfort and achieving a dignified and peaceful death, which includes maintaining personal control and accepting declining health status.
Nursing responsibility for dying clients
The major nursing responsibility for clients who are dying is to assist the client to a peaceful death.
Hospice Care
Focuses on support and care of the dying client with a life expectancy of 6 months or less and the family, with the goal of facilitating a peaceful and dignified death.
Palliative Care
An approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families facing the problem associated with life-threatening illness, through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems, physical, psychosocial and spiritual.
Pain Control
A method of managing pain in dying clients to ensure comfort.
Providing Spiritual Support
Offering emotional and spiritual assistance to clients and their families during the dying process.
Supporting the Family
Providing care and assistance to the family of the dying client.
Postmortem Care
Care provided to the body after death, including the management of bodily changes.
Rigor Mortis
The stiffening of the body that occurs about 2 to 4 hours after death, starting in involuntary muscles and progressing to the extremities.
Algor Mortis
The gradual decrease of the body's temperature after death, falling about 1°C (1.8°F) per hour until it reaches room temperature.
Livor Mortis
The discoloration of surrounding tissues after blood circulation has ceased due to the breakdown of red blood cells.
Grieving
A normal, subjective emotional response to loss that is essential for mental and physical health.
Situational Loss
Loss that occurs due to a specific situation, such as loss of a loved one or a job.
Developmental Loss
Loss that occurs as part of the normal developmental process, such as aging or life transitions.
Actual Loss
A loss that is tangible and can be recognized, such as the death of a loved one.
Perceived Loss
A loss that is felt by an individual but may not be recognized by others.
Anticipatory Grief
Grief that occurs before an impending loss, allowing individuals to prepare emotionally.
Disenfranchised Grief
Grief that is not openly acknowledged or socially supported.
Complicated Grief
Grief that is prolonged and significantly impairs an individual's ability to function.
Unresolved Grief
Grief that remains unresolved over time and affects an individual's mental health.
Inhibited Grief
Grief that is suppressed and not expressed outwardly.
Advance Healthcare Directives
Legal documents that outline a person's preferences for medical treatment in case they are unable to communicate their wishes.
Do-Not-Resuscitate Orders
Orders that prevent medical personnel from performing CPR in the event of cardiac arrest.
Organ Donation
The process of giving one's organs for transplantation after death.
Euthanasia
The practice of intentionally ending a person's life to relieve suffering.
Aid in Dying
Providing assistance to a person in ending their own life, often in the context of terminal illness.
Nurse's Role in Death
Nurses must consider the entire family as requiring care in situations involving loss, especially death.