Block 3 unit 1-6
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Hub
Simple device that copies data and sends it to every device connected to it; Legacy Device
Switches
Uses ASICs to help path Determination.
Learn MAC address of each connected devices
Break up Collision Domains
Switches are fast and have adjustable speed/bandwidth.
Switches Segment networks
PPP
Peer-to-peer; Connecting directly to another device without the need of a network
STP or IEEE 802.1D
Spanning tree protocol; Loop Prevention Protocol
Ensures efficient and reliable data transmission
UDLD
Detects traffic flowing in direction due to bad TX/RX and shuts down the port
CDP
Cisco Discovery Protocol; Stores MAC, VLAN, Management IP, system names etc.
Similar to LLDP
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
Non-proprietary protocol that allows neighboring devices to learn abut each other
Stores MAC, VLAN, Management IP, System name, etc
802.1q
Non-proprietary trunking Protocol
ISL
Cisco proprietary VLAN trunking protocol
Switching Methods
Store-and-forward, Cut-through, and Fragment-free
Store-and-forward
Stores entire frame into memory and checks it for errors using CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check)
Slow but high level of error-free traffic
Cut-Through
Copies destination MAC to memory and sends the frame through
Used for speed
Fragment-Free
Hybrid of Cut-through & Store-and-Forward
Checks 64 bytes before sending it off
Most errors occur in the first 64 Bytes
Loops
Multiple paths to the same destination
Can cause, Broadcast Storms, Multiple frame copies, and Multiple Loops
Broadcast Storms
Network devices rebroadcasting data to the network
Multiple frame copies
Device receives multiple frame copies from different LAN segments
Multiple loops
Loops can occur within loops, consuming bandwidth.
Spanning tree protocol IEEE 802.1D is used to prevent loops
VLAN
Logical (or IP) grouping of Network devices
Layer 3 Routing Process
VLAN benefits
Increased Security
Flexibility and Scalability
Removes geographical barriers
VLAN 1 by default
VLANS are made with a number and Description (Ex: VLAN 10 is named Sales)
Trunk Port AKA Trunk Link
Connection that carries multiple VLANs; Having Multiple different VLANS on one cable
Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
Cisco Proprietary VLAN Trunking
IEEE 802.1Q
Open Standard VLAN trunking
Management VLAN
Used for Telnet, SSH, SNMP, and Syslog
Should NEVER be assigned to VLAN 1
Router
Connects 2 or more lines from different networks. These form internetwork.
Routing
Sending a packet from one device to another one a different network
Multilayer switches (MLS)
Can operate at layer 2 and 3 of OSI Model.
Sometimes referred as a Layer 3 Switch
External Components of a switch
Console Port, Auxiliary port, network interfaces
Console Port
Allows local configuration of a Switch
Auxiliary Port
Allows configuration of a switch via a Modem. Is often disabled due to security concerns
Internal Components of a Switch
ROM, Flash Memory, NVRAM, and RAM
ROM
Read only memory; Diagnostic and Boot-up Routines
Flash Memory
Stores the OS
NVRAM
Stores the startup Configuration and loads it into RAM
RAM
Running configuration; Used for operations
Gateways
Router that sends IP packets between networks/subnets
Autonomous System (AS)
Defined by RFC 1930; A network that works without human interference (Most networks)
Types of Gateways
Interior Gateway, Exterior Gateway, and Default Gateway.
Interior Gateway
Routers Moving Information WITHIN a Network
Exterior Gateway
Routers Moving Information BETWEEN networks
Default Gateway
Access Point to a network
Networking Challenges
Connectivity, reliable service, Network Management, and Flexibility
Connectivity
Interconnected devices, media, and speeds
Reliable Service
Up-Time; consistent access to a network
Network Management
Troubleshooting capabilities/Centralized support
Flexibility
Expansions, upgrades, and new apps/services
Network Segmentation
Routers and switches are used to segment networks.
Routers break up broadcast domains.
L3 Broadcast
IP prefix for a subnet/network
Protocols
Rules that govern how devices communicate
Path Determination
Routers build & Maintain routing tables using Routing Protocols
Packet Switching
Sending data (Or packets) from router to router
As the data travels, it's destination MAC changes.
The IP source and Destination stay the same
Conditions in which a packet is discarded
TTL (Time-to-live) Expires
Version number of packet header is wrong
Error in Transmission
Packet is fragmented and the fragmentation flag isn't set
ROUTED protocols
Deliver the messages
IP, ARP, Hello Protocol, & ICMP
Hello Protocol AKA Neighbor Discovery
Enables network devices to learn about other network devices.
ICMP - Internet Control Message Protocol
Reports errors with IP packet processing
ROUTING protocols
Responsible for Path Determination & Packet Switching.
Build and Maintain Routing Tables.
RIP, EIGRP, OSPF, BGP
Different types of Routes
Static, Default, and Dynamic
Static Routes
Manually configured by System Administrator
AD=1 is the most trusted (Because there's nothing higher than 1 in Binary)
Dynamic Routes
Routers use information to build and main routing tables;
Finds the most efficient way to reach it's destination
Default Routes
Gateways of Last Resort
Type of Static route
Used by router if no other path is known to the destination
Path Length
Most relied upon metric
Hop count
number of internetworking devices from source to destination
Metrics to determine best route
Reliability, Delay, Bandwidth, and Load
Delay
How long it takes the packet to move to the destination
Bandwidth
Available traffic capacity of a link
Load
How much traffic is on the network/How busy it is
Distance Vector Algorithms
Algorithms that call for each router to send it's entire routing table (Similar to Hello protocol and CDP)
Advantages of Distance Vector Algorithms
Simple to understand and config.
Less processor demand.
Cheaper
Disadvantages of Distance Vector Algorithms
Limited by hop count (Max of 15)
Doesn't support VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking)
Builds routing table from neighbors (Explanation: they could be wrong)
Link State Algorithms
Also called Shortest Path First (SPF)
Builds Topological map of the area into memory.
Interior Gateway Protocols
RIP (limited to 15 hops & is used in Distance Vector)
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First, is used in Link State)
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
Advantages of OSPF
Supports large networks
Fast convergence
No routing loops
Supports classless routing
Smaller updates
Disadvantages of OSPF
Complex topology
Needs highly trained staff
Takes up allot of memory
SPF algorithms use more processing power
EIGRP
Metrics: Bandwidth & delay
Known as “Balanced Hybrid” because it combines advantages
Resembles both Distance Vector and Link State Algorithms
Advantages of EIGRP
Fast convergence when feasible successor is available
Smaller updates
Scales to large networks
VLSM supported
Disadvantages of EIGRP
High memory (AKA money) requirements
Routing algorithm is complex
No area concept
BGP
BETWEEN AS (Autonomous System)
Loop free
Doesn't use metrics like Delay, hop count, or bandwidth instead is based off of network policies set by administrators
Core layer
Core of the network. Also called High Speed Backbone.
Transmits large amounts of data quickly and reliably.
Core Layer Failure causes
Faulty Link or device
Core Layer Protocols
Uses routing protocols with low convergence times (Fast & efficient Layer 2 switching devices)
Distribution Layer
Communication point between access layer and core layer. Provides routing, filtering, WAN access, & determines how many packets access the core layer.
Determines fastest way to send data
Distribution Layer Policies
Uses tools likes: Access lists, packet filtering, for , security, and network policies.
Routes betweens VLANs.
Aggregation point for multiple access sileitches and must be capable of handling large amount of traffic
Client Connection
Connects multiple desktop devices to the Distribution Layer
Many access points and low cost
Shared & switched bandwidth devices
Filters based on MAC
Subnet
Network within a network
Logic division of a network of connected devices based on IP
Subnet Process
3 parts of an IP, Network (1-126 and 128-228), Subnet Mask, and Host Portion (0-255)
Subnetting: Networking portion borrows bits from the host portion
Subnetting rules
Beginning of Default mask and class cannot change
Class B network and cannot be 255.0.0.0 or 255.255.255.255
Classes must start with default mask, however subnet mask may change if it follows previous rules
Benefits of subnetting
Reduced network traffic
Optimized performance
Simplified management
Class A Subnetting
Up to 8,388,608 available subnets per class A address.
Takes in Host requirements when Subnetting
Class A provides most available subnets
Class B subnetting
Up to 32,768 subnets
Also takes in Host requirements when Subnetting
Class C Subnetting
Used for small networks (Just like Class C networks)
Least amount of borrowable bits
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
Written with IP address followed by a / and the subnet number: Example 192.168.12.10/27
Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM)
Used for Subnetting a network
Subnets can be broken into further subnets
Allows more efficient use of IP addresses
Topological map
Visual Representation of a network
Can be physical or logical
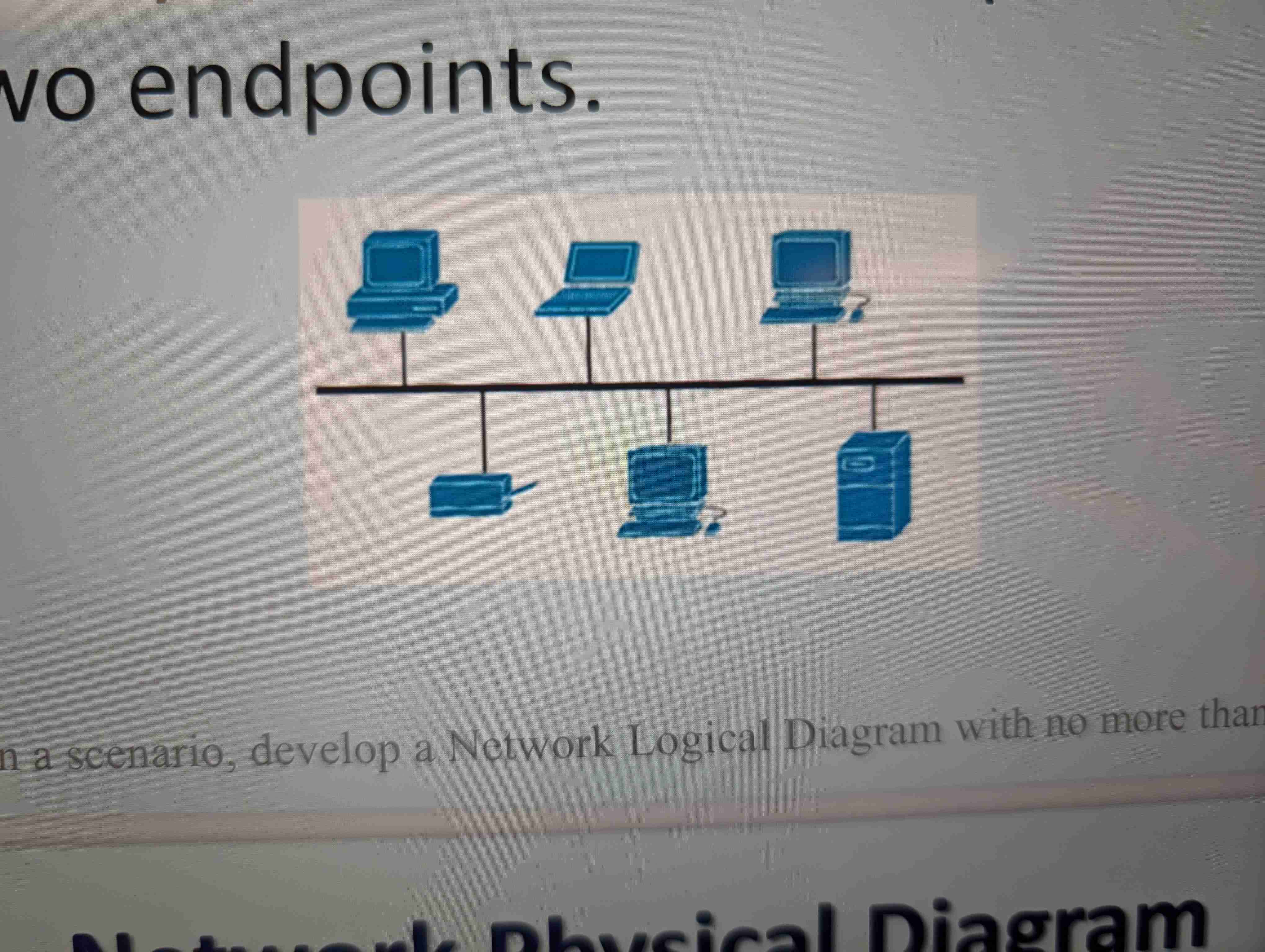
Bus topology
All nodes (aka devices) connects by central medium (or bus) which has exactly 2 endpoints
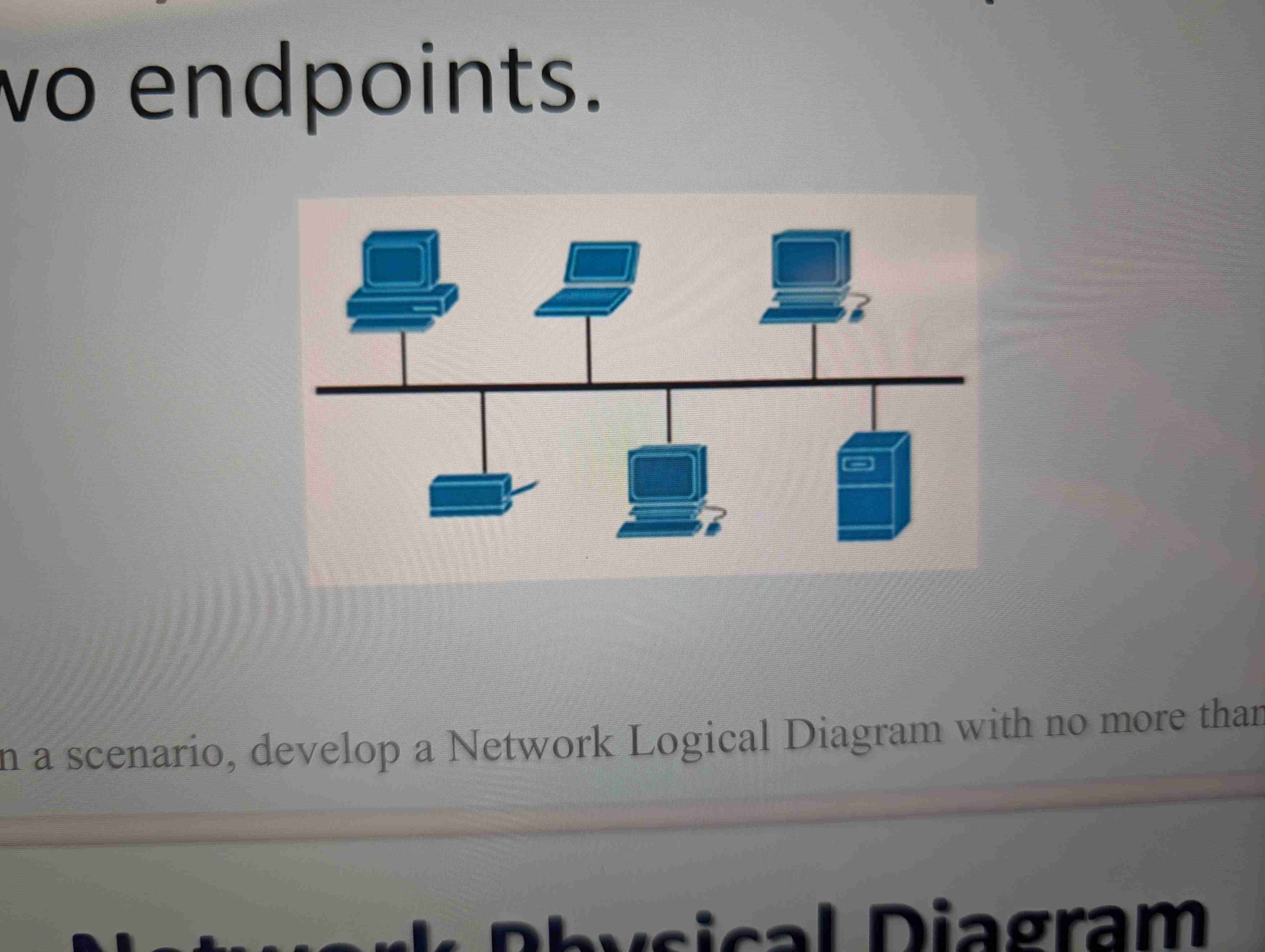
Bus Topology benefits & Disadvantages
Easy to configure
Requires less cable length
Disadvantages
Hard to pinpoint a problem
If the central bus goes down, so does the network.
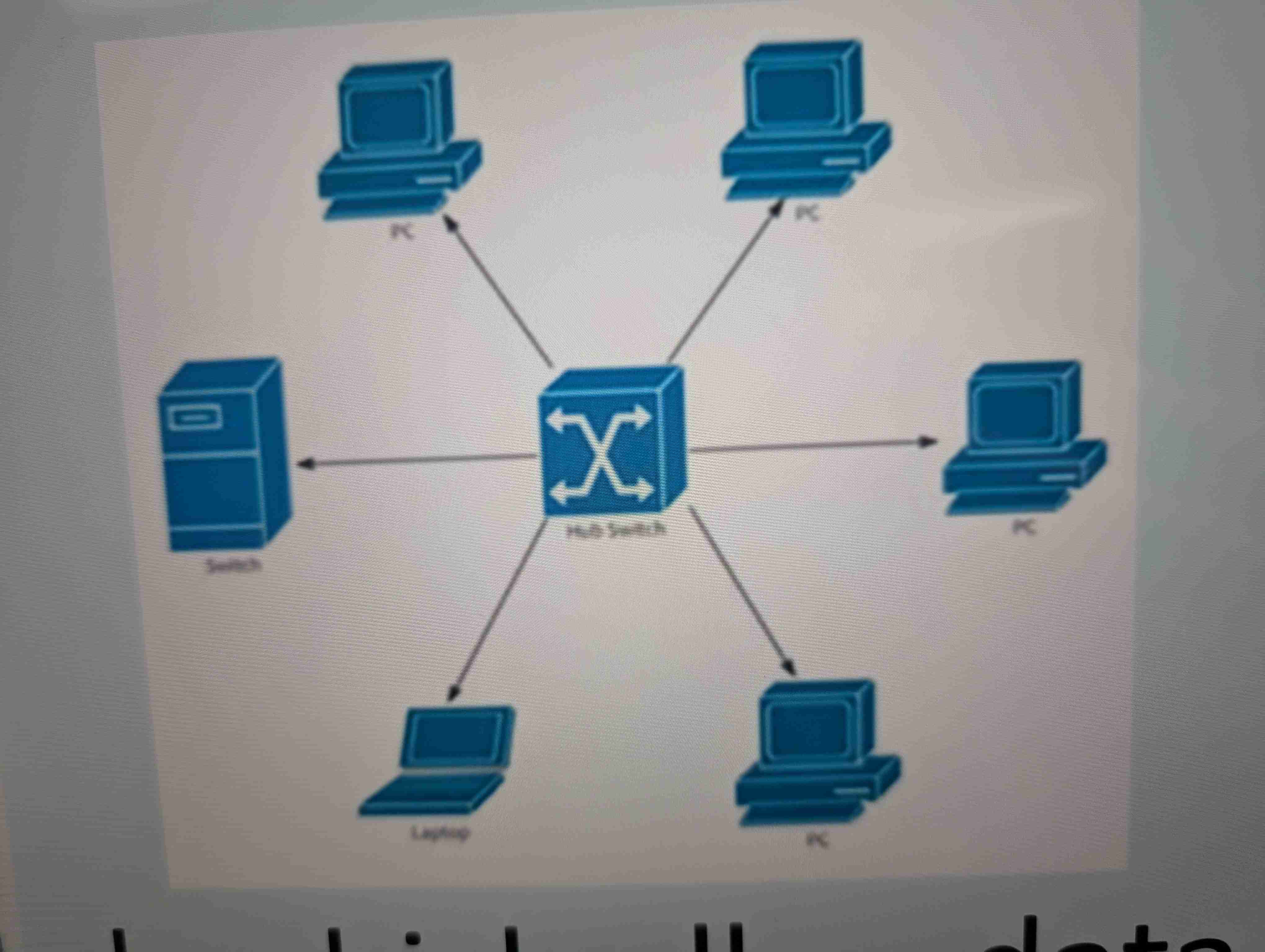
Star Topology
One central hub/switch which all data passes through to reach each device
Most common topologies
Very reliable due to individual devices not affecting the network if they crash.
Disadvantages
Higher cable costs
If central hub/switch fails, no connected devices can access it
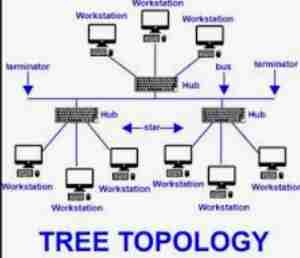
Tree topology
Hybrid of Bus & Star Topology
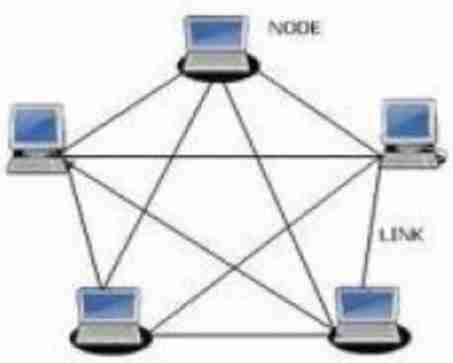
Mesh Topology: Full Mesh
Every node is directly connected to every other node (Easy to make loops)
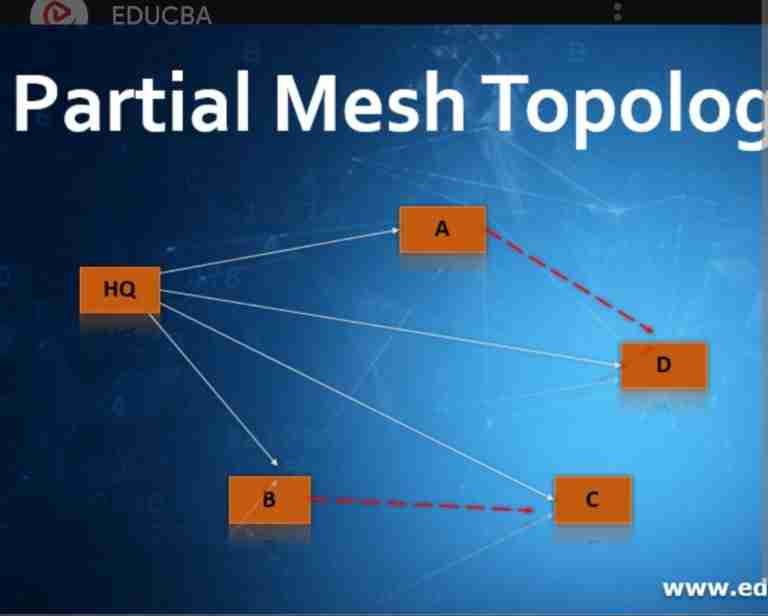
Mesh Topology: Partial Mesh
Nodes are only connected to the nodes they interact with the most