Bones, Skeletal, & Tissue System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the name for the science concerned with the study of bone?
Osteology
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Two types: Biological and Mechanical
Mechanical
Protects internal organs
Facilitates movement
Supports the body (weight bearing)
Biological
Stores and releases fat
Produces blood cells
Stores and releases minerals
How many bones are humans born with? How many do we have at adulthood?
300-350 at birth
206 at adulthood
Describe: The mineral storage of bones
The inorganic matrix of bone is composed of calcium and phosphorus, these give bones rigidity and account for 2/3 of the weight of bone
95% of calcium and 90% of phosphorus in the body are in our bones and teeth
Magnesium and sodium salts are also stored in bones
Describe ways in which the skeleton protects our body/organs
Skull/vertebral column house the central nervous system (brain/spinal chord)
The thoracic cage (ribs) protects the heart, lungs, great vessels, liver, and spleen
The pelvic cavity supports and protects pelvic organs
What are the two types of bone tissue?
Compact bone (cortical): dense, smooth, and homogenous
Spongy bone (cancellous/trabecular): open, sponge-like space, with small pieces of bone. (Surrounded by compact bone)
What are the 5 types of bone?
Long
Short
Flat
Irregular
Sesamoid
Describe: Long Bones
Longer than they are wide
Used for mechanical strength
Ex) femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, ulna, radius
Describe: Short Bones
Cube shaped
Used for multi-directional motion
Ex) carpal bones of the hand/wrist, tarsal bones of the feet/ankle
Describe: Flat Bones
Thin and flat (large surfaces for muscle attachment)
Used for mechanical protection of soft tissues beneath
Ex) Cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapulae
Describe: Irregular Bones
Complicated shapes that cannot be classified as long, short, or flat
Provide mechanical support for the body structures
Ex) Vertebrae, hyoid bone, sphenoid bone, facial bones
Describe: Sesamoid Bones
Most sesamoid bones are unnamed
Protects from additional friction and use, can form in palms and soles
Ex) Only one type is present in all normal human skeletons so it has a name: the patella (kneecap!)
Define: Closed Reduction
When a broken bone is manipulated and set into its natural
position without surgery
Define: Open Reduction
Requires surgery to expose the fracture and reset the bone.
The breaking of which bone can release fat globules into the bloodstream and result in respiratory distress and death?
A fractured diaphysis of the femur
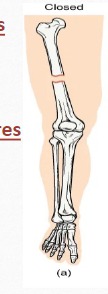
What are the 8 types of bone fractures?
Closed
Open
Transverse
Spiral
Comminuted
Impacted
Greenstick
Oblique
Describe: Transverse fractures
Occurs straight across the long axis of the bone
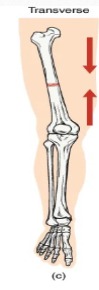
Describe: Oblique fractures
Occurs at an angle that is not 90 degrees
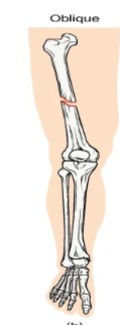
Describe: Spiral fractures
Bone segments are pulled apart as a result of a twisting motion
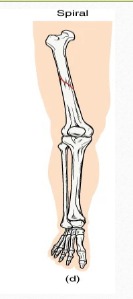
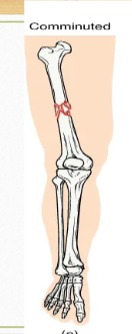
Describe: Comminuted fractures
Several breaks result in many small pieces between two large bone segments
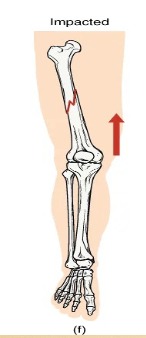
Describe: Impacted fractures
One fragment is driven into the other, usually as a result of compression
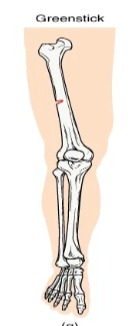
Describe: Greenstick fractures
A partial fracture in which only one side of the bone is broken
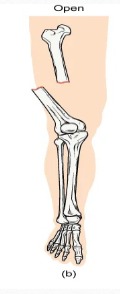
Describe: Open fractures
A fracture in which at least one end of the broken bone tears through the skin, carries a very high risk of infection
Describe: Closed fractures
A fracture in which the skin remains intact
What are the 4 stages of bone repair?
Hematoma formation and inflammation
Granulation formation (also called fibrocartilaginous callus formation)
Callus formation (or bony callus formation)
Remodeling
Describe: Hematoma formation + Inflammation
Activation of coagulation cascade
Changes of local environment
Inflammatory cells and molecules are released
Clear necrotic tissues and recruit osteoprogenitor cells
Describe: Granulation (fibrocartilaginous callus formation)
Active proliferation of osteoprogenitor cells
Angiogenesis
Extracellular matrix production
Describe: Bony callus formation
Soft and hard differentiation of MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) according to the mechanical environment
Initial stabilization of fracture, then replaced by calcified tissue
Describe: Bone remodeling
Long process (can take YEARS)
Resorption of remaining cartilage
Restoration of the Haversian system
No scar formed
Define: The Haversian system
The Haversian system, also known as the osteon, is a fundamental structural unit of compact bone. It consists of concentric layers of bone tissue called lamellae, surrounding a central canal called the Haversian canal. Which contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. The lamellae are composed of collagen fibers and mineralized matrix, providing strength and support to the bone.
Why are calcium ions (Ca2+) needed in the body?
for bone mineralization
for tooth health
regulation of the heart rate and strength of contraction
blood coagulation
contraction of smooth and skeletal muscle cells
regulation of nerve impulse conduction
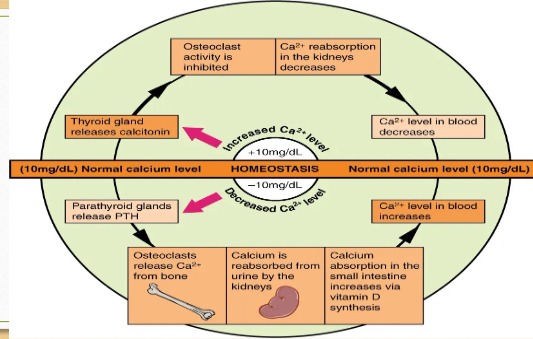
What is the normal amount of calcium in the blood?
The normal level of calcium in the blood is about 10 mg/dL.
How are calcium levels maintained? (homeostasis)
When Ca2+ levels are low: Osteoclasts dissolve and break down old or damaged bone cells and release Ca2+ to be reabsorbed by the kidneys to increase Ca2+ in blood.
When Ca2+ levels are high: The thyroid releases calcitonin, which inhibits osteoclast activity.
What are osteoBLASTS (not osteoCLASTS)?
Osteoblasts are cells that form bone tissue.
What are the three ways bones are classified?
Shape
Location
Dynamic structure
Define: Axial skeleton
80 bones
Protect internal organs
Include: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
Describe the bone structure of the skull
Cranium is the entire skull
Brain case is the rear and top of the cranium
Facial bones are the front of the skull
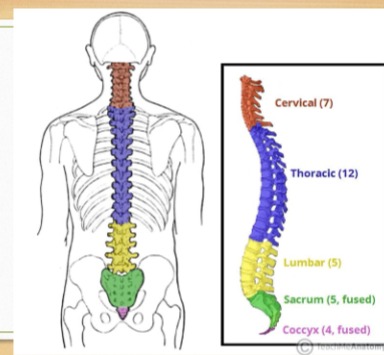
Describe the vertebral column
Called: spine, spinal column, or backbone
Flexible hollow structure containing spinal cord
Comprised of 33 vertebrae
Occipital bone to tip of coccyx
Describe the regions of the vertebral column
C1-C7: Cervical
T1-T12: Thoracic
L1-L5: Lumbar
S1-S5: Sacrum (fused)
Co1-Co4: Coccyx (fused)
Describe the thoracic cage
Also called the rib cage
12 pairs of ribs (24 total)
First 7 pairs of ribs are attached to the sternum directly by cartilage (called true ribs)
8-10th pairs are attached to the 7th rib by cartilage (false ribs)
The 11th and 12th are not attached to the sternum (spine only) called floating ribs.
What is the function of the spine?
Protects the spinal cord from any mechanical injury by enclosing the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), spinal cord, and nerve roots
Protects internal organs like the heart and lungs
Serves as the attachment point for several muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones
Describe: the embryonic development of the human skull
3rd week of embryonic development
Notochord develops along the length of the embryo
Notochord tissues enlarge and form neural tube which will form the brain and spinal cord
4th week of embryonic development
Mesoderm tissue located on either side of the notochord thickens and separates into block-like tissue structures called somite
Somite enlarge and split into several parts, the middle is called a sclerotome
Sclerotomes consist of embryonic tissue called mesenchyme, which will give rise to fibrous connective tissues, cartilage, and bones.
Define: Appendicular skeleton
126 bones total
64 bones in upper appendicular
62 bones in lower appendicular
Includes pectoral girdle (arm attachment), arms, pelvic girdle (leg attachment), and legs
Compare and contrast the axial and appendicular skeletons