Exam 3 (wood/secondary growth)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Apical vs lateral meristems in plant growth
Apical meristems are found at the tips of roots and shoots, responsible for primary growth, while lateral meristems, such as the vascular cambium and cork cambium, contribute to secondary growth, increasing the thickness of stems and roots.
primary growth
lengthening up (taller) and roots growing further down (deeper)
secondary growth
widening (girth) and spreading out in the roots
what does vascular cambium produce
Vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem, contributing to the plant's growth in thickness.
what does cork cambium produce
Cork cambium produces cork cells that form the outer protective layer of the plant, known as the periderm.
What cells are formed to the inside and outside of the vascular cambium?
The vascular cambium produces secondary xylem (wood) to the inside and secondary phloem to the outside, facilitating the plant's growth in diameter.
primary xylem and phloem formation
Primary xylem and phloem are formed during a plant's primary growth from the procambium located in the apical meristems
secondary xylem and phloem formation
secondary xylem and phloem develop later during secondary growth from the vascular cambium
what tissues form the bark?
Bark consists of ALL the tissues external to the vascular cambium, including secondary phloem and periderm
function of secondary phloem
transports water and organic solutes between roots and leaves
function of periderm
A suberized layer that protects and insulates underlying tissue
function of lenticels
allow for gas exchange between living stem or root cells and the outside air
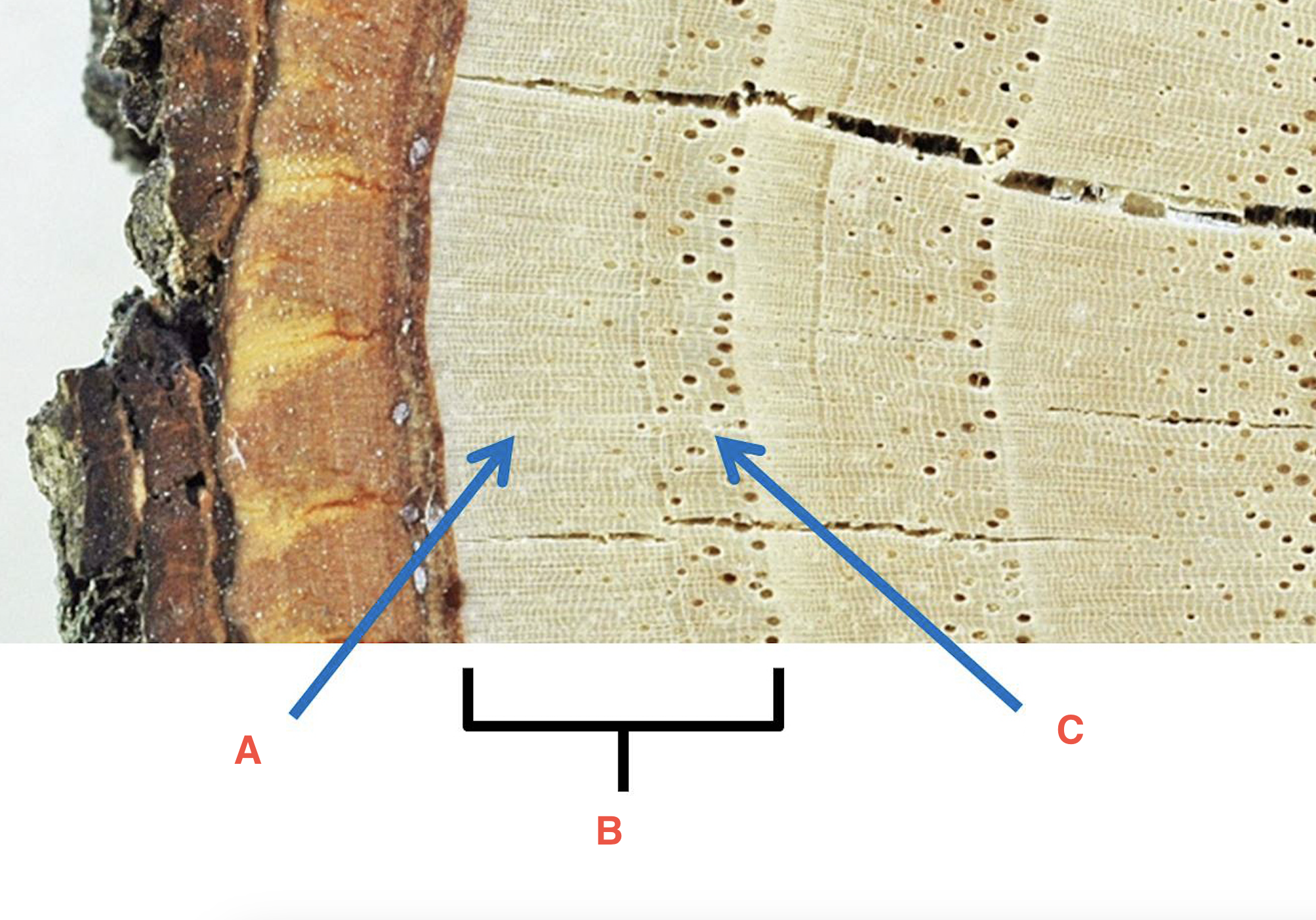
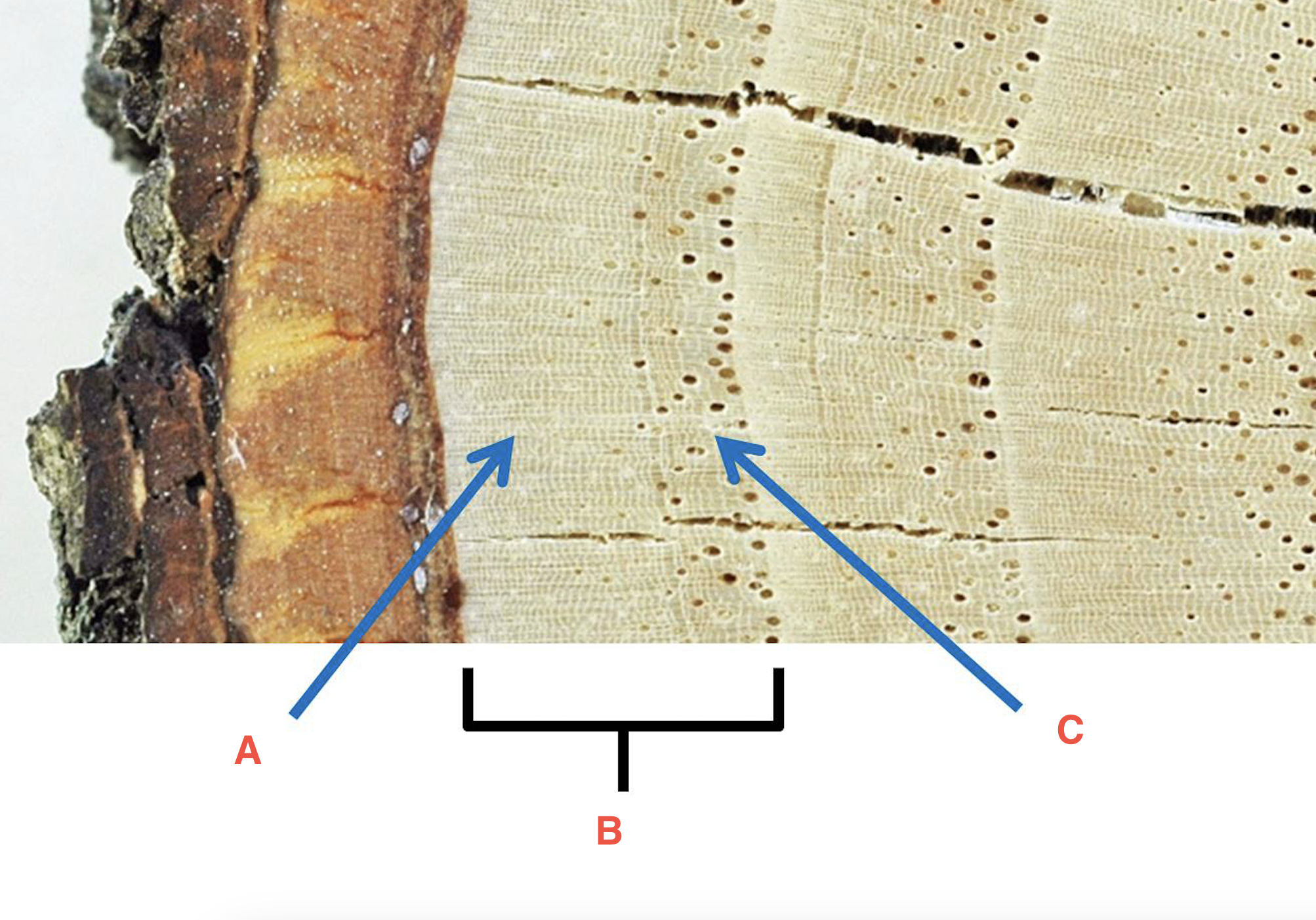
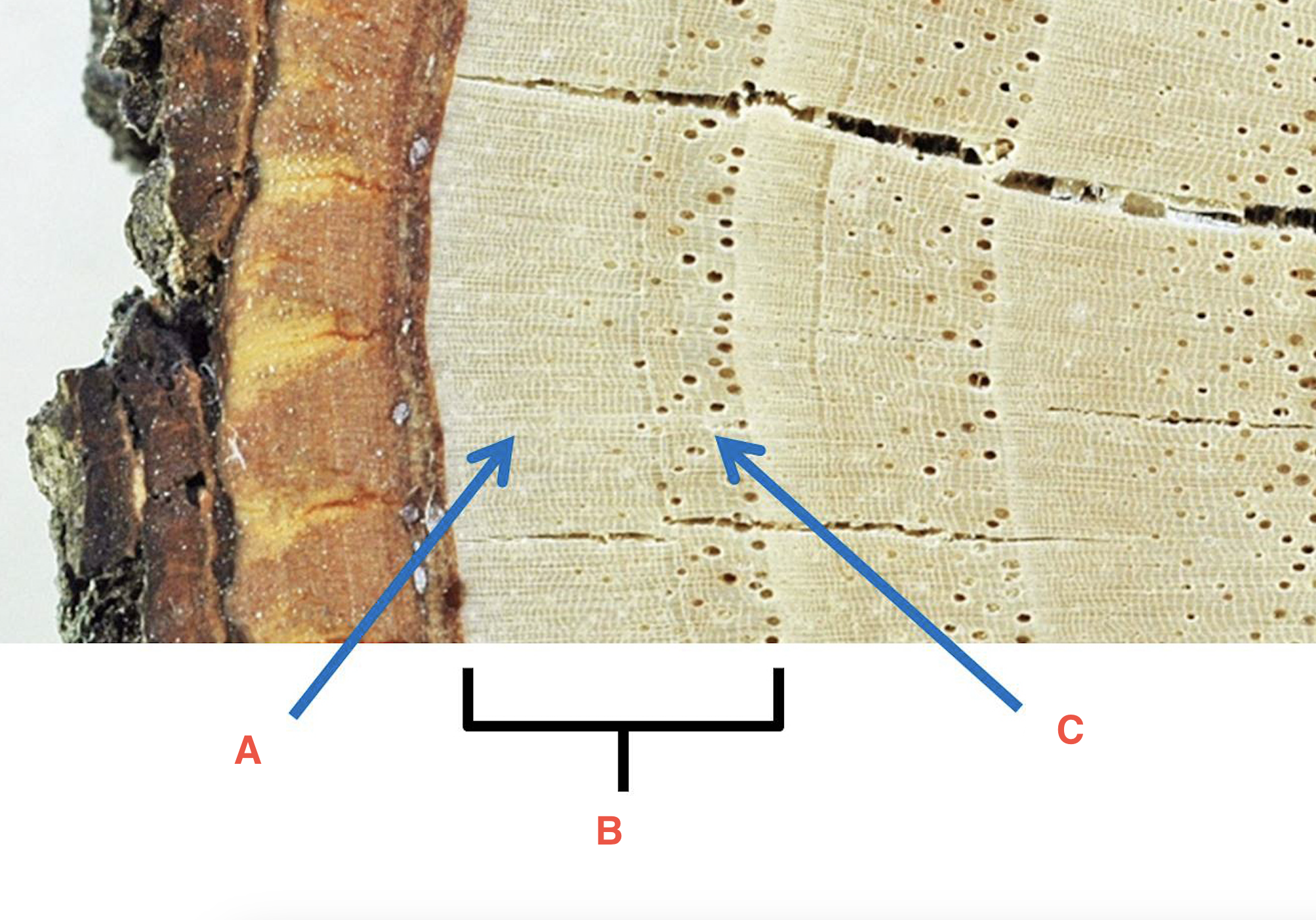
heartwood
the dead, inner wood, which often comprises the majority of a stem's cross-section (secondary xylem)
sapwood
the living, outermost portion of a woody stem or branch that still transport materials
softwood
xylem consists primarily of tracheids; NO fibers or vessel elements. Found in cone-bearing trees (conifers) like pine, spruce, larch, fir and redwood
hardwood
xylem includes tracheids PLUS fibers and vessel elements. Found in dicots native to temperate and tropical regions such as oak, maple, ash, walnut, and hickory
trachieds
water conducting cell in the xylem
vessel elements
parts of the building blocks of vessels that transport water (pipes)
pines vs oaks
Pines have softwood (conifers)
Oaks have hardwood (dicots)
what groups of plantrs show secondary growth?
Conifers and dicots (NOT monocots)
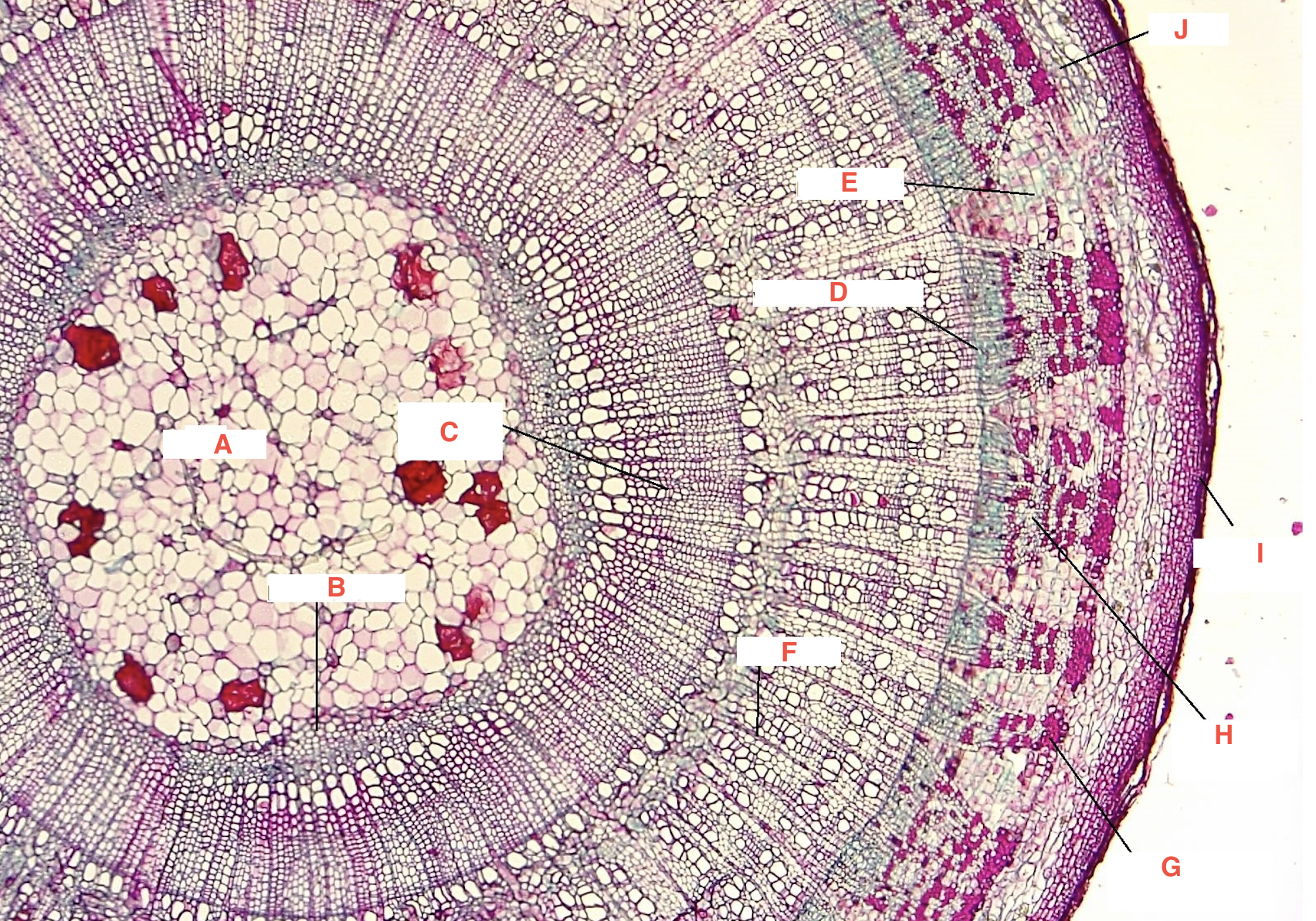
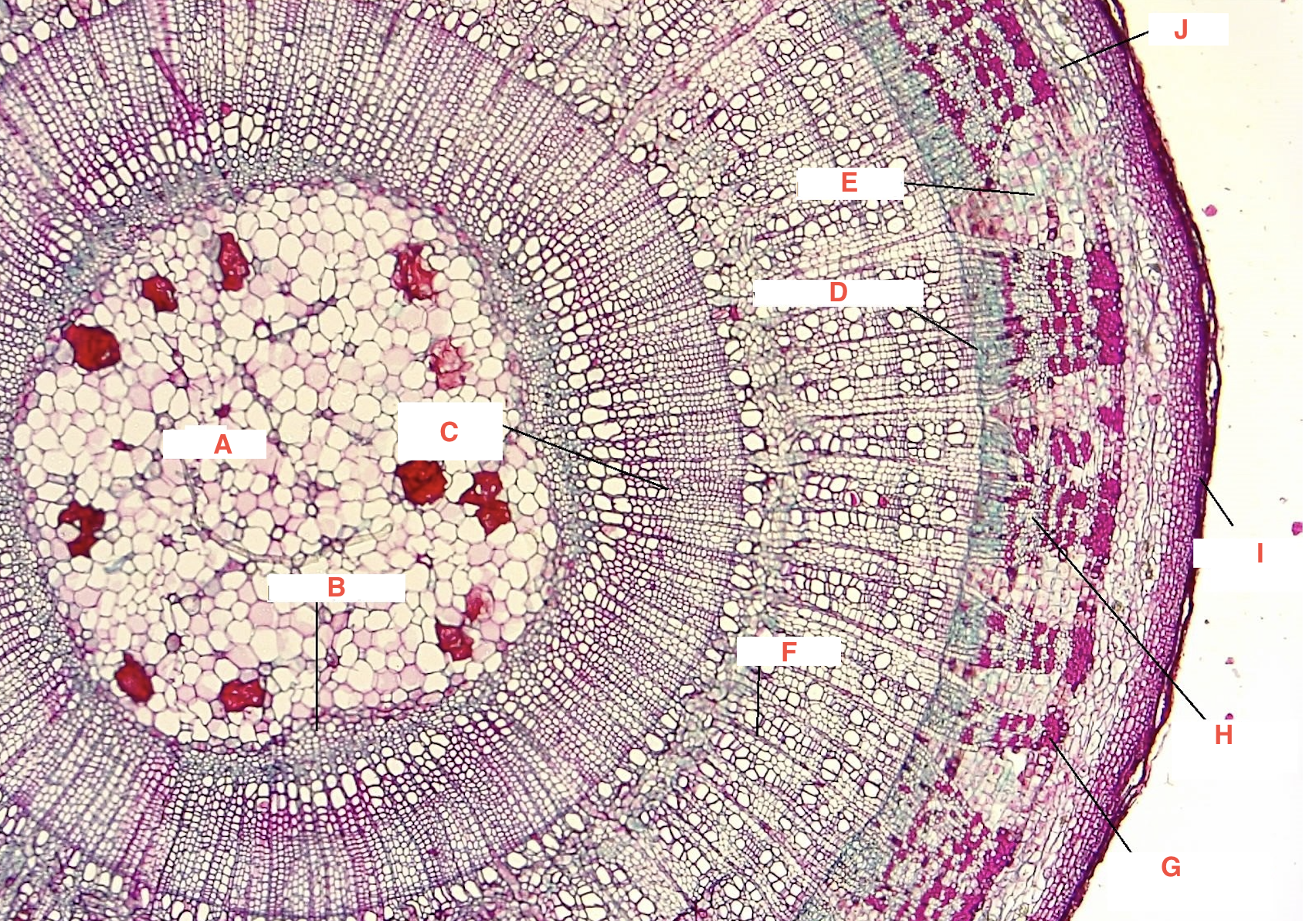
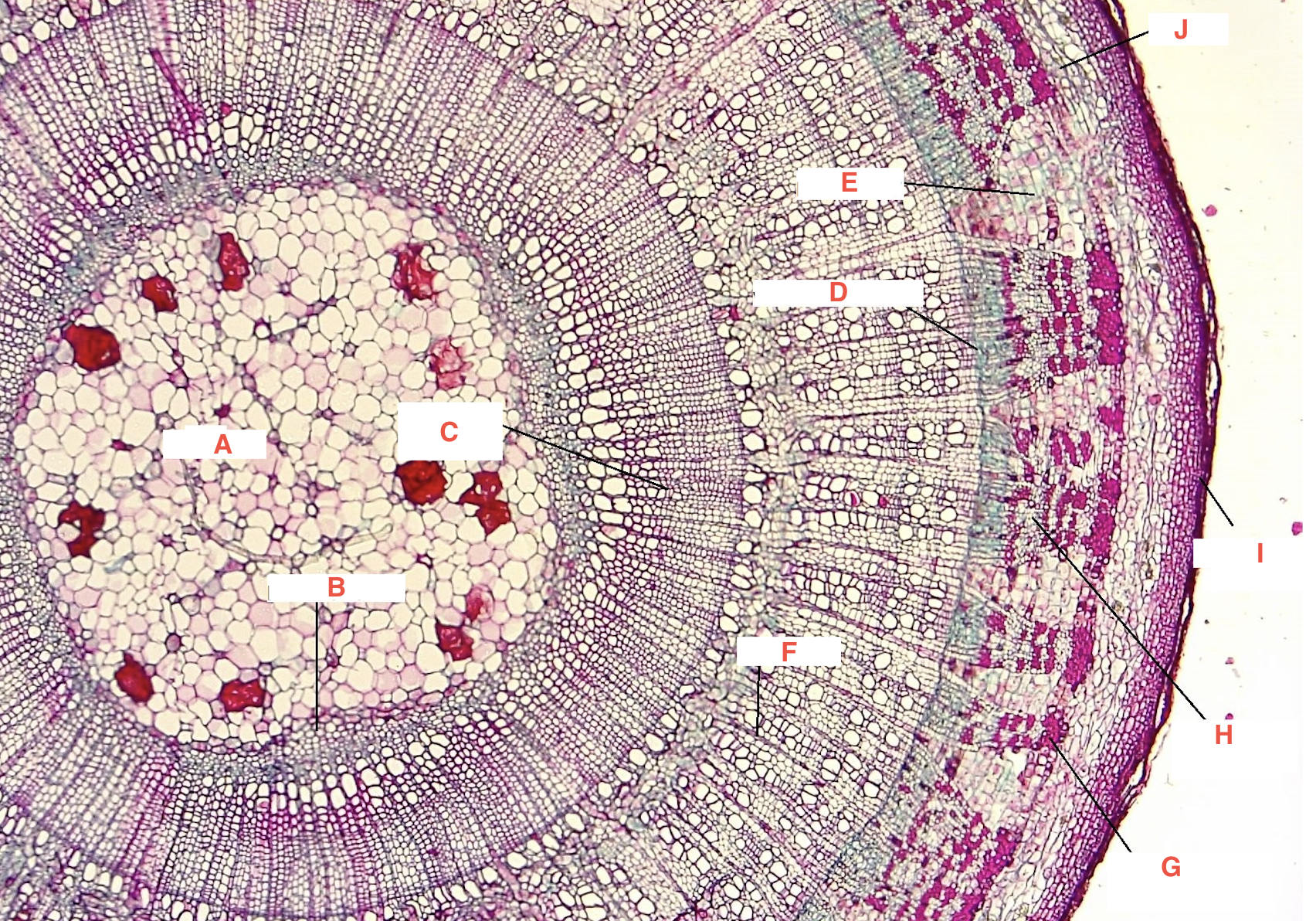
A
pith
C
spring wood
A
summer wood
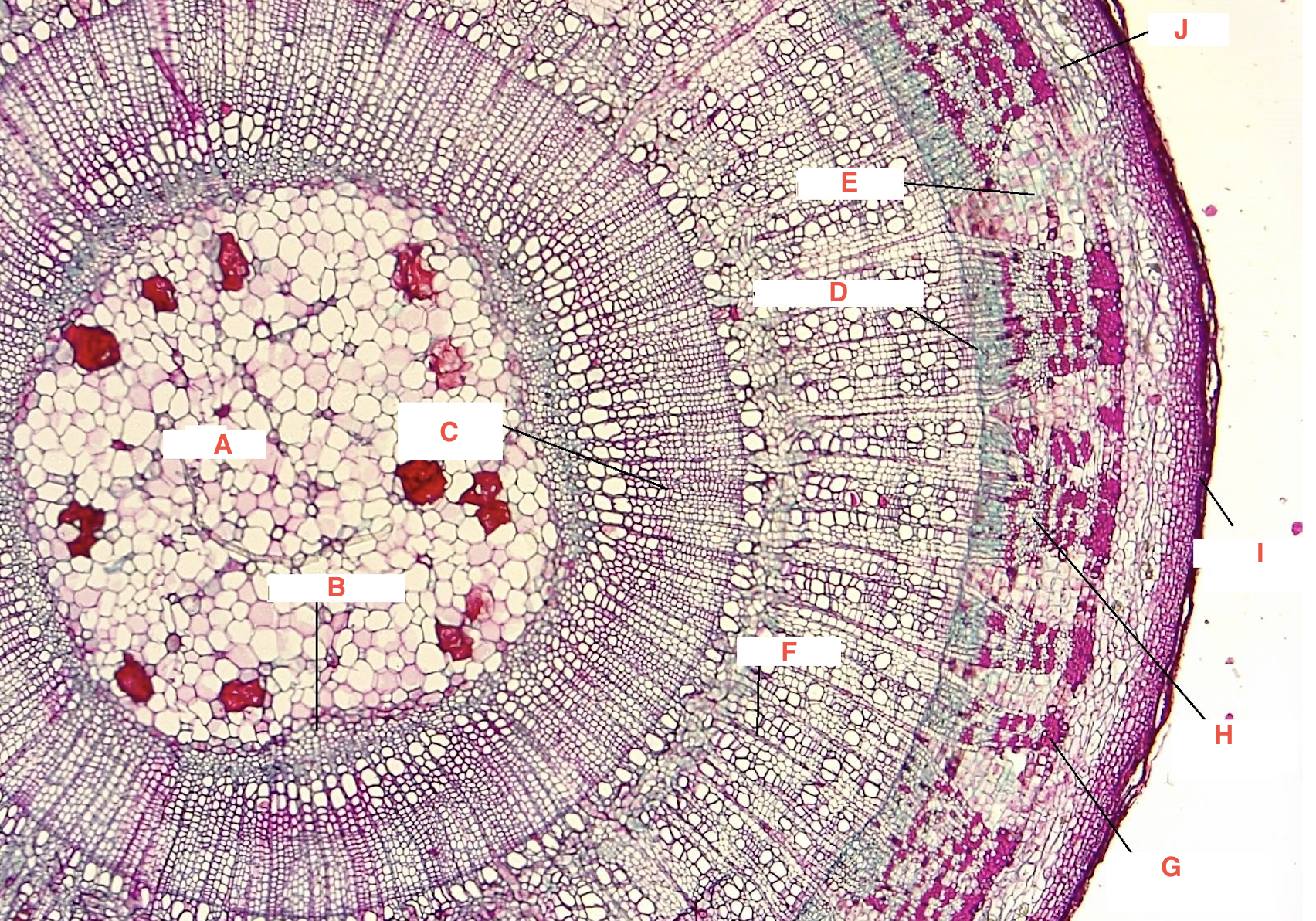
B
primary xylem
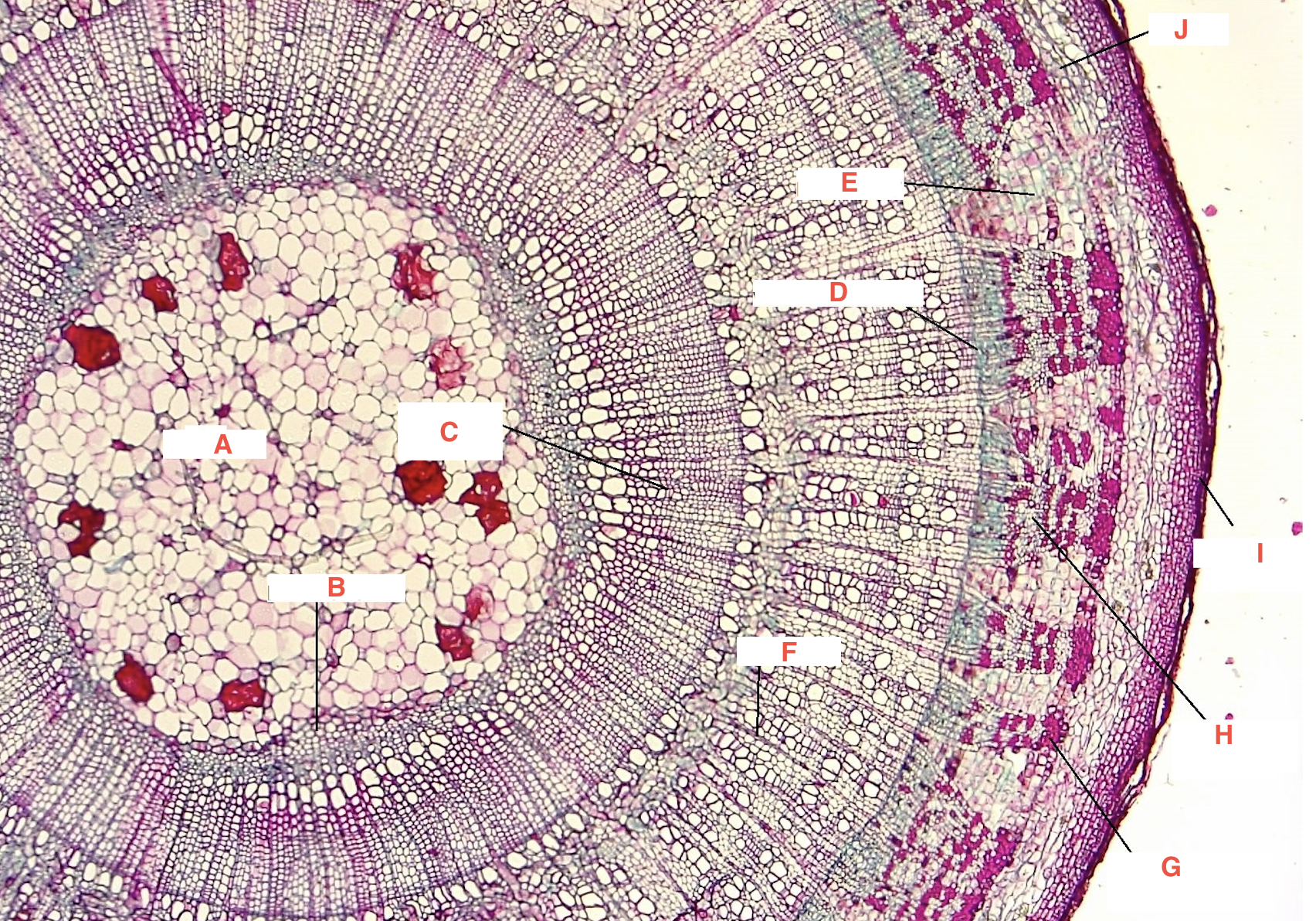
G
phloem
cork cambium
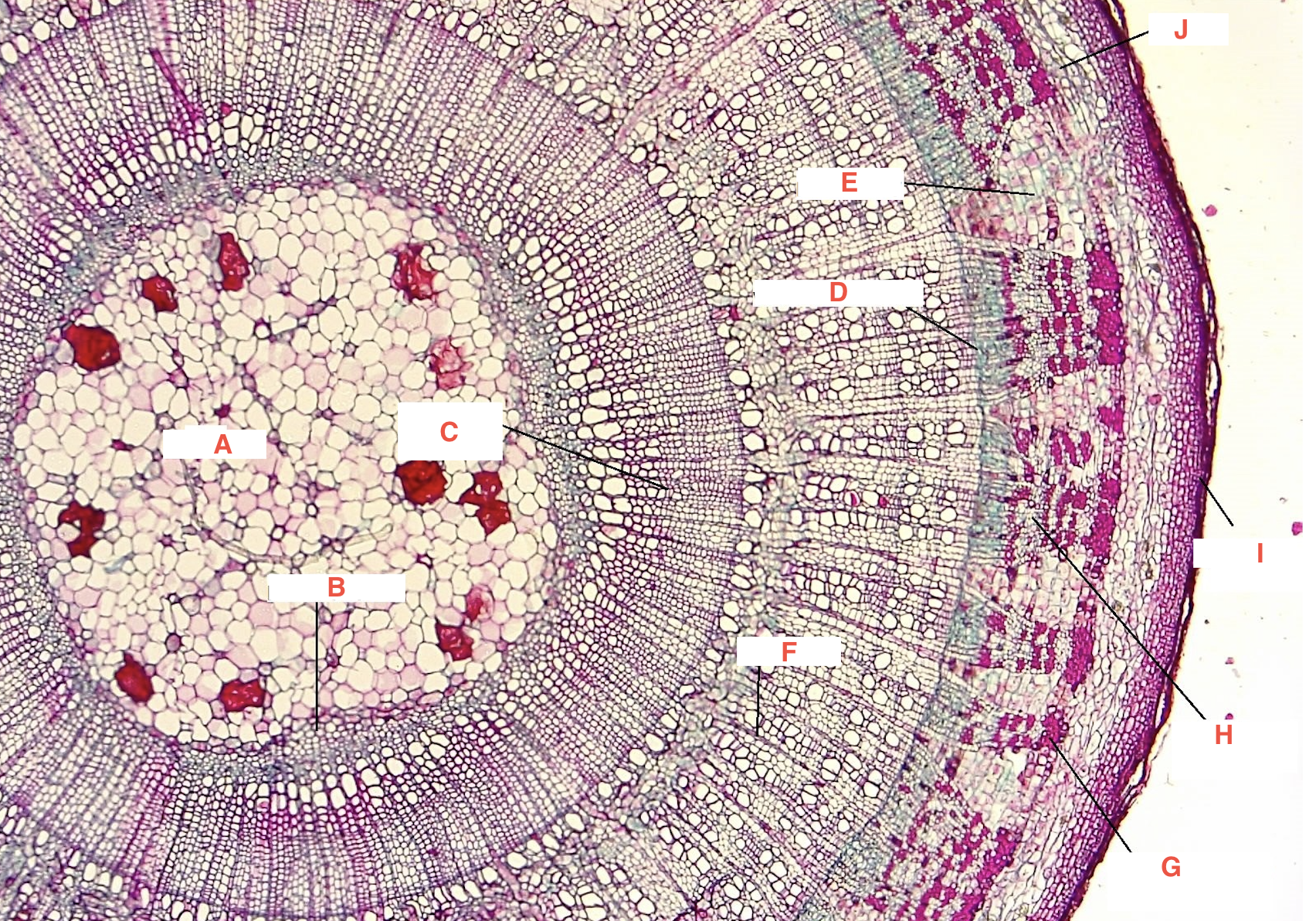
D
vascular cambium
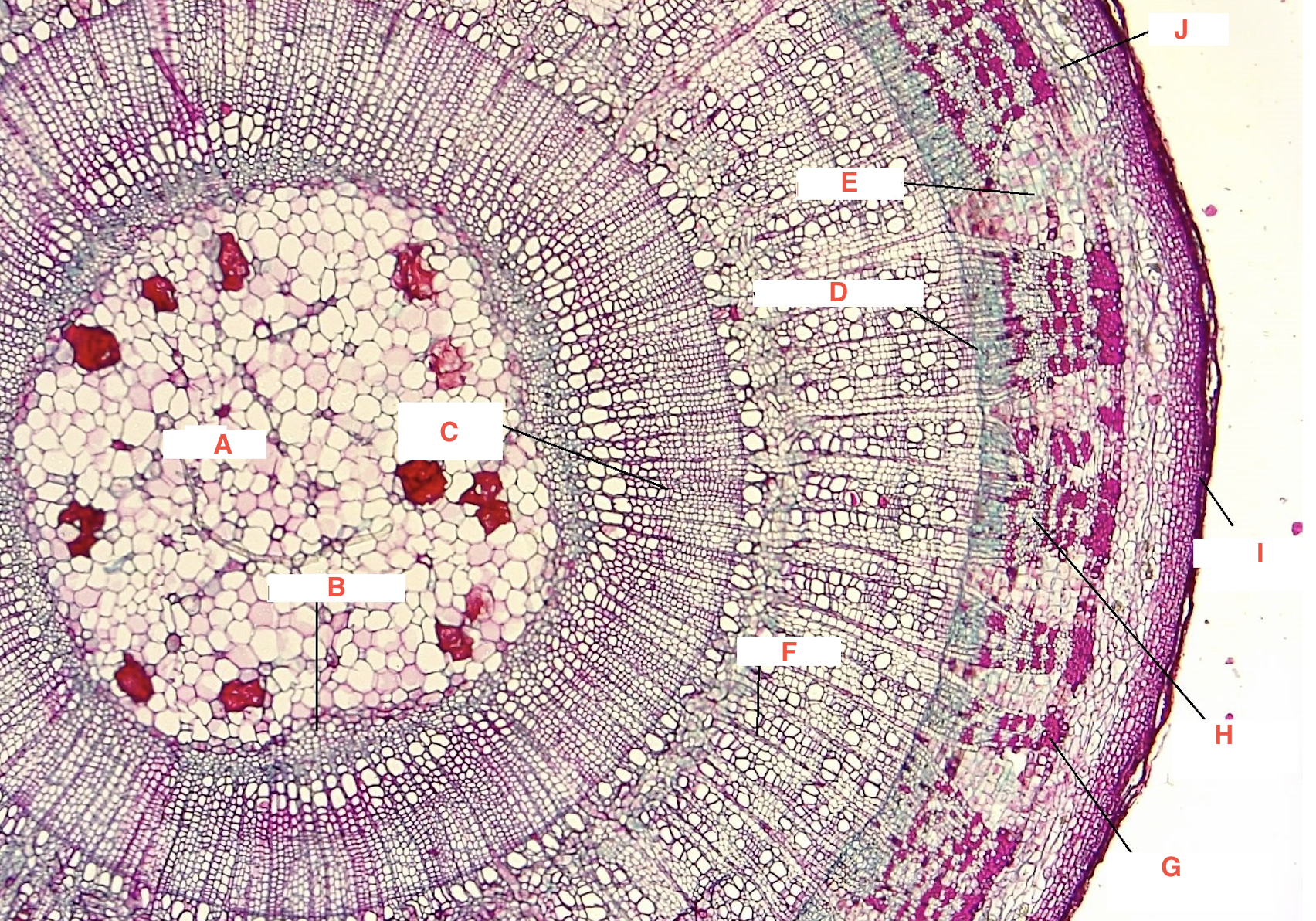
C
secondary xylem
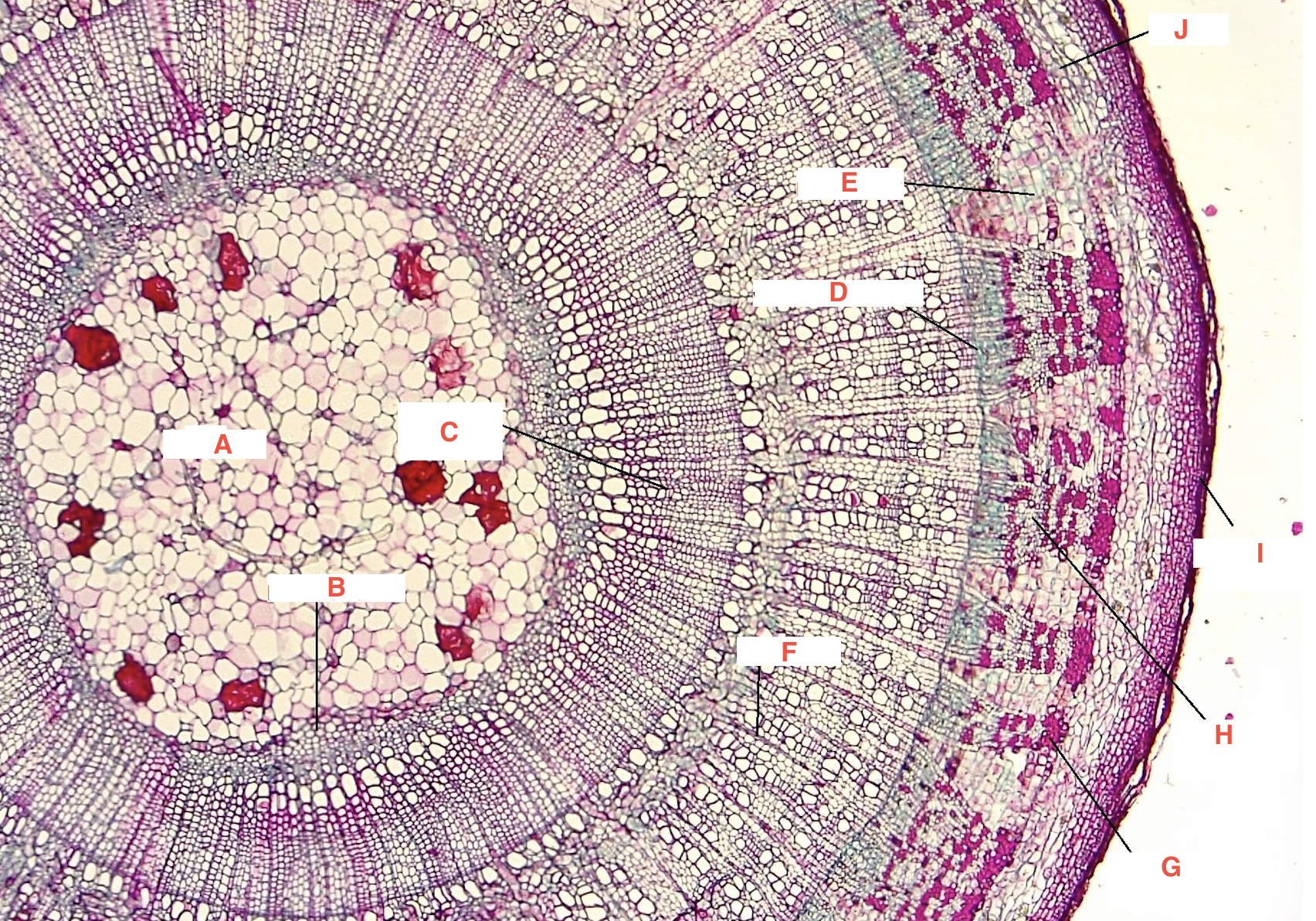
J
cortex
F
xylem ray
E
phloem ray
B
Growth Ring