Experiment C - Extraction
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Extraction
A method for the separation of organic compounds based on
solubility differences between molecules
Performed with two immiscible solvents (one P and one N-P) in a separatory funnel - usually polar aqueous and non-polar organic
2-Naphthol Structure
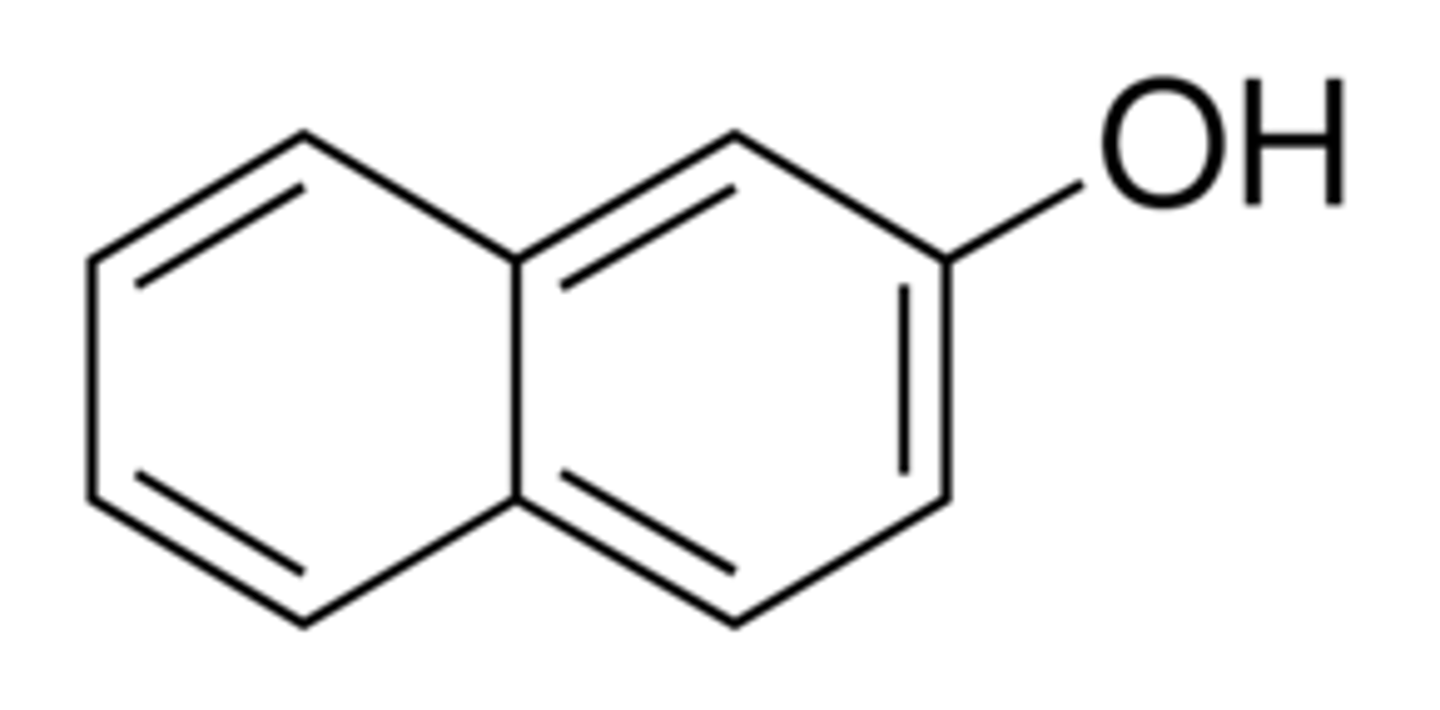
2-Naphthol details
Similar to an alcohol - both have OH group attached to a carbon.
Irritant
The conjugate base of 2- napthol is resonance stabilized (pi bonds in the rings) and thus increases the acidity
Can be deprotonated with a base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form a water- soluble salt, but cannot be deprotonated by a weaker base
such as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
2-Naphthol pKa
9.5
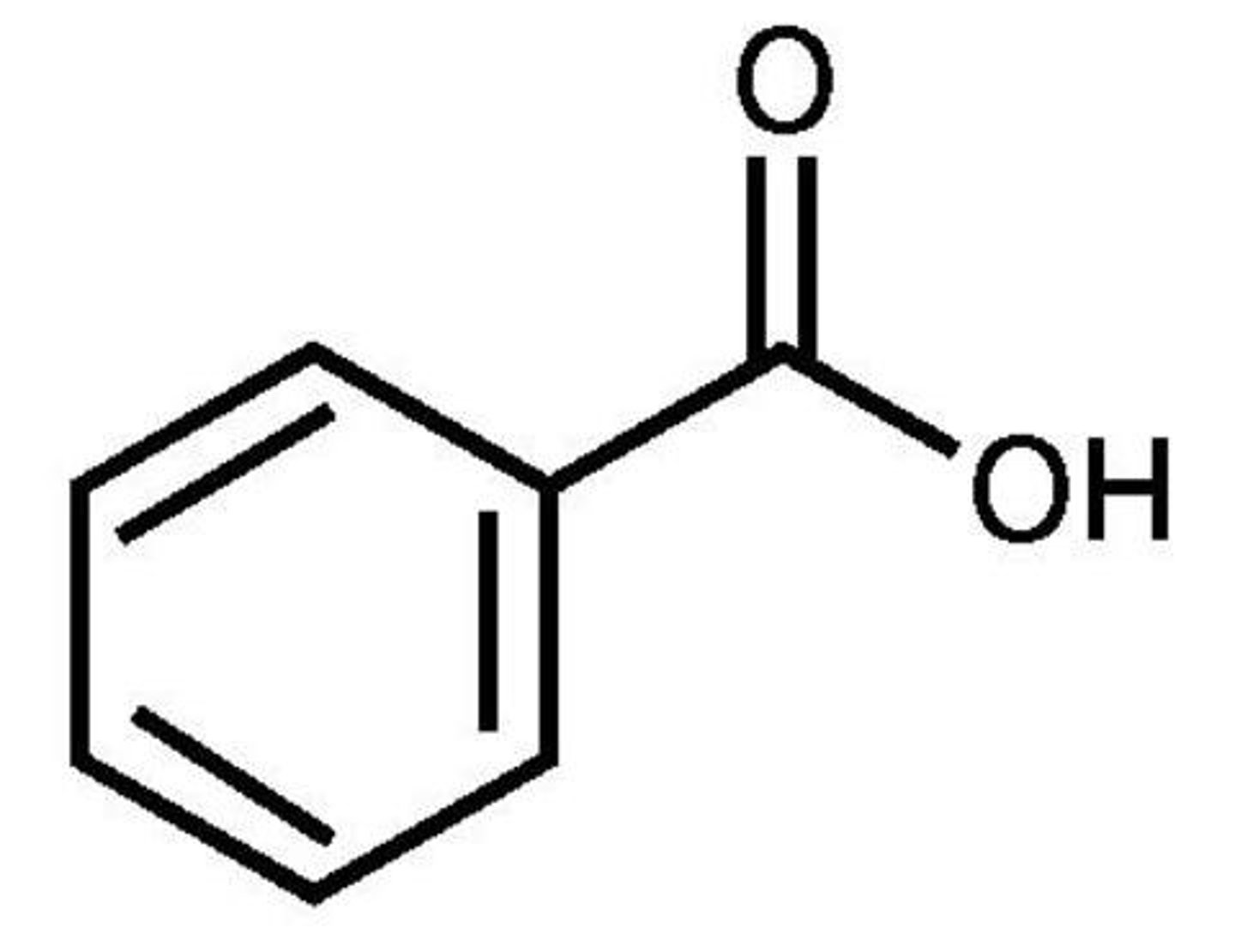
Benzoic acid
Highly acidic - COOH functional group
Won't be removed by a strong acid, use a weak acid instead
Benzoic acid pKa
4.17
tBME
Irritant and flammable
Benzoic acid structure
P-dimethoxybenzene structure
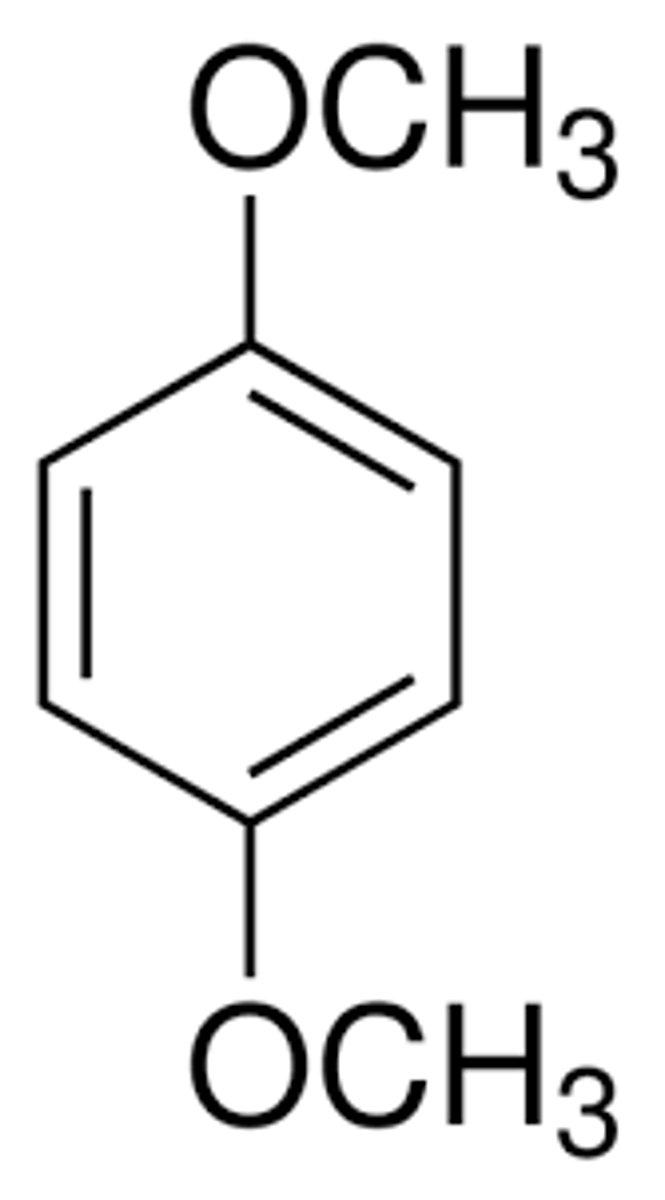
P-dimethoxybenzene details
Neutral compound, irritant
NaOH and HCl
Corrosive and toxic
Summary of extraction
Organic layer: all three compounds will dissolve in this layer (tBME)
Aqueous layer: The conjugate bases of each acid are much more polar species and are thus
water soluble
Extraction of benzoic acid: Using an aqueous solution of the weak base sodium bicarbonate
(NaHCO3), we can remove benzoic acid from the organic layer into the aqueouslayer (as its polar salt) - benzoic acid can then be recovered from the aqueous layer by adding a strong acid like conc. HCl. The sodium salt of benzoic acid will be
protonated to regenerate benzoic acid, which can be collected by carrying out a
vacuum filtration
Extraction of 2-Naphthol: 2-napthol can then be separated from p-dimethoxybenzene present in the organic layer (tBME), by extraction with an aqueous solution of a stronger base, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) followed by acidifying the solution with conc. HCl to regenerate 2-Napthol, which can be collected by carrying out a vacuum filtration
Extraction of p-dimethoxybenzene: the organic layer is treated with a drying agent to remove any traces of aqueous material and later gravity filtered into a preweighed round bottom flask - p-dimethoxybenzene is recovered by placing the flask on a rotary evaporator to remove tBME solvent
Which is more polar, benzoic acid or sodium benzoate?
Which is more likely to dissolve in water?
Sodium benzoate is more polar because of the ionic ONa bond, so it is more likely to dissolve in water
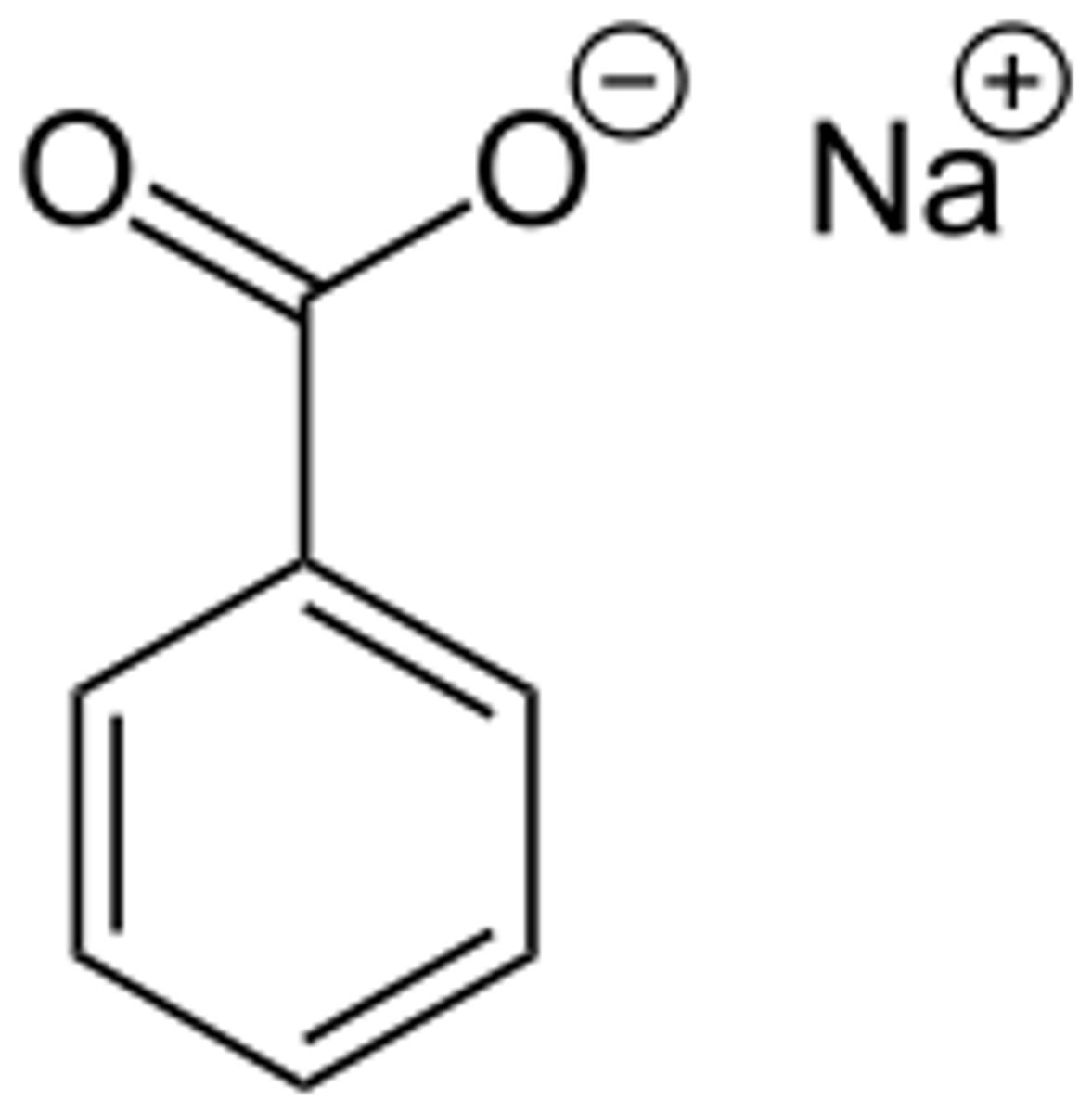
Reaction of benzoic acid and sodium
bicarbonate
Benzoic acid (acid) + sodium bicarbonate (base) --> sodium benzoate (conj. base) + H2O (conj. acid) + CO2
General procedure
1. Obtain 25 mL of tert-Butyl methyl ether (tBME) -
Add this and the 3 solids to the separatory funnel - swirl gently to dissolve.
2. Add 15 mL of 10% sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) solution - swirl/shake with frequent venting --> drain lower aqueous layer into a clean 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask (bicarbonate extract (sodium benzoate))
3. Repeat step 2
4. Add 15 mL of 10% sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution - shake the funnel with frequent
venting - drain the lower, aqueous layer into a clean 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask (labeled
hydroxide extract (sodium naphthoxide))
5. Add concentrated hydrochloric acid (4 pipettefuls - enough to be acidic) to each of the two labelled flasks using a dropper bottle,thoroughly mixing with a clean glass stirring rod.
6. Cool each flask in an ice-water bath,
for 2 min, vacuum filter both, wash with about 1-2 mL of cold water, empty filtrate and continue to pull vacuum - leave to dry for next week
7. Transfer contents of separatory funnel into a 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask - add anhydrous CaCl2 pellets (drying agent)
8. Preweigh a 100 mL round bottom flask.
9. Gravity filter the contents into a 100 mL round bottom flask - place on a rotary evaporator - dry until next week
Following week: weigh 3 solids, calculate % recovery, find melting point ranges - submit your products in correctly labeled vials (as per syllabus instructions) to your TA
Waste Disposal
1. Pour out the COLLECTED Acidic Filtrates into a Specially labeled container "WASTE
ACIDIC FILTRATES".
2. Rinse both the flasks (from Step 5) each with 2-3 mL of Acetone. Pour into container
labeled "Acetone rinsings".
3. Dispose of the drying agent into the Biohazards waste box.
4. Dispose of any used glass pipettes ONLY into the RED SHARPS CONTAINER.
Benzoic acid reaction
benzoic acid + NaHCO3 --> sodium benzoate + H2O + CO2
2-Naphthol reaction
2-Naphthol + NaOH --> sodium phenoxide + H2O
Partition coefficient
K = solubility of solute in organic layer / solubility of solute in aqueous layer
Anhydrous
Ex. Anhydrous MgSO4/Anhydrous CaCl2
Anhydrous MgSO4 will react with water to form the hexahydrate (clumpy solid)
Anhyd. MgSO4 will not entirely remove water layer... (rather - It binds with the water present in the organic solvent).
Add a spatula of anhyd. MgSO4 to the solution in the erlenmeyer flask and swirl...if there is free flowing powder like a snow globe, you have added enough - However, if you still observe clumping in the center of the flask - then you need to continue adding more anhyd. MgSO4