gastric acid secretion ulcers and GORD
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the role of Gastric acid
Aids food digestion
optimises pepsin activity
affects drug absorption
defence mechanism against pathogens-bactericidal
Which cells are found in the small intestine
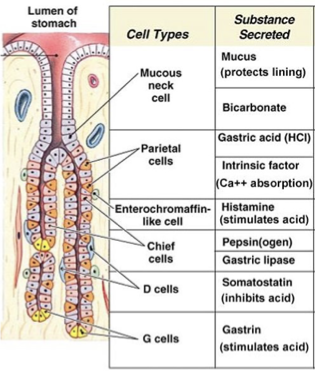
Describe the stomach anatomy
Where is gastric acid produced
parietal cells
forms HCL
stomach pH 2-3
How is HCl produced
CO2 + H20 → H2CO3
H2CO3 dissociates into bicarbonate and H+
H+ is secreted into the lumen in exchange for K+
Using H+/K+ ATPASE
Bicarbonate is secreted into the plasma in exchange for Cl-
Cl- into lumen through ion channels
H+ and Cl- → HCl
Na+/K+ balance restored
What pathways control GA secretion
Neuronal and hormonal pathways
Muscarinic pathway and parasympathetic system
Which hormone controls gastric acid secretion
Histamine
Where is histamine released
Enterochromaffin-like cells
Which cells activate gastric acid secretion
Parietal cell H2 receptors
Control of Gastric Acid Secretion in Parietal Cells step 1

ACh from nerves acting on M3 receptors
stimulated in response to sight, smell, taste of food

Step 2
Histamine from ECL cells acting on H2 receptors
increases H+/K+ ATPase activity

Step 3
Gastrin from G cells
acts on cholecystokinin receptors in ECL
acts directly on parietal cell
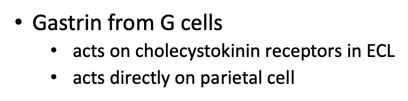
Step 4
PGE2
inhibits HCl release from parietal cells
stimulates bicarbonate secretion

Simulation of Gastric Acid Secretion

Initiated by food in stomach
Reflex stimulation of enteric nerves
G cells directly responsive to foodstuffs

Inhibition of Gastric Acid Secretion

Inhibited by neural and hormonal reflexes
Somatostatin from D cells
Inhibit histamine release from ECL
Directly inhibit parietal cells
Inhibit gastrin release

stage 1 of gastric acid secretion, cephalic phase
Stimulus: Sight, thought, and smell of food.
Pathway:
Cerebral cortex → Conditioned reflex.
Stimulation of taste and smell receptors → Hypothalamus and medulla oblongata → Vagus nerve.
Effect: Prepares stomach for digestion.
Stage 2 Gastric acid secretion, gastric phase
Stimulus:
Stomach distension: Activates stretch receptors via vagovagal and local reflexes.
Food chemicals and pH: G cells respond to peptides, caffeine, and rising pH.
Effect: Gastrin release → Stimulates stomach secretions and activity.
Stage 3 intestinal phase
Stimulus: Low pH, partially digested food, fats, or hypertonic solutions in the duodenum when the stomach empties.
Effect:
Enteric gastrin briefly released to blood.
Slows stomach activity to coordinate digestion in the small intestine.
How does the mucus barrier protect the stomach
Gel polymer of hydrated mucin glycoproteins
Secreted by surface mucous epithelial cells
Generates a continuous alkaline mucus barrier
Protects stomach lining from acid and pepsin
Mucus production under hormonal control

Mucosal damage
If damage occurs
this can have pathological effects
Mucous damaging products are produced more than mucosal protecting products
Peptic Ulcer

Ulceration of stomach and duodenum
Symptoms: heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating
Cause: H.pylori, chronic NSAID use, smoking, stress
Complications: death, gi bleeding,perionitis,cancer
H.pylori
H.pylori damages protective mucus layer
the bacteria colonise the stomach mucosa
Acid passes through weakened mucus layer causing an ulcer
GORD
Symptoms: heartburn, acid reflux, bloating, belchng, pain swallowing
Complications: ulceration, scarring, cancer
doesn’t generate mucus or bicarbonate, contents damage the stomach
H.pylori
thrives in acidic environment
common in population
asymptomatic
How can we treat
Antibiotic therapy
Amoxicillin, metronidazole, clarithromycin
but some resistance
Treatment: Bismuth chelate

Toxic effect on bacteria
Inhibits bacterial adhesion
Inhibits bacterial proteases

Treatment: Antacids
Simple neutralisation of stomach acid
Sodium bicarbonate (Alka Seltzer)
HCO3- buffers H+
Calcium carbonate (Tums, Rolaids)
CO32- buffers H+
Aluminium hydroxide (Gaviscon)
OH- binds H+
Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia)
OH- binds H+

SCAM acronym
not very effective
can affect the absorption of other medications
can be contraindicated
Treatment: inhibit acid secretion
Targets:
Muscarinic antagonists – obsolete
H2 antagonists
Cholecystokinin receptor antagonists
Proton pump inhibitors

Muscarinic Antagonists

M1 selective antagonist eg. pirenzipine
Inhibits vagus-induced histamine release
Non-selective muscarinic antagonist eg. atropine
Also has direct effects on parietal cells

H2 Receptor Antagonists
blocks histamine receptor
eg. cimetidine, famotidine
Histamine released from ECL
H2 receptors on parietal cells

H2 Receptor Antagonists
disadvanatges
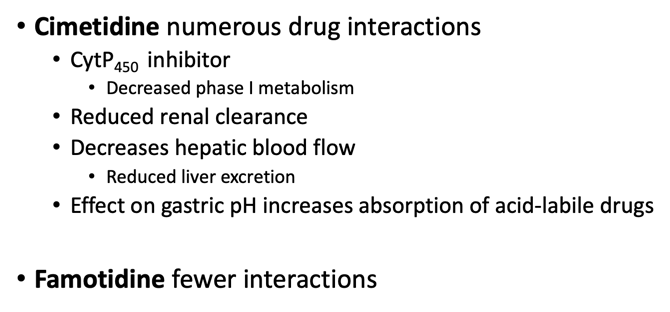
Cimetidine numerous drug interactions
CytP450 inhibitor
Decreased phase I metabolism
Reduced renal clearance
Decreases hepatic blood flow
Reduced liver excretion
Effect on gastric pH increases absorption of acid-labile drugs
Famotidine fewer interactions
PPI profile
Irreversibly block H+/K+ ATPASE in parietal cell
Prevent H+ secretion, inhibits HCl
example: omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole
PPI MOA
Passes through stomach→ enteric capsule
Absorbed in SI into blood
Accumulate in acid environment of parietal cell canaliculi
Activated as pro-drug
Prolonged effect
Irreversibly blocks proton pump
Potassium competitive acid blockers
Don’t need to be activated, much faster than PPI, stable in acid conditions don’t need capsule
Example of PPI
Binds to K+
Inhibit H+/K+ ATPase
eg. vonoprazan

Combination Therapy

PPI plus antibacterial therapy
Decrease acid secretion
Eliminate helicobacter
Combination therapy very effective
Most ulcers heal after 1-2 months

Treatment: Cytoprotective drugs
Enhances mucosal barrier
Alginates: e.g. gavison, forms a barrier between acid and stomach
Sucralfate: Protective barrier at site, stimulate mucus + prostaglandins which act on parietal cells which inhibits HCL secretion
Affects absorption of other meds
Treatment: Prostaglandin agonists
Prostaglandin inhibits HCl
so we use analogues e.g. misoprostol
Effect of Prostaglandin agonists
reduces gastric acid and pepsin secretion via inhibition of ECL cell
stimulates mucus and bicarbonate secretion by epithelium
increases mucosal blood flow by dilator action on arterioles
BUT CAN INDUCE LABOUR
Treatment: NSAID
Block COX, reduces prostaglandins
LEADS to GI irritation
How do NSAIDS affect GI, mechanisms
Direct irritation of stomach lining
Inhibit prostaglandin production via action on COX
Removes cytoprotective effects
Decreases platelet aggregation – increased bleeding
Stomach PG production is mainly by the COX-1 isoform
Celecoxib selective COX-2 inhibitors spare stomach

Achlorhdria
Lack of HCl in stomach
side effect of PPI, surgery, H.P, cancer
PPI
Can affect Vitamin D absrotion
Provide a named example of the drugs
Antibiotics - amoxicillin, metronidazole, clarithromycin
Antacids - sodium bicarbonate (Alka Seltzer), calcium carbonate (Tums, Rolaids), aluminium hydroxide (Gaviscon), magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia)
Muscarinic antagonists – pirenzepine, atropine
H2 receptor antagonists - cimetidine, famotidine,
Proton pump inhibitors - omeprazole (Prilosec), esomeprazole (Nexium), pantoprazole, vonoprazan
Cytoprotective drugs – alginates (Gaviscon), sucralfates, prostaglandin analogues (eg. misoprostol)