Comprehensive Guide to Common Cold Management: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, and OTC Treatments
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the common cold primarily caused by?
Viral infection of the upper respiratory tract.
How many cases of the common cold occur annually in the US?
Approximately 1 billion cases.
What is the leading cause of work and school absenteeism?
The common cold.
What is the most common virus responsible for colds?
Rhinovirus.
What are some other viruses that can cause colds?
Coronaviruses, Parainfluenza, Respiratory syncytial virus, Adenoviruses, Human metapneumovirus.
What happens after the virus binds to the epithelial cell?
It replicates and causes symptoms.
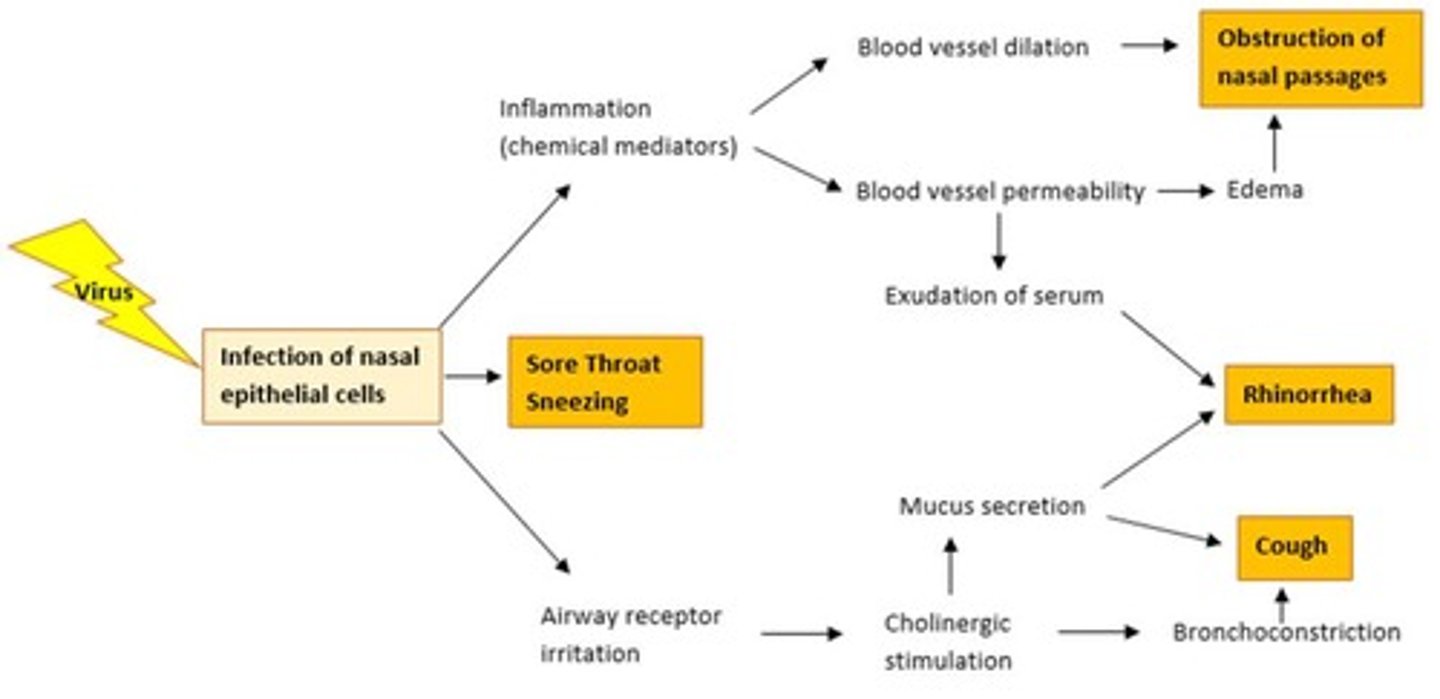
When does peak viral concentration occur after infection?
Between days 2 to 4.
What is the typical duration of cold symptoms?
7 to 14 days.
What are the initial symptoms of a cold?
Sore throat, nasal symptoms, cough.
What is the goal of therapy for the common cold?
Reduce bothersome symptoms and prevent transmission.
What are some non-pharmacologic treatments for colds?
Increased hydration, adequate rest, nutritious diet, saline nasal sprays, humidification.
What is the mechanism of action for decongestants?
Stimulate alpha adrenergic receptors to constrict blood vessels, decreasing mucosal edema.
What is a common oral decongestant?
Pseudoephedrine.
What are first-generation antihistamines known for?
Causing sedation and drowsiness.
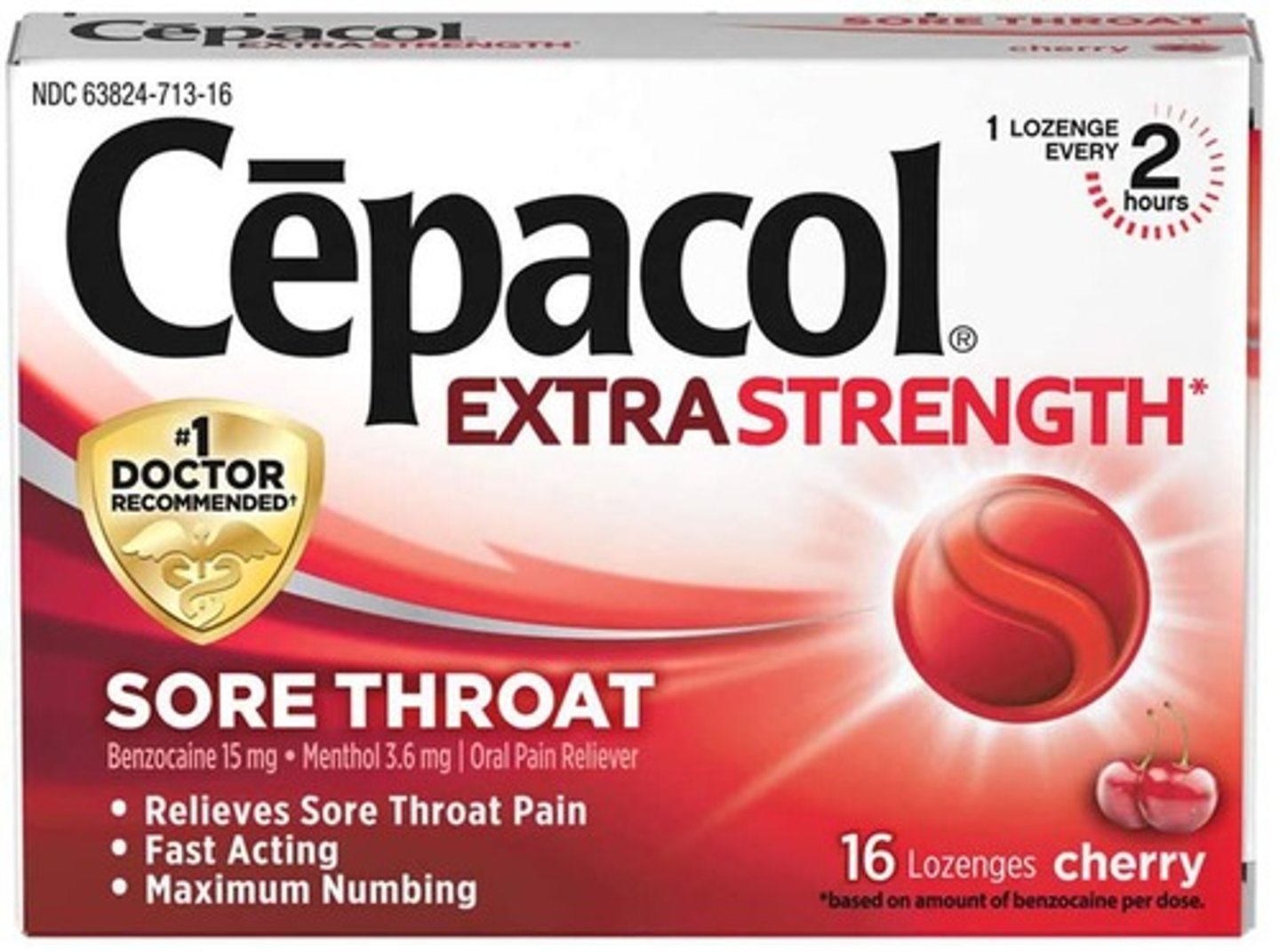
What is a common cough suppressant?
Dextromethorphan.

What is the role of inflammatory mediators in cold symptoms?
They activate neurogenic reflexes and cause symptoms like sneezing and nasal fluid hypersecretion.
What is the typical temperature associated with a cold?
No higher than 100.4°F.
What are some common physical assessment findings in a cold?
Slightly red pharynx and tender sinuses on palpation.
What is the role of IgA and IgG antibodies in a cold?
They end viral replication and resolve the infection.
What is the effect of cholinergic nerves during a cold?
Stimulate vasodilation and increase blood flow.
What are some examples of non-pharmacologic treatments for sore throat?
Salt gargles and warm broths.
What is the typical onset of cold symptoms after infection?
1 to 3 days.
What is the half-life of Sudafed 24 hour?
6 hours
What is the recommended dosage of Ephedrine nasal drops?
2 - 3 drops/sprays in each nostril no more than every 4 hours
What is the maximum dosage for Oxymetazoline nasal spray?
2 doses per day, with 2 - 3 drops/sprays in each nostril no more than every 10 - 12 hours
What are common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) of decongestants?
CV stimulation (elevated BP, tachycardia, palpitations, arrhythmias) and CNS stimulation (restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, tremors, fear, hallucinations)
What is rebound congestion?
A condition that can occur after using topical decongestants for multiple days, leading to worsened congestion
What is the difference between first-generation and second-generation antihistamines?
First-generation antihistamines are sedating, while second-generation antihistamines are better tolerated and often non-sedating.
Name two first-generation antihistamines.
Diphenhydramine and Doxylamine
What is the risk associated with using aspirin in children and teens?
Risk of Reye's syndrome, especially if used during a viral illness
What are common analgesics used for pain and fever?
Aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen
What is the recommended use for benzocaine lozenges?
Can be used every 2 to 4 hours for sore throat relief
What is the purpose of antitussives?
To suppress cough
What is the purpose of protussives?
To make cough more effective by loosening mucus in productive cough
What is the maximum dosage for Guaifenesin?
120 mg/24 hours
What is required for codeine-containing cough products in Texas?
A prescription is needed regardless of the concentration
What should be avoided in pregnancy regarding cold medications?
Avoid extra strength, max strength, long-acting products, and systemic decongestants
What is the recommendation for breastfeeding mothers regarding certain medications?
Pseudoephedrine, dextromethorphan, guaifenesin, benzocaine, camphor, and menthol are generally considered okay.
What special considerations should be taken for geriatric patients using decongestants?
Caution is advised due to higher likelihood of cardiovascular disease and hypertension.
What is the role of zinc in treating colds?
High local concentrations may block rhinovirus adhesion and inhibit viral replication.
What effect does high-dose vitamin C have on colds?
It does not prevent colds but may reduce their duration by approximately 8% in adults and 14% in children.
What is the potential benefit of echinacea for colds?
There might be a small benefit in prevention and treatment, but data is conflicting.
What is the effect of elderberry on colds?
It does not prevent colds but may reduce their duration by about 2 days and severity by about 58% compared to placebo.
What is the key takeaway regarding the treatment of colds?
Colds are self-limiting; treatment should focus on symptomatic care with only necessary ingredients.