Core Concepts-L16-Effector Mechanism of T cells
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
explain CD4 T helper differentiation
driven by signal 3 cytokines from APC
JAK/STAT pathways activate master transcription factors
Th-1- Tbet
Th-2-GATA3
Th18- ROR gamma t
BcI6- Tfh
naive CD8- what do they require? what do they do?
signal 1-TCR-MHC I
costimulation-CD28 to CD80/86
cytokine polarisation
use perforin and granzymes or Fas-FasL pathways
how are T cell responses regulated?
CTLA-4 and PD-1 are inhibitory receptors
cytokines always modulate responses- IL-10, TGF beta
talk about the phases of cell mediated immunity
induction of response by antigen recognition in the lymphoid organs
T cells expansion and differention
differentiated effector T cells enter circulation
migration of effector T cells and other leukocytes to site of the infection
effector T cells encounter antigens in peripheral tissues
activation of effector T cells
how do T cells enter and exit?
naive T cells are always circulating
cross the high endothelial venues and need homing molecules
CCR7(guides it to the lymph node) senses CCL21 and L selectin- allows rolling
receive survival signals
uses S1P gradient to leave via efferent lymph
how do effector T cells stay in lymph nodes etc?
held in the lymph node to allow differentiation and clonal expansion
down regulate CCR7(keeps it in the lymph node) and S1PR to bring them into circulation
expression of adhesion molecules like E/P selectin to roll and bind loosely
VLA-4 for firm adhesion
types of memory in T cell?
memory central- Tim- circulate through lymph nodes express CCR7 and L selectin
effector memory- patrol peripheral tissue
explain the CD8 function and the phases
viruses replicates in tissues, DC’s detect via TLR3/7 became activated. up regulation of CCR7 to bring it to lymph nodes
viral proteins are processed by proteasome and transported via TAP loaded onto MHC I
3 signals- cytokine support by IL-2 proliferation from CD8 and Th1 cells enhances proliferation
differentiation and effector function of T cells
Th1- IL-12, IFN gamma- activate macrophages and help CD8
Th2- IL4- combat parasites and allergy responses
Th17- IL6- TGF beta and recruit neutrophils
Th1 effector functions and the steps
cytokine secretion- IFN gamma to activate macrophages and enhance killing and supports CD8 T cell differentiation
B cell hel- B cell present antigens on MHC II and secretes IFN- gamma and helps with class switching
trafficking to tissue- Th1 leaves efferent lymph to tissue
macrophages present MHC II and Th1 binds and costimulates with CD40(macro) and CD40L on Th1 and cytokines by Th1 amplify activation
IFN gamma from Th1 activates macrophages killing mechanisms like reactive oxygen/nitrogen, phagosome/lysosome fusion
how are parasites/helmith get treated?
pathogen is detected by DC, it is processed and up regulate CCR7 to migrate the the lymph nodes and present MHC II to CD4 naive T cells
polarising signals like iL-4 from DCs- activate STAT6 and triggers GATA3 TF to make Th2
proliferation by IL-2
B cells will recognise antigens and become activated and present to Th2 cells which helps with IgE and IgG antibodies
TH2 cells!!
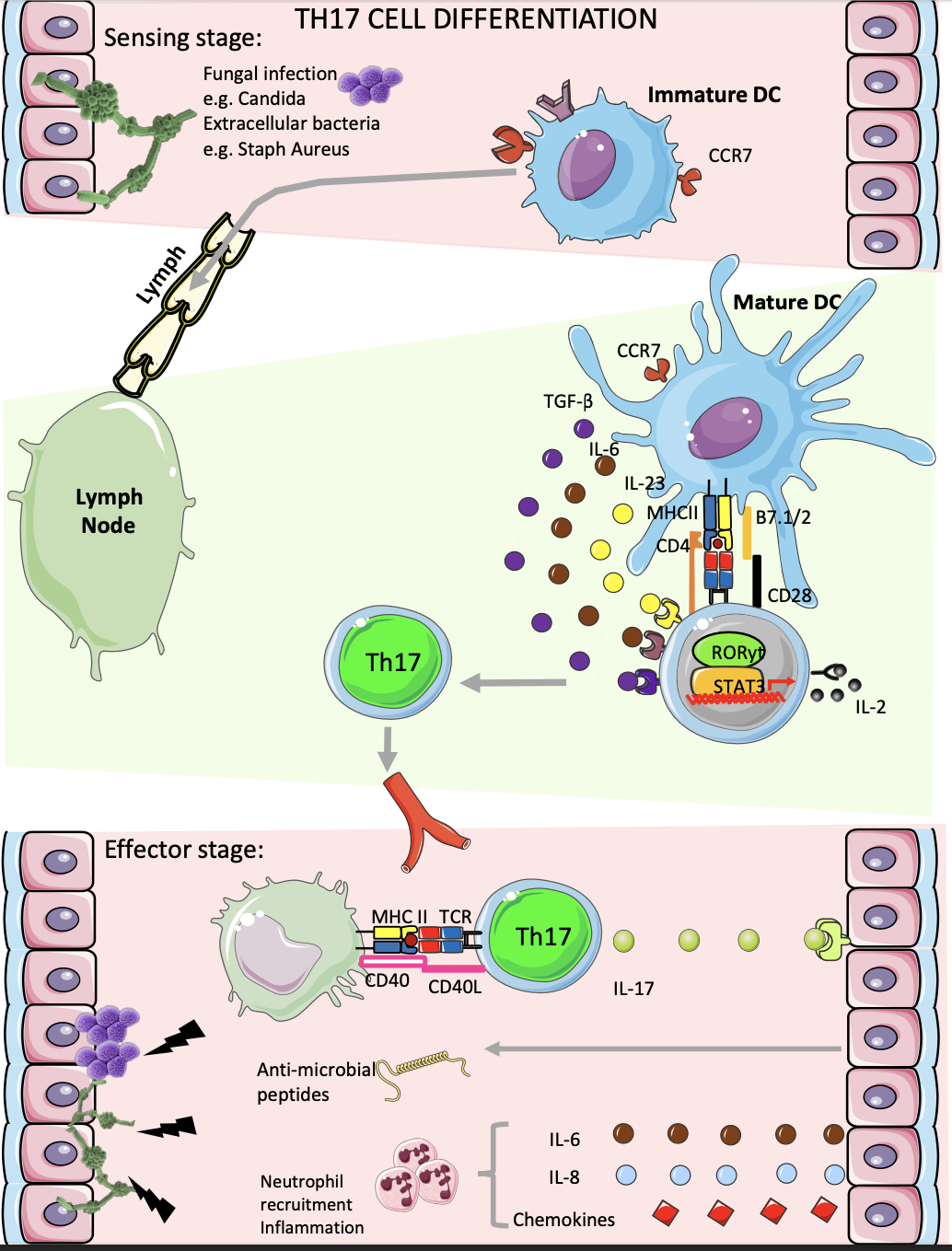
how are extracellular bacteria and fungal infections dealt with?
Th17 cells
activated by DC present antigen to MHC II
polarising cytokines like TGF-beta, IL6,IL-23 to activate STAT3 to induce RORgammaT
make IL-17 cytokines- induces antimicrobial peptides and chemokine like IL-8/IL-6 for neutrophil recruitment
what do Tfh cells do? what type of cells are they?
isnide- B cell follicles in lymphoid organs
help b cells during germinal centre and help with class switching
make IL-21