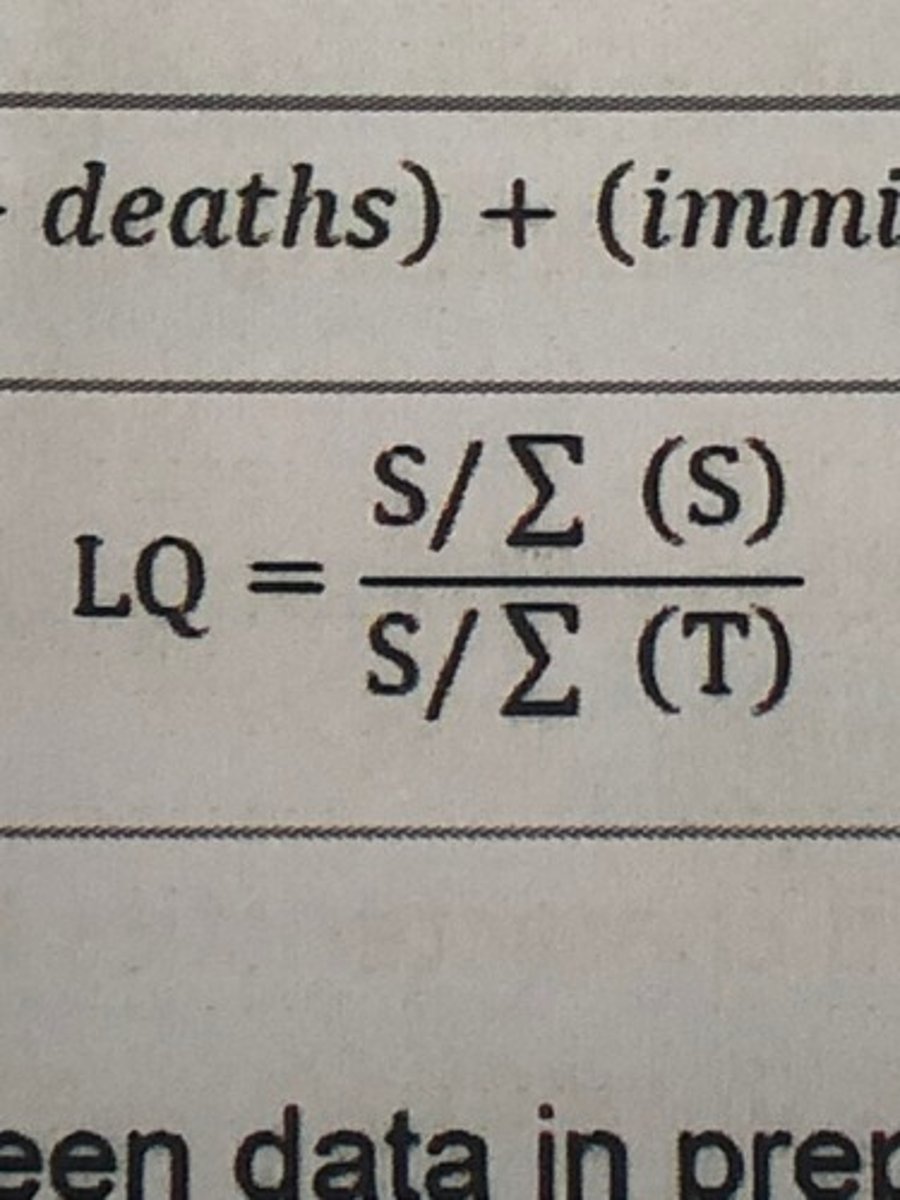Geography EA Revision QCAA
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
Natural change
the difference between birth rate and death rate, expressed as a percentage
Natural decrease
When the number of births is lower than the number of deaths
natural increase
the growth rate of a population; the difference between birthrate and death rate
population growth
increase in the number of people who inhabit a territory or state
population growth rate
explains how fast a given population grows
birth rate (crude birth rate)
the number of live births per 1,000 members of the population in a year.
death rate (crude death rate)
is equal to the number of deaths per 1,000 members of the population in a year.
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
population density
Number of individuals per unit area
Annual population growth rate
The rate at which a population is increasing owing to natural increase and migration - birth rate minus death rate plus or minus migration
Ageing population
a population with a rising average age
dependent population
those people that rely on others for support for the goods and services they consume, usually the very young and very old
dependency ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
Human Development Index (HDI)
Indicator of level of development for each country, constructed by United Nations, combining income, literacy, education, and life expectancy
maternal mortality
death of a mother during pregnancy, childbirth or within six weeks of delivery
Migration
Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location.
net migration
The difference between the level of immigration and the level of emigration.
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate.
pull factors
Factors that induce people to move to a new location.
push factors
Factors that induce people to leave old residences.
population flow
the total aggregate count of people who entered a country
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but has not migrated across an international border
asylum seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country in the hope of being recognized as a refugee
refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
Emigrant/emigration
A person who leaves a country or region to live elsewhere.
Immigrant/Immigration
people who travel over borders of different countries
slum
a district of a city marked by poverty and inferior living conditions
Shanty Settlements
areas of homemade housing with scavenged materials
Ghettos
Sections of towns and cities in which Jews were forced to live.
migrant worker
a person who moves from place to place to find work
Urbanisation
Increase in the proportion of the countries population living in towns and cities
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
Population Density Formula
total population ÷ total land area
Curde birth rate formula
Births per 1000 = (births per year ÷ total population) x 1000
Crude death rate formula
Deaths per 1000 = (deaths per year ÷ total population) x 1000
Rate of natural increase as a percentage formula
(CBR - CDR) x (100 ÷ 1000)
Net migration formula
Immigration number - emigration number
Total population growth formula
Population + (births - deaths) + (immigration - emigration)
Location Quotient (LQ) formula