Intro to Biochemistry
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4/9/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
living organisms are composed of about
25 chemical elements
what four elements make up the bulk of living matter?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
mass number
at the top in atomic standard notation
protons + neutrons
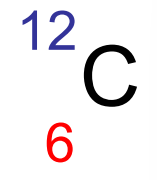
atomic number
at the bottom in standard notarion
# of protons
# of electrons if neutrlal
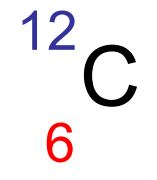
isotopes
atoms of an element that have different number of neutrons
radioisotopes
isotopes that emit radiation when decaying; radioactive
used in carbon dating: measuring the decay of carbon-14 (radioisotope) to determine age of sample
what holds compounds together?
intramolecular forces
intra meaning within - between atoms in a compound
ionic bond
nonmetal and metal
form molecules
covalent bond
two nonmetals
sharing of electrons
non polar and polar
nonpolar: equal electron sharing, Cl-Cl
polar: unequal electron sharing, H-Cl
polarity gives macromolecules its characteristics
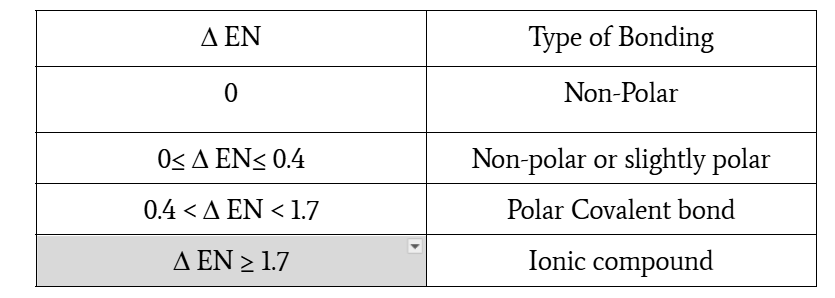
EN differences and bond type
0≤ Δ EN≤ 0.4, non-polar or slightly polar
0.4 < Δ EN < 1.7, polar covalent bond
Δ EN ≥ 1.7, ionic compound
intermolecular forces
forces between molecules/ molecules and ions
much weaker than intramolecular forces
types of intermolecular forces
london dispersion: in all molecules and atoms
dipole-dipole: in polar molecules
hydrogen bonding: in molecules containing hydrogen bonded to F, N, or O
ion-dipole: mixtures of ionic compounds and polar compounds
london dispersion forces
also called van der waal’s forces
weakest force
all molecules contain them
nonpolar molecules
ex. H2, O2, Cl2, CH4
dipole-dipole forces
exist between polar molecules only
slightly negative and slightly positive sides of dipoles interact with each other
ex. HCl
hydrogen bonds
exist between polar molecules that contain H-F, H-O, or H-N nonds
F, O, N are the most electronegative elements
ex. H2O, HF, NH3
ion-dipole
very strong due to fully charged ion
between fully charged ion and polar moelcules
ex. Na+ and H2O
stronger forces =
higher melting point
higher boiling point
why does H2O have a higher boiling point than CH4?
water has hydrogen bonding, which is strong intermolecular force
methane is nonpolar and only has weak london dispersion forces
stronger forces in water require more energy (higher temperature) to break
a single CO2 molecule is held together by
intramolecular covalent bonds
dipole-dipole forces occur between
polar molecules
Ion induced dipole
Prescience if ion induces a temporary dipole in a non polar molecule