Control & Coordination Revision
==Chapter 2.1 & 2.2==
Multi Cellular Organisms:
- Cells make up tissue
- Tissue form organs
- Organs are part of systems
- Systems make up an organism
Multi Cellular Organisms → Systems → Organs → Tissues → Cells
Cells: The smallest structural unit of living organisms
Organs: Different types of tissues grouped together to perform a particular function
System: Different organs working together to achieve a specialized function to keep an organism working.
Tissue: A collection of similar cells that perform a particular function.
Homeostasis:
- The maintenance of your constant internal environment, this includes temperature, pH, glucose and water.
- Any change (stimuli) in the internal environment needs to be detected (by receptors) so the body can respond.
- If a response is required this needs to be communicated to effectors, so a change can be made so the internal environment can be returned to normal.
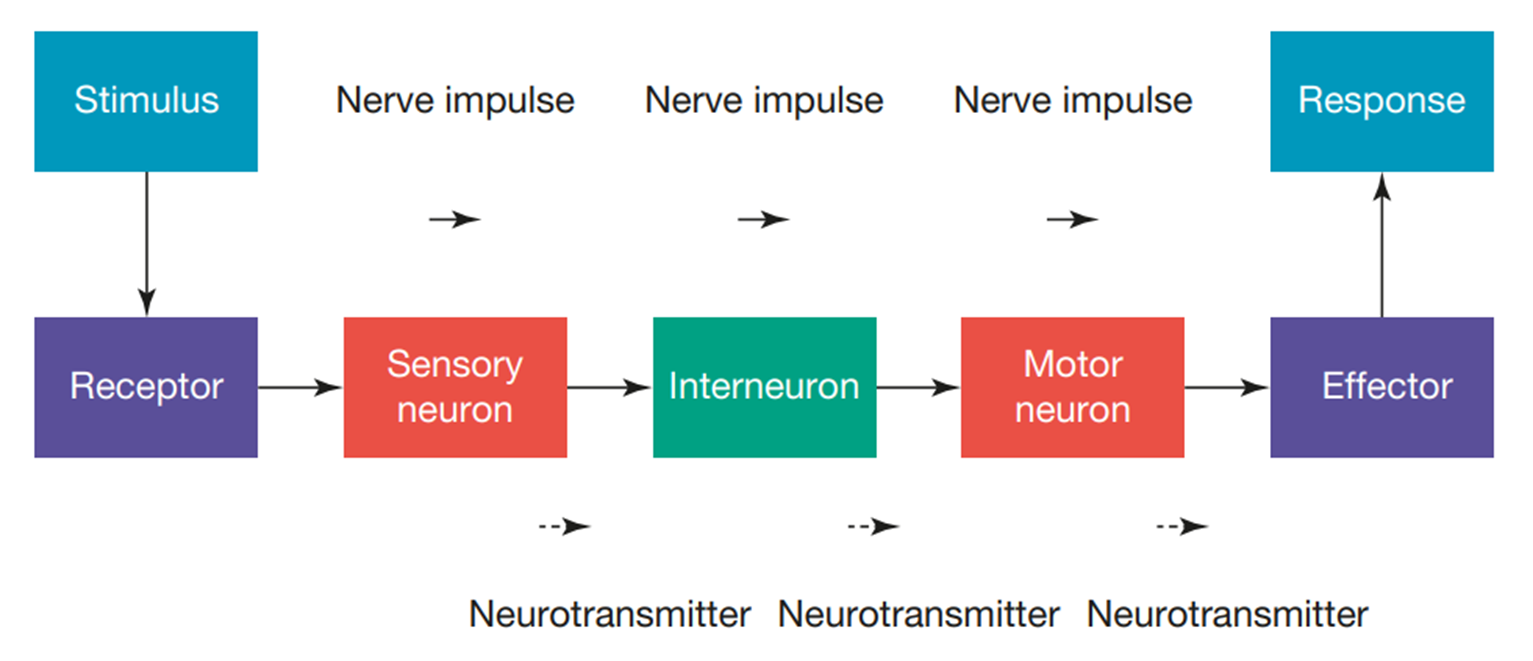
Stimulus-response model:
Stimulus → Receptor → Control Centre → Effector → Response
Stimuli: anything your body needs to respond to. This can be external e.g. something dangerous or it can be internal e.g. blood sugar.
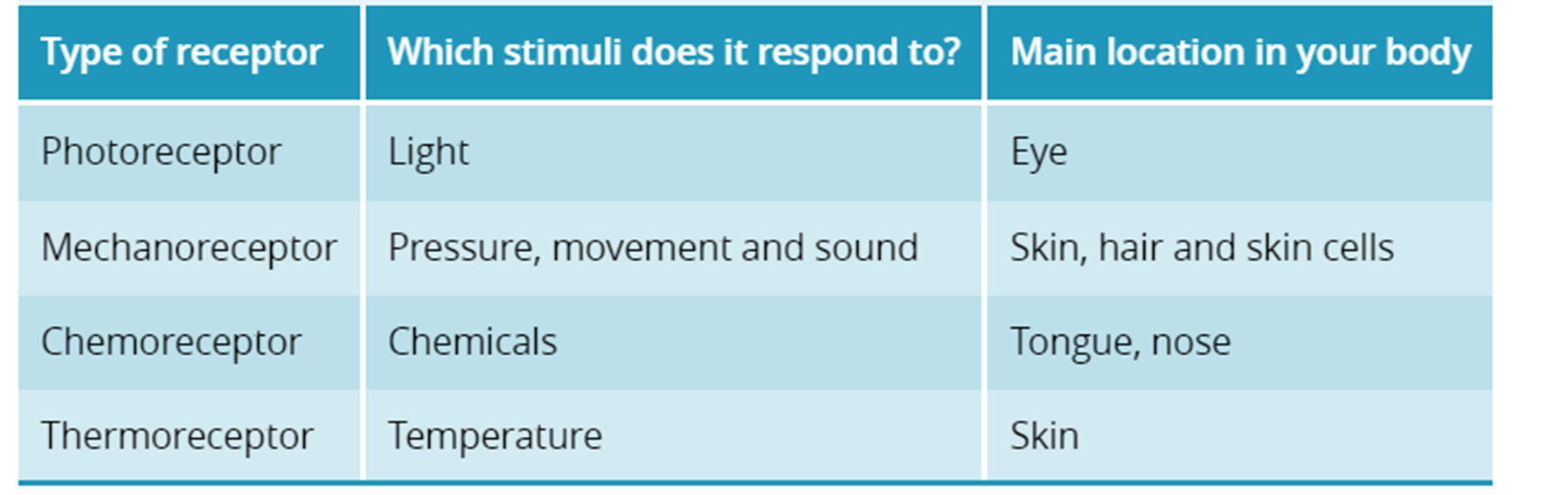
Receptors: Identify changes inside or outside the body. There are different specialized receptor cells in different body parts, e.g. photoreceptors in the eye detect light, and thermoreceptors in the skin detect temperature.
 Control Centre:
Control Centre:
- Once the stimulus is detected by the receptor a message is sent from the receptor to the brain.
- The brain is the control center.
- Here the message is processed, and the brain then decides how best to respond.
- Then a message is sent to the effector.
Effectors: receive messages from the brain e.g. muscles or glands. Give the body’s response to the original stimulus e.g. if you are hot sweat glands produce sweat.
Stimulus → Receptors → Sensory neuron → Relay Neuron → Brain → Motor neuron → Effector → Response
e.g. Heat from the sun → Thermoreceptor → Brain → Effector glands → Body sweats
Types of Feedback:
Negative Feedback: Something that will go up and down and try to stay in an optimal range. e.g. blood pressure, body temperature.
Positive feedback: Only decreases/Increases and will have more and more or less and less. e.g. childbirth, ovulation.
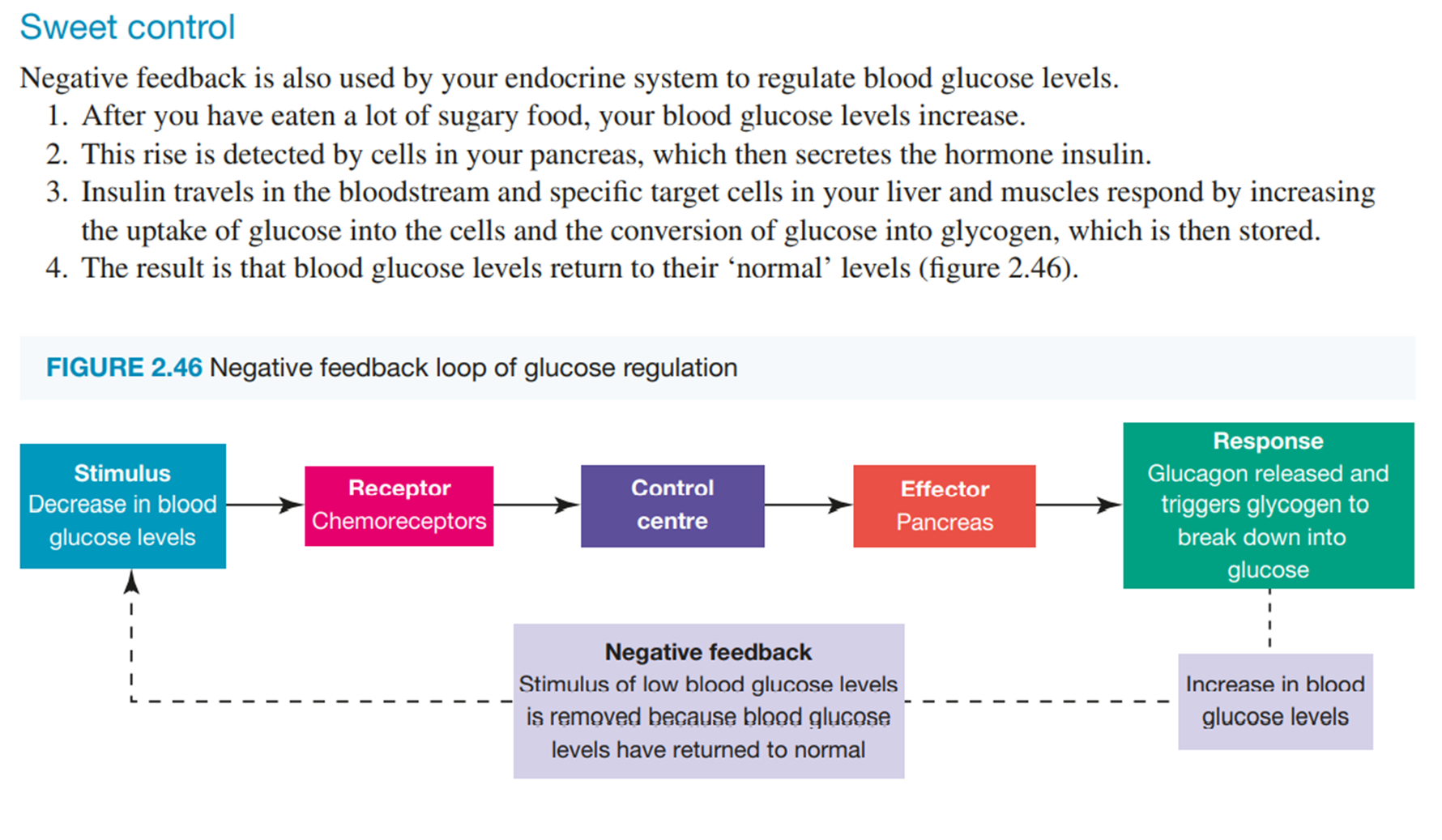
Glucose & Negative Feedback:
- regulating glucose (blood sugar levels) in your body involves negative feedback.
- If an increase of glucose is detected the pancreas responds by releasing insulin.
- Insulin triggers the liver to uptake glucose and store it for later.
This then lowers the blood glucose levels.
Stimulus (increase in blood glucose level) → Receptor (chemoreceptor) → Control Center → Effector (Pancreas) → Response (Insulin released and triggers glucose uptake from cells and storage as glycogen)
==Chapter 2.3 - Nervous System==
Nervous system: responsible for all we think, do, and feel.
3 Main functions:
- receive information
- process information
coordinate a response to information
- Essentially the nervous system is the body’s communication system
- It allows messages to travel all over the body
- Messages will either be sent from:
- the body to the brain
- the brain to the body
- Made of special cells called neurons
2 Parts of the Nervous System:
- central nervous system - made of the brain and spinal cord
- peripheral nervous system - made of all other nerves in the body
Neurons - specialised cells:
specialised cells that make up the nervous system as called neurons
join together to make nerves
these nerves pass messages all around the body
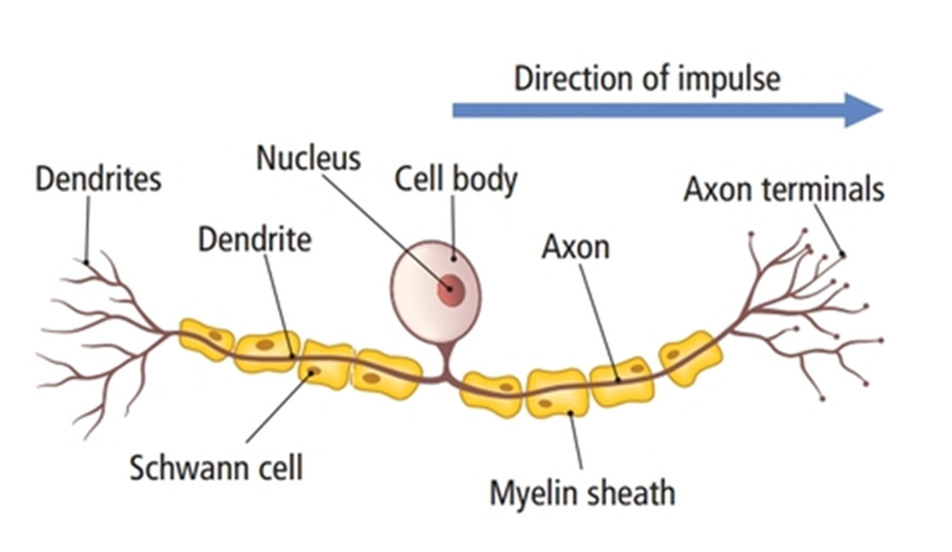
Parts of a Neuron:
Dendrite: receive messages from other neurons and pass the message on to the soma
Soma: Cell body, contains the nucleus
Nucleus: Cell control centre
Axon: carries electrical message from the soma to the axon terminal
Axon terminal: The end of the axon, release chemicals called neurotransmitters, into the synapse
Synapse: The space between neurons.
Why is there space between neurons?
neurons do not touch, instead there is a space called the synapse between neurons.
Because they don’t touch they need something to cross the spare (synapse) between them.
Chemicals called neurotransmitters cross the synapse and communicate messages from one neuron to the next.
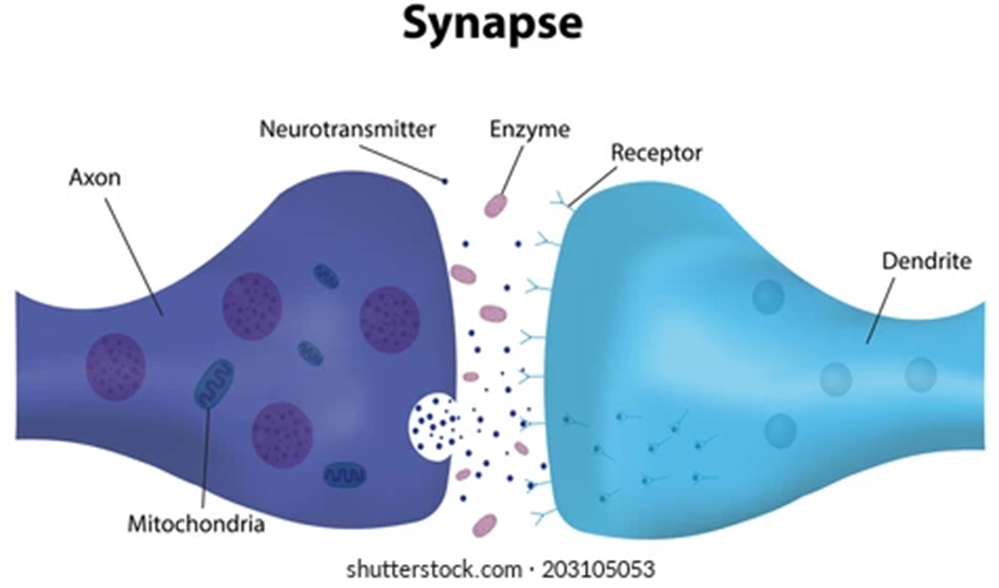 Electrochemical messages:
Electrochemical messages:messages in the nervous system are called electrochemical messages, this is because:
- Inside the neuron the messages travel as an electrical impulse
- Outside the neuron the message travels as chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Stimulus → Dendrite → Cell body (nucleus) → Axon
Types of neurons:
- sensory neurons
- motor neurons
- interneurons
Sensory Neurons:
- carry messages from the body to the brain
- Takes messages from the 5 senses to the brain to be processed
Motor Neurons:
- Carry messages from the brain to the body, including muscles
- Muscles then move and respond
Interneurons:
Only found in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Connect with sensory neurons and motor neurons in the peripheral nervous system
Carry messages up and down the spinal cord and in the brain
 Reflex actions:
Reflex actions:Your response is faster than normal because the message to move away does not come from your brain but rather from your spinal cord
Reflexes Response:
Message received at the senses → Messages travel along sensory neurons to spinal cord, connects with interneurons → Interneurons in spinal cord detects danger → Interneurons sends message along motor neurons to muscles → Muscles move to get away from danger
Summary:
Normal Concious Response:
- Sensory neurons
- to interneurons in spinal cord
- to brain
- to interneurons in spinal cord
- to motor neurons
Reflex:
- sensory neurons
- to interneurons in spinal cord
- to motor neurons
==Chapter 2.4 - Getting the message==
Sense Organs:
- sense organs are used to detect stimuli ( such as light, sound, touch, taste and smell) in your environment
- Examples of human sense organs are your eyes, ears, skin, tongue and nose
- These sense organs contain special cells called receptors
Types of Receptors:
Thermoreceptors - Temperature
Mechanoreceptors - Pressure
Chemoreceptors - Nose and Taste buds
Photoreceptors - light
Noiciceptors (pain receptors) - pain
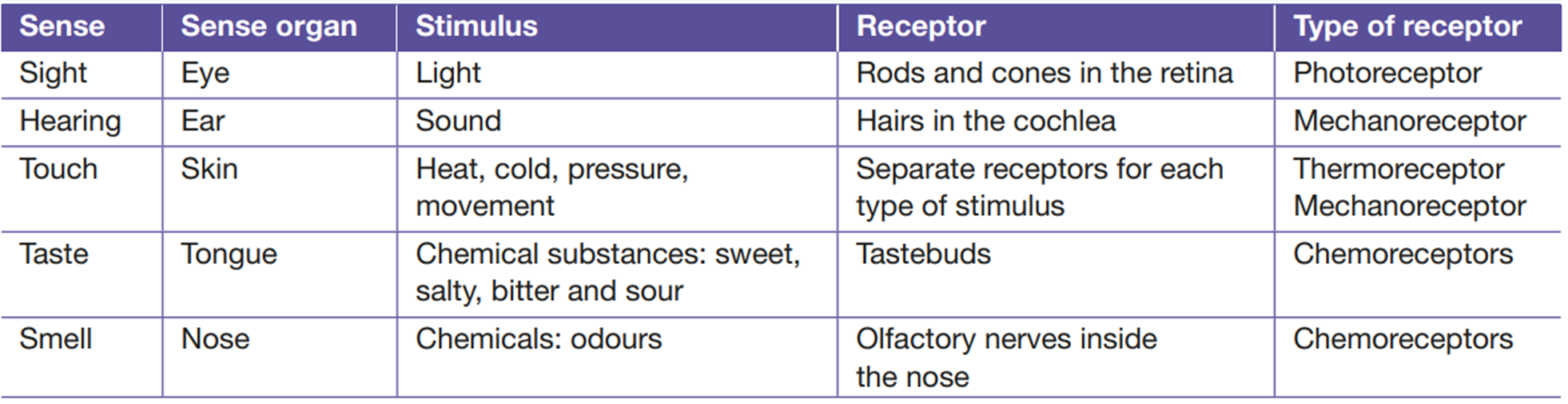 Touch: Skin contains - pain receptors, mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors
Touch: Skin contains - pain receptors, mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors
Smell: The nose contains chemoreceptors that send a message via the olfactory nerve to the brain
Taste: Chemoreceptors in the tongue recept taste
==Chapter 2.5 - The brain==
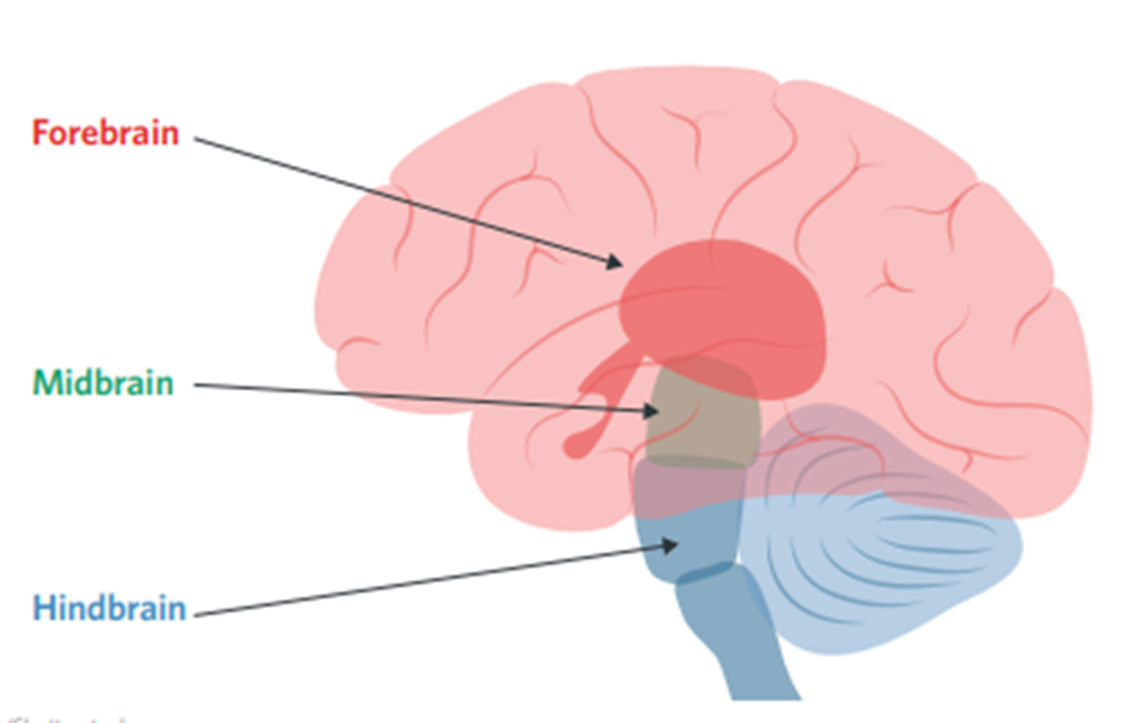
3 Main Parts:
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Hindbrain
Hindbrain:
- Connects the spinal cord and the brain
- Responsible for:
- Breathing
- Basic movement
- Balance
Midbrain:
- sits in the middle
- helps regulate alertness (from being fully awake of deeply asleep)
- Some reflexes (sneezing and coughing)
Forebrain:
- Contains:
- Cerebrum (including the cerebral cortex): thinking and planning
- Thalamus: filters sensory information
- Hippoampus: creates new long term memories
Cerebrum:
- the largest part of the brain
- responsible for thinking, planning and voluntary movement
- divided into two hemispheres
- each hemisphere is made of 4 lobes
- cerebral cortex is 2-3mm thick
Hemispheres:
- the cerebrum is divided into 2 halves called the left and right hemispheres
- the 2 hemispheres are joined by a bridge of nerves called the corpus callosum. this is how the two halves communicate.
Left Hemisphere:
- logic
- language
- maths
- analysis
- reasoning
- controls the right side of the body
Right Hemisphere:
- creativity
- expression
- emotion
- imagination
- facial recognition
- controls the left side of the body
4 Lobes: (there are 8 lobes in total, 4 in each hemisphere. e.g. left frontal lobe)
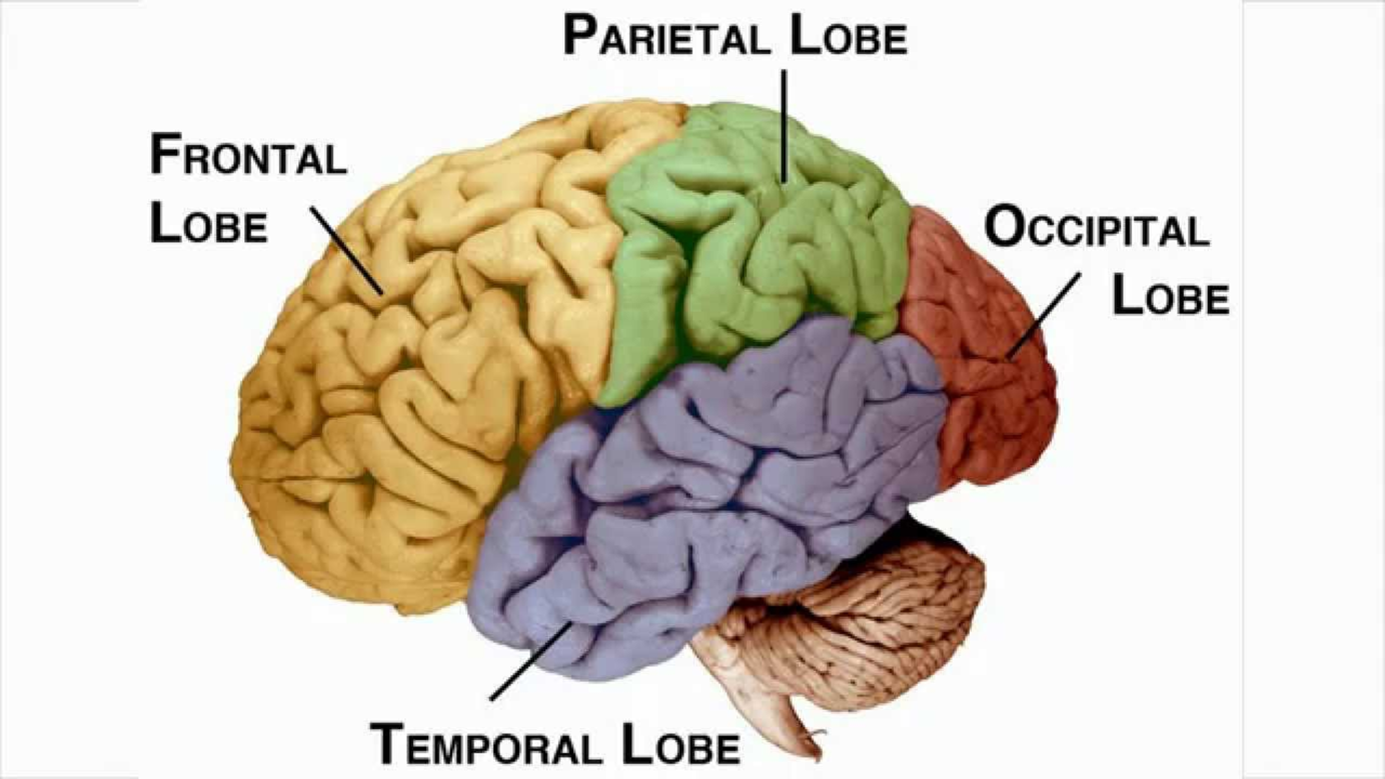 Frontal - movement
Frontal - movement
- problem solving
- emotional traits
- reasoning (judgement)
- speaking
- voluntary motor activity
Parietal - sensation of touch
- knowing right from left
- sensation
- reading
- body orientation
Occipital - vision
- vision
- colour perception
Temporal - sound/hearing
- understanding language
- behaviour
- memory
- hearing
Cerebellum:
- balance
- coordination and control of voluntary movement
- fine muscle control
Brain stem:
breathing
body temperature
digestion
alertness/sleep
swallowing
 ==Chapter 2.6 - Endocrine System==
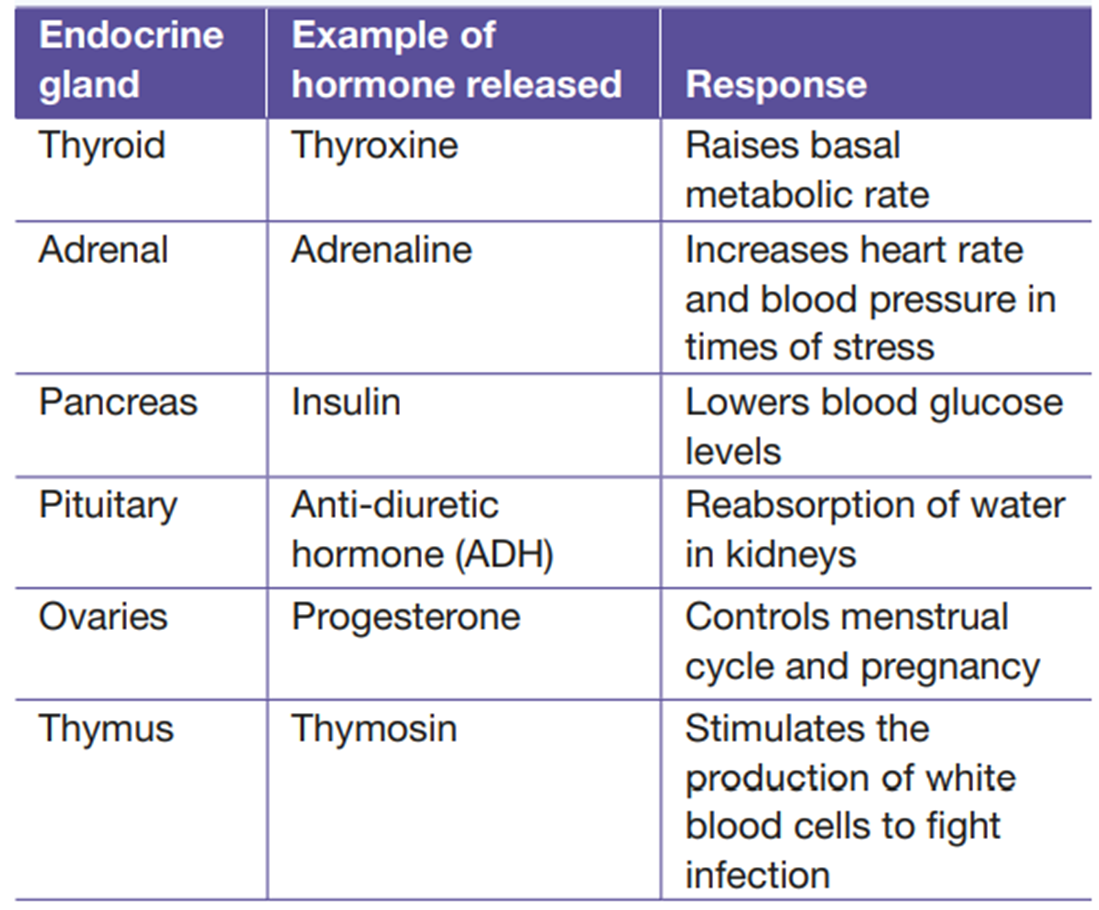
==Chapter 2.6 - Endocrine System==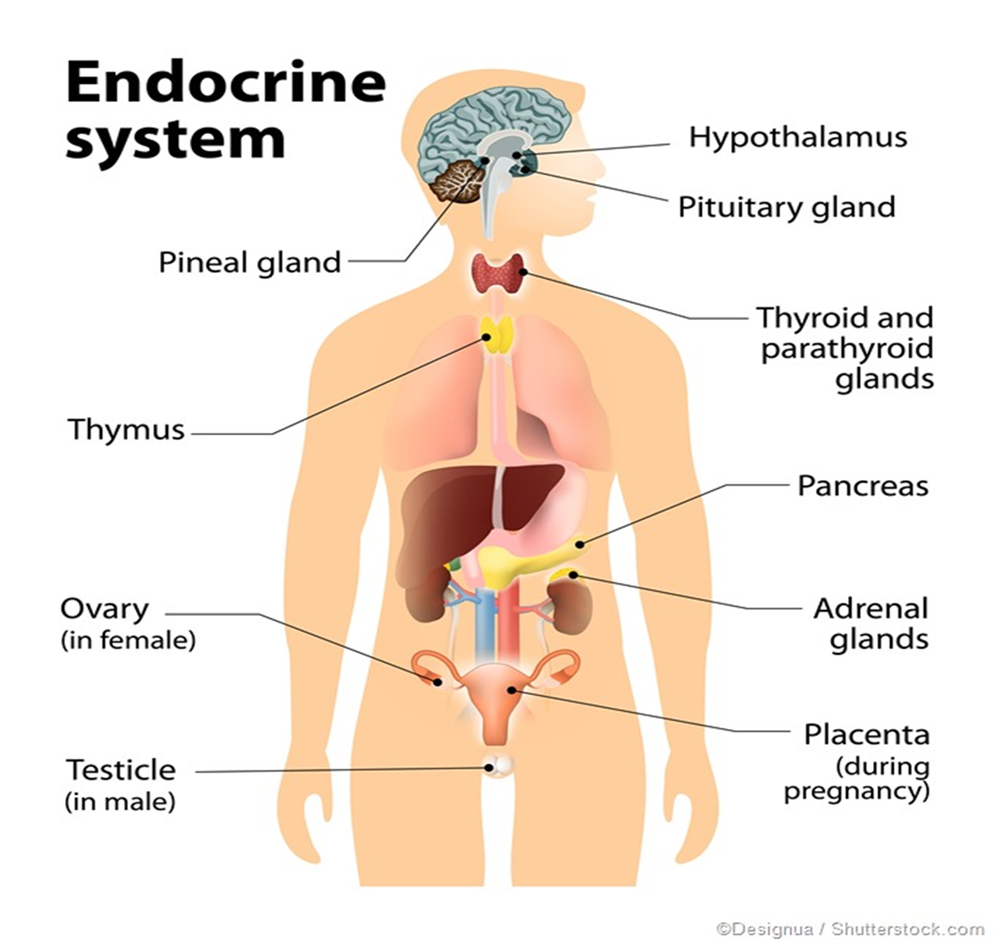 Hormones:
Hormones:your nervous system is not the only means of controlling and coordinating activities in your body
your endocrine system uses chemical messengers called hormones
hormones are made by glands and released into your blood stream
only particular cells will respond to hormones, these are called target cells and they are receptors for those hormones
Hormones control functions such as:
growth
metabolism
development
sexual reproduction
stress
 Pituitary Gland:
Pituitary Gland:in the brain
controls many other endocrine glands
- thyroid
- ovaries/testes
Influences: water balance in the body, growth
Hypothalamus:
- in the brain
- sends hormones to the pituitary gland to control its release of hormones to the other endocrine glands
- influences temperature, growth, appetite, sensation of pain and pleasure
Pineal Gland:
in the brain
produces melatonin
controls body’s sleep wake cycle
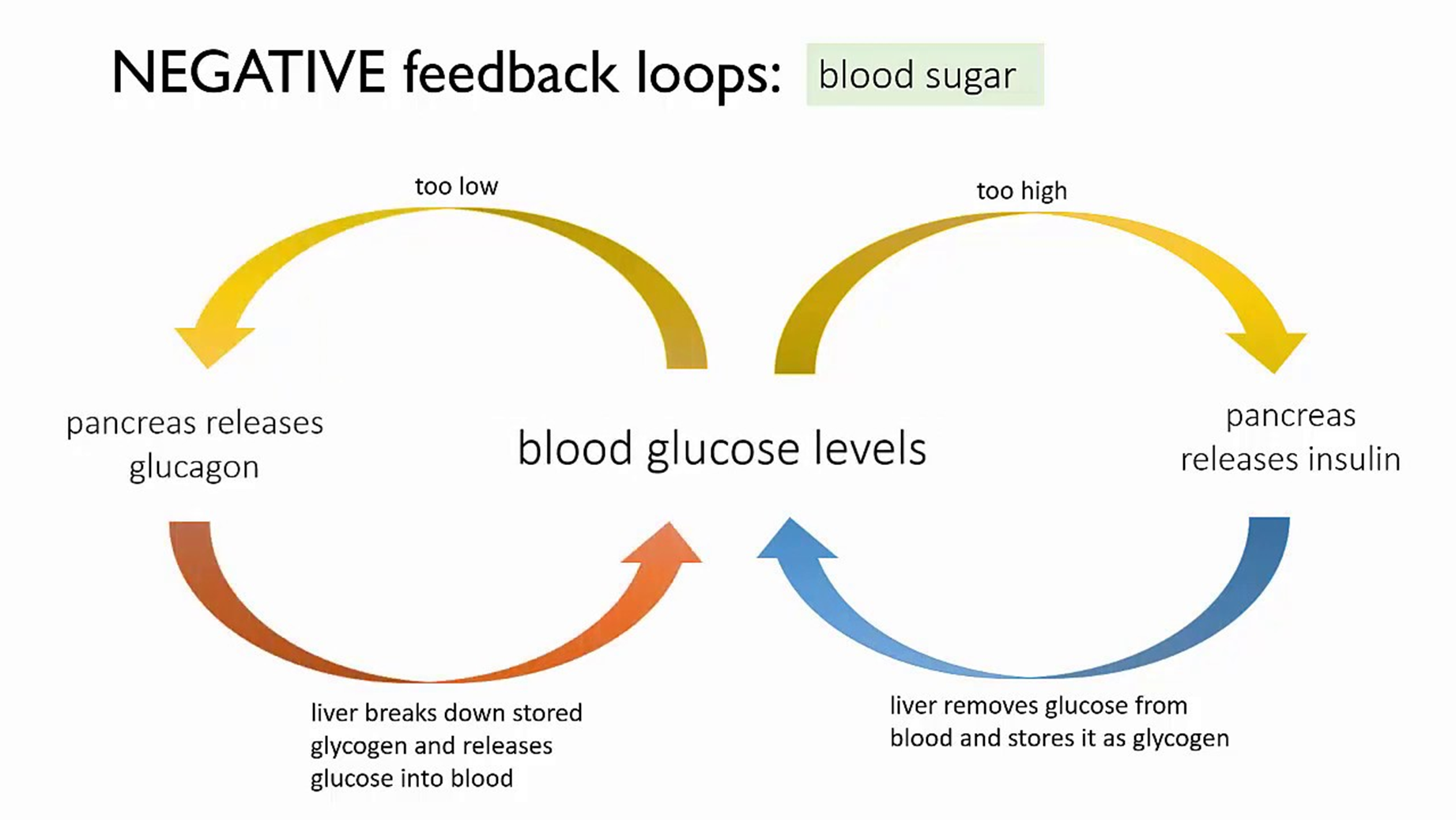
 Pancreas and insulin:
Pancreas and insulin:insulin is a hormone
it is secreted by your pancreas when you have high blood sugar
insulin works on target cells in your liver
your liver then absorbs more glucose
this then lowers your blood sugar
this is an example of negative feedback in action
Pancreas and Glucagon:
- glucagon is a hormone
- it is secreted by your pancreas when you have low blood sugar
- target cells in your liver
- glycogen is broken down to form glucose
- glucose then increases your blood sugar levels
- this is an example of negative feedback
Insulin:
- hormone
- secreted by pancreas
- works with liver
- decreases blood sugar levels
Glucagon:
hormone
secreted by pancreas
works with liver
increases blood sugar levels
==Chapter 2.8 - The Brain and Emotions==
The 6 basic emotions:
- happiness
- sadness
- fear
- disgust
- anger
- surprise
Limbic System:
the limbic system is made up of a collection of structures within your brain
the limbic system is involved in:
- memory
- controlling emotions
- decision making
- motivation
- learning
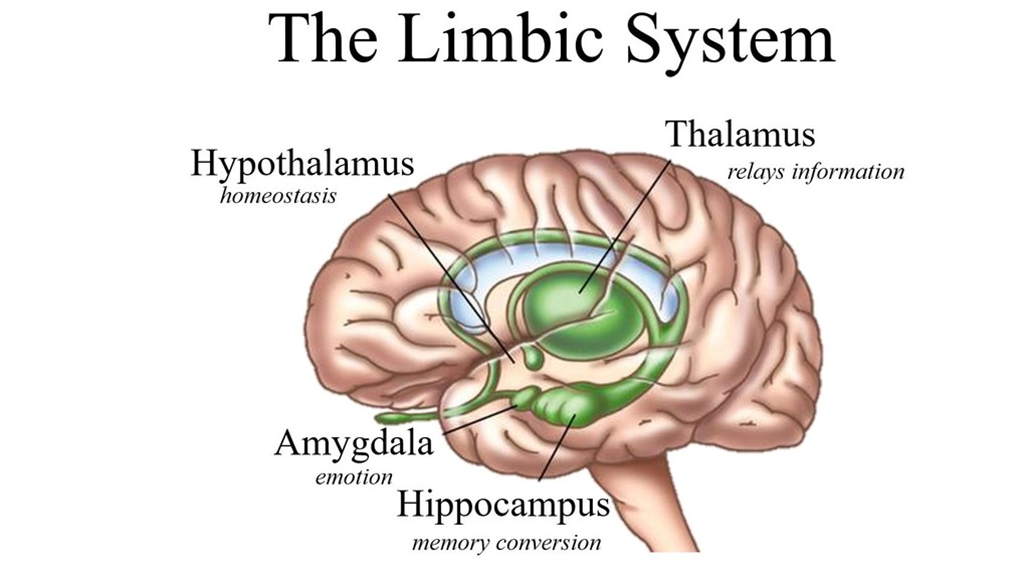 Parts of the brain involved with emotion:
Parts of the brain involved with emotion:thalamus
hypothalamus
hippocampus
amygdala
Fight or flight response: when you feel angry, your hypothalamus responds by sending messages to your pituitary gland to instruct your adrenal glands to release adrenaline.
- this hormone acts to
- increase your heartrate
- dilate your pupils
- constrict skin blood vessels
- shut down digestion
Amygdala:
- your fight or flight response originates in your amygdala
- it is this tiny part of your limbic system that decides the emotional value of what is happening
- it may sense a particular facial expression or tone as being threatening, or it may detect an event that was previously tagged as being a negative experience
Brain Chemistry:
- neurotransmitters are chemicals involved in passing messages between your neurons
- within your brain, there are many neurotransmitters that influences how you feel and react
- serotonin
- noradrenaline
- dopamine
Noradrenaline:
- noradrenaline can act like the accelerator
- it can promote alertness, better focus and concentration
- your brain also needs this chemical to form new memories and to transfer them to your long term storage
Serotonin:
- acts like the brakes on your emotions
- it can produce a calming effect and is important for maintaining a good mood and feelings of contentment
- it also plays a role in regulating memory, appetite and body temperature
- low levels of it can produce insomnia, depression and aggressive behaviour
Dopamine:
- is important for healthy assertiveness and happiness
- dopamine levels can be depleted by stress or poor sleep
- too much alcohol, caffeine and sugar may also lead to reduced dopamine activity in your brain