HEMA 311: Hgb Metabolism
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
95% of RBC cytoplasmic content
Molecular weight of 64k Da
Transport oxygen and nitric oxide (NO)
Contributes to acid-base balance (by binding and releasing hydrogen ions)
X-Ray Crystallography
Hgb structure was first described using?
Methemoglobin (MetHgb)
Other term for oxidized Hgb
Heme Composition
A central atom of divalent ferrous iron with a ring consisting of: (atoms)
Carbon (C),
Hydrogen (H), and
Nitrogen (N)
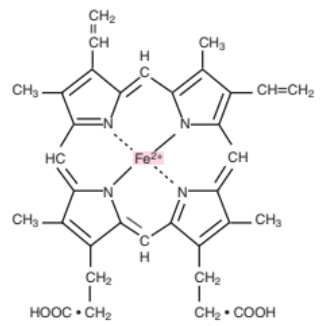
Ferroprotoporphyrin IX
Other term for Heme (Ferro = Iron) (Protoporphyrin IX = Heme ring)
Protoporphyrin IX
Other term for the heme ring (C + H + N)
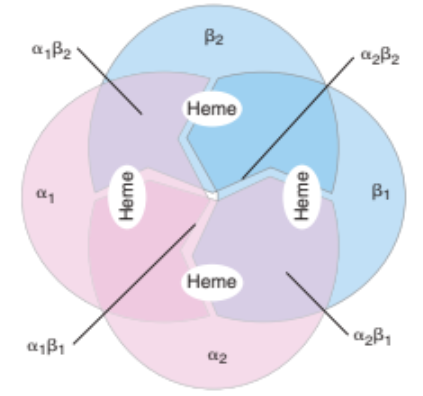
Globin Chains
Consists of two identical pairs of unlike polypeptide chains
Hgb Primary Structure
Refers to amino acid sequence of polypeptide chains
Hgb Secondary Structure
Refers to chain arrangements in helices and nonhelices
Hgb Tertiary Structure
Refers to arrangement of helices into a pretzel-like configuration
E7 and F8
Between what helix group of the globin chain is a heme group suspended in?
Proximal Histidine
Other term for F8
Distal Histidine
Other term for E7 and is only a residue
Hgb Quaternary Structure
Tetramer; describes the complete Hgb molecule
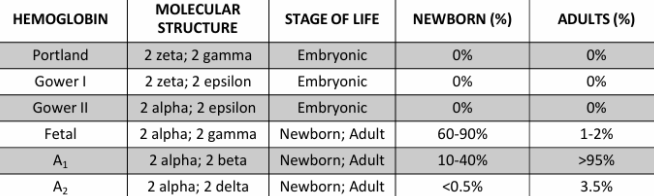
Adult Hgb A
2 α-globin chains (α1 and α2)
2 β-globin chains (β1 and β2)
important for stability of Hgb quaternary structure
Glycation
Post-translational modification formed by non-enzymatic binding of various sugars to globin chain amino groups
HbA1c
Most characterized glycated Hgb; glucose attaches to N-terminal valine of β-chain
Normal value of 4-6%
Pronormoblast stage
Erythrocyte precursor where heme and globin biosynthesis begins
Reticulocyte / Polychromatic Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte precursor where heme and globin biosynthesis still occurs but eventually end
Ferrochelatase
Heme synthase that catabolizes ferrous Iron + protoporphyrin IX to make heme
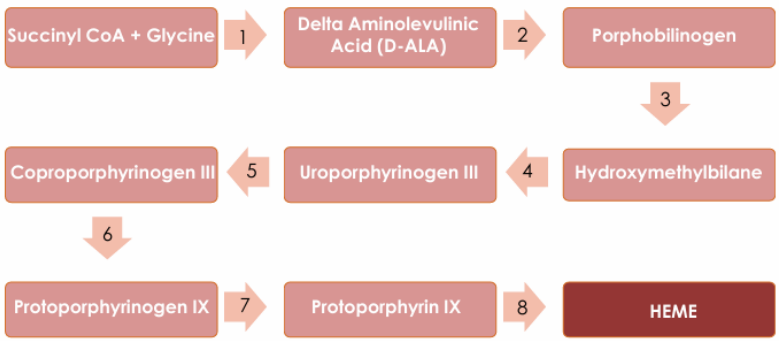
Transferrin
Plasma protein that carries iron in ferric state to developing RBCs
Brought into endosome for acidification to release iron into mitochondria
Mitochondria
Organelle that reduces ferric iron to ferrous iron and combines it with protoporphyrin IX (to make heme)
Cytoplasm
Environment that contains organelles where heme is joined to globin chains
Normal Hemoglobin
.
1.34 mL
Volume of oxygen per gram of Hgb
Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PO2)
Defined in terms of amount of oxygen needed to saturate 50% of Hgb (P50 value)
P50 = 27 mmHg
PO2 Normal Value
P50 = >27 mmHg
Right shift in hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve and occurs in:
increased 2,3-BPG
acidosis (lowered pH) = Bohr effect (curve due to change in pH)
increased temp
increased partial pressure of CO2 (PCO2)
P50 = <27 mmHg
Left shift in hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve and occurs in:
decreased 2,3-BPG
alkalosis (lowered pH) = Bohr effect (curve due to change in pH)
decreased temp
decreased partial pressure of CO2 (PCO2)
fetal Hgb
Myglobin
Rhabdomylosis
Myoglobin is released into plasma due to damage to the muscles
Nitric Oxide (NO)
A vasodilator that attaches to cysteine on the globin chain, forming S-nitrosoHgb
Vasoconstriction: NO transported by free Hgb away from vessel wall (Hgb outside RBC)
Vasodilation: NO transported by Hgb towards vessel wall
Dyshemoglobins
Dysfunctional Hgbs that are unable to transport oxygen
Methemoglobinemia
Increase in methemoglobinemia
Toxic Methemoglobinemia
Acquired form of MetHgbemia that occurs in normal individuals after exposure to exogenous oxidant
Nitrites
Primaquine
Dapsone
Benzocaine
<25% = Asymptomatic
30% = Cyanosis or Hypoxia symptoms
>50% = Coma or Death
Chocolate Brown
Color of blood in MetHgb
Hemiglobin
Other name of MetHgb
Hereditary Methemoglobinemia
NADH-CYB5R3: gene mutation involved that causes enzyme defects in hereditary MetHgbemia (autosomal recessive pattern) (Type 1)
Globin Gene Mutation: α- , β- , and γ-globin genes are mutated, producing structurally abnormal polypeptide chain that favors oxidized ferric iron that produces MetHgb called “M hemoglobin / Hb M” (autosomal dominant pattern) (Type 2)
Sulfhemoglobin (HgbS)
Formed by addition of sulfur atom to pyrrole ring of heme
Pyrrole Ring of Heme
5-membered heterocyclic ring that involves the nitrogen (N) that binds to iron
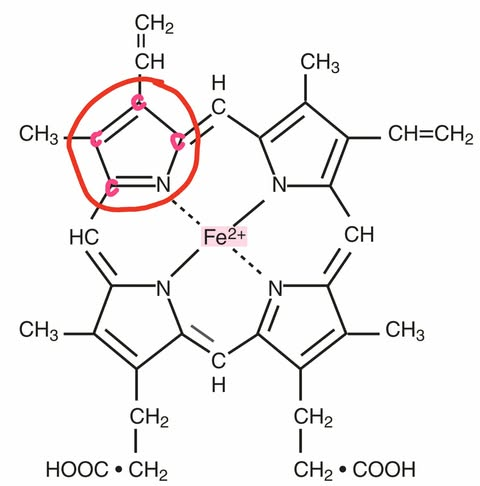
Porphyrin Ring
4 pyrrole rings joined together by methine bridges (=CH-)
Greenish
Color of blood with HgbS (due to C. perfringens / C. welchii “old name lang niya”)
Mauve-Lavender
Color of blood in sulfhemoglobinemia
Carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)
Results from combination of carbon monoxide (CO) with heme iron
causes left shift in hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve
toxic effects appear at blood levels of 20-30% COHb
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Termed as the “silent killer” because it is an odorless and colorless gas
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Diagnosis is made if COHb levels is:
>3% in nonsmokers
>10% in smokers
Cyanmethemoglobin Method
Golden standard for Hgb assay