AST
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:45 PM on 10/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
Astronomy
the scientific study of planets, stars, galaxies, and the universe as a whole
- focused on measuring positions of and finding patterns among the stars
- focused on measuring positions of and finding patterns among the stars
2
New cards
cosmic address
planet, star, galaxy group, galaxy cluster, and galaxy superstar
- eart, sun, solar system, milky way, local group, lainaka supercluster, universe
- eart, sun, solar system, milky way, local group, lainaka supercluster, universe
3
New cards
Astronomical Unit
the average distance from the sun to earth
4
New cards
the solar system contains...
eight planets: mercury, venus, earth, mars, jupiter, saturn, Uranus, neptune
- dwarf planets: pluto, ceres, eris
- asteroids: ida, eres
- comets: Halley
- dwarf planets: pluto, ceres, eris
- asteroids: ida, eres
- comets: Halley
5
New cards
milky way galaxy
a disk containing more a hundred billion stars, along with gas and dust
- is part of a small collection of a few dozen galaxies called the local group
- the local group itself is part of a vastly larger collection of thousands of galaxies called the supercluster, which is part of the lainaka supercluster
- is part of a small collection of a few dozen galaxies called the local group
- the local group itself is part of a vastly larger collection of thousands of galaxies called the supercluster, which is part of the lainaka supercluster
6
New cards
light travel time
- how long it would take for light to travel a given distance
Light travels through space at the fastest possible speed, and that speed is always the same
Light travels at 30,000 kilometers per second (km/s)
Light travels through space at the fastest possible speed, and that speed is always the same
Light travels at 30,000 kilometers per second (km/s)
7
New cards
light day
- the distance that light traversing 1 day - about 26 billion kilometers - the distance within the solar system
8
New cards
Light - Years
the distance that light travels in 1 year - about 9 trillion kilometers
- distance to the nearest star
- distance to the nearest star
9
New cards
Scientific Method:
- the formal procedure - including hypothesis, prediction, and experiment or observation - used to test, attempt to falsify) the validity of scientific hypothesis and theories
- a systematic, logical process for collecting evidence and using it to test ideas or explanations
Only idea that cannot be tested is not scientific, you choose to accept of reject it on some basis other than evidence
- a systematic, logical process for collecting evidence and using it to test ideas or explanations
Only idea that cannot be tested is not scientific, you choose to accept of reject it on some basis other than evidence
10
New cards
theory
a carefully constructed proposition that takes into account every place of data as well as out entire understanding of how the world works
- a theory that has been used to make testable predictions and all those predictions have been correct
- an idea that has been examined carefully, is consistent with all existing theoretical and experimental knowledge,
and makes testable predictions
- a theory that has been used to make testable predictions and all those predictions have been correct
- an idea that has been examined carefully, is consistent with all existing theoretical and experimental knowledge,
and makes testable predictions
11
New cards
hypothesis
idea that leads to a testable prediction
12
New cards
idea
an untested notion about how something might be
13
New cards
facts
an observation or measurement
14
New cards
law
- is a series of observations that scientists can use to make predictions, but a law has no underlying explanation of why the phenomenon occurs
15
New cards
falsified
proved incorrect
16
New cards
cosmological principle
includes the testable assumption that physical laws that apply here and now also apply everywhere and at all times
17
New cards
occam razor
when we are faced with completing hypothesis that explain all the observations equally well, we should use the one that requires the fewest assumptions
18
New cards
zenith
the point on the celestial sphere located directly overhead from an observer
- the highest point in the sky, directly above your head
- the highest point in the sky, directly above your head
19
New cards
horizon
the boundary that separates the sky from the ground
- half of the sky is below the horizon
- half of the sky is below the horizon
20
New cards
scientific method order
facts obs--> hypothese-->prediction--> test
21
New cards
meridian
you can divide the sky into an eastern half and western half with a line that runs from the horizon at due north through the zenith as due south, divides east and west, over the course of one day, objects will rise in the eastern half of the sky, pass through the meridian, and set in the western half of the sky, pass through the merdian and set in the western half
22
New cards
celestial sphere
an imaginary sphere with celestial objects on its inner surface and earth at its center
23
New cards
day
the time for earth to rotate around its axis
24
New cards
sidereal day
is the time to rotate relative to the fixed stars, earths true orbital period, constellations along the ecliptic form the zodiac
25
New cards
solar day
the time to rotate relative to the sun
26
New cards
if you were transported the earths north or south pole
you would see earth rotate counter/or clockwise each day
27
New cards
altitude
the location of an object above the horizon, measured by the angle formed between an imaginary line from an observer to the object and a second line from the observer to the point on the horizon direction below the object
28
New cards
local astronomical midnight
occurs when the sun is precisely opposite from its position at local noon,
29
New cards
north pole/south pole rotates
counter clockwise, clockwise
30
New cards
latitude
the angular distance from the equator
31
New cards
standing at the north pole
you are standing where earths axis of rotation intersects its surface- standing at the center of the rotating wheel
- objects follow circular paths that always have some latitude
- close to the zenith, objects follow small circles
- objects near the horizon follow large circles
- northing rises or sets each day as earth turns (always see same half of the sky)
- objects follow circular paths that always have some latitude
- close to the zenith, objects follow small circles
- objects near the horizon follow large circles
- northing rises or sets each day as earth turns (always see same half of the sky)
32
New cards
standing at south pole
same thing as north pole but start move clockwise
33
New cards
from the equator looking north
NCP is on the horizon, the stars arc from east to west counter clockwise
34
New cards
latitude 30 degrees s
SCP is 30 degrees from horizon and the stars are going clockwise
35
New cards
circumpolar
referring to the part of the sky, near either celestial pole that can be seen above the horizon from a specific location on the earth
- always above the horizon
- always above the horizon
36
New cards
NCP relation to circumpolar stars
in canadian woods, NCP would be higher in the sky so more circumpolar stars, at lower laditudes, the NCP is near the horizon so less circumpolar stas
37
New cards
solar year
the time for the earth to make one revolution around the sun, measured between two vernal equinoxes
38
New cards
zodiac
the constellations that lie along the plane of the ecliptic
39
New cards
summer solstice
June 21, when the sun is at its northernmost point, sun is at the greatest distance from the celestial equator
40
New cards
winter solstice
December 22, when the sun is at its southernmost point, the sun is also its greatest distance from the equator, dec 21 in northern hem, and june 21 in southern
41
New cards
autumnal equinox
September 22, one of two points where the sun crosses the celestial equator
42
New cards
vernal equinox
one of two points where the sun crosses the celestial equator
43
New cards
where does the sun set
in the west
44
New cards
gregorian calendar
based on the tropical year, the modern calender,
45
New cards
tropical year
the time between one crossing of the vernal equinox and the next
- a tropical year is slightly shorter than the time it takes for earth to orbit the sun
- a tropical year is slightly shorter than the time it takes for earth to orbit the sun
46
New cards
leap year
every 4 years, a year that contains 366 days
47
New cards
tropics
Northern limit. tropic of Cancer
- Southern limit, tropic of Capricorn
- the region on Earth between latitudes 23.5 degrees south and 23.5 degrees north, in which the sun appears directly
overhead twice during the year
- Southern limit, tropic of Capricorn
- the region on Earth between latitudes 23.5 degrees south and 23.5 degrees north, in which the sun appears directly
overhead twice during the year
48
New cards
Procession of the Equinoxes:
the slow change in orientation between the ecliptic plane and the celestial quatro caused by the wobbling of Earth’s axis
49
New cards
days it takes the moon to orbit earth
27 days
50
New cards
synchronous rotation
the moon rotates once on its axis for each orbit around Earth- an effect called synchronous rotation, the moon is not perfectly round but has a bulge on the side closer to earth, earths gravity constantly tags on this bulge which causes its near side to always to fall towards earth
51
New cards
new moon
the phase of the moon which is between earth and the sun, and from the earth we see only the side of the moon not illuminated by the sun, up in the daytime and never visible in the nighttime sky
- appears close to the sun in the sky so it rises with the sun at sunrise, crosses the meridian near noon, and sets in the west with the sun
- appears close to the sun in the sky so it rises with the sun at sunrise, crosses the meridian near noon, and sets in the west with the sun
52
New cards
waxing
the changing phases of the moon as it becomes fully illuminated between new moon and full moon as seen from earth
53
New cards
first quarter moon
the phase of the moon in which only its western half, as viewed from earth, is illuminated by the sun
- occurs one week after a new moon
- one-quarter of the way through its orbit
- rises are noon, crosses the meridian at sunset, and sets at midnight
- occurs one week after a new moon
- one-quarter of the way through its orbit
- rises are noon, crosses the meridian at sunset, and sets at midnight
54
New cards
full moon
- occurs two weeks after a new moon, the sun and moon are opposite in the sky
- rises as the sun sets, crosses the meridian at midnight, and sets in the morning as the sun rises
- rises as the sun sets, crosses the meridian at midnight, and sets in the morning as the sun rises
55
New cards
when the moon is farther than earth from the sun
its in its gibbous phase, when it is closer than Earth to the sun it is in crescent phases
56
New cards
moon phases summary
new moon rises and sets with sun, crosses the meridian near noon, a few days later a sliver of its illumination becomes visible--> waxing crescent
first quarter moon rises at 12 pm and crosses the meridian at sunset and crosses the meridian at sunset and sets at midnight
first quarter moon rises at 12 pm and crosses the meridian at sunset and crosses the meridian at sunset and sets at midnight
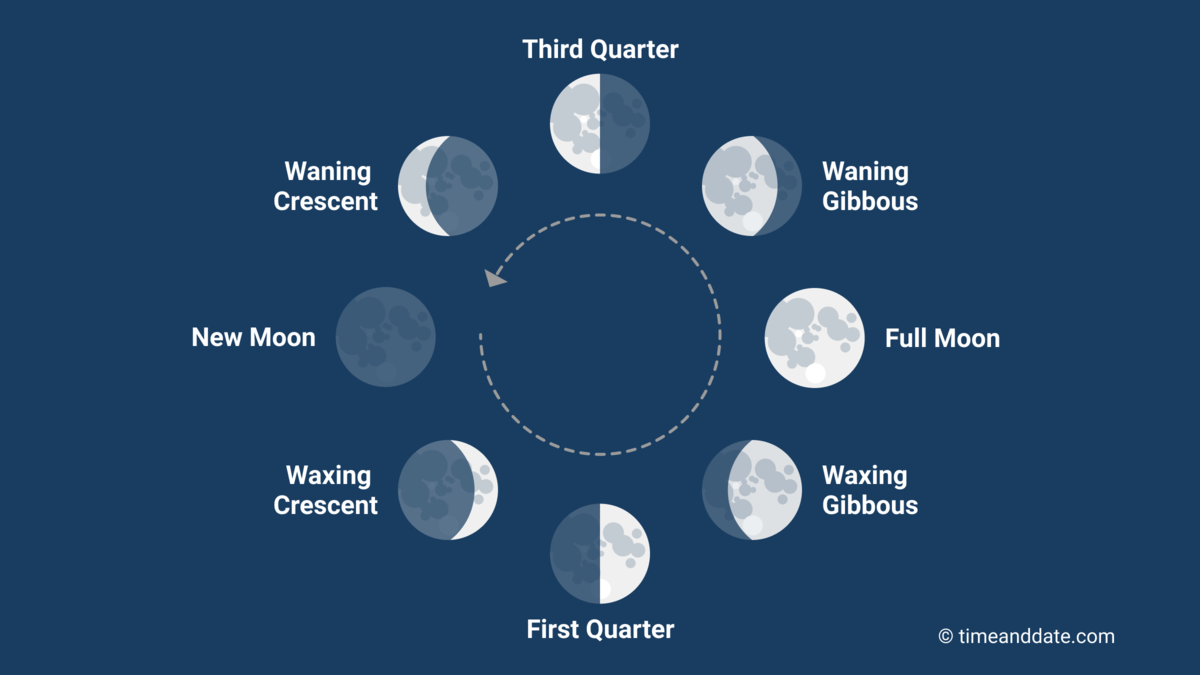
57
New cards
eclipse
occurs when the shadow of an astronomical body falls on another
- the total or partial obscuration of one celestial body by another
- the total or partial obscuration of the light from one celestial body as it passes through the shadow of another celestial body
- the total or partial obscuration of one celestial body by another
- the total or partial obscuration of the light from one celestial body as it passes through the shadow of another celestial body
58
New cards
solar eclipse
occurs when the moon passes between the earth and the sun and casts a shadow on earth
- an event that occurs when the Sun is partially or entirely blocked by the moon
- an event that occurs when the Sun is partially or entirely blocked by the moon
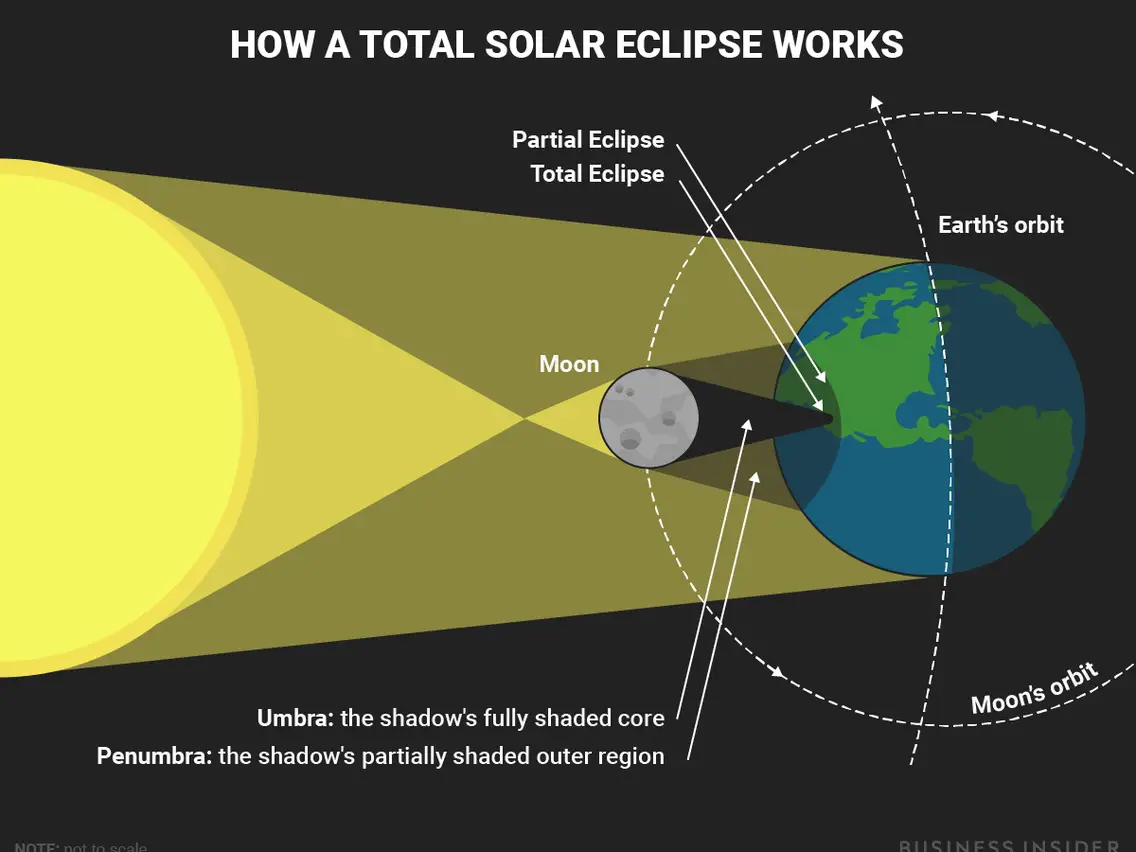
59
New cards
total solar eclipse
occurs when the moon completely blocks the disk of the sun
- at any location, a total solar eclipse never lasts longer than 7 1/2 minutes and is usually significantly shorter - an event that occurs when Earth passes through the umbra of the moons shadow, so that the moon
completely blocks the disk of the sun
- at any location, a total solar eclipse never lasts longer than 7 1/2 minutes and is usually significantly shorter - an event that occurs when Earth passes through the umbra of the moons shadow, so that the moon
completely blocks the disk of the sun
60
New cards
umbra
a region of complete shadow resulting from total obstruction of light
61
New cards
partial solar eclipse
an event that occurs when the earth passes through the penumbra of the moon's shadow so that the moon blocks only a portion of the sun's disk
- occurs when the moon partially covers the disk of the sun
- occurs when the moon partially covers the disk of the sun
62
New cards
annular solar eclipse
occurs when the moon is slightly farther away from earth in its non circular orbit, so it appears slightly smaller
in the sky
- an event that occurs when the apparent diameter of the moon is less than that of the sun, leaving a visible
ring of light (“annulus”) surrounding the dark disk of the moon
Lunar Eclipse:
in the sky
- an event that occurs when the apparent diameter of the moon is less than that of the sun, leaving a visible
ring of light (“annulus”) surrounding the dark disk of the moon
Lunar Eclipse:
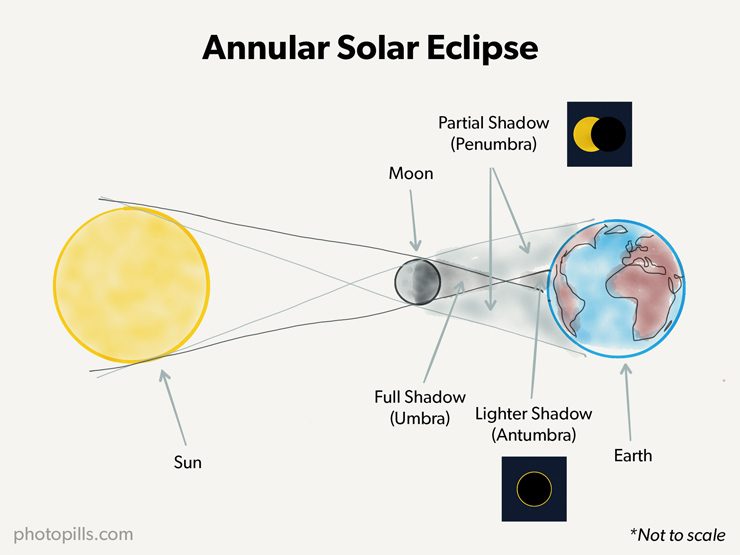
63
New cards
lunar eclipse
- occurs when the moon is partially or entirely in Earth’s shadow
- an event that occurs when the moon is partially of entirely in earths shadow
All observers on the nighttime side of Earth will be able to see a lunar eclipse
- an event that occurs when the moon is partially of entirely in earths shadow
All observers on the nighttime side of Earth will be able to see a lunar eclipse
64
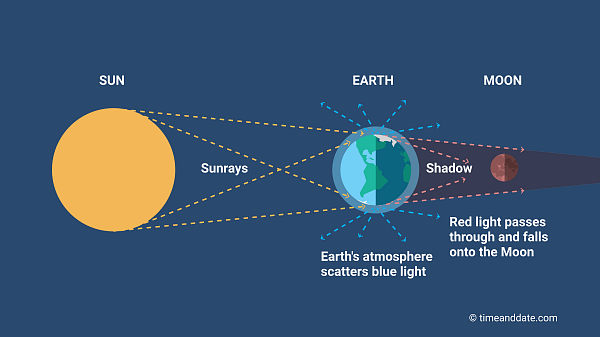
New cards
total lunar eclipse
when the moon is entirely within earths shadow
- may last as long as 1 hour 40 minutes
- an event that occurs when the moon passes through the umbra of earths shadow
The moon often appears red during a total lunar eclipse, because it is illuminated by red light from the Sun that is bent as it
travels through earths atmosphere and hits the moon
- may last as long as 1 hour 40 minutes
- an event that occurs when the moon passes through the umbra of earths shadow
The moon often appears red during a total lunar eclipse, because it is illuminated by red light from the Sun that is bent as it
travels through earths atmosphere and hits the moon
65
New cards
partial lunar eclipse
an event that occurs when the moon passes through the penumbra of Earths shadow
- if earths shadow incompletely covers the moon, some of the disk of the moon remains bright and some of it is
in shadow
- if earths shadow incompletely covers the moon, some of the disk of the moon remains bright and some of it is
in shadow
66
New cards
why don't we see eclipses every month
About twice per year, the orb planes lines up at points called nodes, and eclipses can occur. These two times of year are
sometimes called eclipse seasons
- The orbit of the moon is tilted with respect to the ecliptic, so we do not see eclipses every month
sometimes called eclipse seasons
- The orbit of the moon is tilted with respect to the ecliptic, so we do not see eclipses every month
67
New cards
gravity
the force of attraction between all masses in the universe; especially the attraction of the earth's mass for bodies near its surface
- holds all planets in orbit
- holds all planets in orbit
68
New cards
why is it relevant that the sun is more massive
its gravity shapes the motion of every object in the solar system from the almost circular orbits of some planets to the extremely elongated orbits of comets
69
New cards
geocentric
a coordinate system having the center of earth as its origin
70
New cards
model
a representation (often) mathematical of objects and the interaction between them
- in computing, a simulation to reproduced the behavior of a system in one, two or three dimensions
- in computing, a simulation to reproduced the behavior of a system in one, two or three dimensions
71
New cards
apparent retrograde motion
- movement of the planets with respect to the fixed stars in which the planets appear to move westward for a period of time before resuming their normal eastward motion
- objects in our solar system orbit the Sun at different distances and speeds.
- objects in our solar system orbit the Sun at different distances and speeds.
72
New cards
frame of reference
a system of assumptions and standards that sanction behavior and give it meaning
- a coordinate system within which an observer measures positions and motions
- a coordinate system within which an observer measures positions and motions
73
New cards
Ptolemy
modified the geocentric model with a complex system of interconnected circles to try to obtain more accurate results and explain retrograde motion
- figure where each seperate planet has its own orbit around the earth including the sun, makes lots of circles a swirl
- figure where each seperate planet has its own orbit around the earth including the sun, makes lots of circles a swirl
74
New cards
Nicholas Copernicus
Was not the first person to consider the idea that the sun was at the center of the solar system
- was the first person to develop a mathematical model that made testable predictions about the planetary orbit
- In 1543, he published a heliocentric model in a treatise called de revolutionibus orbium coelestium
(“on the revolutions of the heavenly spheres”) that explained retrograde motion much more simply the Ptolemy’s
- was the first person to develop a mathematical model that made testable predictions about the planetary orbit
- In 1543, he published a heliocentric model in a treatise called de revolutionibus orbium coelestium
(“on the revolutions of the heavenly spheres”) that explained retrograde motion much more simply the Ptolemy’s
75
New cards
Kepler's laws
- the three rules of planetary motion inferred by Johannesburg Kepler from the data acquired by Tycho Brahe
76
New cards
ellipse
- a conic section produced by the intersection of a plane with a cone when the plane is passed through the cone at an
angle to the axis other than 0 degrees or 90 degrees.
- this forms an oval around two points known as foci
- for any point on the ellipse, the sum of the distances to the foci is constant
77
New cards
major axis
the longest axis of an ellipse or ellipsoid; passes through the two foci
78
New cards
semi major axis
half of the longer axis of an ellipse
-the semi major axis of an elliptical orbit is equal to the average distance of the orbiting body from the object
at the focus
-the semi major axis of an elliptical orbit is equal to the average distance of the orbiting body from the object
at the focus
79
New cards
eccentricity of an ellipse
how much the ellipse deviates from a circle, found by dividing the distance between the foci by the length of the major axis
80
New cards
eccentricity
a measure of the departure of an ellipse from circularity; the ratio of the distance between the two foci of an
ellipse to its major axis
ellipse to its major axis
81
New cards
keplers first law
a rule of planetary motion, inferred by Johannes Kepler, stating that planets move in orbits of elliptical shapes
with the sun at one focus
with the sun at one focus
82
New cards
focus
- one of two points that define an ellipse
- a point in the focal plane or a telescope
- a point in the focal plane or a telescope
83
New cards
all of the planets in the solar system have eccentricities smaller than
.25
84
New cards
Kepler's 2nd law
also called law of equal areas
- a rule of planetary motion, inferred by Johannes Kepler, stating that a line drawn from the sun to a planet
sweeps out equal times as the planet orbits the sun
Kepler found that a planet moves fastest when it is closest to the sun and lowest when it is farthest from the sun
- a rule of planetary motion, inferred by Johannes Kepler, stating that a line drawn from the sun to a planet
sweeps out equal times as the planet orbits the sun
Kepler found that a planet moves fastest when it is closest to the sun and lowest when it is farthest from the sun
85
New cards
Kepler's third law
- called harmonic law
- - a rule of planetary motion inferred by johannes kepler that describes the relationship between the period of a
planet’s orbit and its distance from the sun.
- the law states that the square of the period of a planet’s orbit, measured in years, is equal to the cube of the
the semimajor axis of the planet’s orbit, measured in astronomical units: (Pyears)^2 = (A AU)^3
- the squares of the orbital periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the semi-major axes of their orbits
- - a rule of planetary motion inferred by johannes kepler that describes the relationship between the period of a
planet’s orbit and its distance from the sun.
- the law states that the square of the period of a planet’s orbit, measured in years, is equal to the cube of the
the semimajor axis of the planet’s orbit, measured in astronomical units: (Pyears)^2 = (A AU)^3
- the squares of the orbital periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the semi-major axes of their orbits
86
New cards
weight
- in general, relativity the force equal to the mass of an object multiplied by the acceleration of the frame of
reference in which the object is observed
reference in which the object is observed
87
New cards
newtons first law
Objects at Rest Stay at Rest; Objects in Motion Stay in Motion
- the object will remain at rest or will continue moving along a
the straight line at a constant speed until an unbalanced force acts on it
- the object will remain at rest or will continue moving along a
the straight line at a constant speed until an unbalanced force acts on it
88
New cards
force
push or pull of an object
89
New cards
Inertia
the tendency for objects to retain their state of motion
90
New cards
inertial frame of reference
a frame of reference that is not accelerating
- in general relativity, a frame of reference that is falling freely in a gravitational field
Forces that cancel out have no effect on an objects motion
When forces add together to produce an effect, we often use the term net force, or just force
- in general relativity, a frame of reference that is falling freely in a gravitational field
Forces that cancel out have no effect on an objects motion
When forces add together to produce an effect, we often use the term net force, or just force
91
New cards
acceleration
=f/m
any change in speed or direction, the rate at which the speed and or direction is changing
- slowing down means the acceleration is opposite the direction of motion, the cup tips to the right, vs speeding up the acceleration is in the direction of motion as the cup tips to the left
- turning at a constant speed means the acceleration of the cup is perpendicular to the direction of motion
any change in speed or direction, the rate at which the speed and or direction is changing
- slowing down means the acceleration is opposite the direction of motion, the cup tips to the right, vs speeding up the acceleration is in the direction of motion as the cup tips to the left
- turning at a constant speed means the acceleration of the cup is perpendicular to the direction of motion
92
New cards
newtons second law of motion
the laws formulated by Isaac newton, stating that if an unbalanced force acts on a body, the body will have an acceleration proportional to the unbalanced force and inversely proportional to the object's mass
- A = F/m
- the acceleration will be in the direction of the unbalanced forces
- A = F/m
- the acceleration will be in the direction of the unbalanced forces
93
New cards
intertial mass vs gravitational mass
the property of matter that resists changes in motion vs the property of matter defined by its attractive force on other objects
94
New cards
newton (n)
- the force required to accelerate a 1-kilogram (kg) mass at a rate of 1. enter per second p
- where 1 N = 1 kg m/s^2
- where 1 N = 1 kg m/s^2
95
New cards
forces change..
forces change an object's motion - by changing either its speed or its direction
A change in speed is one way the car's motion can change
A change in direction is also a change in motion
A change in speed is one way the car's motion can change
A change in direction is also a change in motion
96
New cards
velocity
The rate and direction of change of an object's position with time
- units: meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h)
- units: meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h)
97
New cards
what causes acceleration
net force causes at acceleration since
- The acceleration depends on the strength of the net force acting on the objects to change its notion
- The acceleration occurs in the direction the net force points
The acceleration that an object experiences also depends on its inertia
- The acceleration depends on the strength of the net force acting on the objects to change its notion
- The acceleration occurs in the direction the net force points
The acceleration that an object experiences also depends on its inertia
98
New cards
newtons third law
the law, formulated by Isaac Newton, stating that for every force there is an equal and opposite force
- if an astronaut pushes on a wrench, the astronaut will go backward and the wrench forward at constant velocities. while in contact with each other, the wrench and the astronauts experience accelerations proportional to the inverse of their masses
- if an astronaut pushes on a wrench, the astronaut will go backward and the wrench forward at constant velocities. while in contact with each other, the wrench and the astronauts experience accelerations proportional to the inverse of their masses
99
New cards
gravitational force
force due to the gravitational interaction between two or more objects
100
New cards
inverse square law
the rule that a quantity or effect diminishes with the square of the distance from the source