Pharmaceutical Factors and Formulations
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Give 3 different types of medicine preparations.
1. Suspension - liquid, rapid onset
2. Tablets
3. Capsules - significant and different than tablets.
What is the advantage of a fast preparation?
Rapid onset, quicker effect eg. Gaviscon acts within minutes, relieves GORD.
What is the link between rate of absorption of drug and the risk of bioavailability problems?
The slower the drug absorption, the higher the risk of bioavailability issues as not all the drug may be absorbed.
What is the coating of a tablet?
Polymers with pH-dependency and limited solubility.
What is bioequivalence?
A different tablet of the same drug has the same pharmacokinetic properties.
identical rate and extent of absorption
How is bioequivalence assessed? (3)
1. Time to peak plasma level (tmax) - once drug is absorbed
2. Peak plasma level (cmax)
3. Bioavailability (F)
What is Cmax related to?
Peak plasma conc - most likely associated with side effects. Depending on the drug formulation, it can reach this quicker. Certain drugs should be taken at the night for this reason.
What are modified or sustained release preparations and what can they be used to do? (2)
Formulated to resist dissolution. They can be used to:
1. Reduce rate of absorption and prolong action - eg. some drugs with short half-life so it dissolves gradually.
2. Deliver drug to specific region of GI tract.
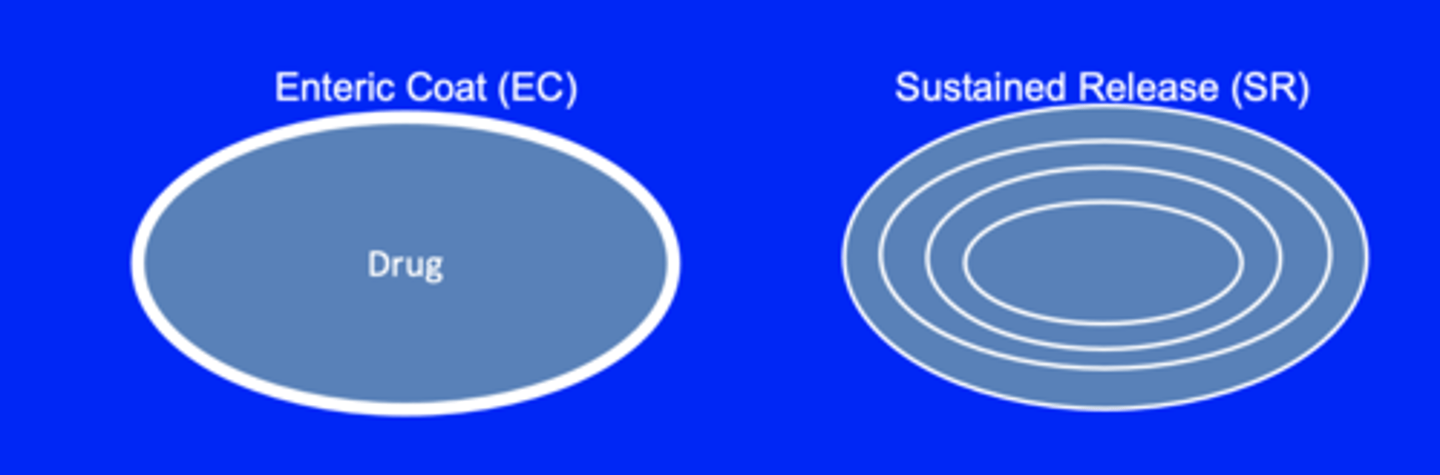
What are the 2 types of ways tablets can be modified ?
Enteric coat - to protect the drug and prevent it from being damaged in the stomach
Sustained release - Slow down absorption of the drug to give a lasting pharmacological effect
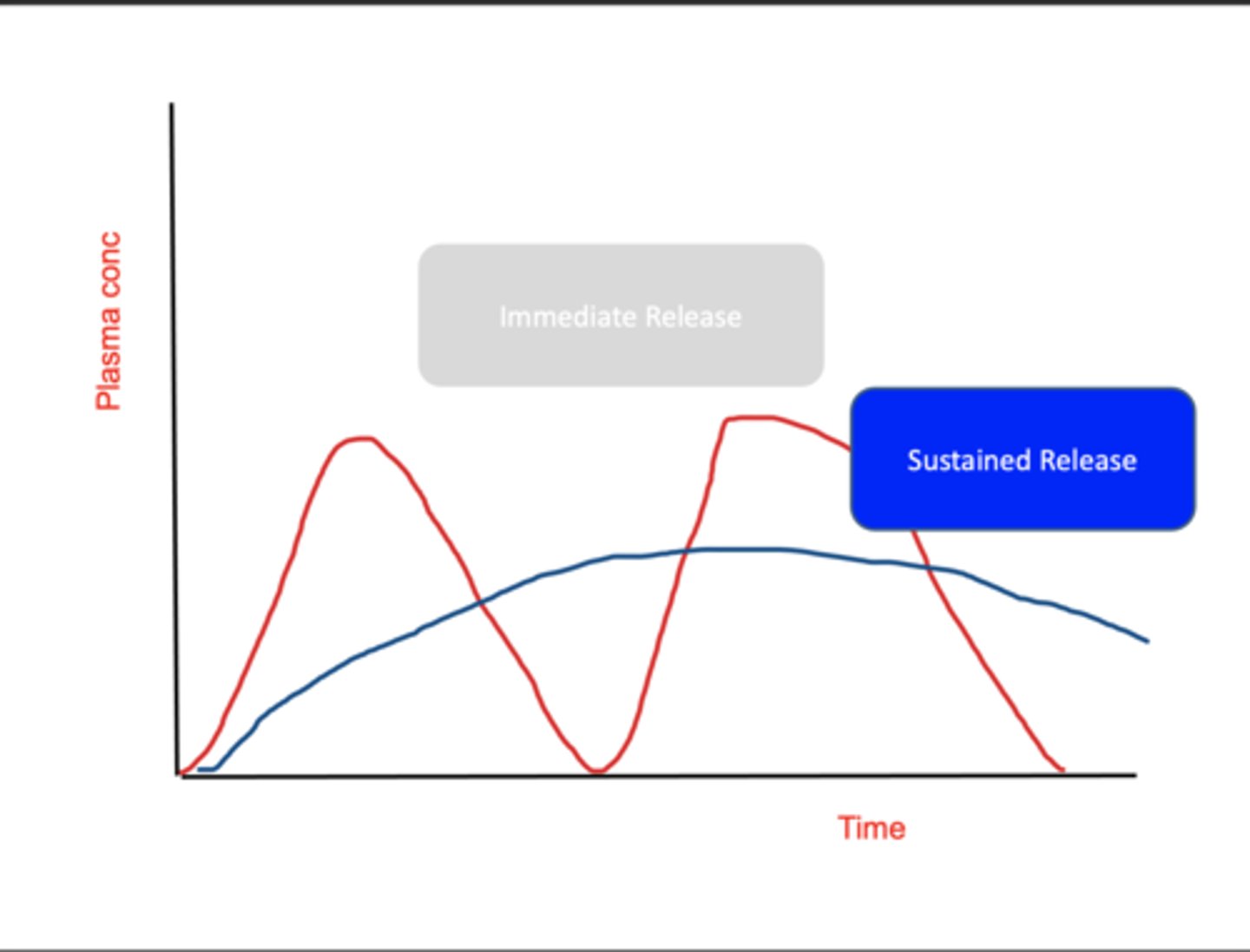
What is the effect of an immediate release and a sustained release on plasma conc?
With immediate release, drug has short half-life and it's rapidly eliminated - significant ups and downs in plasma conc. EG. not ideal for somenoe with high BP.
A sustained release prep maintains drug's plasma conc for longer and prolongs drug's activity.
What are the names of the drugs that SHOULD NOT be swapped as the bioavailabilty can be altered ?
Carbamazepine
Lithium
Cilosporin
What is morphine and its half-life?
short acting Opiod analgesic, 2-3 hour half life hence it would need to be given multiple times a day.
What are the different formulations of morphine?
1. Oramorph - oral suspension for immediate relief, breakthrough pain.
2. Morphogesic SR - sustained release, relief for 12 hours and given b.d. > good for palliative care.
What is Nifedipine and its half-life?
A DHP CCI used in hypertension and angina, with a half-life of 2 hours.
What formulations of Nifedipine should and shouldn't be given?
1. Immediate release is associated with increased cardiac events.
2. Should be used as long-acting (Adalat LA) once daily to smooth out ups and downs. {resulting in a consistent blood pressure}
What does it mean by omeprazole being acid labile? How can this be counteracted?
- Once it goes in the stomach, pH rearranges the drug and it's useless.
- Formulate it as enteric coated (blue polymer outside drug).
What is one important thing to mention to patients when prescribing omeprazole?
To swallow it whole - if they chew the capsule, they'll break down the coat and it will be chewed up by gastric acid and be ineffective.
What is the key feature of the polymer in enteric-coated drugs and how is this important in its absorption? (2)
1. Is pH sensitive, so polymer can survive acid in the stomach, but in duodenum, the rise in pH (to 5-5-6) causes it to break down and drug is released.
2. Acts systematically to inhibit proton pumps in parietal cells and suppress acid release.
When is IV omeprazole given?
In emergencies. (bleeding ulcer, gastroscopy)
What are skin patches?
Patches that are formulated with ethanol to enhance skin protection and provide sustained release eg. GTN for angina and fentanyl.
When are fentanyl patches used?
Replace oral morphine, an opioid-like analgesic used in palliative care when patient can't swallow.
When patients can't swallow after a stroke, how do you administer a drug?
Review meds, may need to give drugs via Naso Gastro-tube or IV.
When patients can't swallow after a severe infection, how do you administer a drug?
IV antibiotics.
When patients can't swallow during palliative care, how do you administer a drug? (2)
1. Morphogesic no longer swallowed so switched to fentanyl patches.
2. Or to diamorphine via a syringe driver.
What are different formulations of insulin drugs? (3)
1. Short-acting: soluble rapid onset and short duration.
2. Intermediate action: given sc, a suspension with protamine that is useful for b.d. regimens.
3. Long-acting: large crystals w/ high zinc content, slow onset and long duration.
What are depot injections? Give an eg.
1. To aid compliance or convenience, given i.m. as a thick oily suspension weekly/monthly. The thickness slows down diffusion rate from injection site.
2. Avoids first-pass metabolism - bioequivalence issue.
3. EG. norethisterone in oil (contraception) given every 8w.
What is a negative of depot injections?
Prolonged action of certain drugs given i.m. mean their side effects are also prolonged, eg. in Fluphenazine for schizophrenia.