WGU D564 Theories of Personality actual questions with 100% accurate solutions + rationales (PASSED)
1/465
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
466 Terms
Big Five
a model of personality that includes five major dimensions—neuroticism, extraversion, openness, agreeableness, and conscientiousness—on which each person is scored
description
how people characterize an individual's personality, examining differences between people
development
how an individual's personality changes over their lifetime, influenced by biological factors and experiences
factors
quantitative dimensions used to describe personality encompassing a broad range of behaviors and often have underlying biological variables
individual differences
how people differ in terms of their personality traits, behaviors, and characteristics
personality
enduring traits and behaviors that define individuals and contribute to their uniqueness
personality theories
frameworks and approaches that aim to understand individual characteristics, behaviors, and development
types
categories of people (e.g., introverts) with similar characteristics that are used to describe personality; each person belongs to one category, and there are no partial memberships within a category
traits
quantitative measures used to describe personality; each trait focuses on a specific set of characteristics (e.g., openness to experience) and gives each person a score, indicating where they fall on a scale from low to high in that trait
The "three Ds" of personality
description (how to characterize individuals), dynamics (motivation and adaptation), and development (influences and changes)—are central concerns in personality psychology theories.
personality dynamics
the processes that reveal a person's personality, specifically on how their motivations drive their actions
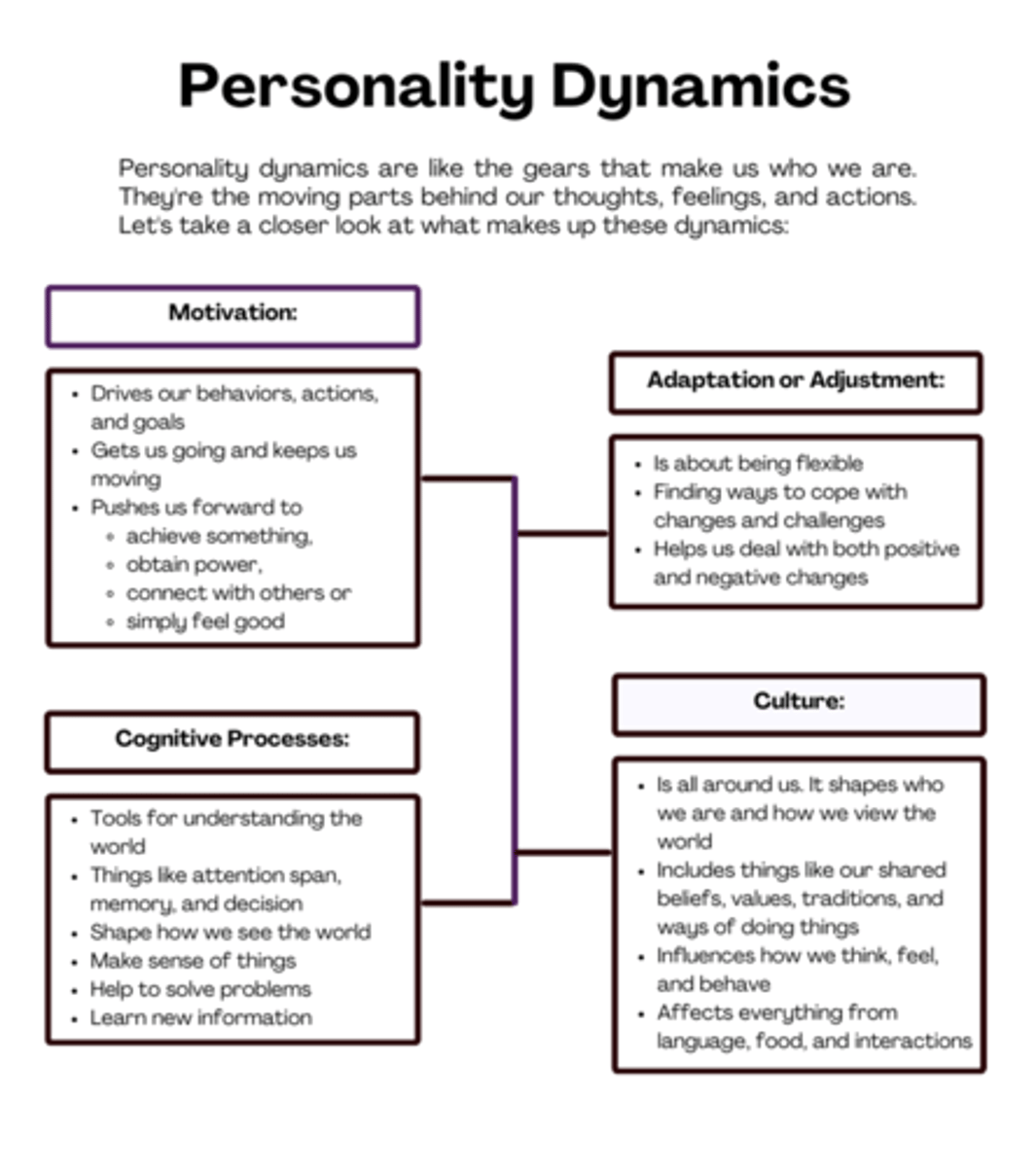
adaptation
the process of adjusting and dealing with the external world and its demands to effectively function in different situations
biological influences
the impact of genetic factors and heredity on shaping an individual's personality traits and characteristics
personality development
how an individual's personality traits and characteristics change and evolve over their lifetime
What are personality traits?
Characteristics that make one person different from another and describe an individual's personality.
3 multiple choice options
Which psychological approach to personality suggests that personality is divided into distinct categories and that individuals belong to one specific category with no partial memberships?
The type approach
3 multiple choice options
What is a primary characteristic of the nomothetic approach in the study of personality in psychology?
The nomothetic approach compares many people and their behaviors based on a few numerical scores, making it difficult to understand one whole person.
3 multiple choice options
Which term refers to the ways in which individuals adjust to the changing demands and opportunities of the world around them?
Adaptation
3 multiple choice options
Which term refers to the unique characteristics that relate to individual behavior and experience?
Personality
3 multiple choice options
Which quality of a theory indicates its capacity to explain broad ranges of personalities and behaviors?
Comprehensiveness
3 multiple choice options
What are the fundamental aspects that all theories of personality must address?
Description, dynamics, and development
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the scientific approach in personality psychology?
Theoretical constructs are made testable through operational definitions and hypotheses.
3 multiple choice options
Which role do cognitive processes have on personality?
Shaping personality dynamics
3 multiple choice options
What does motivation provide to a person's behavior?
Direction
3 multiple choice options
Which factor is a prominent role in personality dynamics, according to Sigmund Freud?
Unconscious dynamics
3 multiple choice options
What was an important premise of Freud's theory of personality?
The unconscious mind is more important than the conscious mind.
3 multiple choice options
Which topic is important for theories of personality development to address?
How personality is influenced by learning
3 multiple choice options
What is one of the two primary components of personality development, based on modern theories?
Experience
3 multiple choice options
What role does biology have in influencing personality development in early childhood?
Biological factors, including genetics, can contribute to the predisposition of certain personality traits in early childhood.
3 multiple choice options
How do personality theories explain personality?
Through description, dynamics, and development
3 multiple choice options
Why do theorists in the psychoanalytic tradition tend to emphasize the preschool years?
Because the preschool years are where a person's personality is primarily developed
3 multiple choice options
What is a common theme among modern theories of personality dynamics?
How a person thinks is an important aspect of personality.
3 multiple choice options
What do all personality theories have in common?
Consideration of the description, motivations, and origins of personality
3 multiple choice options
Which method of measuring personality provides the most precise description of characteristics?
Traits
3 multiple choice options
Which term best describes consistent styles of behavior and emotional reactions present from infancy onward, presumably due to biological influences?
Temperament
3 multiple choice options
Which issue primarily investigates how biology affects personality?
Biological influences
3 multiple choice options
Which issue focuses on understanding the traits that distinguish people?
Individual differences
3 multiple choice options
What should scientific instruments, such as personality assessments, be able to measure accurately?
The construct they claim to measure
3 multiple choice options
applied research
research that is conducted to solve real-world problems
basic research
research that is conducted to add to the scientific body of knowledge
correlational research
a research method in which scientists study how two or more things are connected to each other
experimental research
a scientific method where researchers carefully design and control experiments to understand how changes in one thing (the independent variable) affect another thing (the dependent variable)
reliability
a concept that pertains to the consistency of a scientific instrument's measurements
validity
a concept that indicates that a test accurately measures what it claims to measure
verifiability
the requirement that a theory can be tested through observable, measurable methods
What is the benefit of experimental research in psychology?
It allows researchers to make cause-effect conclusions by manipulating independent variables and observing differences in dependent variables between experimental and control groups.
3 multiple choice options
What is the goal of conducting basic research?
To advance scientific knowledge
3 multiple choice options
Why are humanistic researchers interested in studying the whole person?
They want individuals to fulfill their potential by prioritizing their overall well-being.
3 multiple choice options
Which subject would be the focus of a case study examination?
A group of disorders
3 multiple choice options
Which research condition invalidates the results of a self-report assessment?
The subject gives a false answer on the assessment.
3 multiple choice options
What assumption is central to the scientific method?
Determinism
3 multiple choice options
What does reliability measure in a research study?
The consistency of the test results
3 multiple choice options
Which example indicates test validity?
The test measures what it claims to measure.
3 multiple choice options
Which aspect of personality operates outside of a person's awareness?
The unconscious
3 multiple choice options
Which statement represents a characteristic of types as an approach to describing personality?
It uses qualitative groupings to categorize people with similar personality characteristics.
3 multiple choice options
Which scenario demonstrates the use of factors to describe personality?
The Big Five model of personality is used to score each person in a group on five dimensions of personality.
3 multiple choice options
What does validity intend to measure in a research study?
Whether a research study assesses the intended outcomes
3 multiple choice options
What does a correlational study examine?
The potential relationship between factors
3 multiple choice options
What is a characteristic of the scientific culture of psychology?
Laboratory research setting
3 multiple choice options
Which cognitive component significantly affects personality dynamics, according to modern theories of personality?
How people label experiences
3 multiple choice options
What is a common theme among modern personality theories related to culture?
Motivations that direct personalities are related to culture.
3 multiple choice options
What is the relationship between verifiability and disconfirmation in a personality theory?
They are opposites, as one finds support for a theory, and the other refutes a theory.
3 multiple choice options
What is the animus in Jung's psychoanalytic model?
The male spirit that is repressed in women
3 multiple choice options
Which question corresponds to the experiential approach to personality development?
Can personality change in adulthood?
3 multiple choice options
What is an example of a topic addressed by personality development theories?
How life experiences influence personality
3 multiple choice options
How are the theories of Freud and Jung similar?
Both addressed the importance of the unconscious mind in personality.
3 multiple choice options
Which personality traits did Hans Eysenck propose in his biological model?
Psychoticism, extraversion, and neuroticism
3 multiple choice options
Which Big Five personality trait is associated with helping behaviors and altruism?
Agreeableness
3 multiple choice options
Which assumption of personality theories did Walter Mischel challenge?
That behaviors are consistent across different contexts
3 multiple choice options
What do the first four levels of Maslow's hierarchy of needs have in common?
They are based on deficiency motivation.
3 multiple choice options
Which theorist proposed a system of psychological counseling called client-centered therapy?
Rogers
3 multiple choice options
How does Freud explain the individual personality differences between people?
Personalities are influenced by the use of ego defense mechanisms, which results in different behaviors.
3 multiple choice options
Which issue is related to personality development?
How personality is influenced by heredity
3 multiple choice options
What is a component of personality?
Long-standing traits
3 multiple choice options
What is a common theme among modern theories of personality dynamics?
How a person thinks is an important aspect of personality.
3 multiple choice options
Which characteristic is associated with experimentation as a method for personality research?
It puts hypothesized cause-effect relationships to a direct test.
3 multiple choice options
Which individual first proposed the major concepts of the psychoanalytic model of personality?
Sigmund Freud
3 multiple choice options
Which individual first proposed a theory about personality in the form of archetypes?
Carl Jung
3 multiple choice options
Psychodynamic Lense
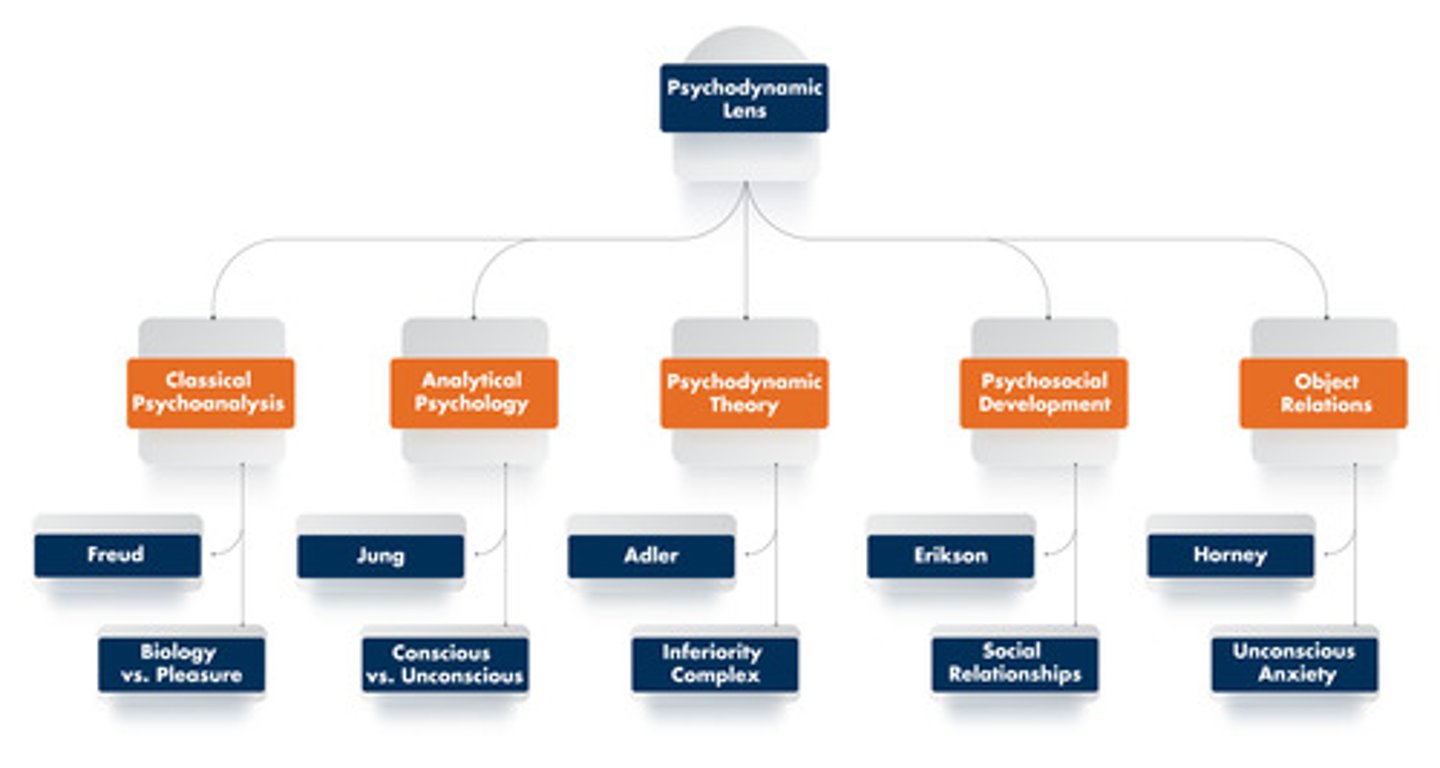
adaptation and adjustment
the process of modifying one's behavior and mindset to fit into society and effectively manage life's challenges
biological influences
factors related to a person's genetics and physiological aspects that contribute to their personality development
cognitive processes
mental activities such as thinking, reasoning, and perception, which play a crucial role in shaping personality
conscious experience and thought
awareness of one's thoughts and feelings, considered important in Adler's psychology
individual differences
variations in personality, behavior, and motivations among individuals
trust versus mistrust
trust (or mistrust) that basic needs, such as nourishment and affection, will be met
autonomy versus shame/doubt
sense of independence in many tasks develops
initiative versus guilt
take initiative on some activities, may develop guilt when success not met or boundaries overstepped
industry versus inferiority
develop self-confidence in abilities when competent or sense of inferiority when not
identity versus. confusion
experiment with and develop identity and roles
intimacy versus isolation
establish intimacy and relationships with others
generativity versus stagnation
strive to create and nurture things that will outlast them, often by having children or creating a positive change that benefits others
integrity versus despair
reflect on life, accept its meaning, and come to terms with mortality
Trust vs. mistrust
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 1
0-1 yrs
Trust (or mistrust) that basic needs, such as nourishment and affection, will be met
Autonomy vs. shame/doubt
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 2
1-3 yrs
Sense of independence in many tasks develops
Initiative vs. guilt
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 3
3-6 yrs
Take initiative on some activities, may develop guilt when success not met or boundaries overstepped
Industry vs. inferiority
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 4
7-11 yrs
Develop self-confidence in abilities when competent or sense of inferiority when not
Identity vs. confusion
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 5
12-18 yrs
Experiment with and develop identity and roles
Intimacy vs. isolation
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 6
19-29 yrs
Establish intimacy and relationships with others
Generativity vs. stagnation
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 7
30-64
Contribute to society and be part of a family
Integrity vs. despair
Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage 8
65+ yrs
Assess and make sense of life and meaning of contributions