Connective Tissue and Skin
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
connective tissue
cells separated by a matrix of loosely or densely packed intercellular material. Matrix consists of fibers and of loose or dense ground substance.
Fibroblasts
most abundant, large, star-shaped, produce fibers
Fixed macrophages
irregularly shaped and utilized to engulf invaders and damaged cells
Adipocytes
fat cells, number varies between types of connective tissue
Mesenchymal cells
stem cells, respond to local injury or infection by dividing to produce new cells
Melanocytes
produce melanin (dark brown pigment); common in epithelial tissue but also found in connective tissue; give tissue a dark color and differ in number in individuals
Free macrophages
like fixed macrophages but are free to circulate throughout connective tissues. When within the blood are called monocytes
Mast cells
small, mobile cells found near blood vessels; secrete histamine and heparin to stimulate local inflammation in response to injury/infection
Lymphocytes
migrate throughout body and increase in number where tissue damage occurs; can develop into plasma cells which produce antibodies
Microphages (e.g. neutrophils and eosinophils)
migrate throughout body and respond to chemicals released by macrophages and mast cells. These are also phagocytic
Collagen fibers
relatively thick, thread-like, composed of collagen and occur in long, parallel bundles. Can withstand much force when pulled along axis.
Elastic fibers
thinner and form complex networks; branched. Return to original length after stretching.
Reticular fibers
highly branched and delicate supporting networks. Able to resist forces applied from many directions
Areolar connective tissues
Location: found below epithelium in most parts of the body. Made up of fibroblasts with elastic and collagenous fibers.
Function: strength, elasticity, support
Made up of: collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers arranged randomly
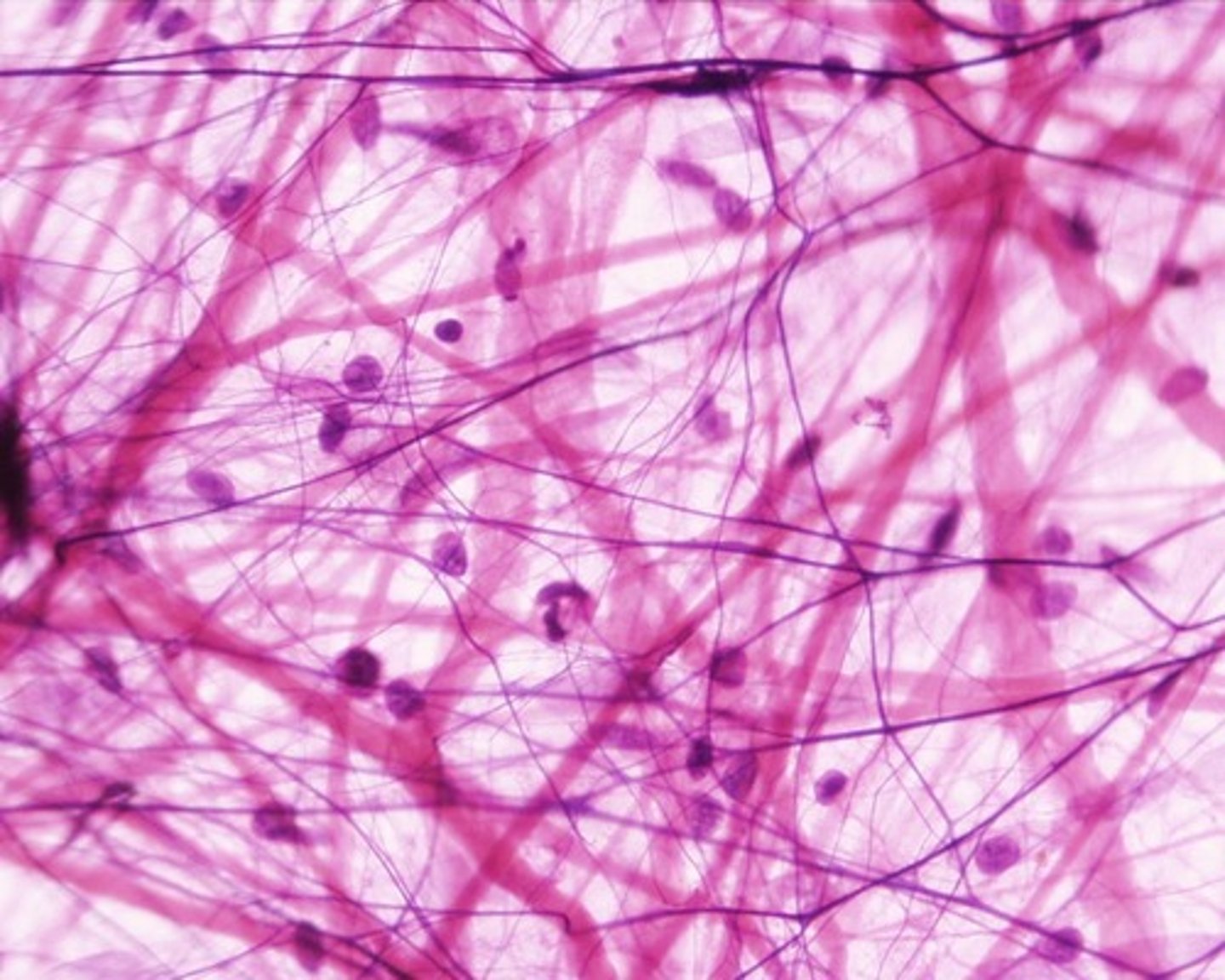
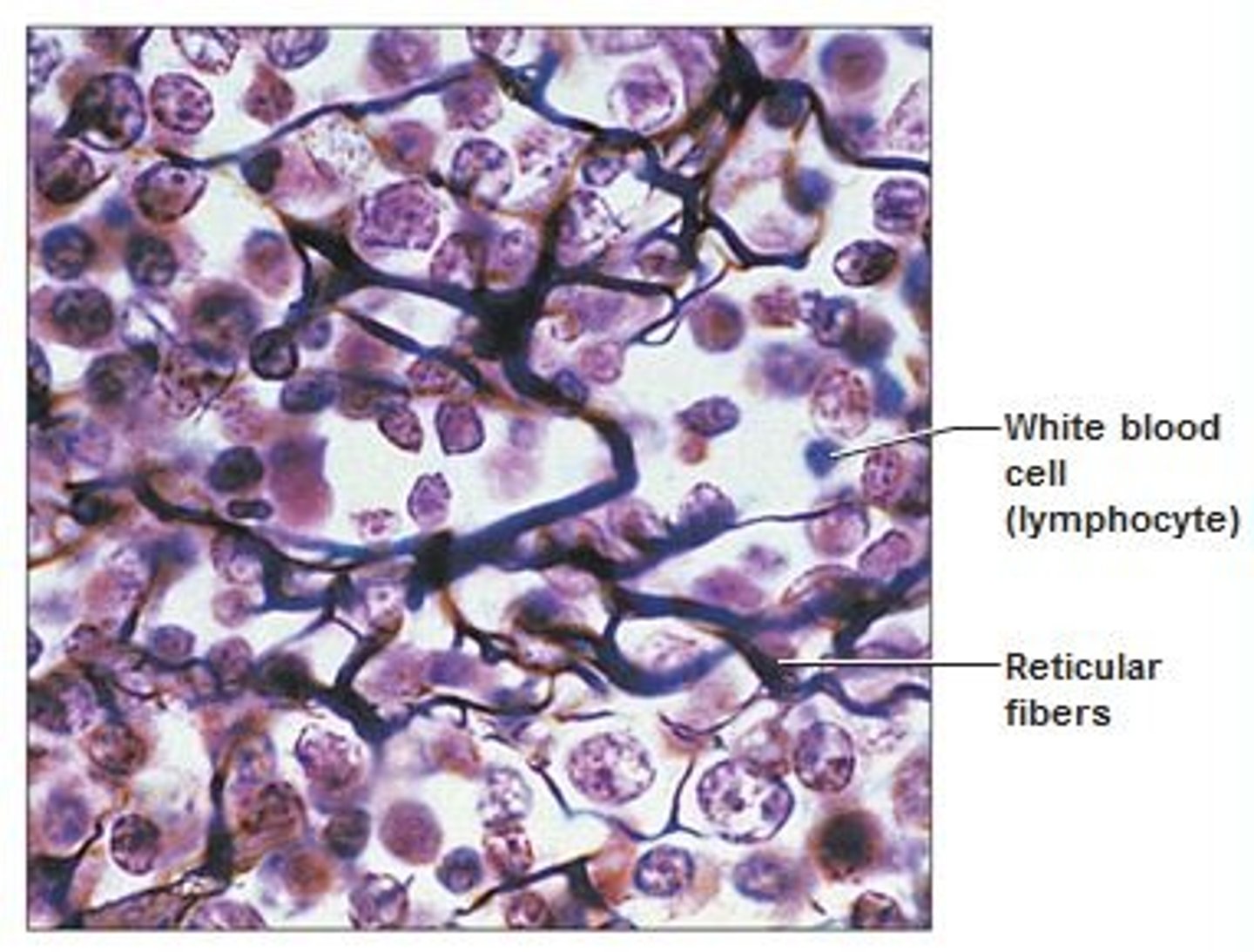
Reticular connective tissue
Resembles areolar tissue but the matrix is made up of only reticular fibers.
Found in bone marrow, spleen, liver, and lymph nodes
Function: forms storma of organs, binds together smooth muscle, filters and removes worn out blood cells in spleen
Made up of: fine interlacing network of reticular fibers
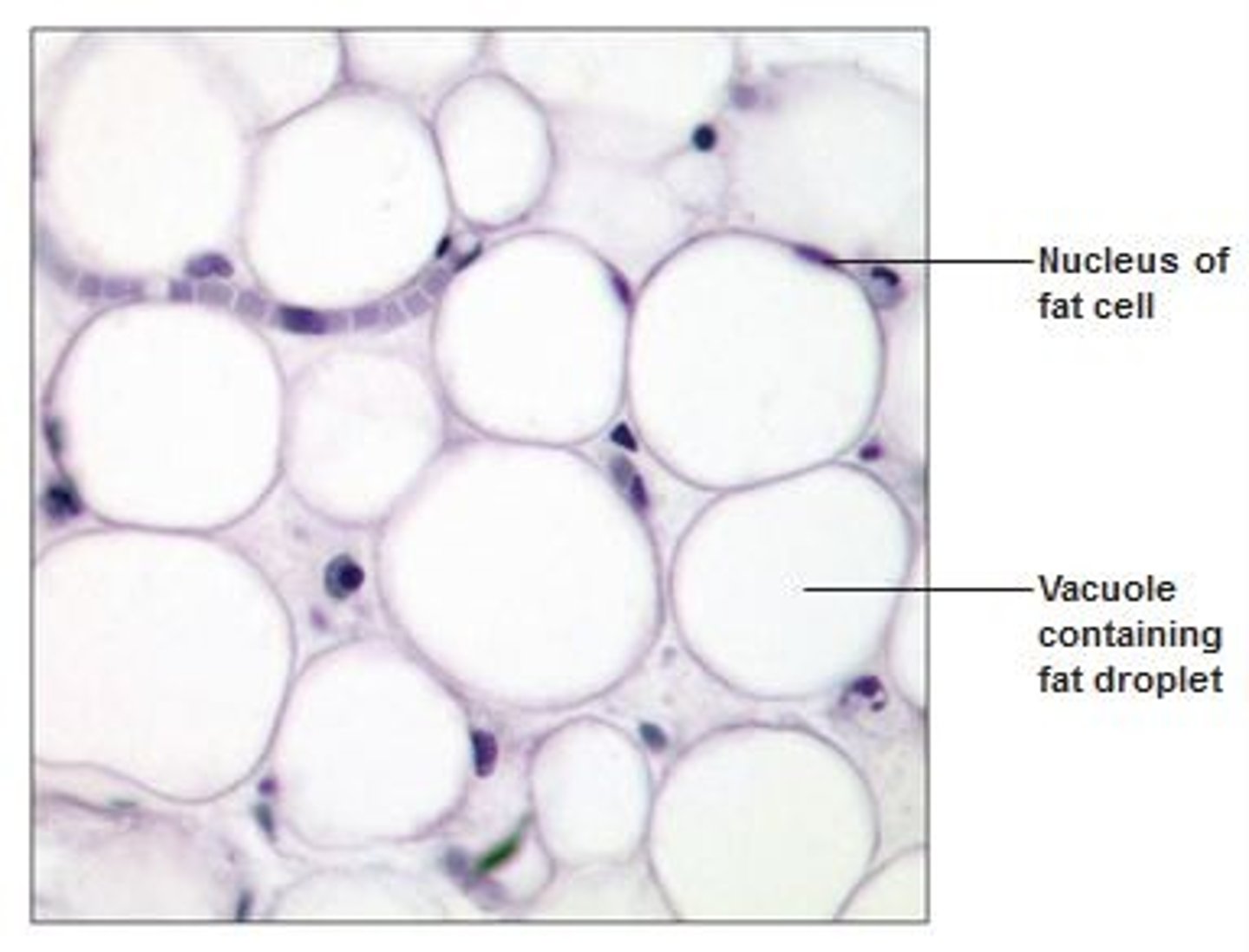
Adipose connective tissue
Has modified fibroblasts which store fat and thus become swollen, pushing the nucleus to the edge of the cell. Widely distributed throughout the body
Function: reduces heat loss through skin, energy reserve, supports and protects organs
Made up of: specialized connective tissue, stores triglycerides in fat droplets in cells
dense regular connective tissue
Thickly packed collagenous fibers in a regular, parallel arrangement. Contains fibroblasts and a few elastic fibers.
Found in: tendons, ligament, aponeuroses, and covering skeletal muscle (deep fasciae)
Function: strong attachment between bodily structures to withstand pulling force along its axis
Made up of: thickly packed collagen fibers
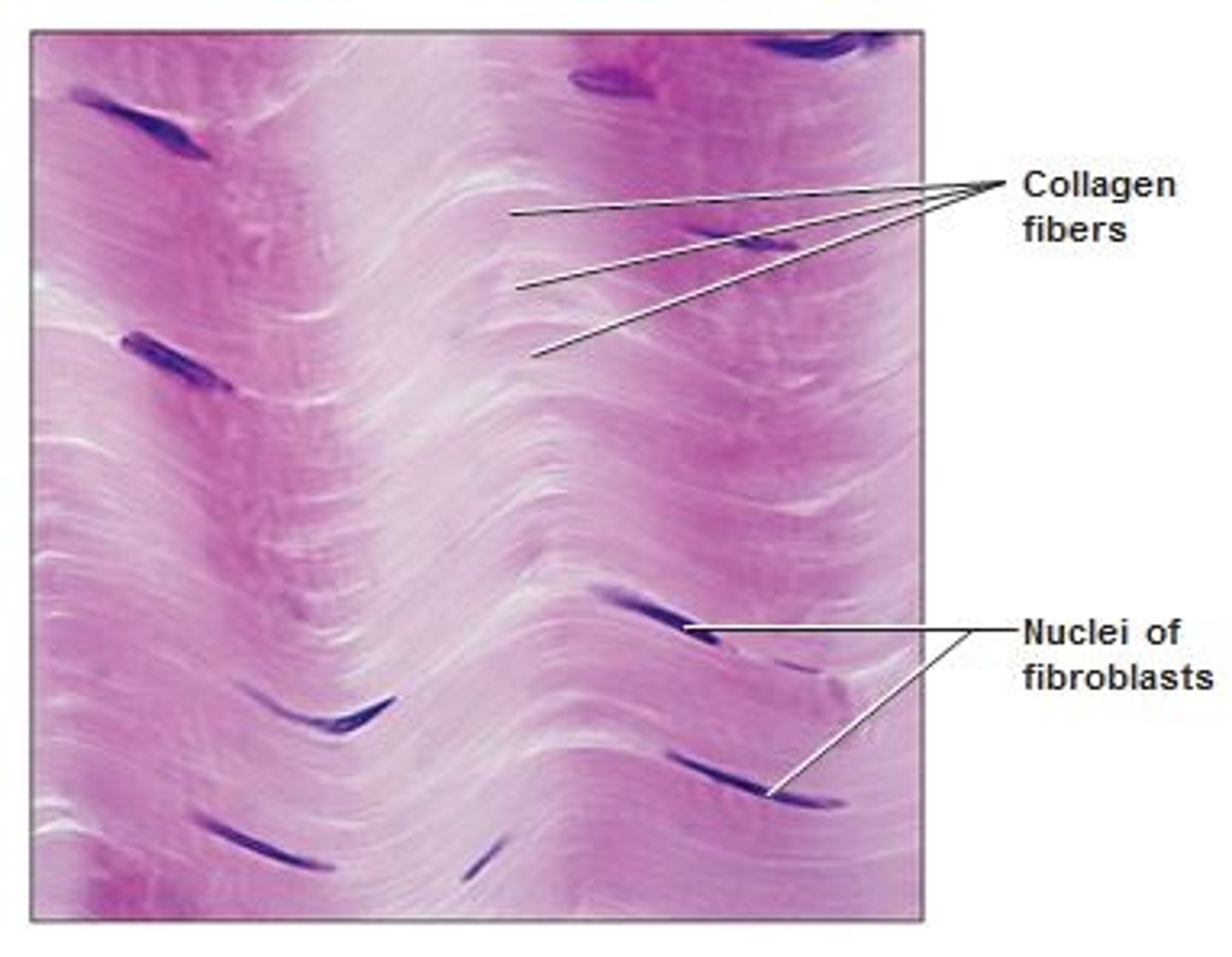
Dense irregular connective tissue
resembles dense regular connective tissue except the collagenous fibers are irregularly arranged. Also contains fibroblasts and a few elastic fibers.
Found in: fibrous capsules of organs and joints, periostea, perichondria, nerve and muscle sheaths, and makes up the dermis
Function: provides pulling strength in several directions
Made up of: tightly packed collagen fibers "irregularly" arranged
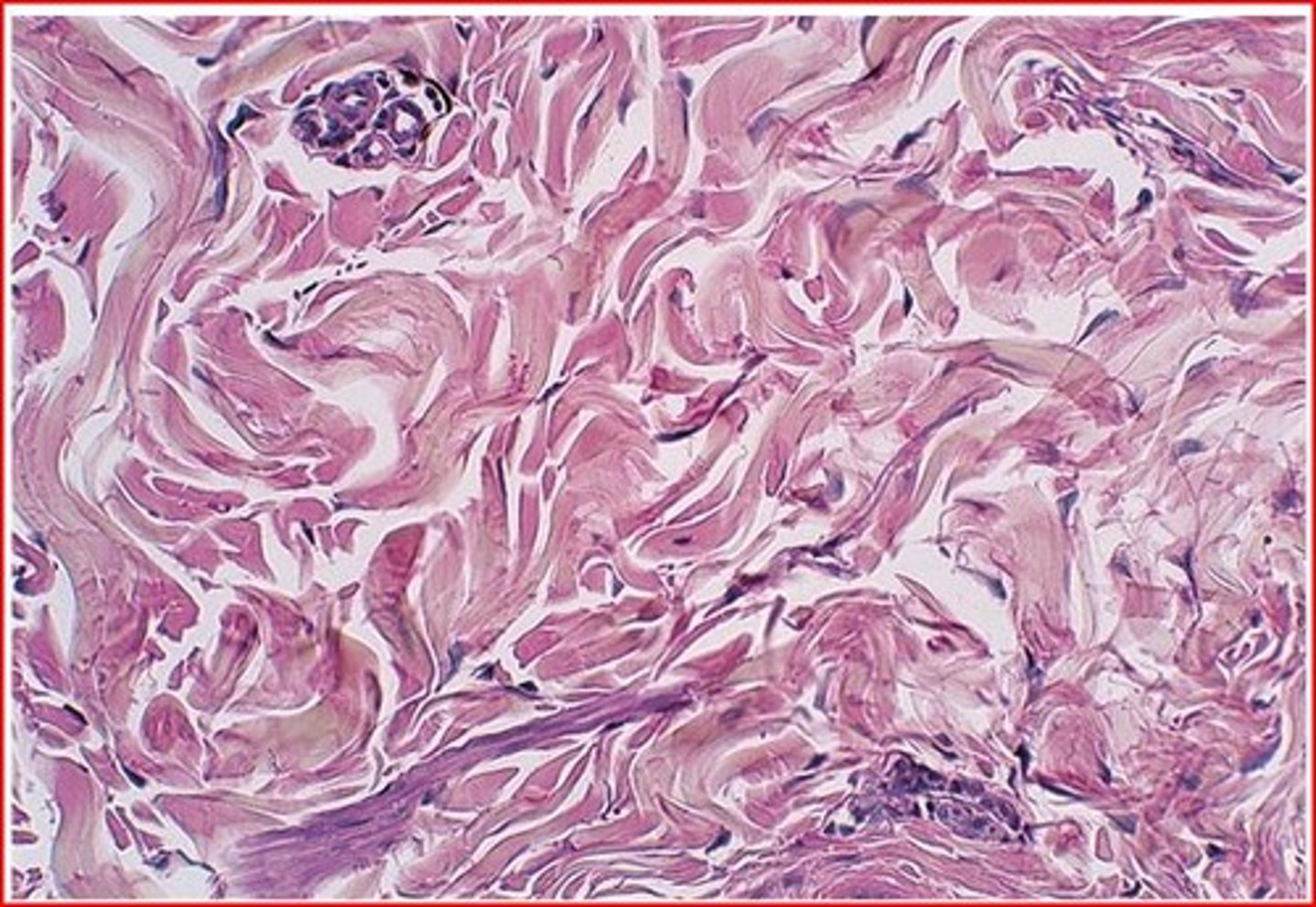
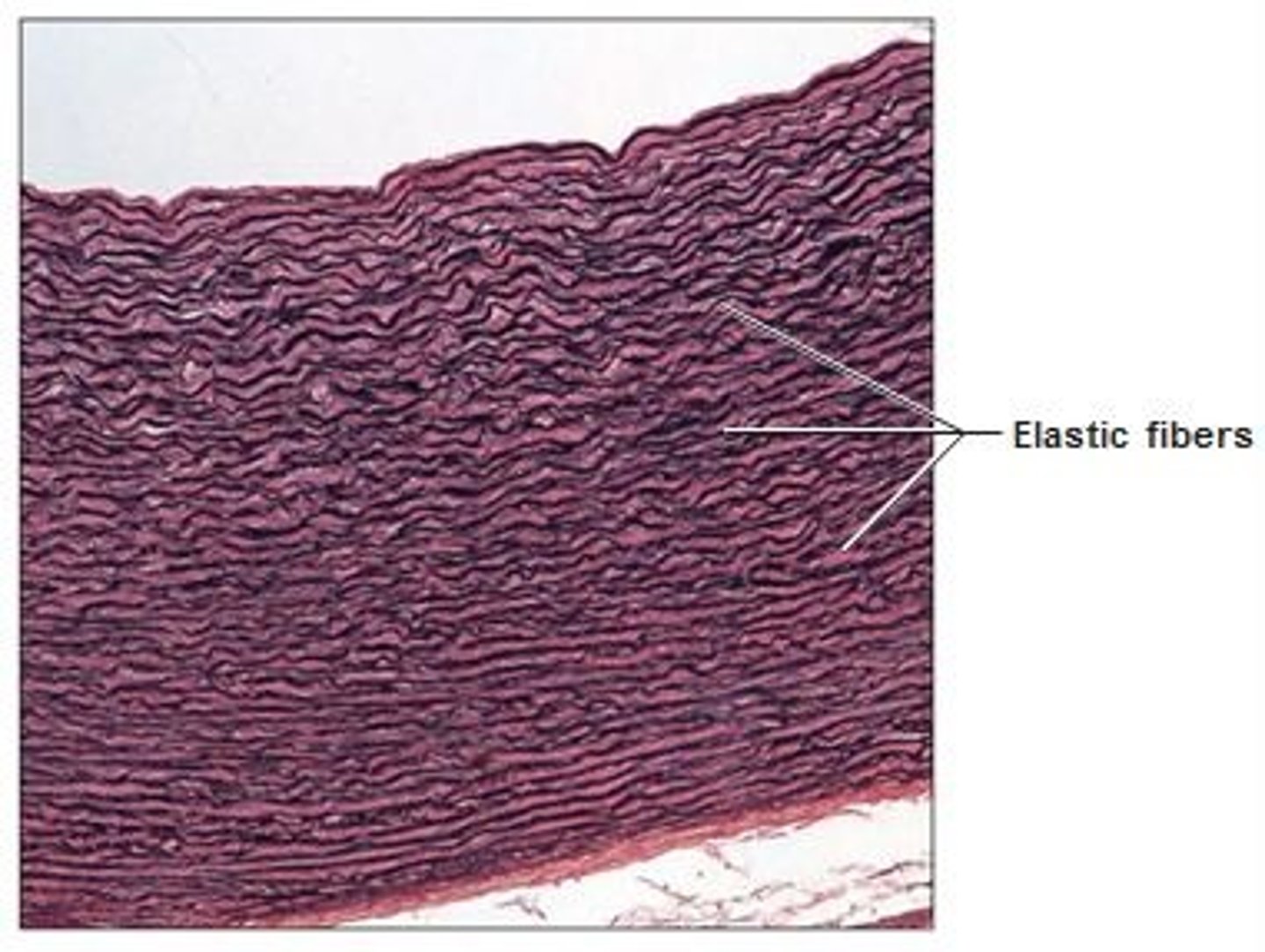
Elastic connective tissue
Predominance of elastic fibers with fibroblasts embedded in between.
Found in: walls of the aorta and other blood vessels, in the vocal cords, surrounding respiratory passages, and ligament flava and ligamentum nuchae of spinal column. Often underlies transitional epithelium
Function: stretching of various organs, strong, can recoil
Contains: largely of elastic fibers
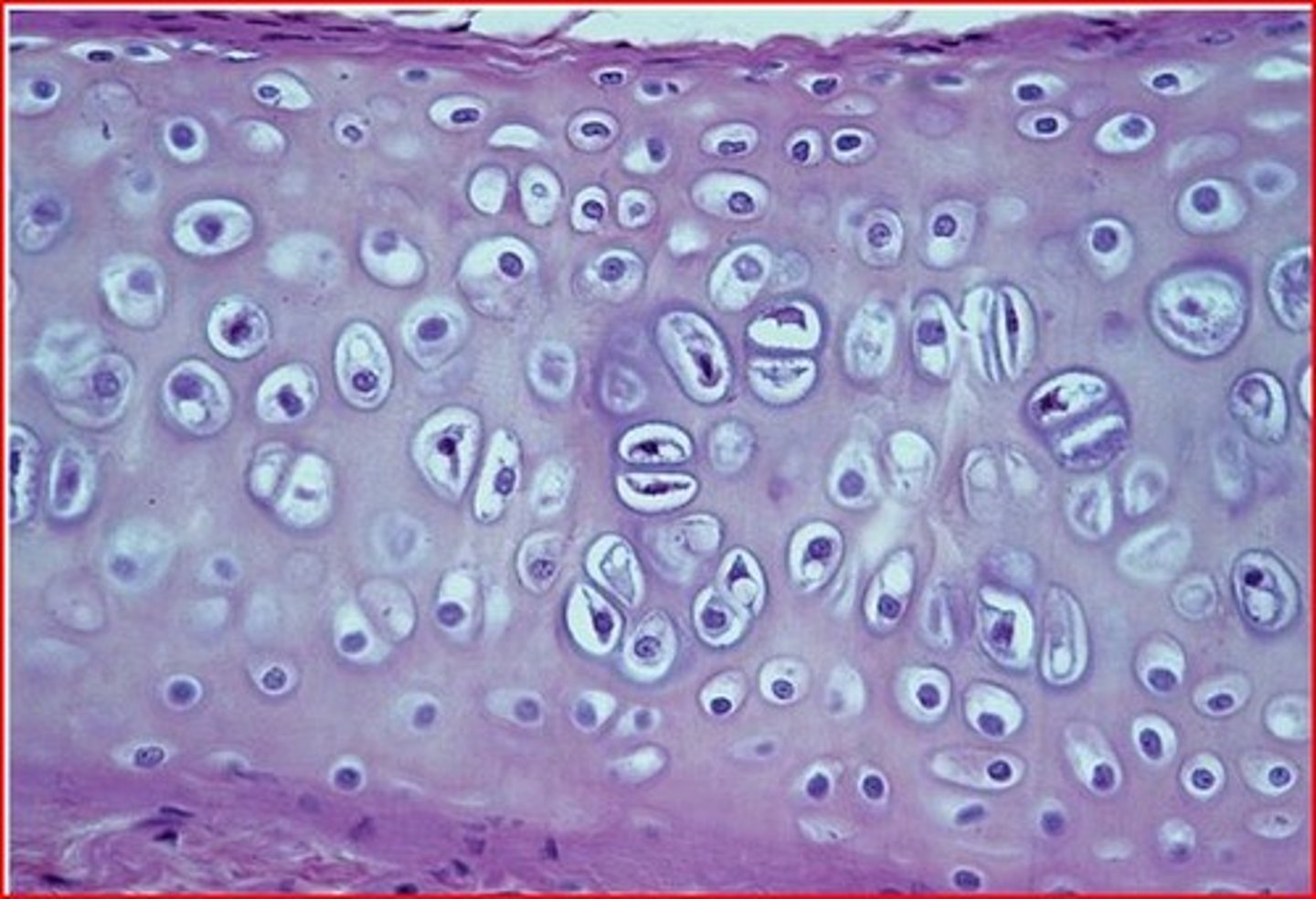
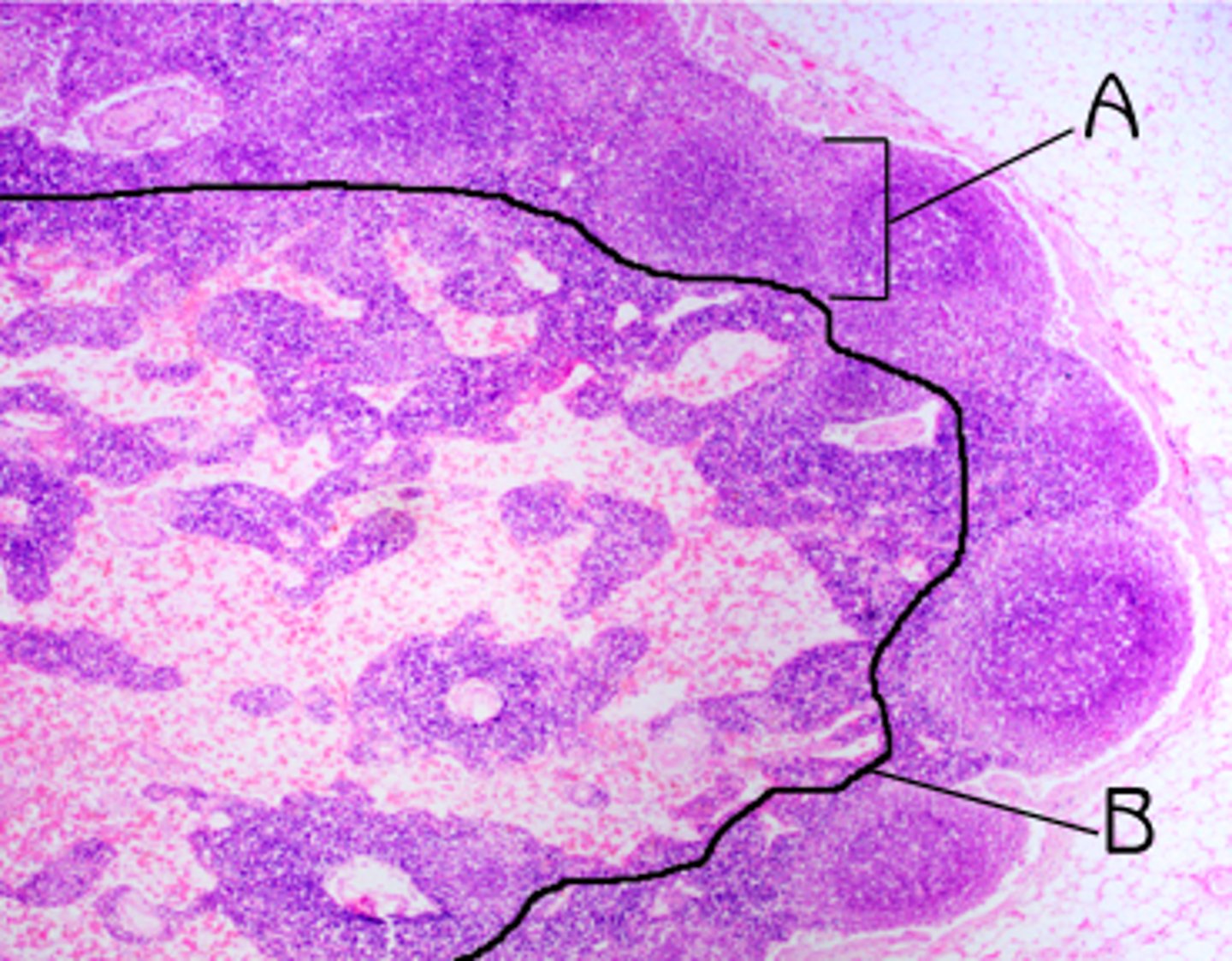
Cartilage
a supporting connective tissue. made up of chondrocytes (cartilage cells) surrounded by a semisolid gel-like matrix. Avascular. (note presence of chondrocytes)
Hyaline cartilage
maxtrix of tightly packed collagen fibers not easily seen under light microscope. Clear, glassy appearance.
Found in: tracheal rings, costal cartilages of the ribs, cartilage of nose, larynx and covers bone surfaces at synovial joints
Function: tough but flexible, smooth surface for joints, flexibility, support
Weakest (can be broken)
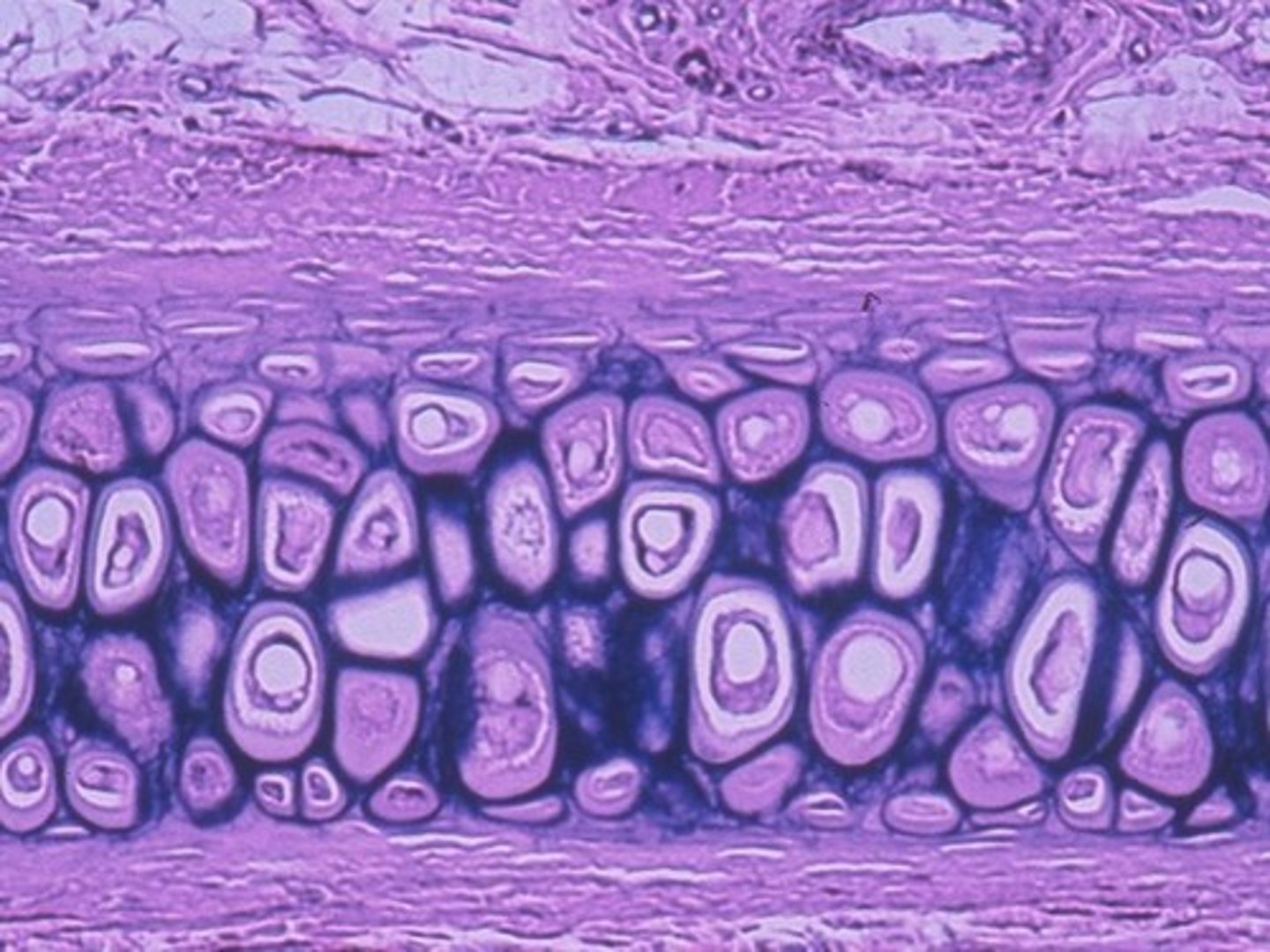
Fibrocartilage
Matrix is supported by collagenous fibers which are densely packed and regularly arranged. Feather like appearance.
Very tough and durable, strongest of the cartilages
Location: intervertebral discs, makes up the menisci of the knee joint and in the symphysis pubis.
Function: support, join 2 structures together, strength, rigidity
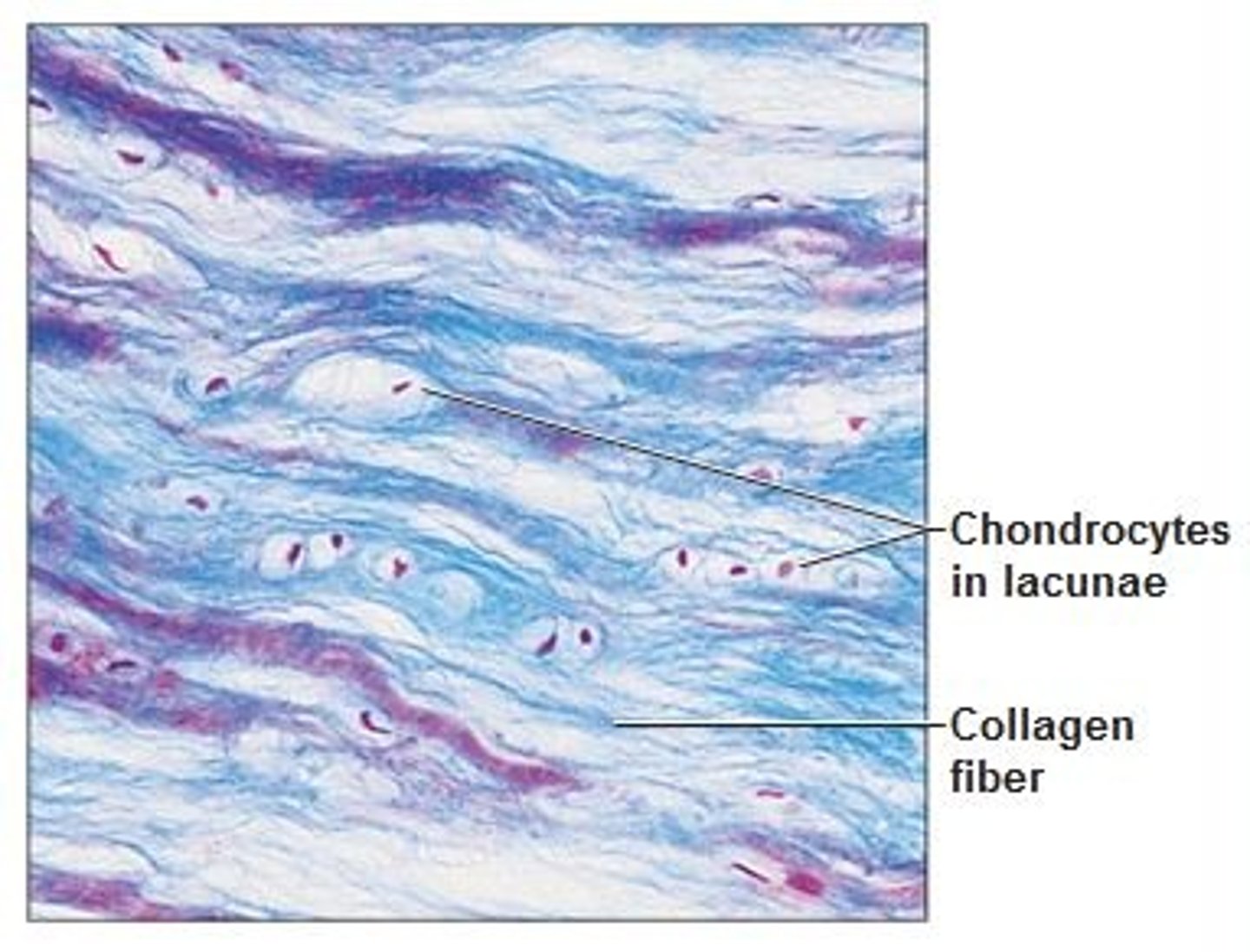
Elastic cartilage
Matrix is supported by elastic fibers which make it resilient and flexible, are less densely packed, and are arranged irregularly. Threadlike network of elastic fibers.
Location: pinna, epiglottis, and auditory canal
Function: strength, elasticity, maintain shape
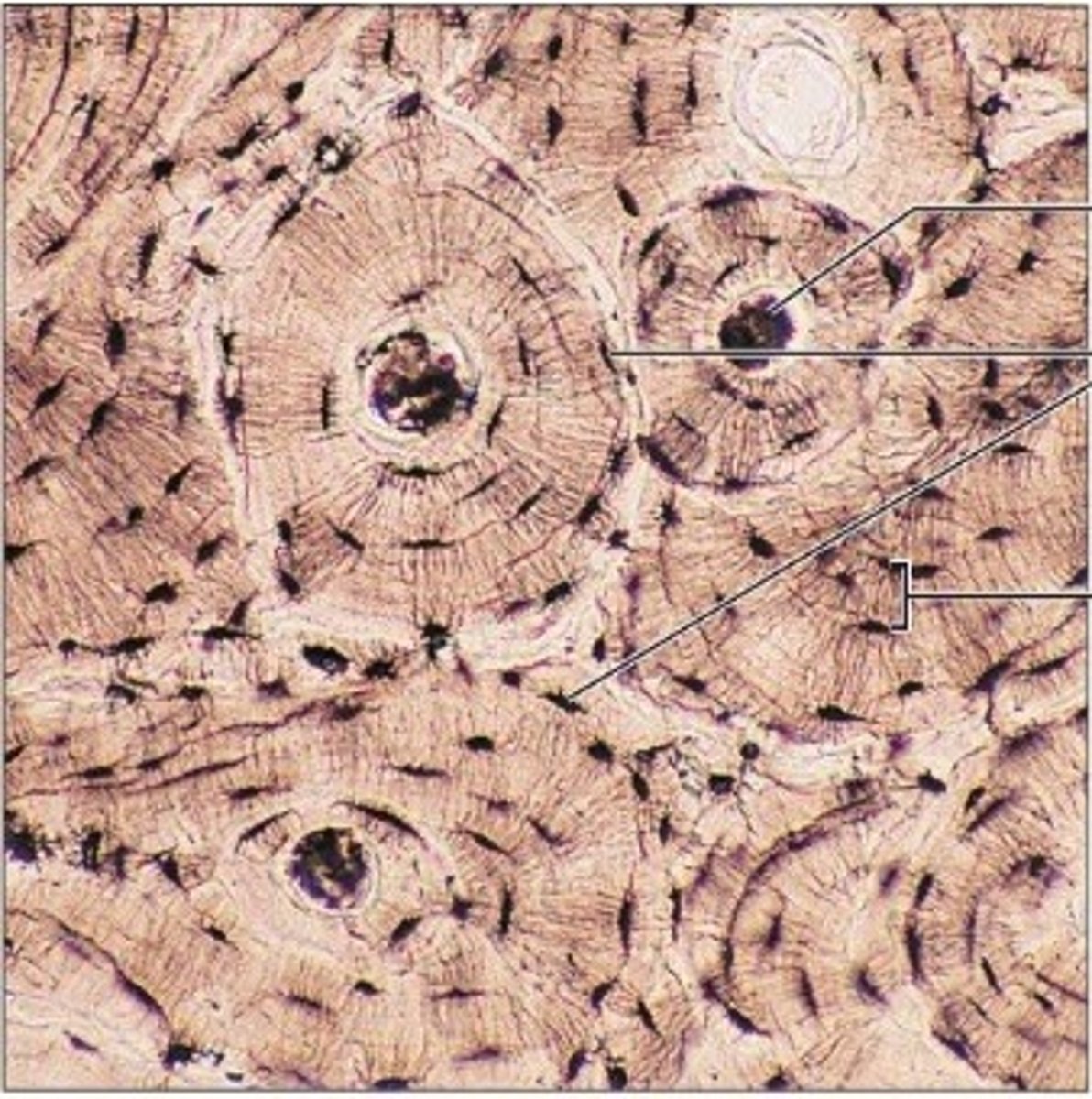
Bone
a supporting connective tissue; one-third of its matrix consists of collagenous fibers
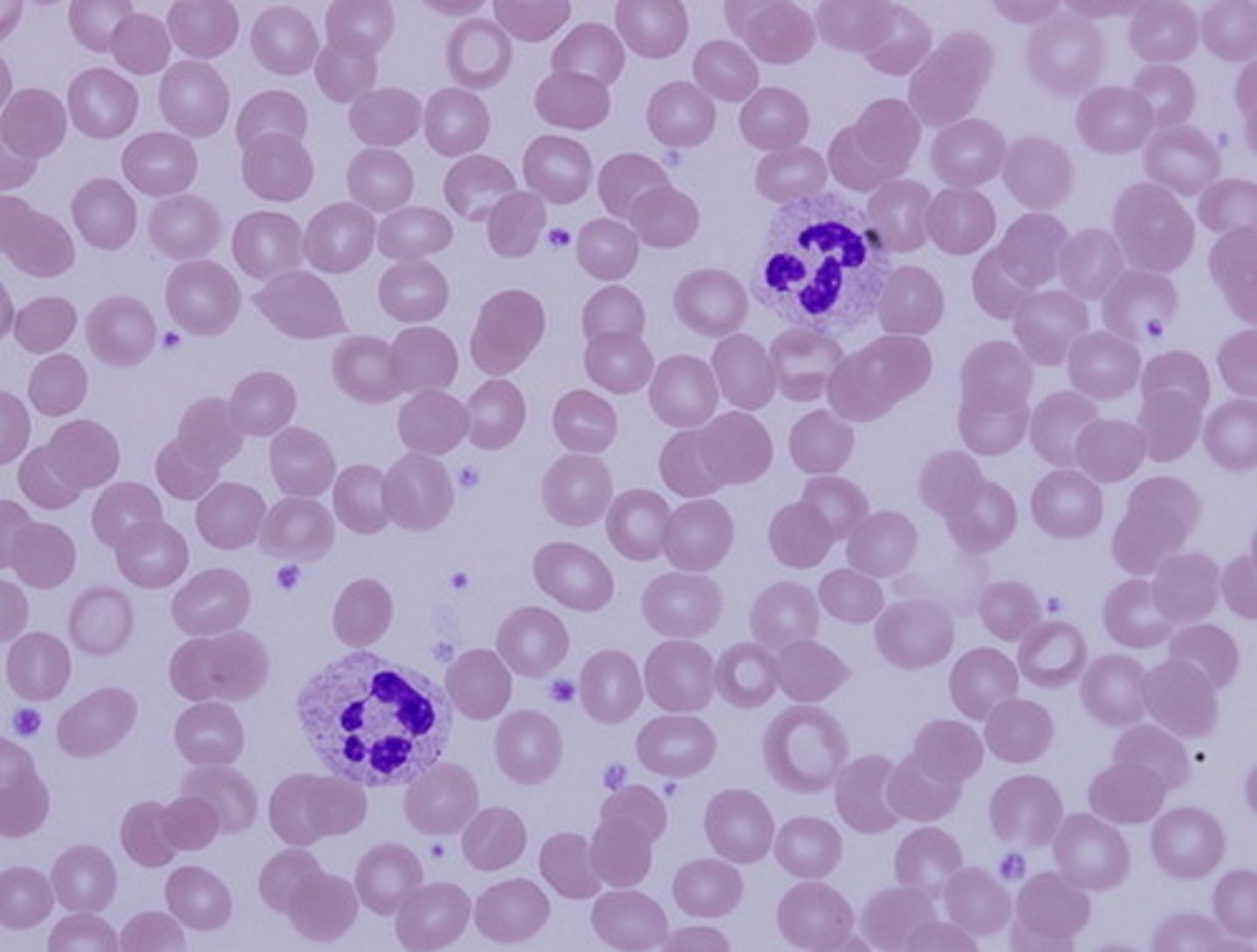
Blood
a fluid connective tissue
Lymph
also considered a fluid connective tissue
Epidermis
5 layers: deep to superficial
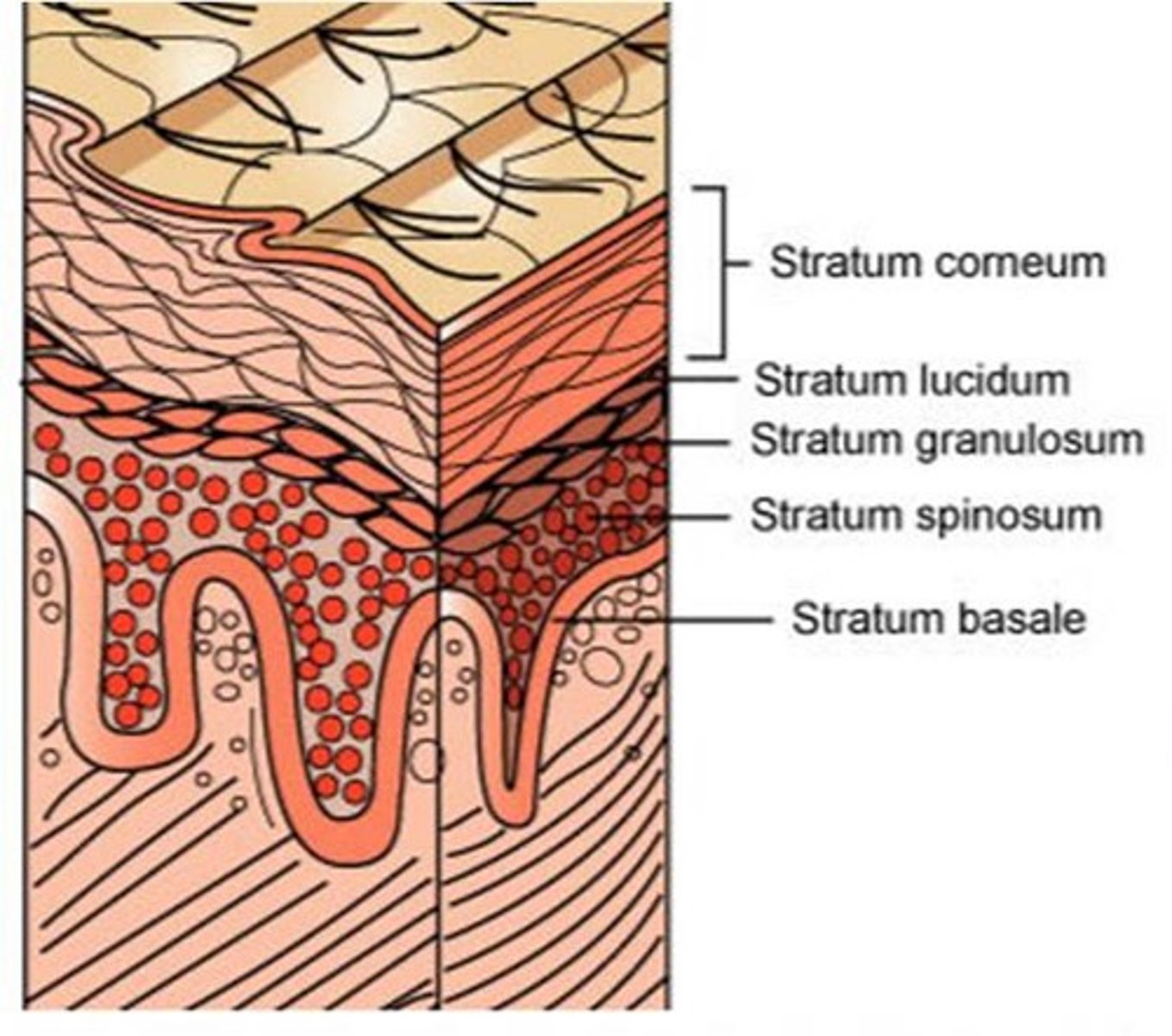
Stratum basale or stratum germinativum
base, cell division
Stratum spinosum
thick layer, slower/less cell division
Stratum granulosum
cells start to die, dead cells give substance (waterproof)
stratum lucidom
only found in thick skin
Stratum corneum
most superficial, thickest layer
Carotene
the yellow pigment of the skin, Vit-A precursor, stratum corneum
Melanin
Formed by melanocytes, protect from UV
thin vs thick skin
Thick skin covers front of hands, bottoms of feet
Thin skin covers rest of the body
Dermis
divided into papillary and reticular regions
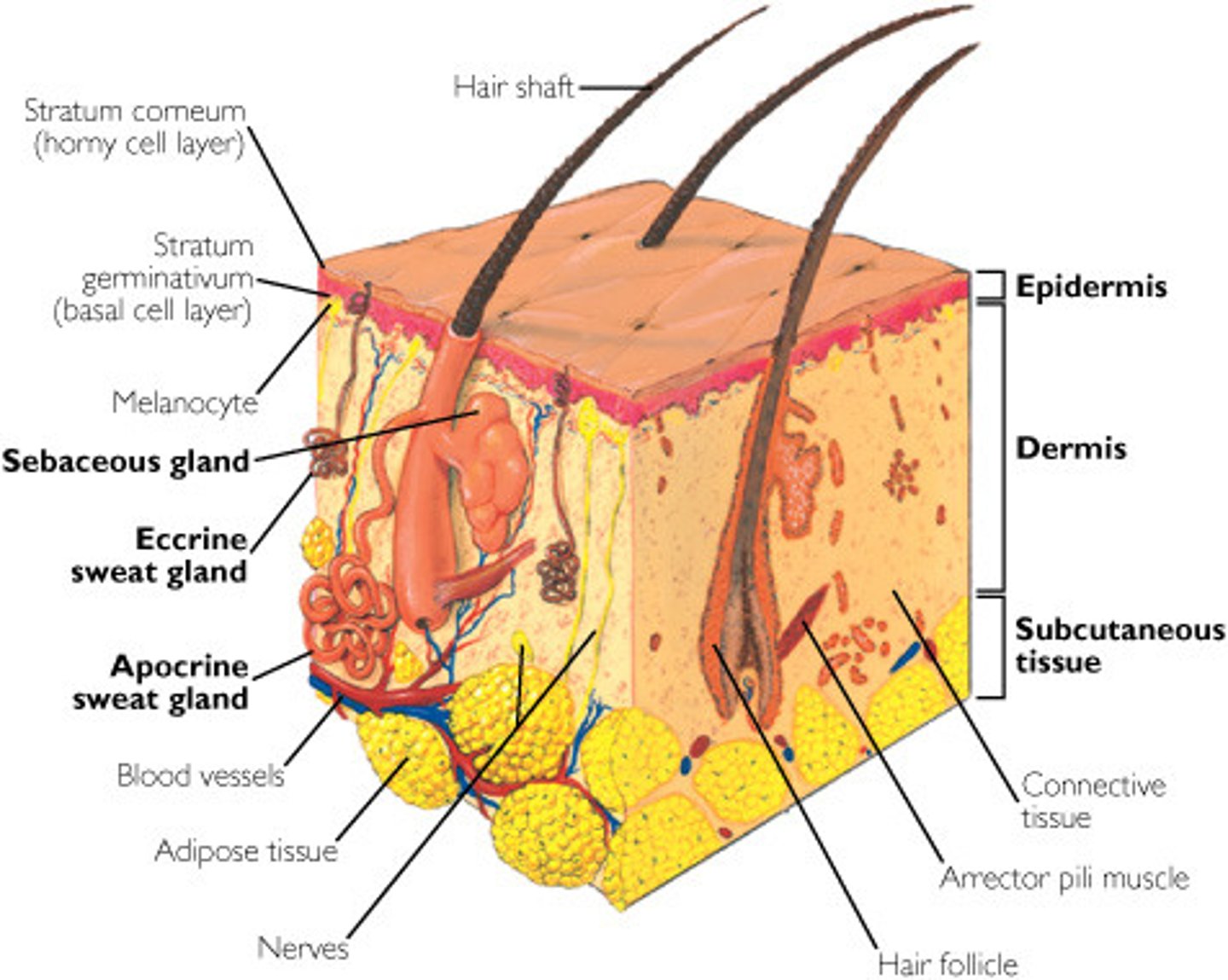
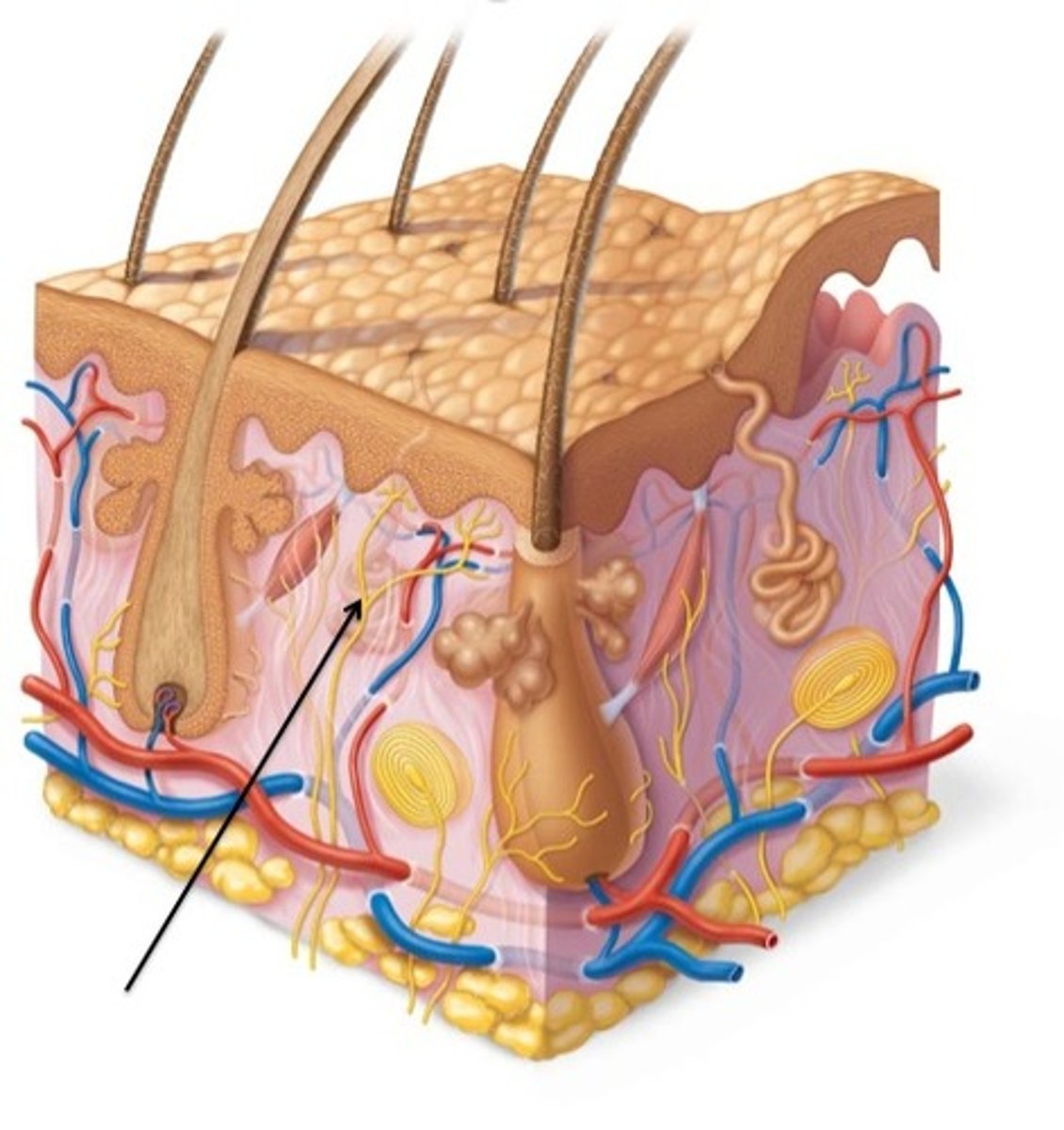
blood vessels
cells in dermis need nutrients, helps with temp. regulation
nerve fibers
sensations, protects us
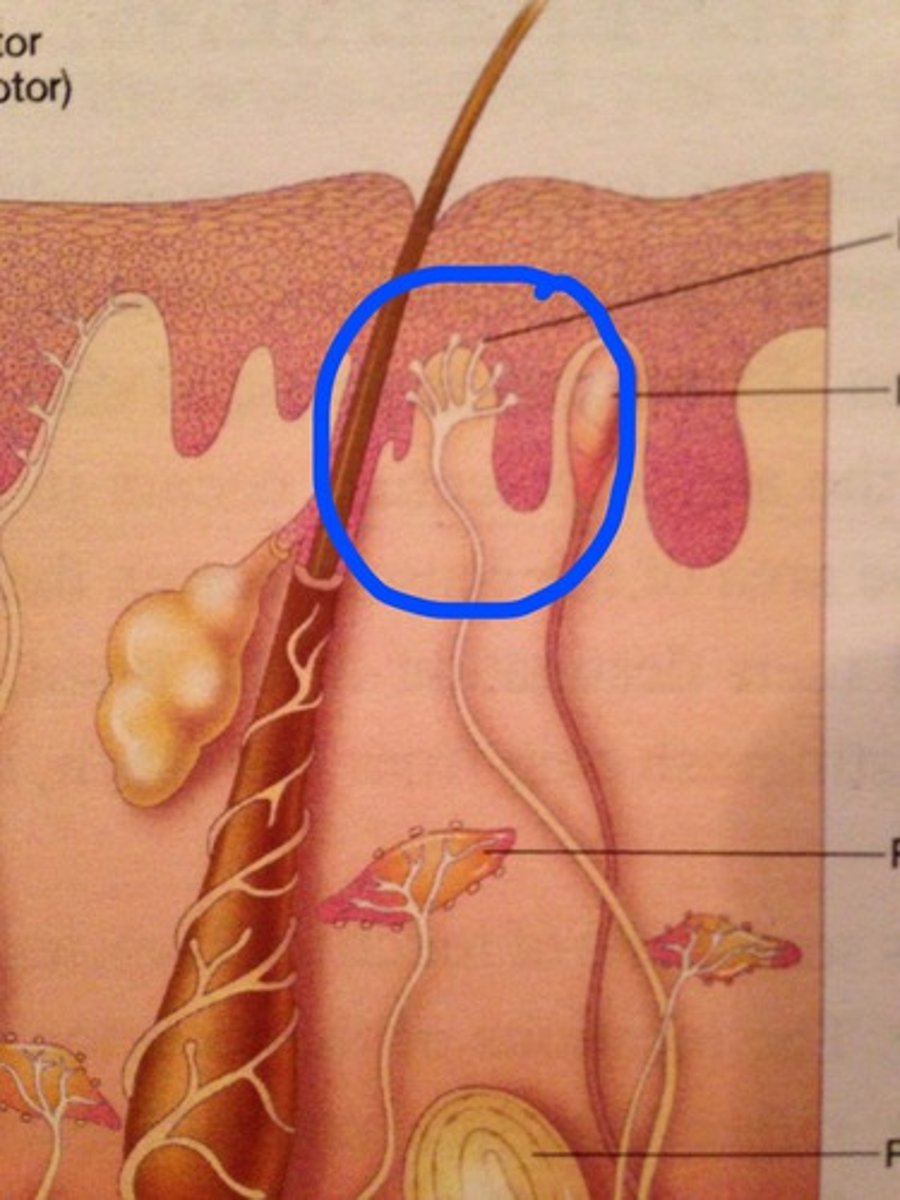
sebaceous glands (sebum)
surrounds hair follicles, make sure hair/skin stay moisturized
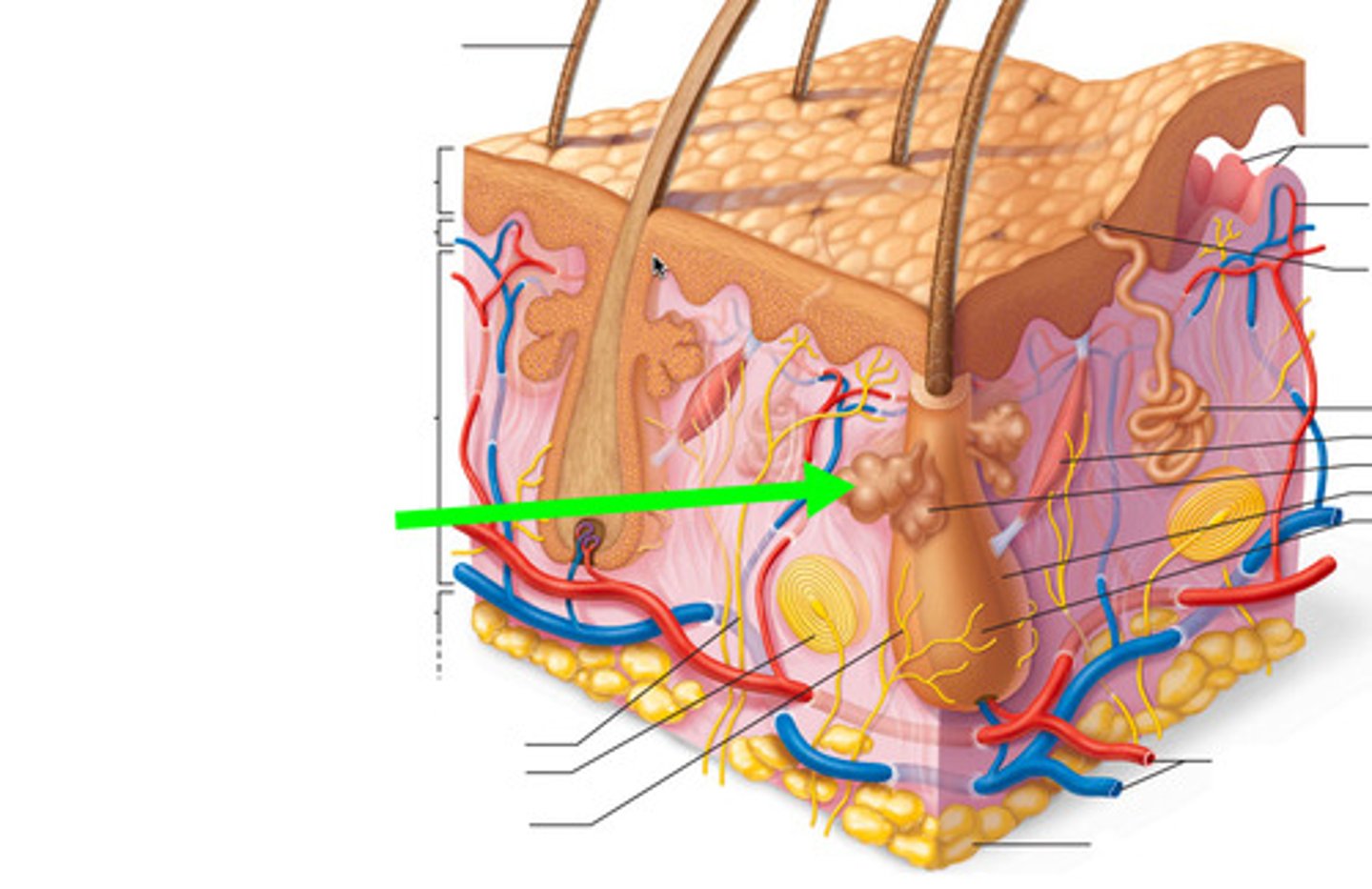
sudoriferous apocrine glands
fatty sweat, body odor, groin, armpits, start more at puberty
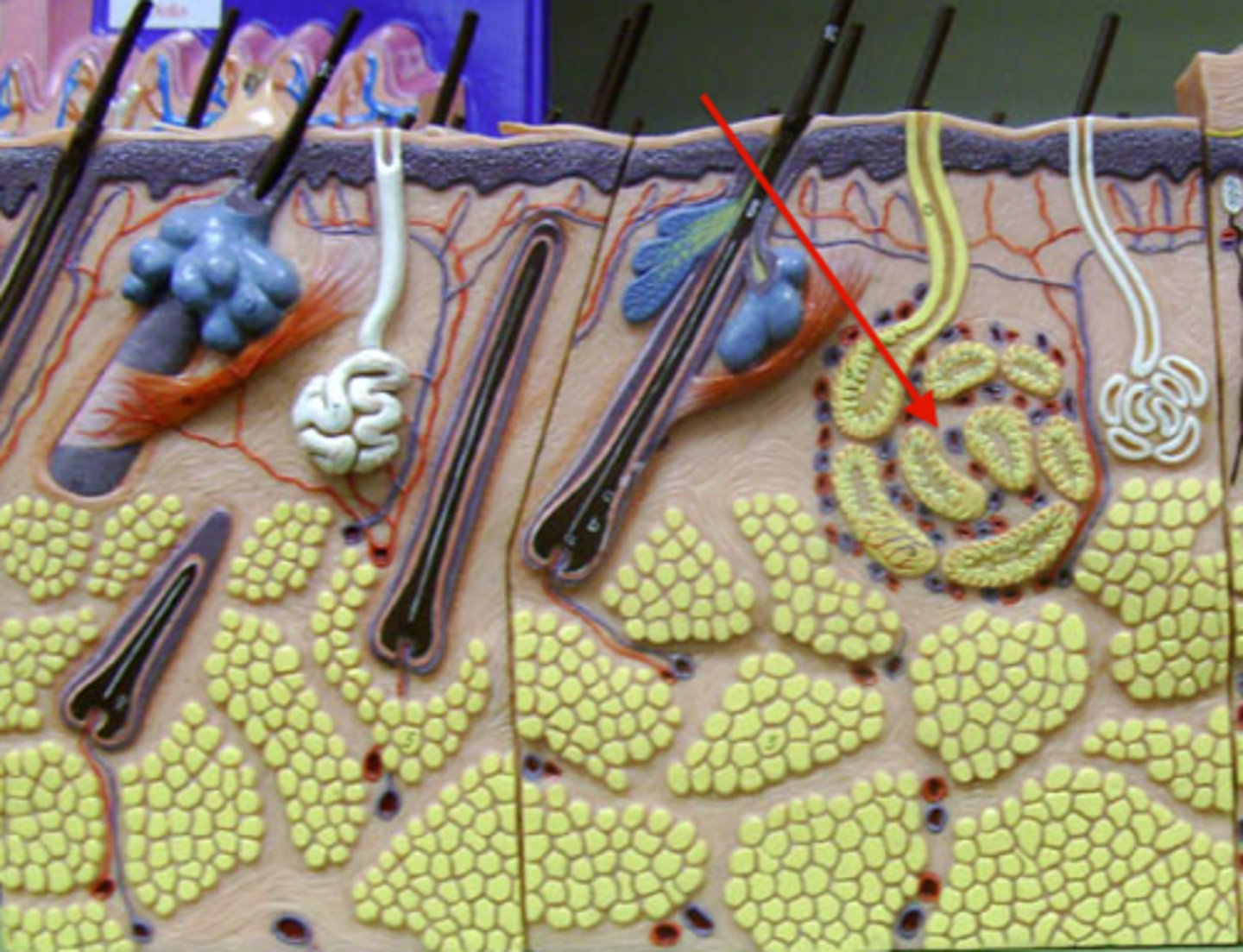
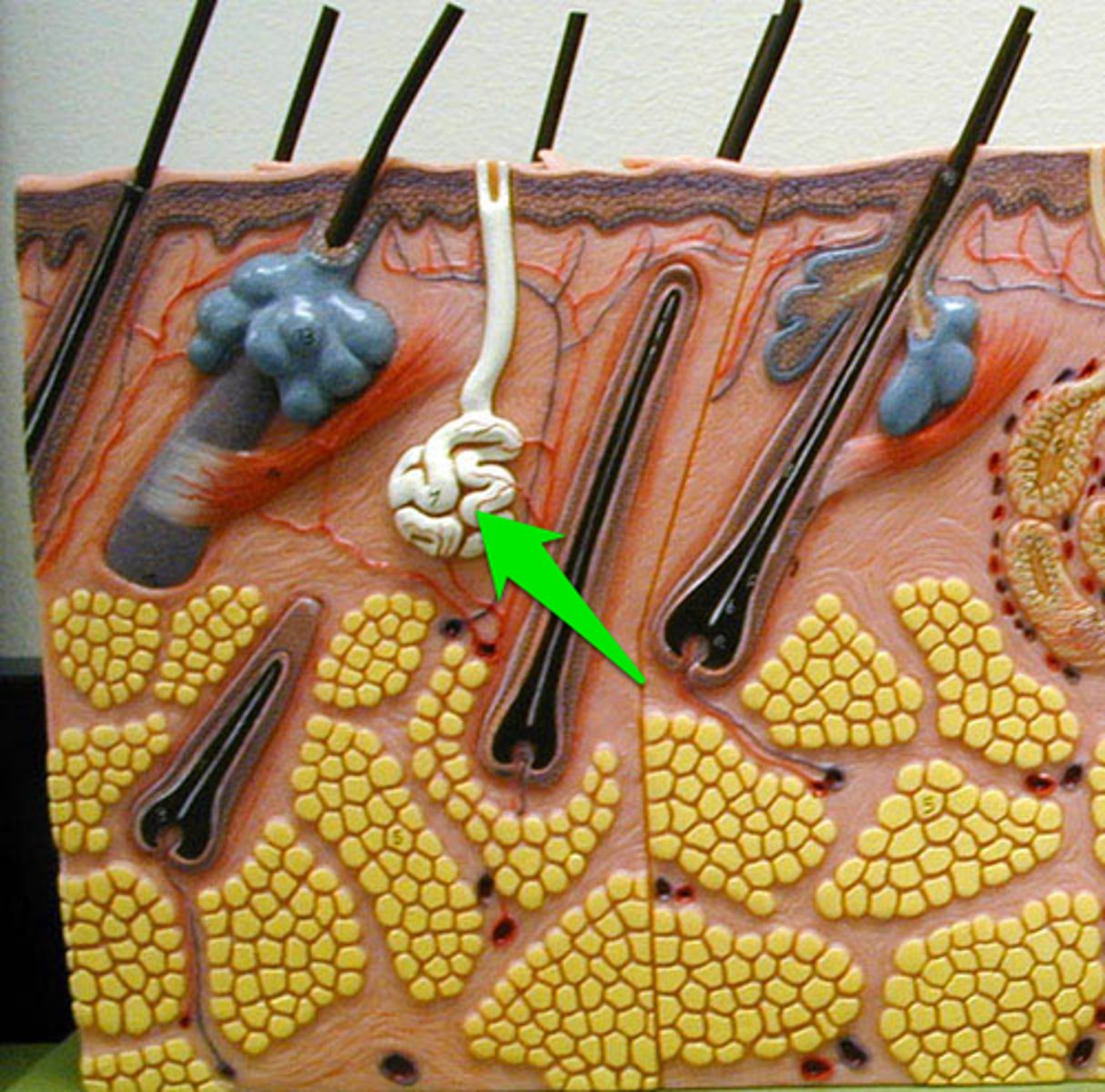
sudoriferous eccrine gland
pores; hands, face, watery secretion, have them at birth
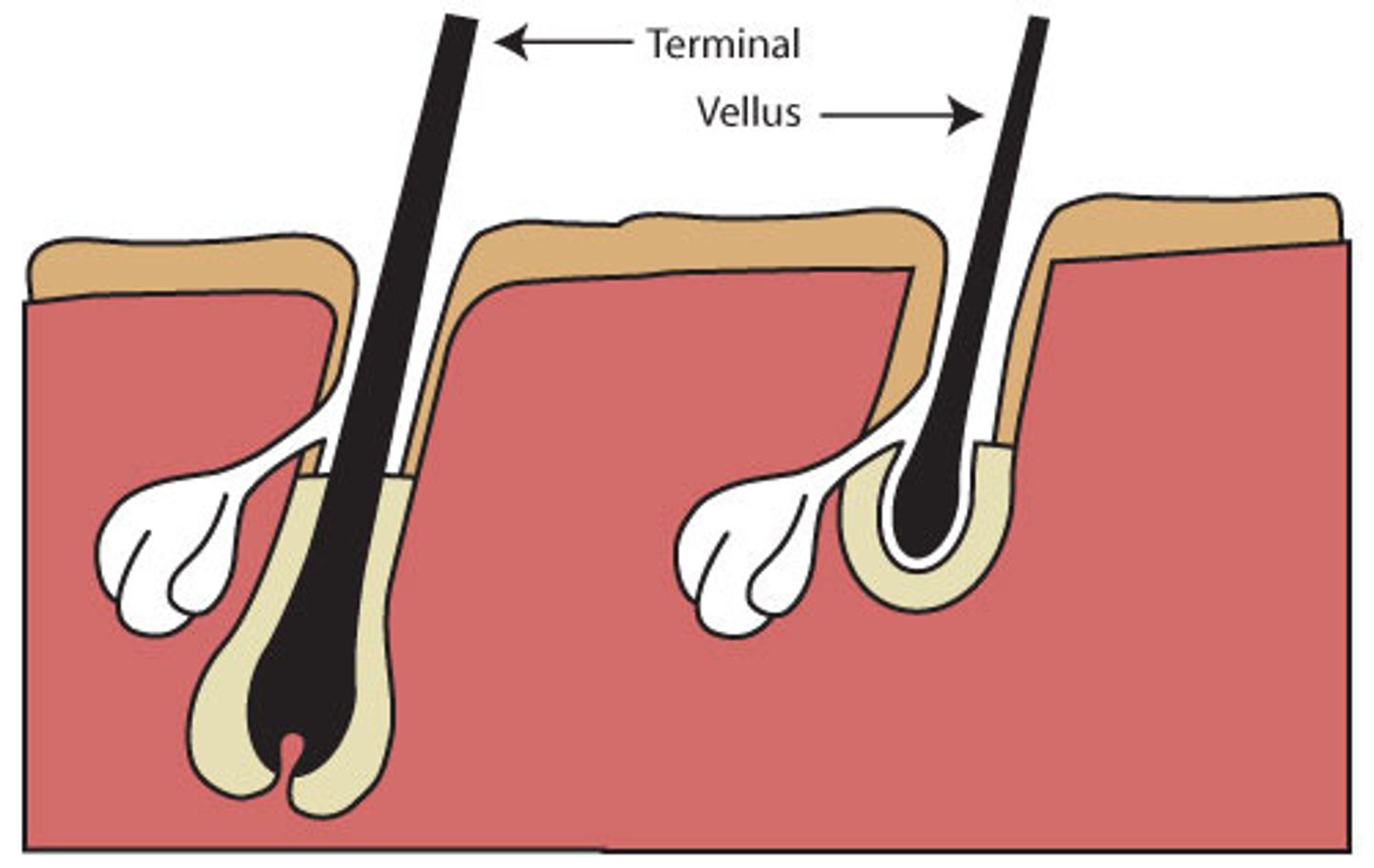
vellus hair
peach fuzz
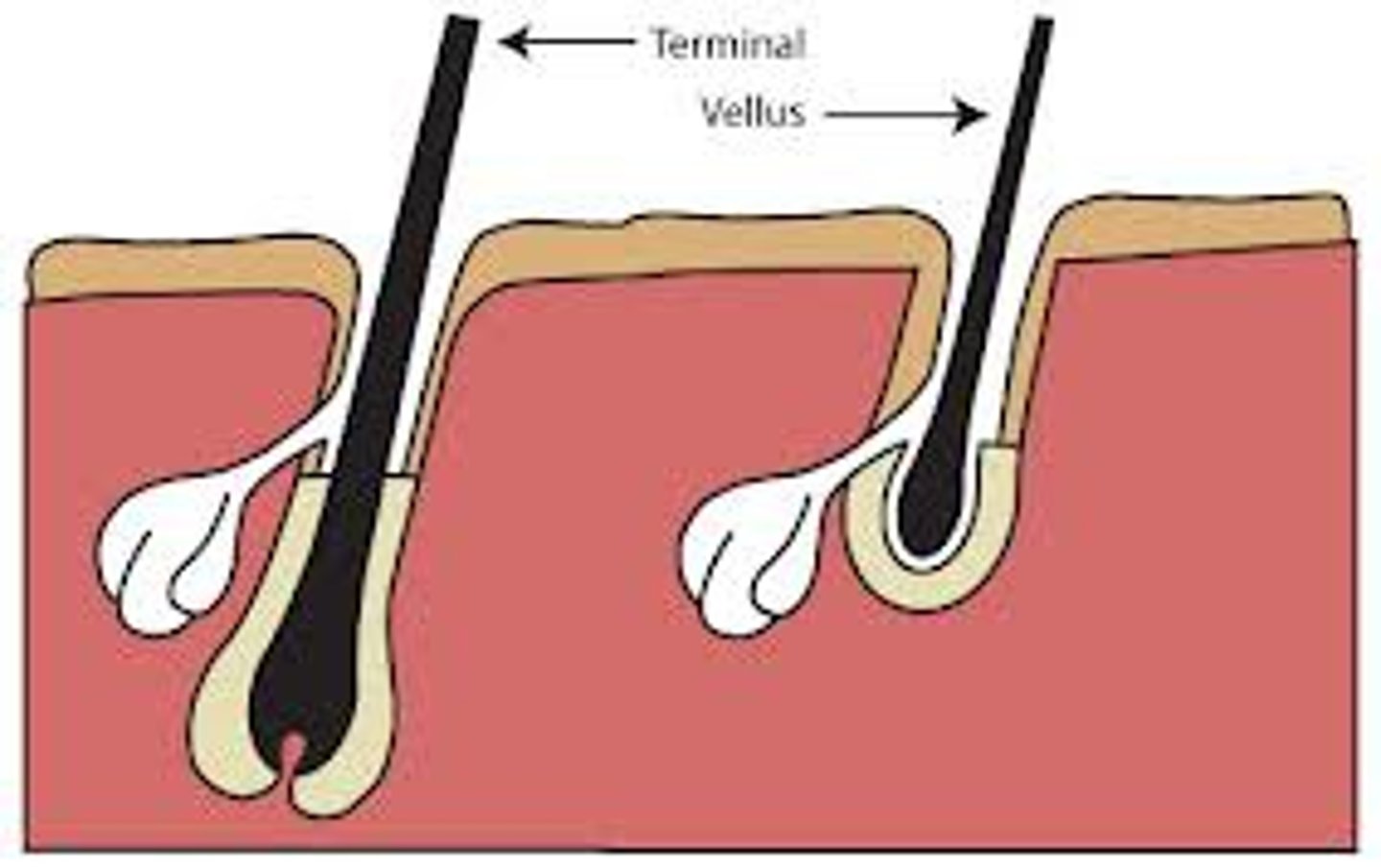
terminal hair
Long, coarse, pigmented hair found on the scalp, legs, arms, and bodies of males and females.
arrector pili muscle
goosebumps, generate heat, smooth muscle
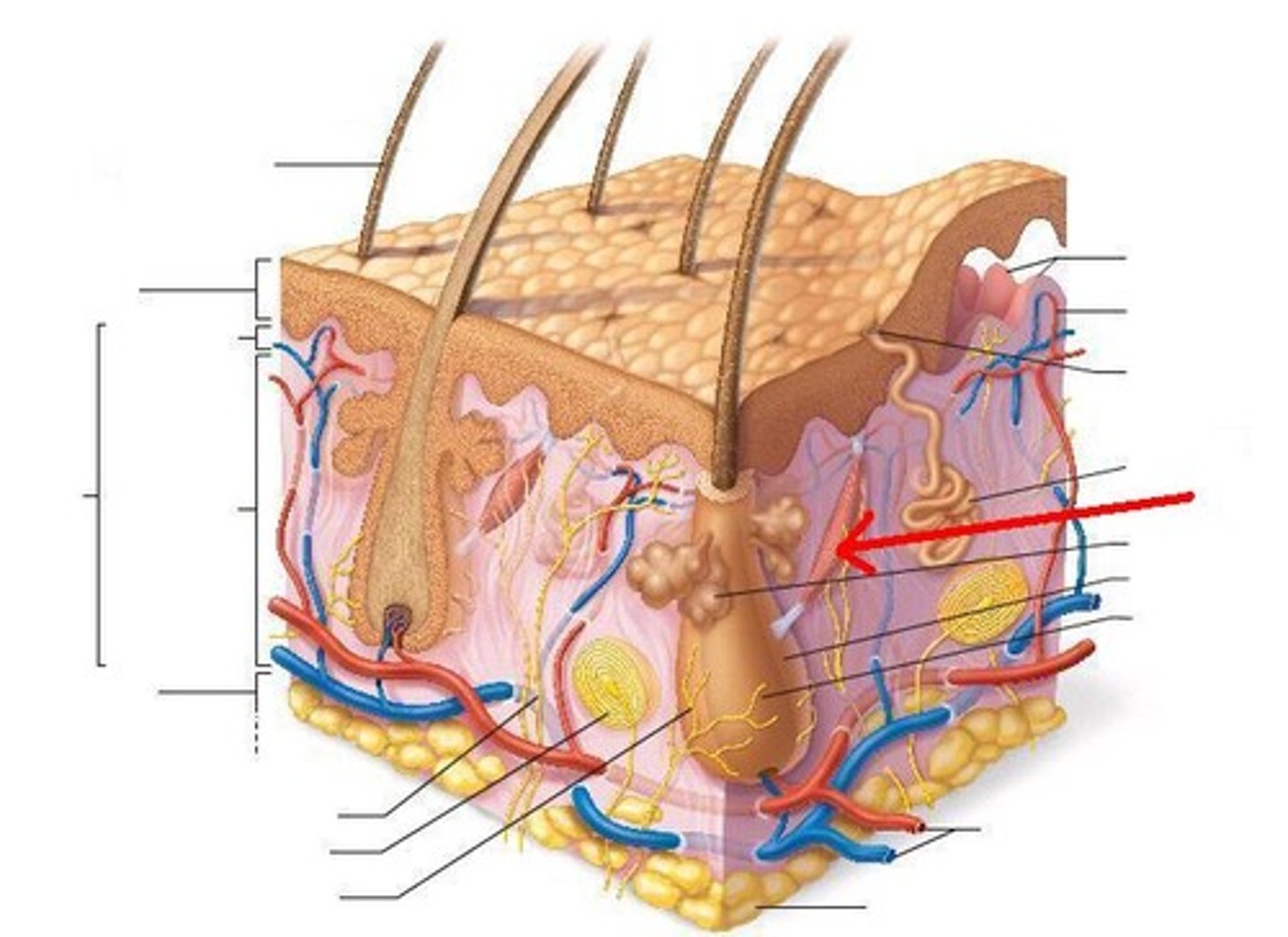
Pacinian corpuscles
deep pressure/vibration receptors, looks like an onion on diagram
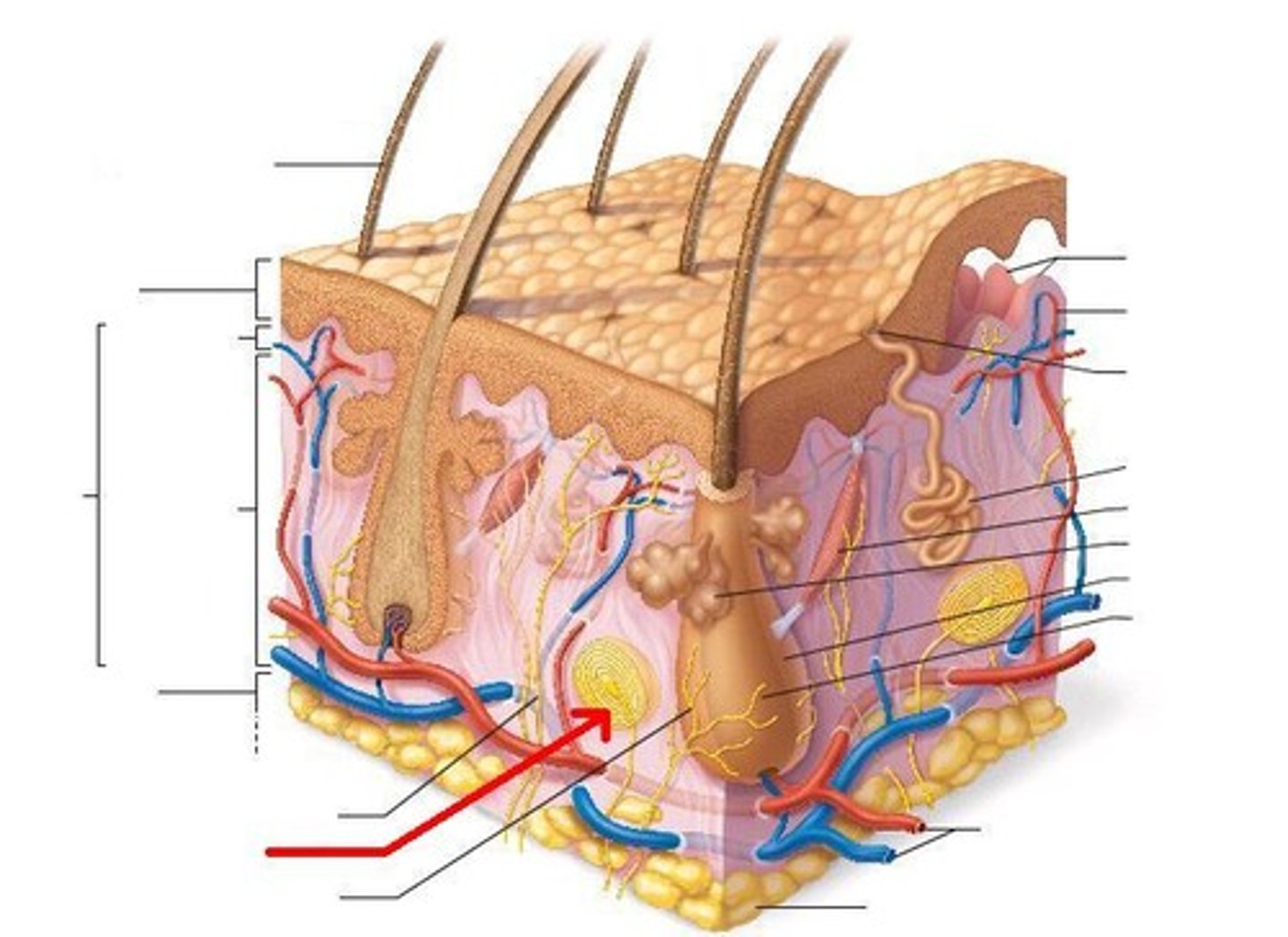
Ruffini corpuscles
detects twisting, stretching of dermis
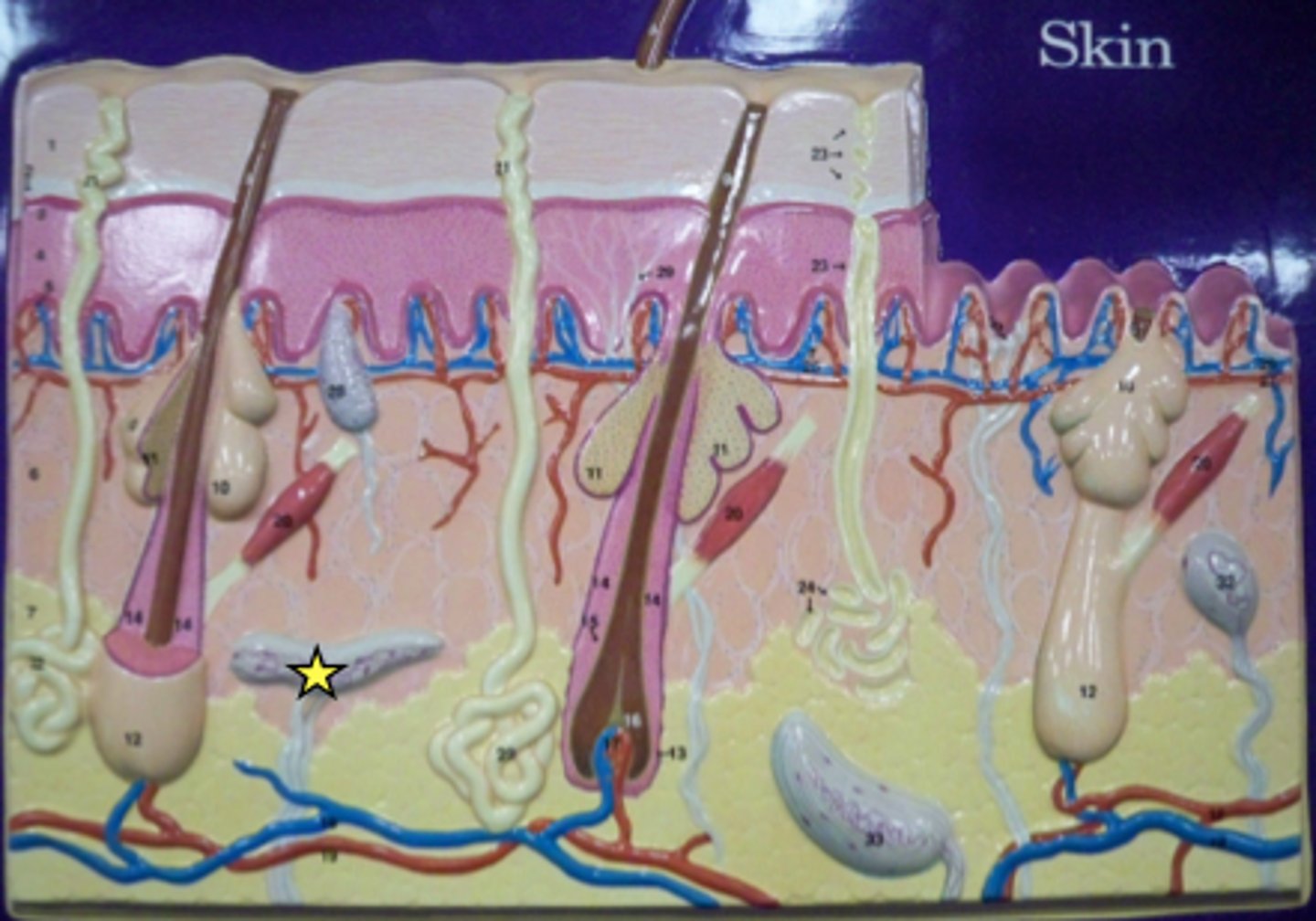
Meissner corpuscles
under the s. basale, detect more fine touch movements
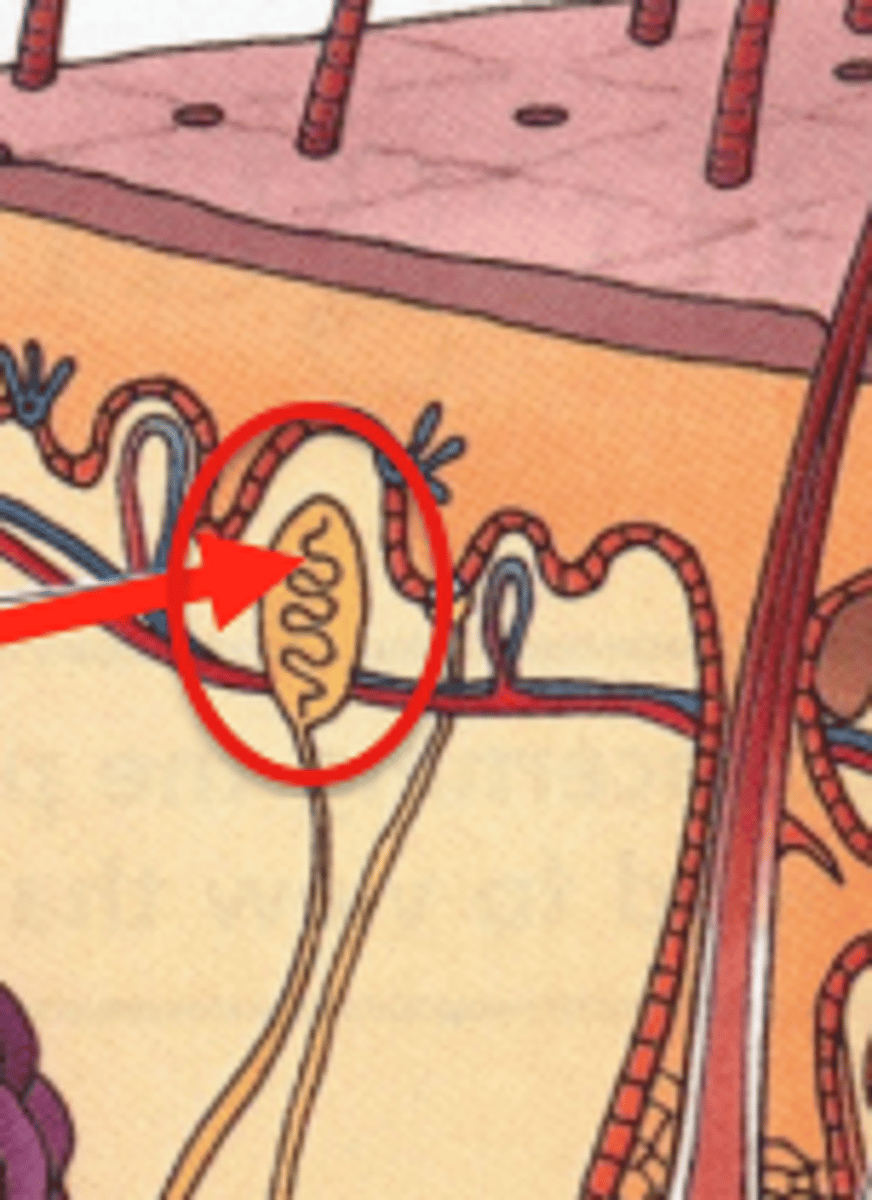
Merkel cells (epidermal)
detect fine touch;s. basale