BSCI201 Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/221
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
1
New cards
Contraction Steps.
1. Nerve impulses stimulate release of neurotransmitter called Acetylcholine.
2. When receptors have been stimulated, the sarcolemma exhibits electrical changes (Negative to neutral charges).
3. The Electrical changes spreads until it reaches the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
4. Sarcoplasmic reticulum stimulates the release of Ca+ ions into sarcomere, which causes myofilaments to undergo a conformational change and slide over one another.
2. When receptors have been stimulated, the sarcolemma exhibits electrical changes (Negative to neutral charges).
3. The Electrical changes spreads until it reaches the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
4. Sarcoplasmic reticulum stimulates the release of Ca+ ions into sarcomere, which causes myofilaments to undergo a conformational change and slide over one another.
2
New cards
What are the functions of the muscles?
Movement
Maintaining posture and body position
Stabilizing joints
Heat generation (especially skeletal muscle)
Maintaining posture and body position
Stabilizing joints
Heat generation (especially skeletal muscle)
3
New cards
Dangerous heat levels are prevented by radiation of heat from the ___ and _____
Skin and sweating
4
New cards
Skeletal muscle tissue is attached to ______.
Is it striated?
Voluntary or not?
Is it striated?
Voluntary or not?
Attached to bones and skin
Striated
Voluntary
Striated
Voluntary
5
New cards
Cardiac muscle tissue is found where? Is it striated?
Only in the heart
Striated
Striated
6
New cards
Where is smooth muscle found? Is it striated? Voluntary?
Walls of hollow organs, stomach, urinary bladder, airways
Not striated
Involuntary
Not striated
Involuntary
7
New cards
What are special characteristics of muscle tissue?
Vascularized and inverted, excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
8
New cards
Myosin has ___ heads and is ____
Globular heads and is at an angle
9
New cards
Actin ____overlaps with myosin
Partially
10
New cards
Actin forms ____ strands
Double twisted
11
New cards
Thick filament has ___ molecules whose head protrude at _______
many myosin molecules.....protrude at opposite ends of the filament
12
New cards
tropomyosin
blocks the attachment site for the myosin crossbridge, thus preventing contraction
13
New cards
Troponin
____ is attached to the protein tropomyosin
14
New cards
Thin filament consists of ____ strands of ____ twisted in a helix plus two types of regulatory proteins: ______ and ______
two strands of actin subunits....regulatory proteins: troponin and tropomyosin
15
New cards
When calcium is present, myosin heads bind to ____. What is formed?
Actin, forms a cross bridge (ATP-->ADP)
16
New cards
Next, myosin heads __1___ and return to normal state, then they __2___ again and under go___3__
1. Detach
2. Bind again
3. Conformational change
2. Bind again
3. Conformational change
17
New cards
What is the sliding filament theory
The actin (thin) filaments of muscle fibers slide past the myosin (thick) filaments during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length.
18
New cards
During the sliding filament theory, what happens to the size of:
I Band
A Band
H zone
M line
I Band
A Band
H zone
M line
I Band: decrease (could disappear)
A Band: (No change)
H zone: Disappears (could just decrease)
M line: No change
A Band: (No change)
H zone: Disappears (could just decrease)
M line: No change
19
New cards
What ATP is used first in skeletal muscle contraction?
Stored ATP
20
New cards
This ATP is produced from direct phosporylation of ADP by CP using the enzyme Creatine Kinase
Creatine phosphate (CP)
21
New cards
What process produces the most ATP
Aerobic catabolism of glucose
22
New cards
Pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid and ATP
Anaerobic catabolism of glucose
23
New cards
What are the three purposes of ATP in muscle contraction?
1. To activate myosin heads (enable cross bridge attachment)
2. Crossbridge detachment
3. Sequestration of calcium ions back into the SR for storage and active transport
2. Crossbridge detachment
3. Sequestration of calcium ions back into the SR for storage and active transport
24
New cards
Why does rigor mortis happen?
Caused by storage of calcium and ATP that stimulate myosin head to bind to actin sites. The binding of the head contracts the muscle but then because no more ATP and C+ are being made, the muscle can't relax and this leads to the body becoming rigid and stiff.
25
New cards
Acetylcholine:
(Neurotransmitter)
Diffuses across synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on sarcolemma.
Diffuses across synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on sarcolemma.
26
New cards
Motor Unit:
The motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscles it innervates.
27
New cards
One motor neuron innervates...
many muscle fibers
28
New cards
One muscle fiber is innervated by...
only ONE neuron
29
New cards
Small motor Units:
Fine movements. Ex. Fingers, eyes.
30
New cards
Large motor units:
Large weight bearing muscles and gross movement. (Thighs, hips).
31
New cards
The force of muscle contraction is affected by:
The number of muscle fibers stimulated.
Relative size of the fibers-hypertrophy of cells increase strength.
Frequency of stimulation.
Sarcomere length.
Relative size of the fibers-hypertrophy of cells increase strength.
Frequency of stimulation.
Sarcomere length.
32
New cards
Muscle Tension:
Force exerted by a contracting muscle.
33
New cards
Load:
Opposing force exerted on the muscle by weight of the object to be moved.
34
New cards
Contraction is...
The generation of force (tension).
35
New cards
Contraction does NOT necessarily cause...
shortening of the
fiber.
fiber.
36
New cards
Shortening occurs when...
tension generated by crossbridges on the thin filament exceeds forces opposing shortening.
37
New cards
Isotonic Contractions:
Muscle changes in length and moves the load. (Bicep Curl)
38
New cards
Isotonic contractions are either...
Concentric or eccentric.
39
New cards
Concentric Contractions:
The muscle shortens and does work.
40
New cards
Eccentric contractions:
The muscle contracts as it lengthens.
41
New cards
Isometric Contractions:
The load is greater than the tension the muscle is able to develop.
(Pushing a wall)
(Pushing a wall)
42
New cards
Tension increases to the muscle capacity but the muscle ______
Neither shortens or lengthens
43
New cards
Speed of Contraction:
Speed at which Myosin ATPase hydrolyzes ATP.
Either Slow or Fast.
Either Slow or Fast.
44
New cards
Major Pathway for ATP production are...
Aerobic respiration & Anaerobic respiration using more glycogen.
45
New cards
Aerobic respiration:
oxidative fiber
46
New cards
Anaerobic respiration using more glycogen:
Glycolytic fiber
47
New cards
What are the 3 major skeletal muscle types?
i) Slow Oxidative Fibers
ii)Fast Oxidative Fibers
iii) Fast Glycolytic fibers
ii)Fast Oxidative Fibers
iii) Fast Glycolytic fibers
48
New cards
Aerobic (endurance) exercise leads to increased...
- Muscle capillaries
- Number of mitochondria
- Myoglobin synthesis
- May convert fast glycolytic fibers into fast oxidative fibers
- Number of mitochondria
- Myoglobin synthesis
- May convert fast glycolytic fibers into fast oxidative fibers
49
New cards
Resistance exercise (typically anaerobic) results in..
- Muscle hypertrophy (due to increase in fiber size) (Myofibril).
- Increased glycogen stores.
- Increased glycogen stores.
50
New cards
A bigger muscle is a...
Stronger muscle (can elicit more force)
51
New cards
Smooth muscle has two layers called?
Longitudinal and circular
52
New cards
Are smooth muscles slow or fast to contract?
Slow-myosin ATPase 10-100 times slower than skeletal
53
New cards
Smooth muscles are ___ shaped and multi or uni nucleated?
Spindle shaped and uninucleate
54
New cards
In smooth muscles, thick filaments and thin filaments arrange..
Diagonally
55
New cards
Thick filaments have heads along...
their entire length
56
New cards
Smooth muscle lacks...
sacromeres & myofibrils
57
New cards
Smooth muscle CELLS lack...
Z lines
58
New cards
Dense Bodies:
Anchor the thin filaments.
59
New cards
Intermediate Filaments:
Attached to the dense bodies and resist tension.
60
New cards
Tropomyosin:
-Present in thin filaments, but does
not block myosin binding sites on actin.
not block myosin binding sites on actin.
61
New cards
If there is no troponin complex such as in smooth muscle, what happens?
Protein calmodulin binds Ca2+
62
New cards
Sarcolemma of smooth muscle cells lack...
T-tubules
63
New cards
Caveolae (caveoli)
Shallow cavities.
Contain extracellular fluid rich in calcium.
Contain extracellular fluid rich in calcium.
64
New cards
Steps of Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Smooth Muscle:
1. Opening of calcium channels in plasma membrane and sarcoplasmic reticulum (Calcium enters cytosol)
2. Calcium ions bind to calmodulin
3. Ca-Calmodulin activates (myosin light chain kinase) MLCK
4. MLCK activates (phosphorylates) myosin
5. Crossbridge cycling (sliding filament theory)
2. Calcium ions bind to calmodulin
3. Ca-Calmodulin activates (myosin light chain kinase) MLCK
4. MLCK activates (phosphorylates) myosin
5. Crossbridge cycling (sliding filament theory)
65
New cards
Contraction of smooth muscle:
- Slow, synchronized contractions.
- Gap junctions (Electrically couple cells)
- Some cells are self-excitatory
- Gap junctions (Electrically couple cells)
- Some cells are self-excitatory
66
New cards
Rate and intensity of contraction may be modified...
by neural and chemical stimuli.
67
New cards
Peristalsis:
Series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed.
68
New cards
Longitudinal layer contracts:
Organ dilates and shortens.
69
New cards
Circular layer contracts:
Organ constricts and elongates.
70
New cards
Cardiac Muscle: Intercalated Disks:
- Gap junctions.
- Desmosomes
- Desmosomes
71
New cards
Aerobic muscle:
Coronary circulation
72
New cards
No cell division after infancy:
Hypertrophy
73
New cards
Can have spontaneous electrical changes:
Pacemaker cells/autorhythmic cells
74
New cards
Autorhythmiccells Percentage:
1%
75
New cards
Contractile cells Percentage:
99%
76
New cards
Cardiac Muscle:
- Striated with sarcomeres.
- Troponin & Tropomyosin.
- T tubules.
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Similar to slow oxidative fibers.
- Troponin & Tropomyosin.
- T tubules.
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Similar to slow oxidative fibers.
77
New cards
How is it Similar to slow oxidative fibers?
Myoglobin
Mitochondria
Slow to fatigue
Mitochondria
Slow to fatigue
78
New cards
Cardiac Muscle: Similarities with Smooth Muscle:
Gap Junction.
Pacemaker cells: autorhyhmic
Innervated by autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Influenced by hormones
Pacemaker cells: autorhyhmic
Innervated by autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Influenced by hormones
79
New cards
Groups of myofibers make up a
Fascicle
80
New cards
In skeletal muscles, calcium is released from the
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
81
New cards
Slow oxidative fibers are what color?
Red
82
New cards
Functions of the Nervous System:
1. Sensory input
2. Integration
3. Output
2. Integration
3. Output
83
New cards
Afferent nerve fibers:
Conduct signals TO CNS (Sensory)
84
New cards
Efferent nerve fibers:
Conduct signals AWAY from CNS (Motor neurons, effector neurons)
85
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Dorsal body cavity surrounded by meninges.
Dorsal body cavity surrounded by meninges.
86
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All neural structures outside of the CNS.
Cranial nerves, spinal nerves and sensory receptors.
Cranial nerves, spinal nerves and sensory receptors.
87
New cards
Peripheral nervous system division: Sensory
Somatic afferent fivers and visceral afferent fibers
88
New cards
Peripheral nervous system division: Motor
Somatic nervous system (voluntary)
Autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
Autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
89
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and para sympathetic
90
New cards
Two principal cell types:
Neurons
Neuroglia
Neuroglia
91
New cards
_______ are the excitable cells that _________
Neurons, transmit electrical signals
92
New cards
_______ (glial cells) are the ______ cells.
(Vary based location)
(Vary based location)
Neuroglia, supporting cells
93
New cards
Special characteristics of neurons
Generally amitotic (no cell division after birth).
High metabolic rate.
Continuous supply of oxygen and glucose.
High metabolic rate.
Continuous supply of oxygen and glucose.
94
New cards
Components of a Neuron:
-Cell body (Soma)
-Dendrites: reception of incoming information
-Axon: transmits electrical impulses called action potentials
-Axon hillock
-Dendrites: reception of incoming information
-Axon: transmits electrical impulses called action potentials
-Axon hillock
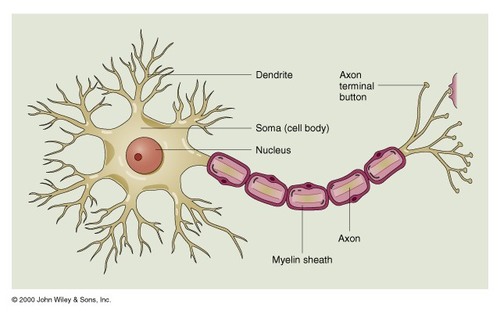
95
New cards
SUPPORTING CELLS IN THE CNS:
Astrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
Oligodendrocytes
96
New cards
Astrocytes:
- Numerous extensions that wrap around neurons.
- Involved in forming the blood brain barrier.
- Regulate brain function
- Involved in forming the blood brain barrier.
- Regulate brain function
97
New cards
Microglia
Macrophages to engulf/destroy pathogens and cell debris.
98
New cards
Ependymal cells:
Ciliated columnar cells
Line the ventricles
Circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Line the ventricles
Circulate cerebrospinal fluid
99
New cards
Oligodendrocytes:
Their extensions myelinate axons of neurons in the CNS
100
New cards
SUPPORTING CELLS IN THE PNS:
Satellite cells: surround neuron cell bodies in the PNS
- Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
- Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)