ANTH1A: Hominin Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:12 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
average brain size: ape
~400 cc
2
New cards
average brain size: graciles
~400 cc
3
New cards
average brain size: robusts
~500 cc
4
New cards
average brain size: habilis
~650 cc
5
New cards
average brain size: erectus
~900 cc
6
New cards
average brain size: heidelbergensis
~1200 cc
7
New cards
average brain size: neanderthalensis
~1500 cc
8
New cards
average brain size: sapiens (AMH)
~1400 cc
9
New cards
What are the main points of The Replacement Model?
- moderns arose in Africa
- moderns replaced all other archaic forms (NO INTERBREEDING)
- moderns replaced all other archaic forms (NO INTERBREEDING)

10
New cards
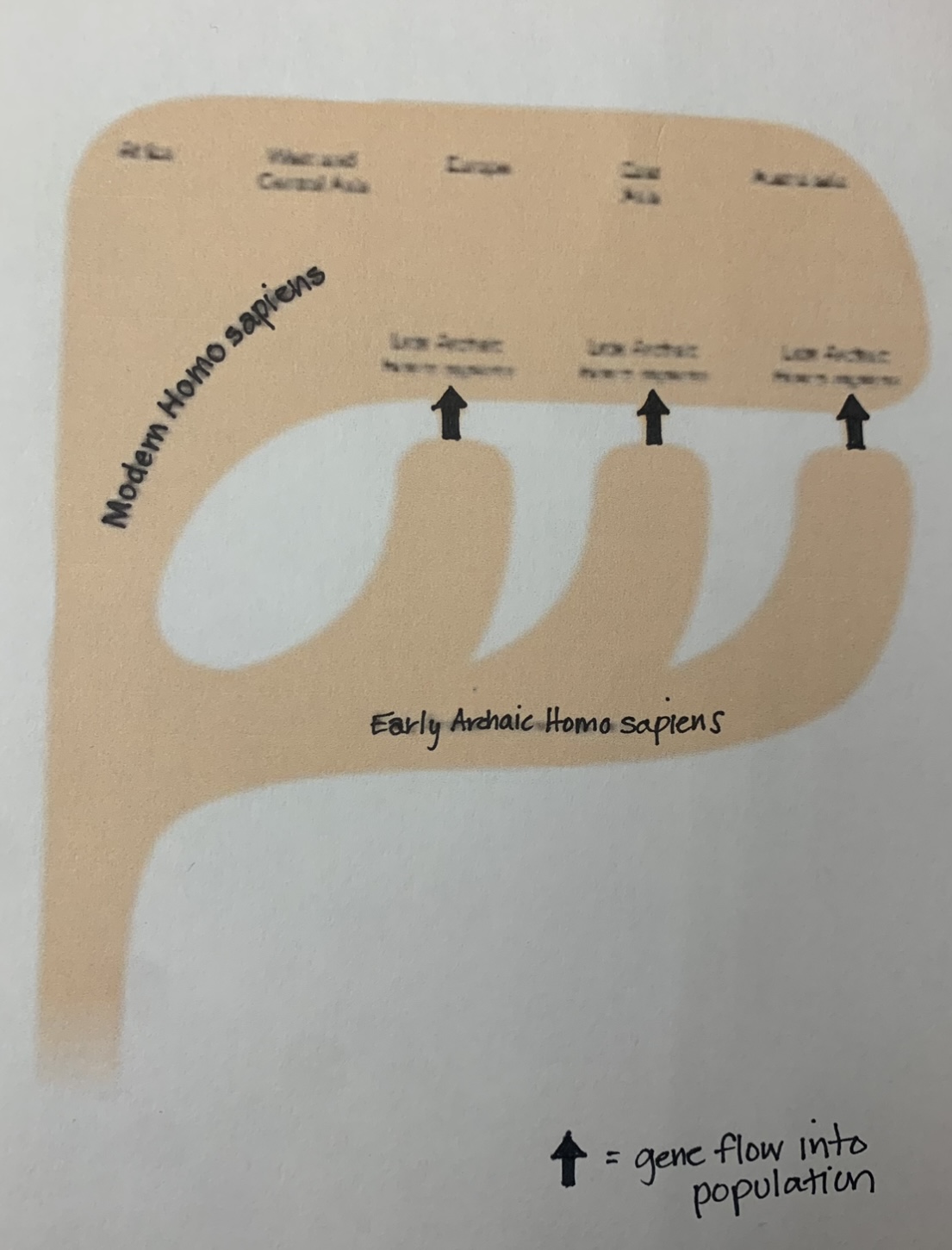
What are the main points of the Multiregional Model?
- moderns arose in different regions
- moderns + archaic interconnected by gene flow (INTERBREEDING)
- moderns + archaic interconnected by gene flow (INTERBREEDING)
11
New cards
What are the main points of the Assimilation Model?
- moderns arose in Africa
- moderns interbred with archaic forms (Neanderthals were genetically swamped)
- moderns interbred with archaic forms (Neanderthals were genetically swamped)

12
New cards
What traits classify hominini (Homo)? (9)
- bipedal
- increasing brain size
- reduced prognathism
- no CP3 honing complex
- thick molar enamel
- parabolic dentition
- smaller teeth
- no crests
- tori (thickened bone)
- increasing brain size
- reduced prognathism
- no CP3 honing complex
- thick molar enamel
- parabolic dentition
- smaller teeth
- no crests
- tori (thickened bone)
13
New cards
What feature of the skull indicates bipedality?
centralized foramen magnum
14
New cards
What feature of the skull indicates quadrupedalism?
intermediate/ posterior FM
15
New cards
What features of the torso indicate bipedality?
- S-shaped spine
- curved iliac blades
- curved iliac blades
16
New cards
What features of the torso indicate quadrupedalism?
- C-shaped spine
- straight iliac blades
- straight iliac blades
17
New cards
What features of the legs/hips indicate bipedality?
- short + broad pelvis
- angled femur
- valgus knee
- angled femur
- valgus knee
18
New cards
What features of the legs/hips indicate quadrupedalism?
- tall + narrow pelvis
- straight femur
- versus knee
- straight femur
- versus knee
19
New cards
define: versus knee
non-locking knee
20
New cards
define: valgus knee
locking knee
21
New cards
What features of the foot indicate bipedality?
- thick tarsal + hallux bones
- short toes
- non-divergent hallux
- 2 arches: longitudinal + transverse
- short toes
- non-divergent hallux
- 2 arches: longitudinal + transverse
22
New cards
What features of the foot indicate quadrupedalism?
- small tarsal bones
- long toes
- divergent hallux
- thinner hallux
- 1 arch: transverse
- long toes
- divergent hallux
- thinner hallux
- 1 arch: transverse
23
New cards
ape vs. human dental characteristic
ape: CP3 honing complex
human: reduced canine
human: reduced canine
24
New cards
ape vs. human: dental arcade shape
ape: parallel
human: parabolic
human: parabolic
25
New cards
ape vs. human: molar enamel thickness
ape: thin molar enamel
human: thick molar enamel
human: thick molar enamel
26
New cards
ape vs. human: facial projection
ape: prognathic
human: flat
human: flat
27
New cards
ape vs. human: locomotive pattern
ape: quadruped
human: bipedal
human: bipedal
28
New cards
Which hominin group used mousterian tools?
Neanderthals
29
New cards
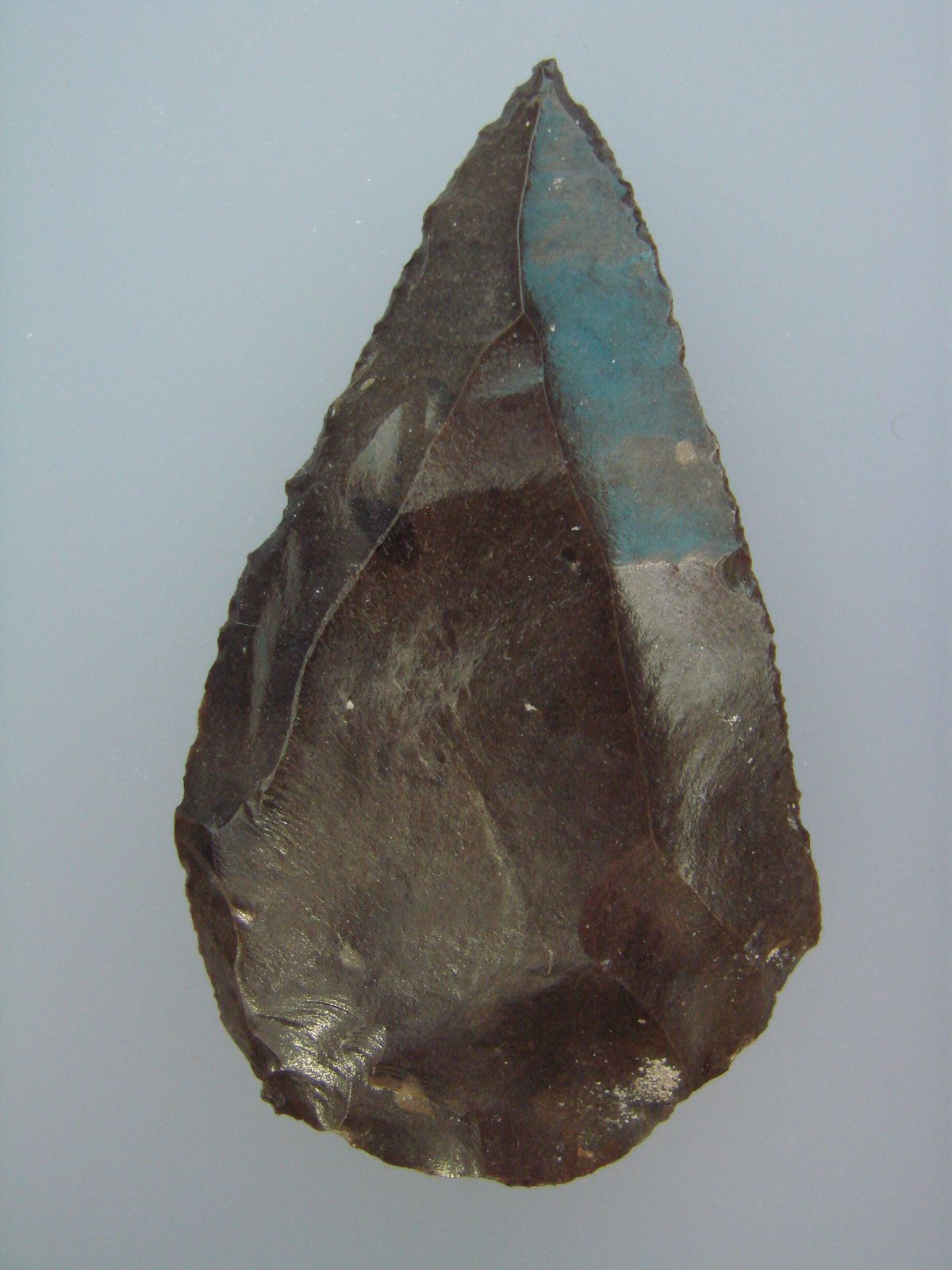

Which type of tool is this?
mousterian (hafted - attached to handle)
30
New cards
Which hominin group used upper paleolithic tools?
AMH
31
New cards
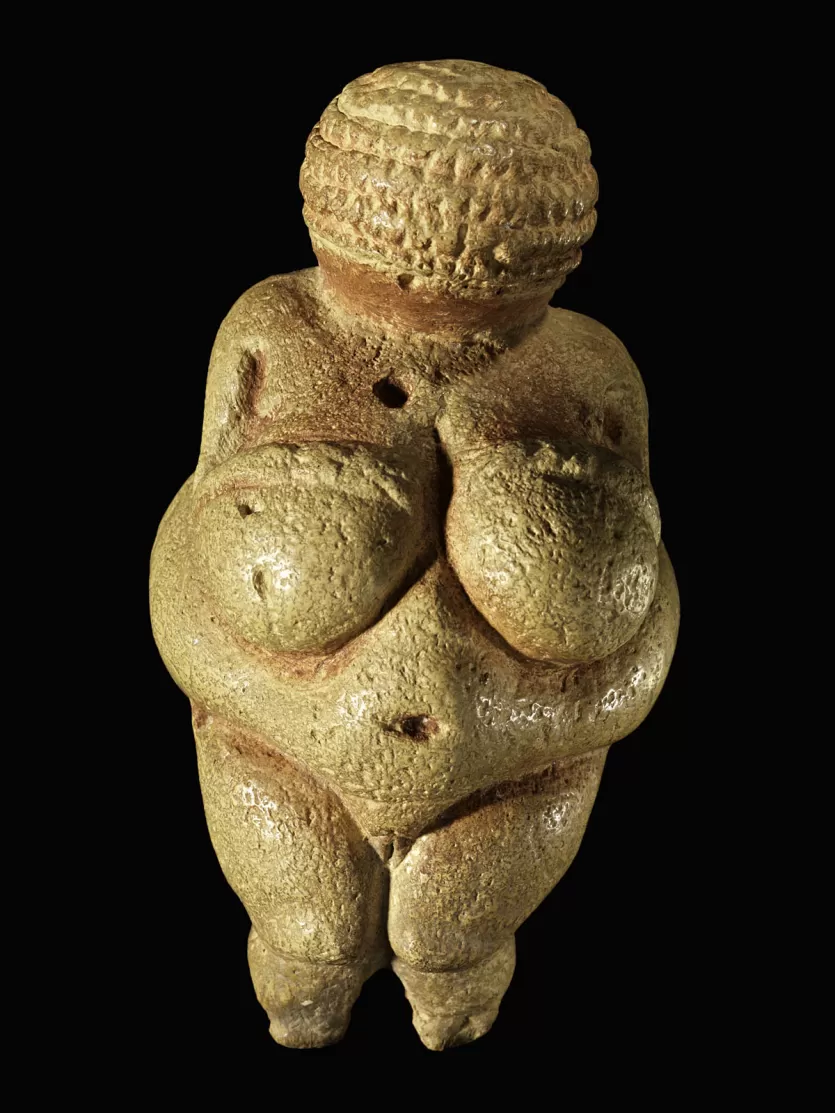

Which type of tool is this?
upper paleolithic
(cave art, personal adornment, + portable art)
(cave art, personal adornment, + portable art)
32
New cards
Which hominin group used Oldowan tools?
H. habilis
33
New cards
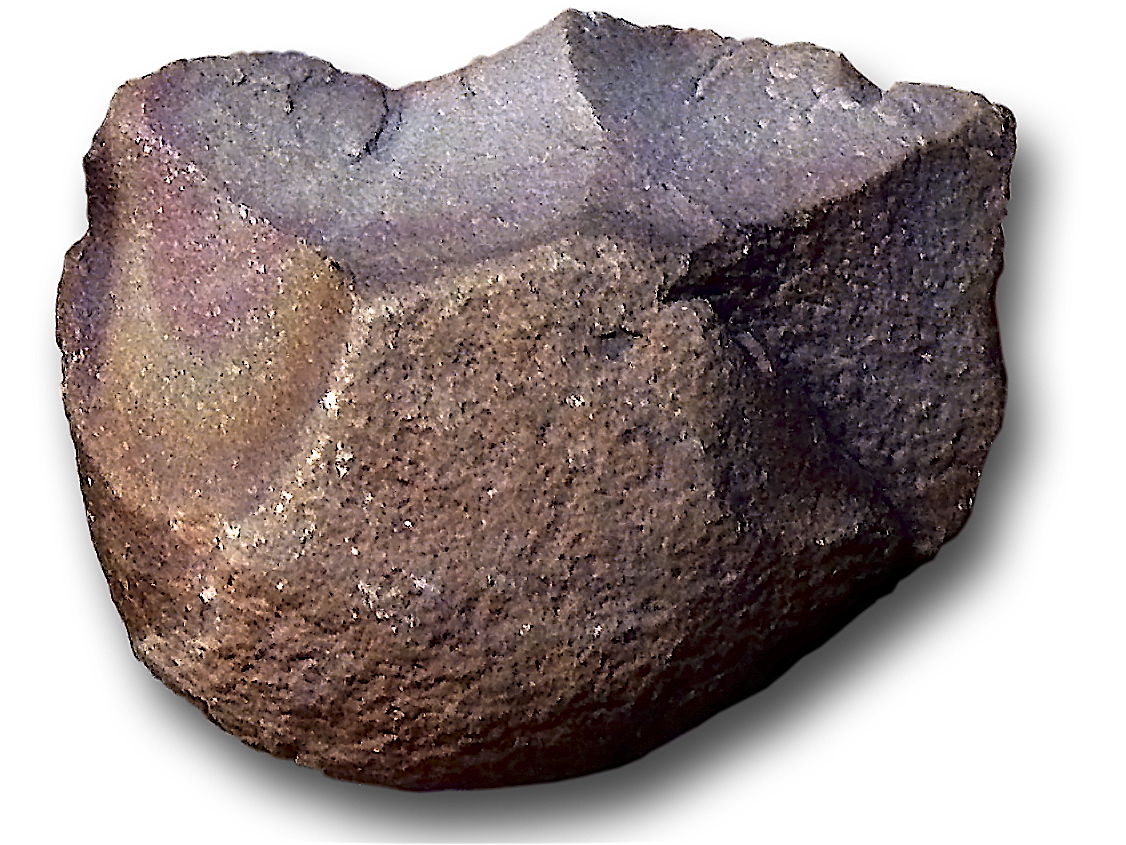

What type of tool is this?
Oldowan
(hammerstone; used to extract bone marrow)
(hammerstone; used to extract bone marrow)
34
New cards
What hominin group use Acheulean tools?
H. erectus
35
New cards
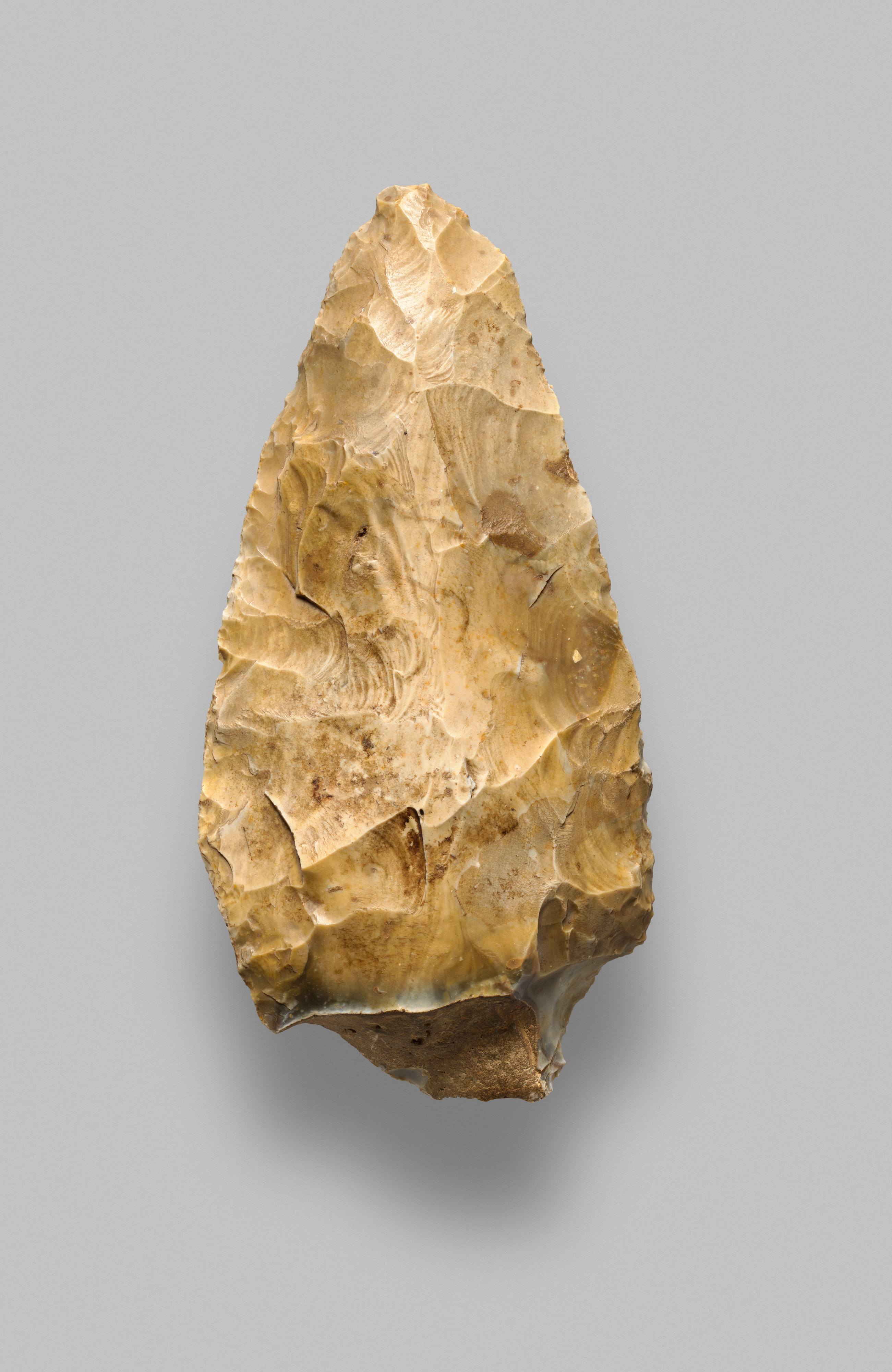

What type of tool is this?
Acheulean
(hand axe; multipurpose tool)
(hand axe; multipurpose tool)
36
New cards
Which 2 of the 5 Australopithecines are considered gracile?
A. afarensis
A. africanus
A. africanus
37
New cards
Which 3 of the 5 Australopithecines are considered robust?
A. robustus
A. boisei
A. aethiopicus
A. boisei
A. aethiopicus
38
New cards
Which region did A. afarensis inhabit?
East Africa
39
New cards
Which region did A. africanus inhabit?
South Africa
40
New cards
Which region did A. robustus inhabit?
South Africa
41
New cards
Which region did A. boisei inhabit?
East Africa
42
New cards
Which region did A. aethiopicus inhabit?
East Africa
43
New cards
What are the 5 types of Australopithecines?
A. afarensis
A. africanus
A. robustus
A. boisei
A. aethiopicus
A. africanus
A. robustus
A. boisei
A. aethiopicus
44
New cards
What countries are part of the Great Rift Valley in Africa?
Ethiopia, Kenya, + Tanzania
45
New cards
What traits separate Australopithecines from other groups? (5)
- small brain size
- prognathic
- crests
- arboreal adaptations (long arms + fingers)
- reduced canines
- prognathic
- crests
- arboreal adaptations (long arms + fingers)
- reduced canines
46
New cards
Average brain size of gracile Australopithecines?
~400 cc
47
New cards
Average brain size of robust Australopithecines?
~500 cc
48
New cards
What physical traits separate A. afarensis? (4)
- no true CP3 hone
- reduced incisors
- C-TNC
- sexually dimorphic
- reduced incisors
- C-TNC
- sexually dimorphic
49
New cards
What physical traits separate A. africanus? (4)
- no true CP3 hone
- reduced incisors
- nuchal crest only
- sexually dimorphic
- reduced incisors
- nuchal crest only
- sexually dimorphic
50
New cards
What physical traits separate A. robustus + A. boisei? (7)
- sagittal + nuchal crest
- dished face
- small anterior teeth (incisors + canines)
- post-canine megadontia
- molarized premolars
- flaring zygomatics
- post-orbital constriction
- dished face
- small anterior teeth (incisors + canines)
- post-canine megadontia
- molarized premolars
- flaring zygomatics
- post-orbital constriction
51
New cards
What physical traits separate A. aethiopicus? (7)
- sagittal crest
- C-TNC
- dished
- small anterior teeth (incisors + canines)
- post-canine megadontia
- molarized premolars
- post-orbital constriction
- C-TNC
- dished
- small anterior teeth (incisors + canines)
- post-canine megadontia
- molarized premolars
- post-orbital constriction
52
New cards
What does post-canine megadontia mean?
the teeth behind the canines, premolars + molars, are huge
53
New cards
What does having post-orbital constriction mean?
the area behind the eyes is pinched in allowing more area for facial muscles
54
New cards
What are the 5 types of Homo?
- H. habilis
- H. erectus
- H. heidelbergensis (archaics)
- H. neanderthalensis
- H. sapiens sapiens (AMH)
- H. erectus
- H. heidelbergensis (archaics)
- H. neanderthalensis
- H. sapiens sapiens (AMH)
55
New cards
Which type of Homo is considered the archaics?
H. heidelbergensis
56
New cards
What type of Homo are considered AMH?
Homo sapiens sapiens
57
New cards
What region did H. habilis inhabit?
Eastern + Southern Africa
58
New cards
What region did H. erectus inhabit?
Africa, Asia, + Europe
59
New cards
What region did H. heidelbergensis inhabit?
Africa, Asia, + Europe
60
New cards
What region did H. neanderthalensis inhabit?
Europe + Middle East
61
New cards
What region did H. sapiens inhabit?
Africa, Asia, + Europe
62
New cards
What is the cranial buttressing system?
a series of thickened ridges (torus) that serve as an adaptation for absorbing stress on the cranium
63
New cards
What parts of the cranium make up the buttressing system?
- supraorbital torus
- sagittal keel
- nuchal (occipital) torus
- angular torus
- sagittal keel
- nuchal (occipital) torus
- angular torus
64
New cards
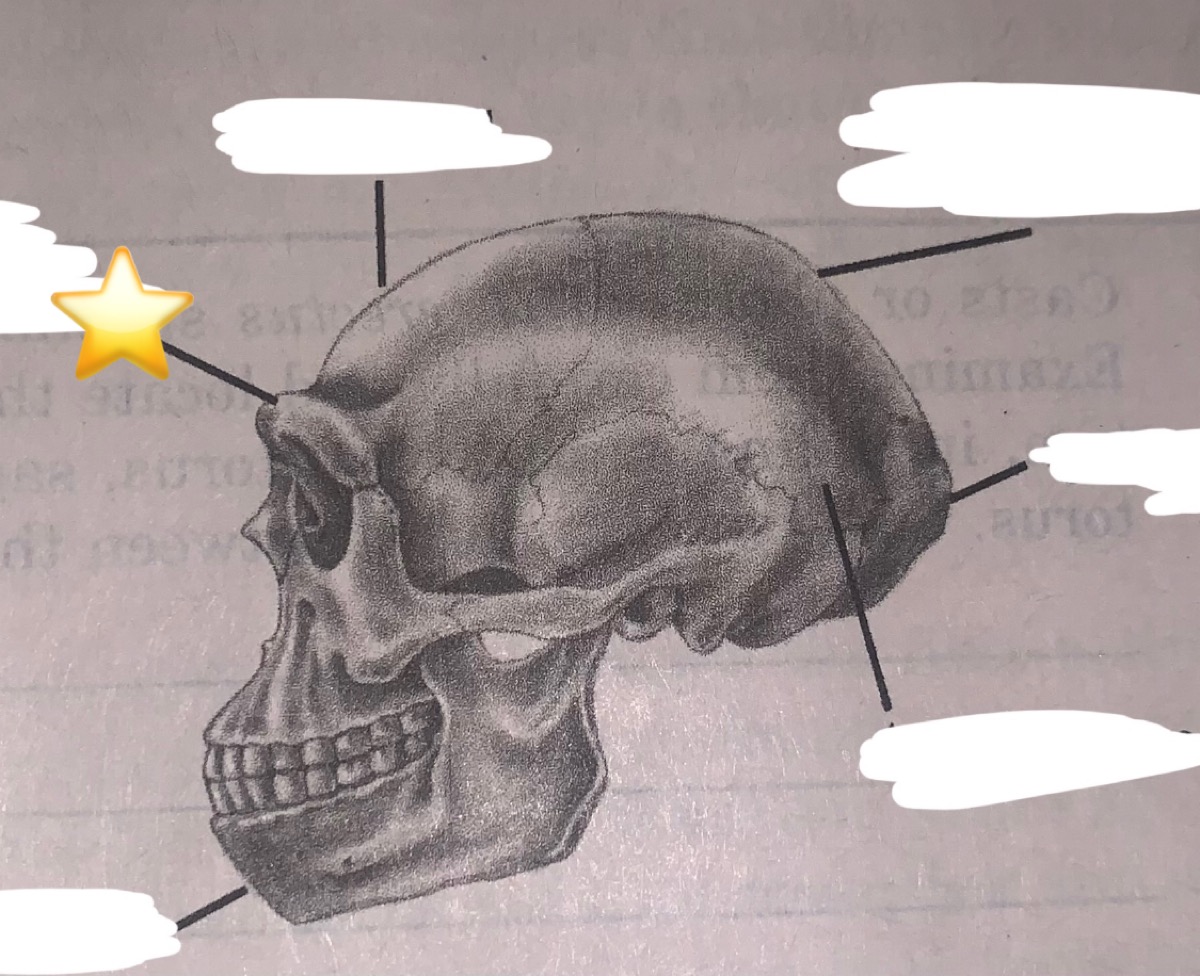
What part of the buttressing system is this?
supraorbital torus
65
New cards
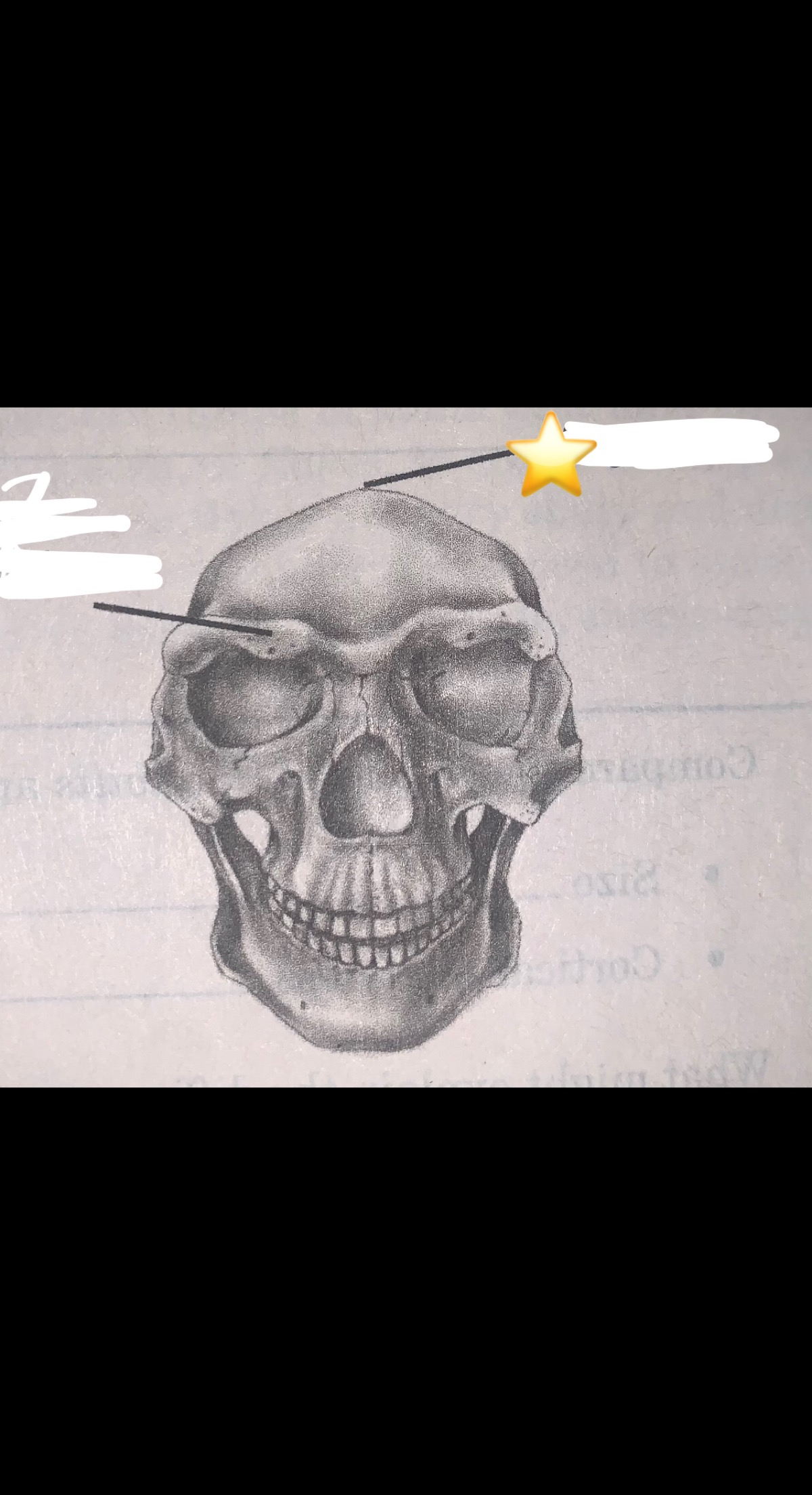

What part of the buttressing system is this?
sagittal keel
66
New cards
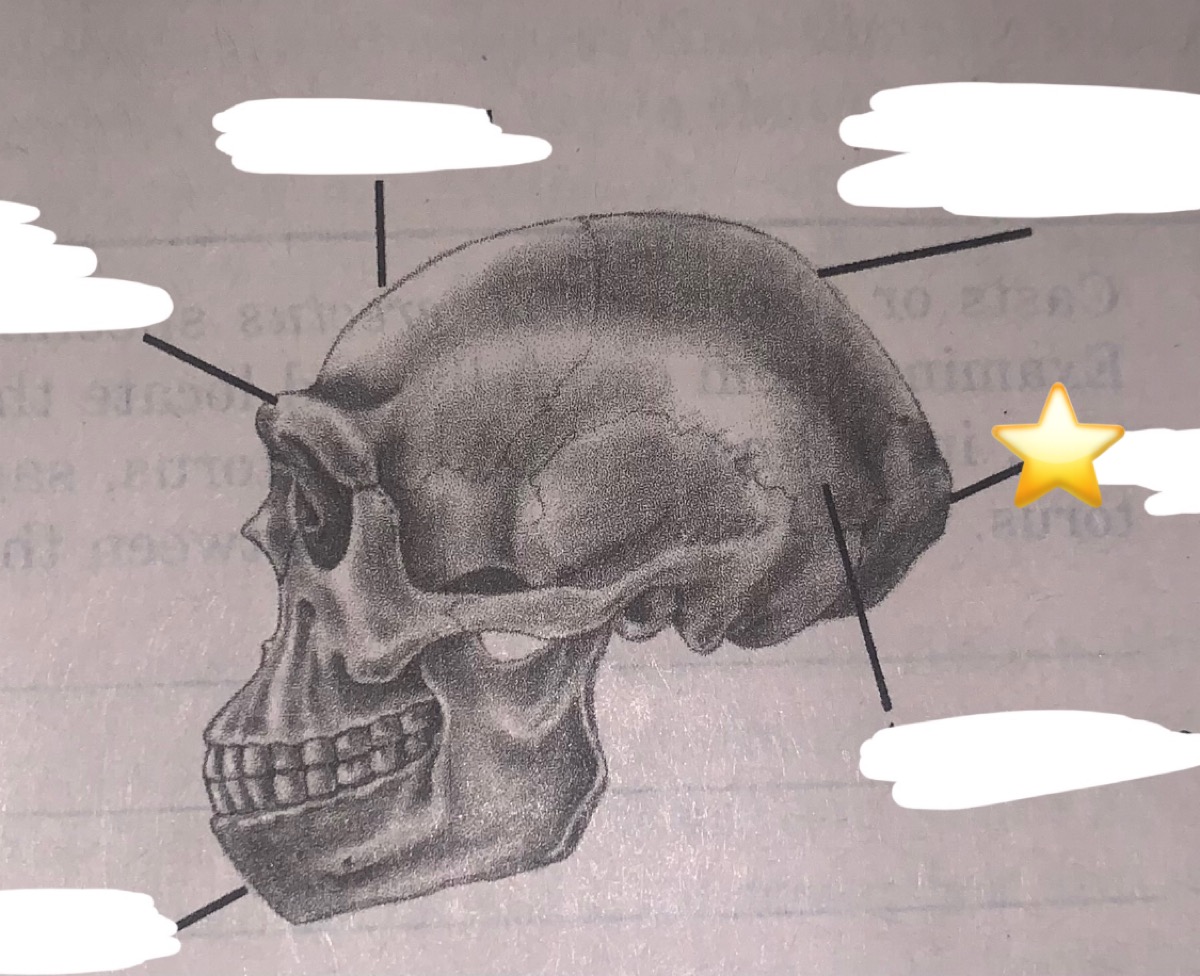
What part of the buttressing system is this?
nuchal (occipital) torus
67
New cards
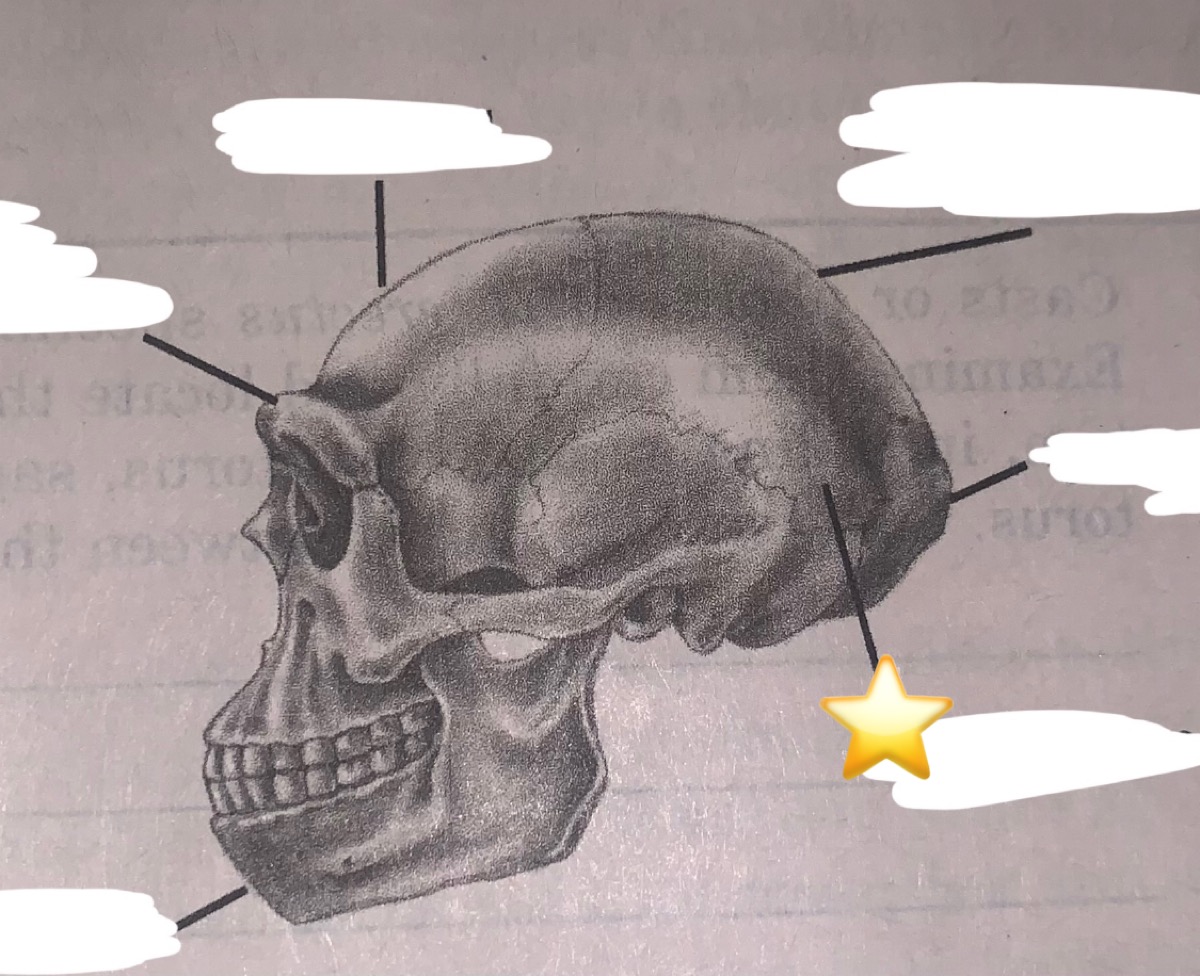
What part of the buttressing system is this?
angular torus
68
New cards
Brain size: Sahelanthropus tchadensis
~350 cc
69
New cards
Brain size: Ardipithecus ramidus (Ardy)
~350 cc
70
New cards
Characteristics of Sahelanthropus tchadensis (3)
- large canines but no honing complex
- centrally located FM
- large brow ridge
- centrally located FM
- large brow ridge
71
New cards
Characteristics of Ardipithecus ramidus (Ardy) (3)
- large canines but no honing complex
- thin enamel
- bipedal morphology (short + broad pelvis; divergent hallux)
- thin enamel
- bipedal morphology (short + broad pelvis; divergent hallux)
72
New cards
What 2 species are the pre-Australopithecines?
Sahelanthropus tchadensis + Ardipithecus ramidus (Ardy)
73
New cards
What physical traits separate H. habilis? (8)
- rounded cranium
- small teeth
- no tori
- reduced prognathism
- sloping frontal bone (forehead)
- small stature
- longer arms
- modern hand/foot
- small teeth
- no tori
- reduced prognathism
- sloping frontal bone (forehead)
- small stature
- longer arms
- modern hand/foot
74
New cards
What physical traits separate H. erectus? (7)
- sloping frontal bone (forehead)
- sagittal keel
- supraorbital torus
- occipital torus
- angular torus
- shovel-shaped incisors
- modern height + limb proportions
- sagittal keel
- supraorbital torus
- occipital torus
- angular torus
- shovel-shaped incisors
- modern height + limb proportions
75
New cards
What physical traits indicate an Asian H. erectus? (3)
- sagittal keel
- angular torus
- shovel-shaped incisors
- angular torus
- shovel-shaped incisors
76
New cards
What physical traits do both African and Asian H. erectus have? (2)
- supraorbital torus (both)
- occipital (nuchal) torus (both)
- occipital (nuchal) torus (both)
77
New cards
What physical traits separate H. heidelbergensis (archaics)? (4)
- sloping frontal bone (forehead)
- supraorbital torus
- occipital torus
- long, low cranium (oval)
- supraorbital torus
- occipital torus
- long, low cranium (oval)
78
New cards
What physical traits separate H. neanderthalensis? (10)
- long, low cranium (oval)
- sloping forehead
- supraorbital torus
- occipital bun
- shovel-shaped incisors
- retro-molar space
- large incisors w/ extreme wear
- large nasal aperture
- short distal limbs
- barrel chest
- sloping forehead
- supraorbital torus
- occipital bun
- shovel-shaped incisors
- retro-molar space
- large incisors w/ extreme wear
- large nasal aperture
- short distal limbs
- barrel chest
79
New cards
What physical traits separate H. sapiens sapiens (AMH)? (8)
- prominent mastoid process
- high, round cranium
- vertical forehead
- orthognathic face (flat)
- gracile skeleton
- small jaws + teeth
- no tori or crests
- prominent chin
- high, round cranium
- vertical forehead
- orthognathic face (flat)
- gracile skeleton
- small jaws + teeth
- no tori or crests
- prominent chin
80
New cards
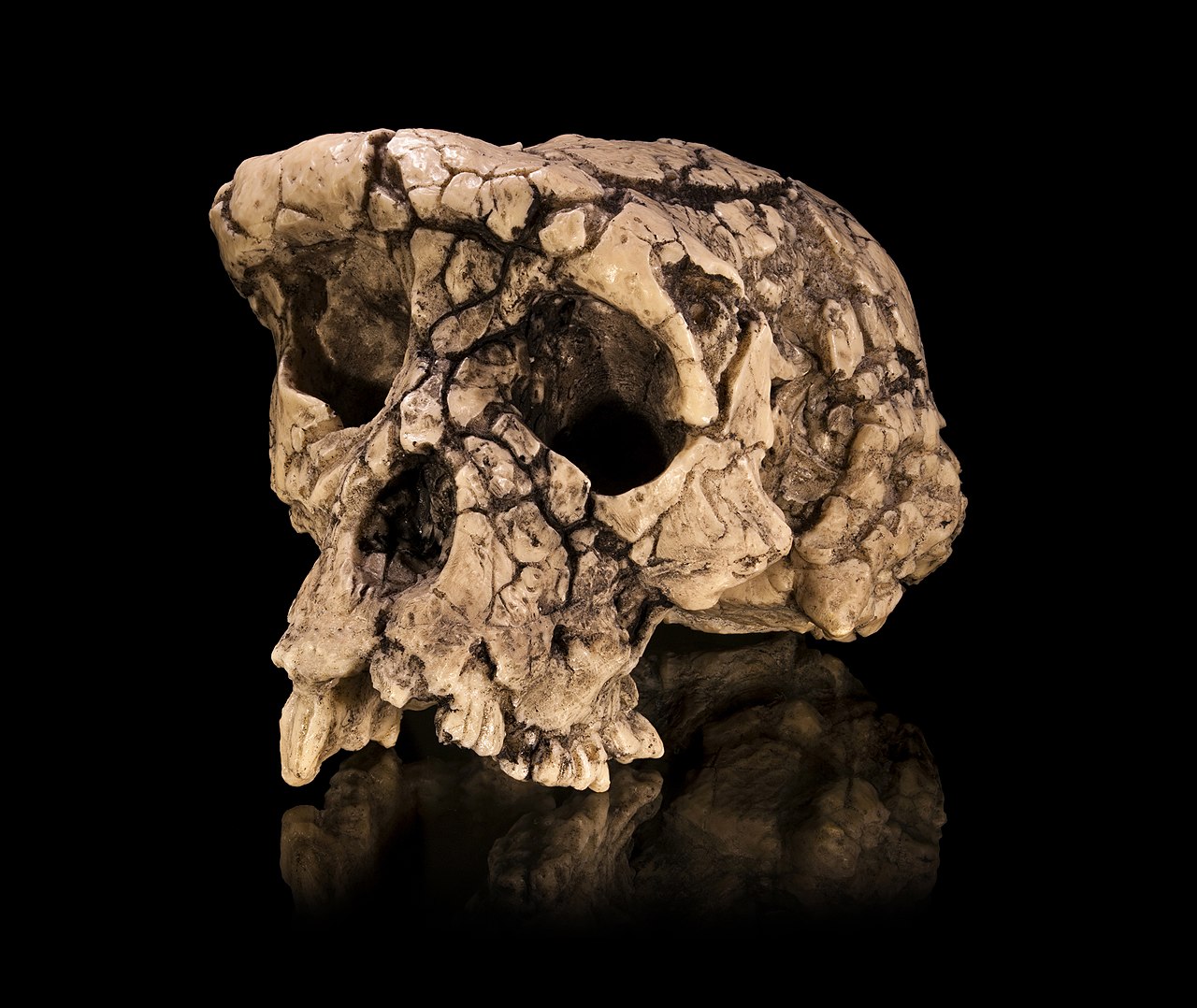

Identify the species
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
81
New cards
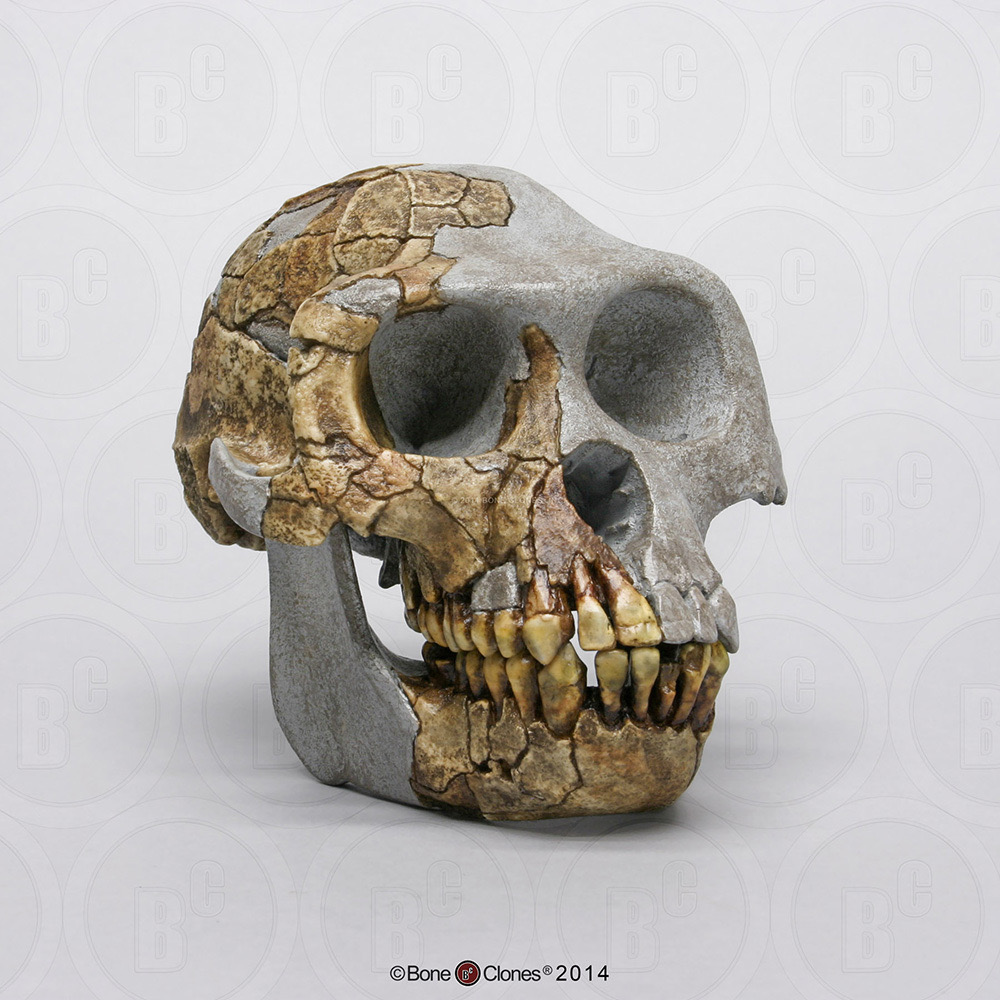

Identify the species
Ardipithecus ramidus (Ardy)
82
New cards
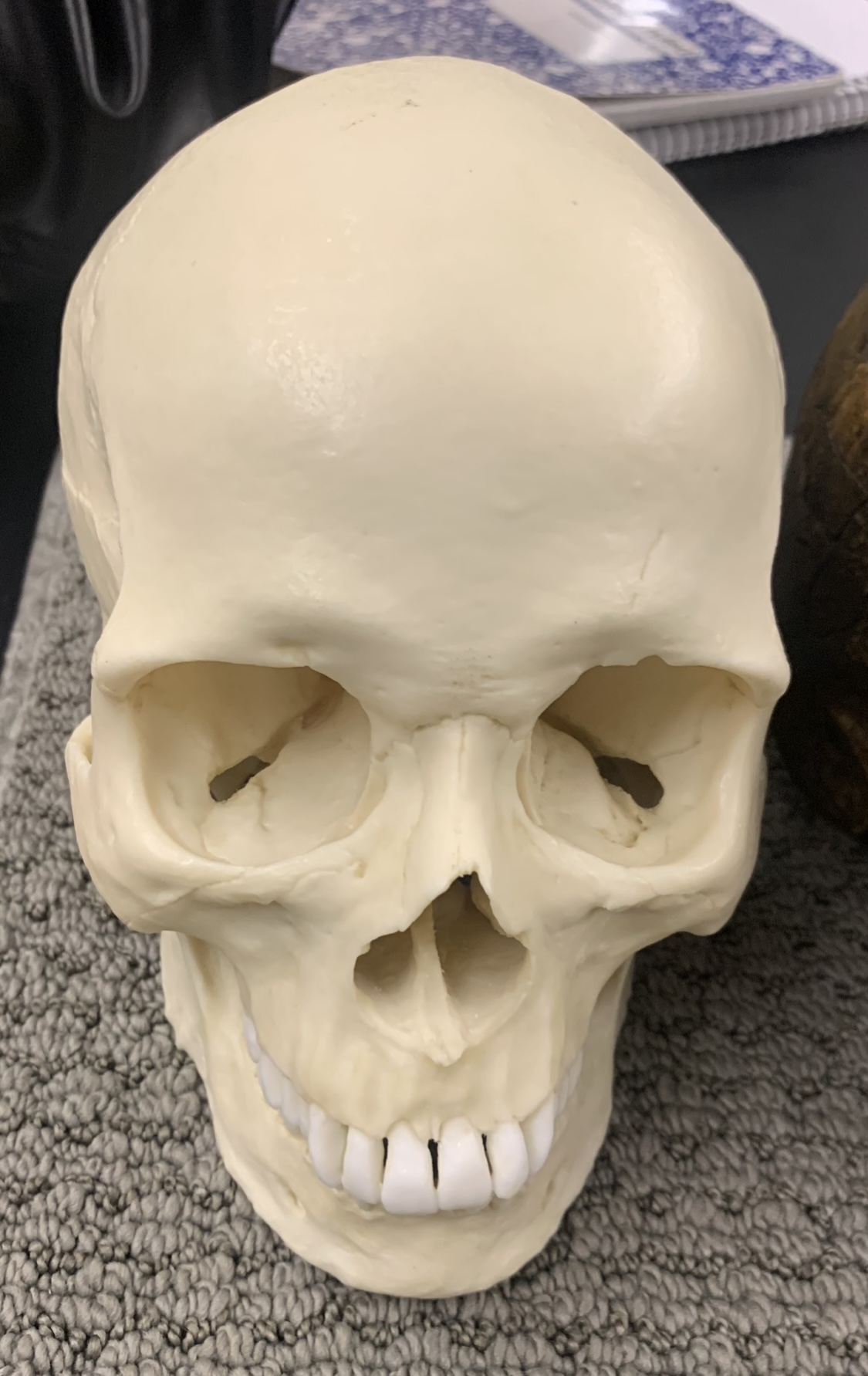
Identify the species
H. sapiens sapiens (AMH)
83
New cards
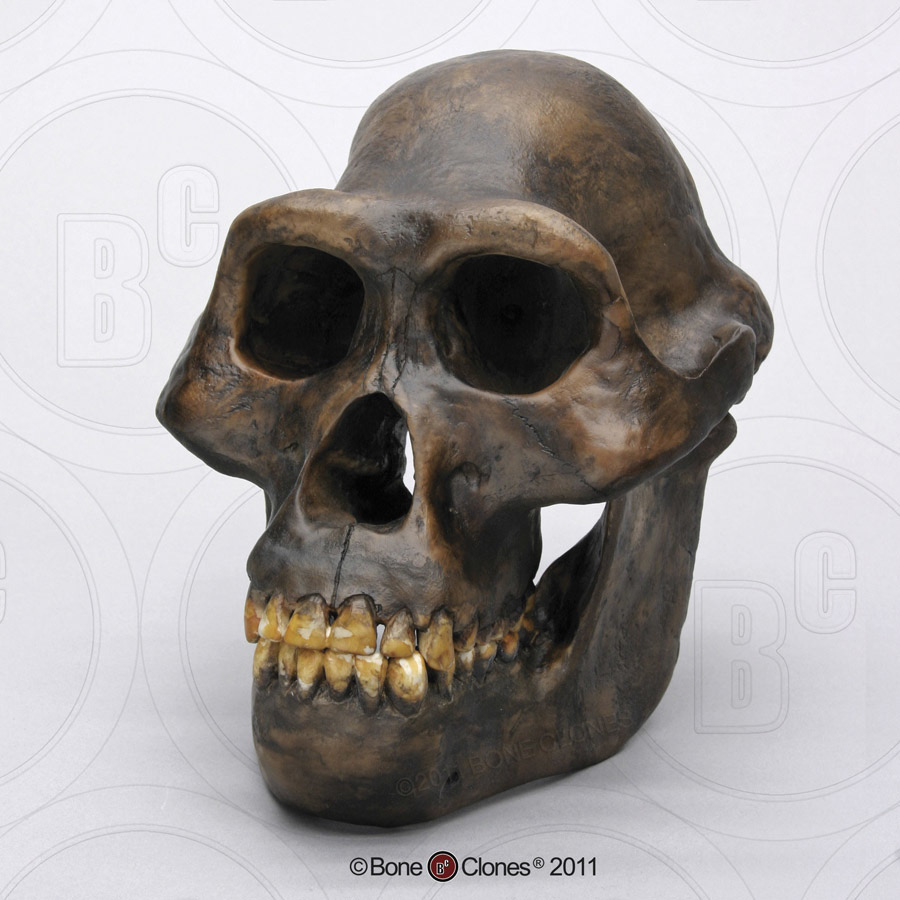

Identify the species
A. afarensis
84
New cards
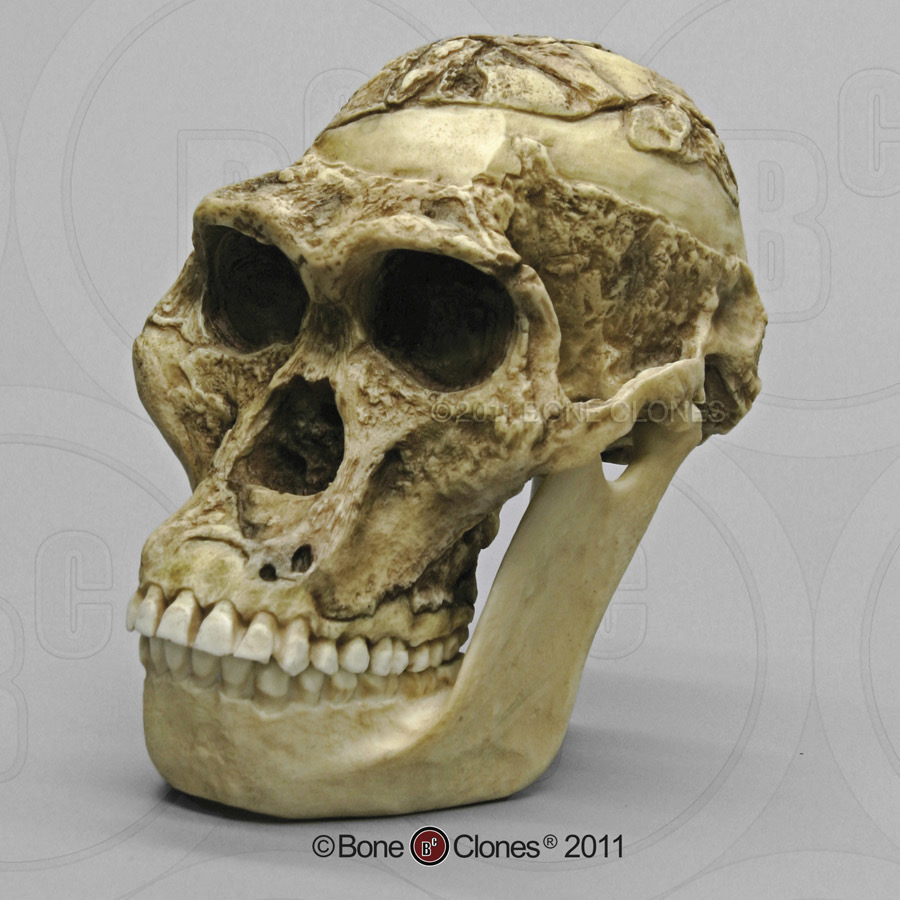
Identify the species
A. africanus
85
New cards
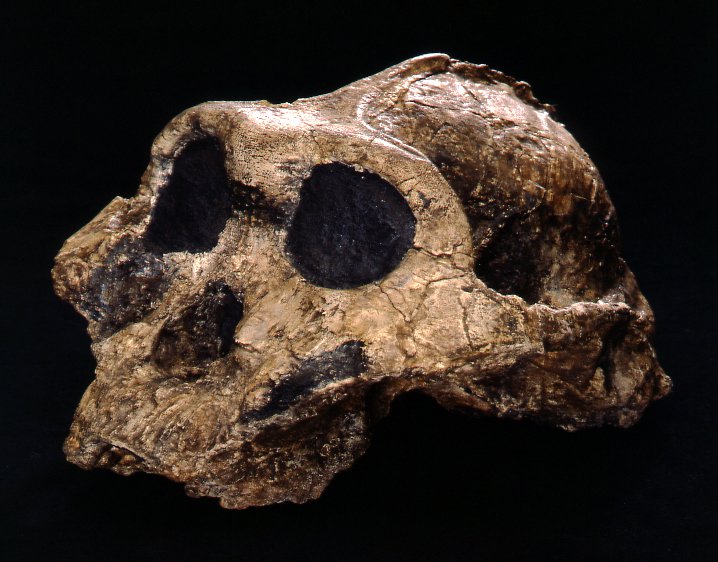

Identify the species
A. robustus
86
New cards
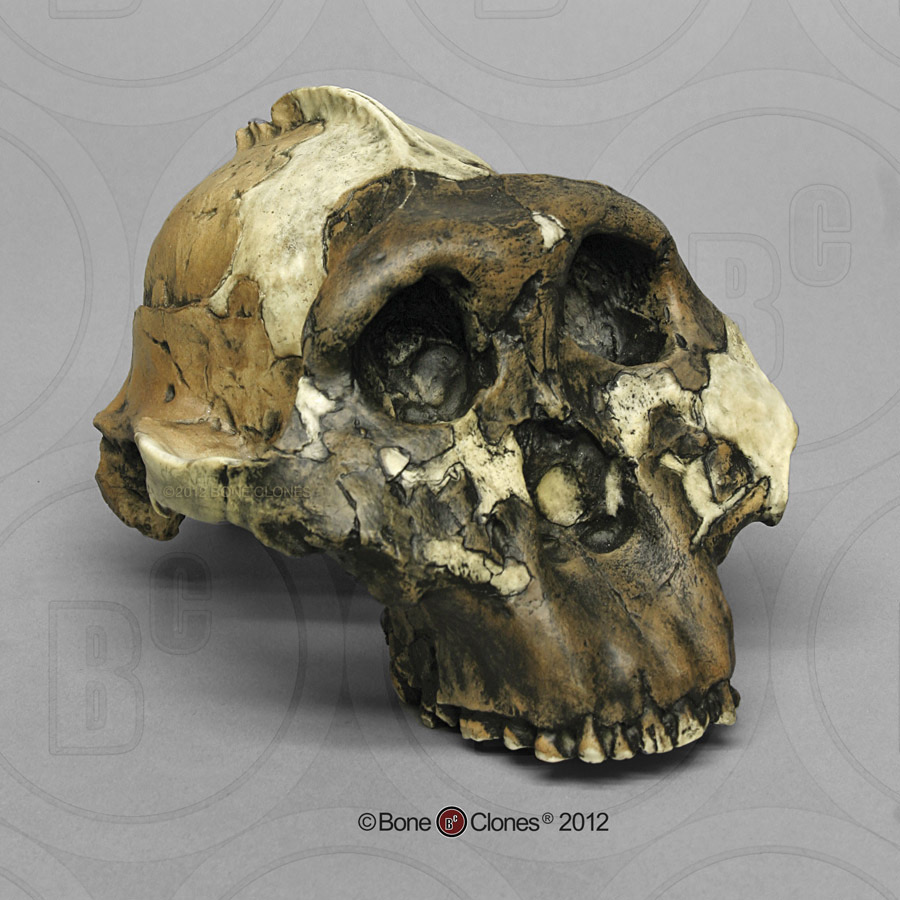
Identify the species
A. boisei
87
New cards
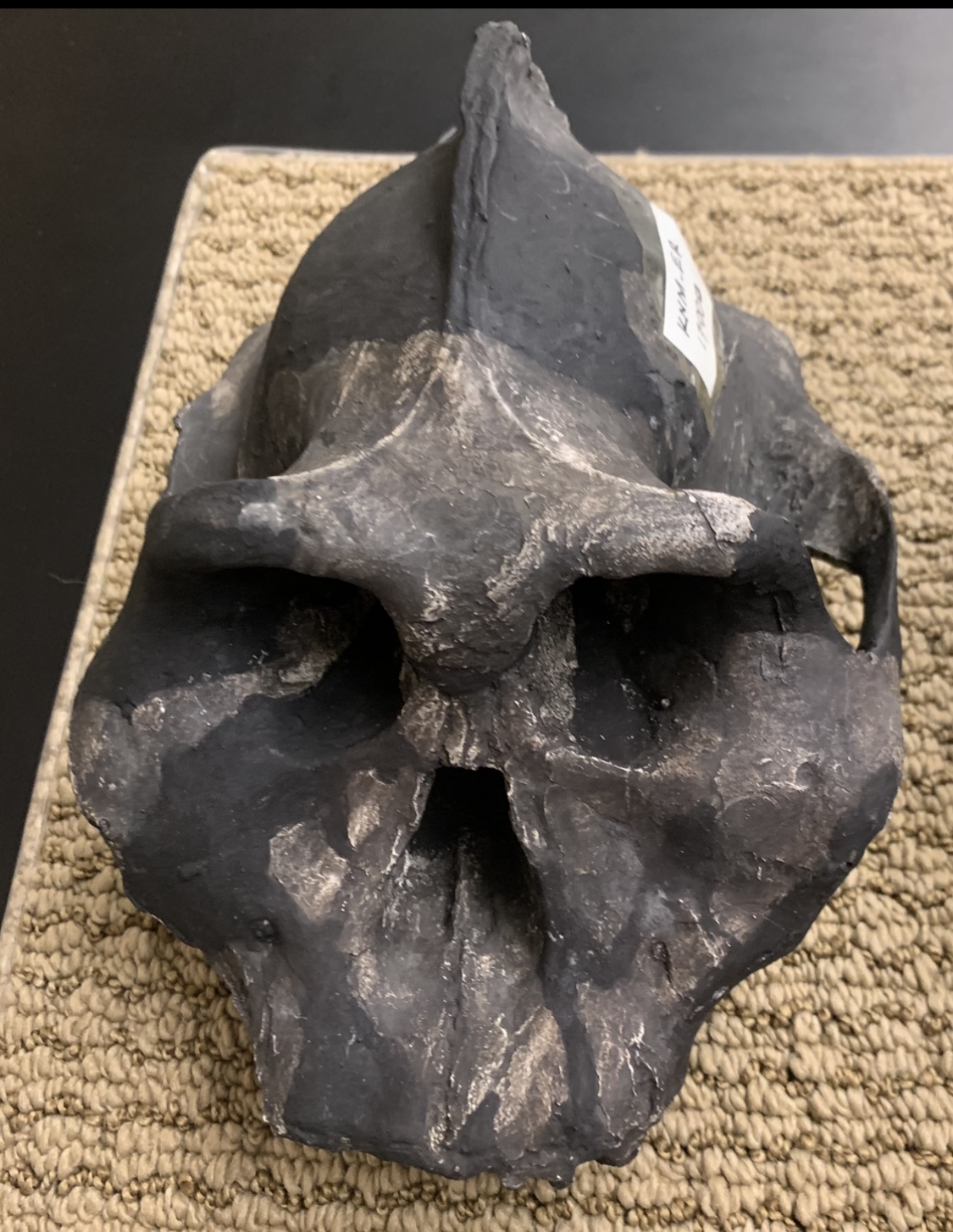

Identify the species
A. aethiopicus
88
New cards
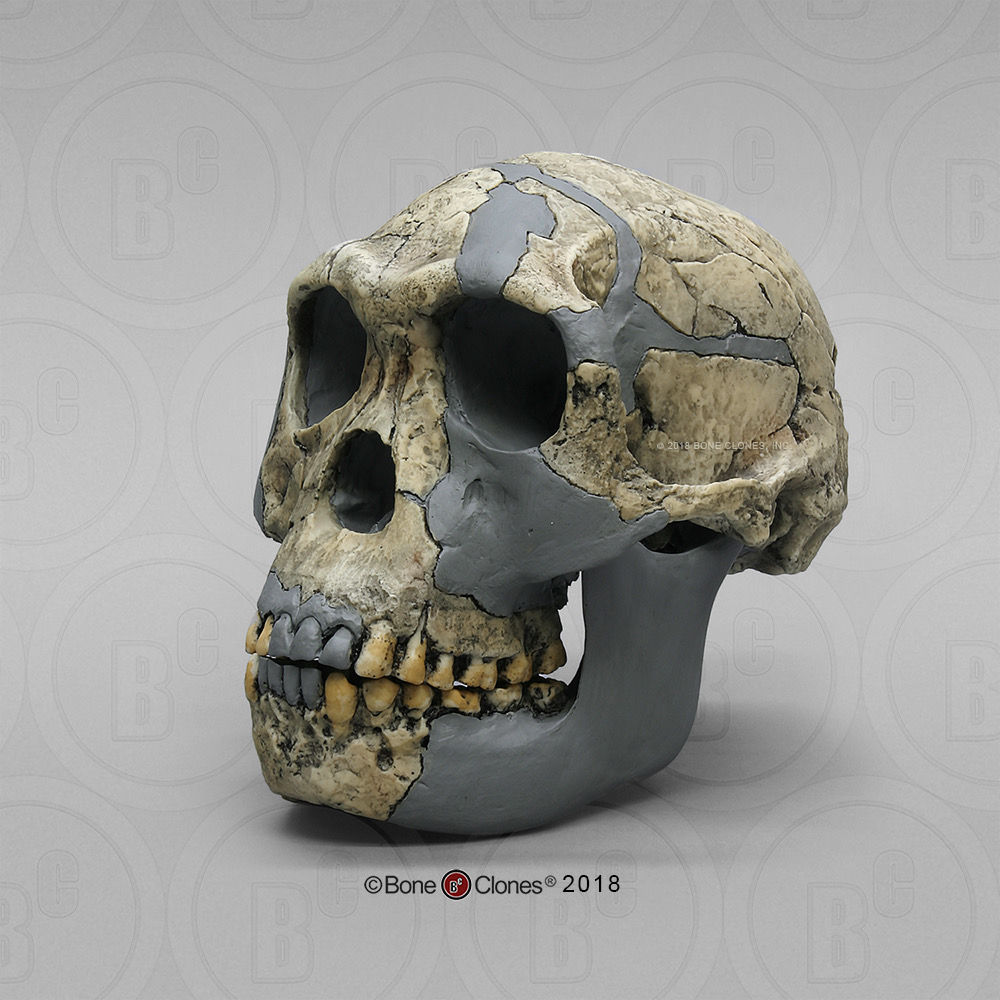
Identify the species
H. habilis
89
New cards
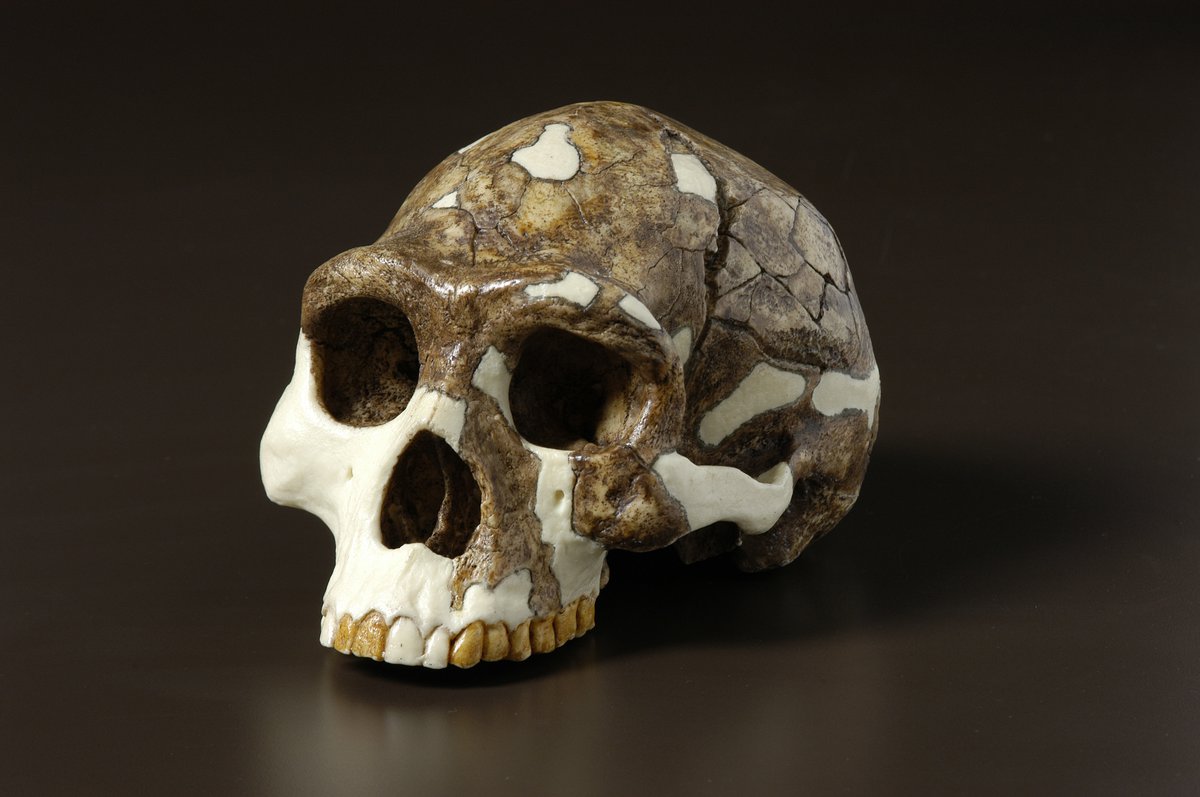

Identify the species
H. erectus
90
New cards
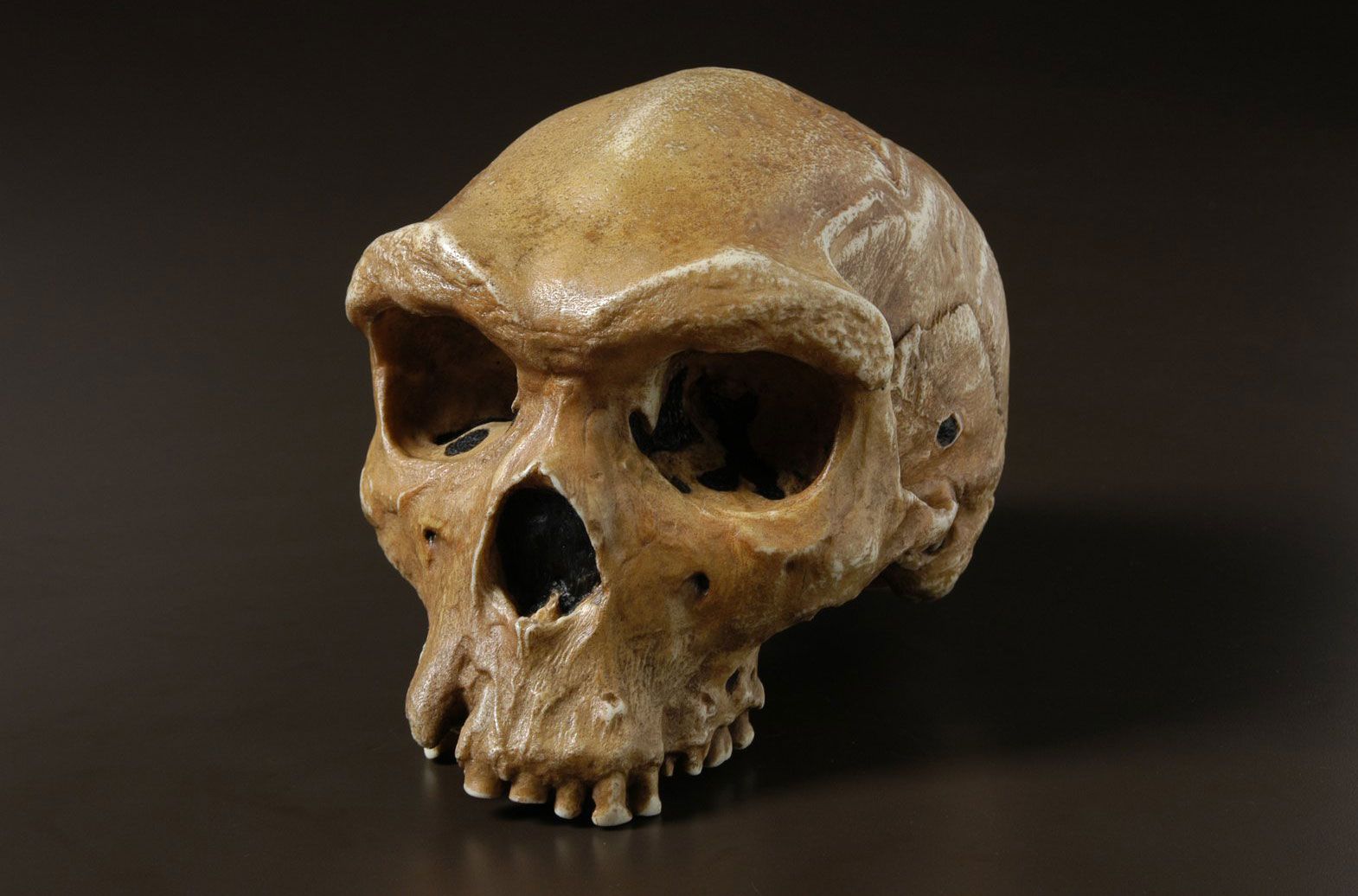

Identify the species
H. heidelbergensis (archaic)
91
New cards
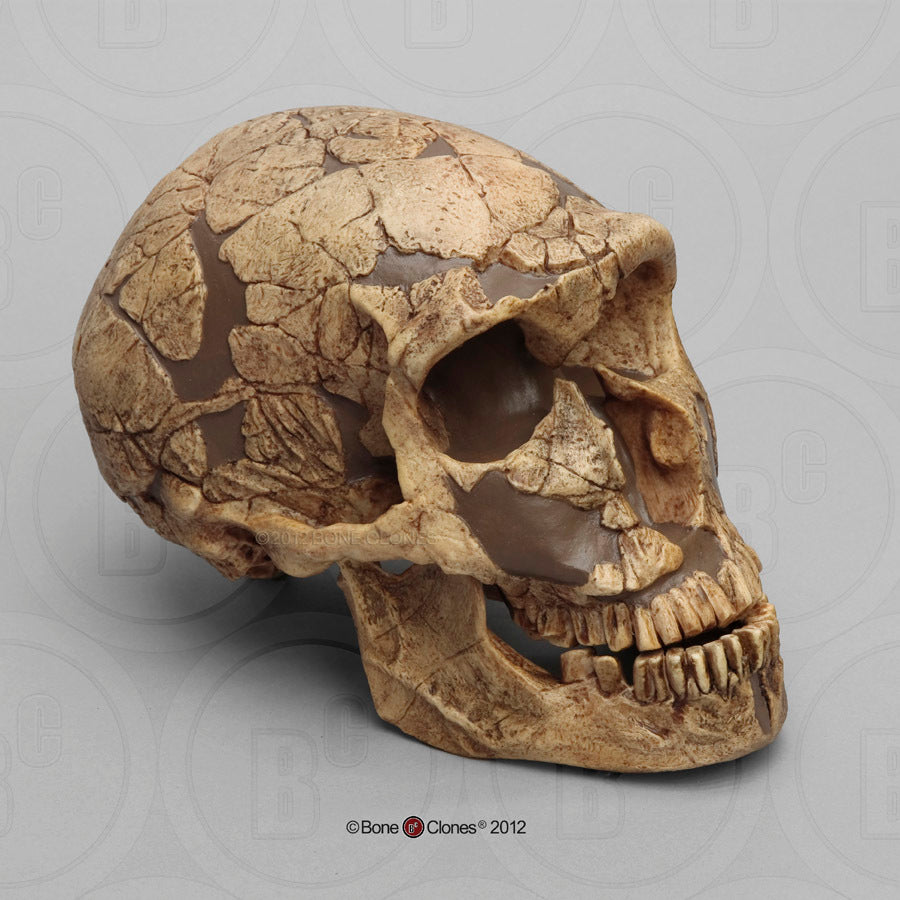

Identify the species
H. neanderthalensis
92
New cards
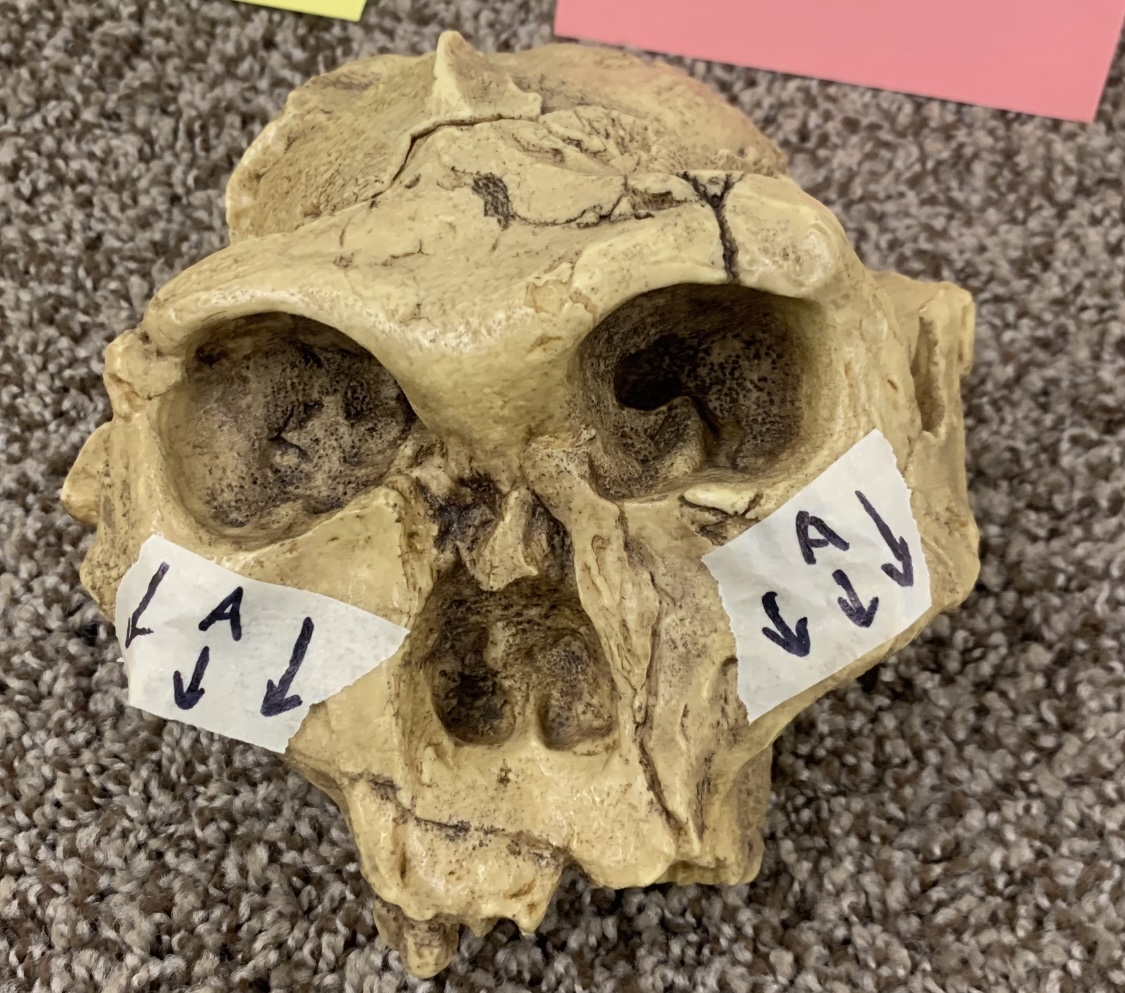
Identify the physical trait
flaring zygomatics
93
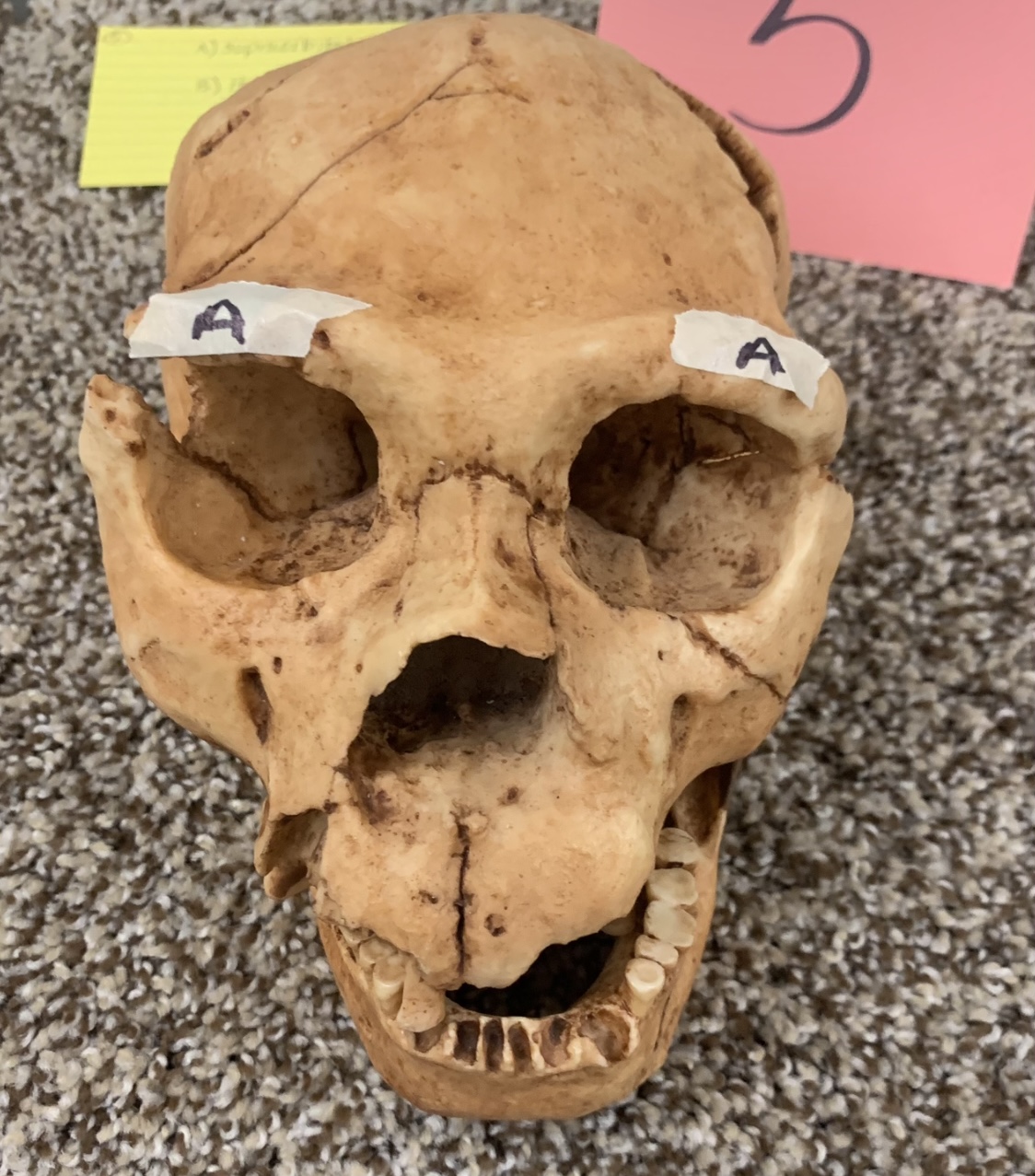
New cards
Identify the physical trait
supraorbital torus
94
New cards
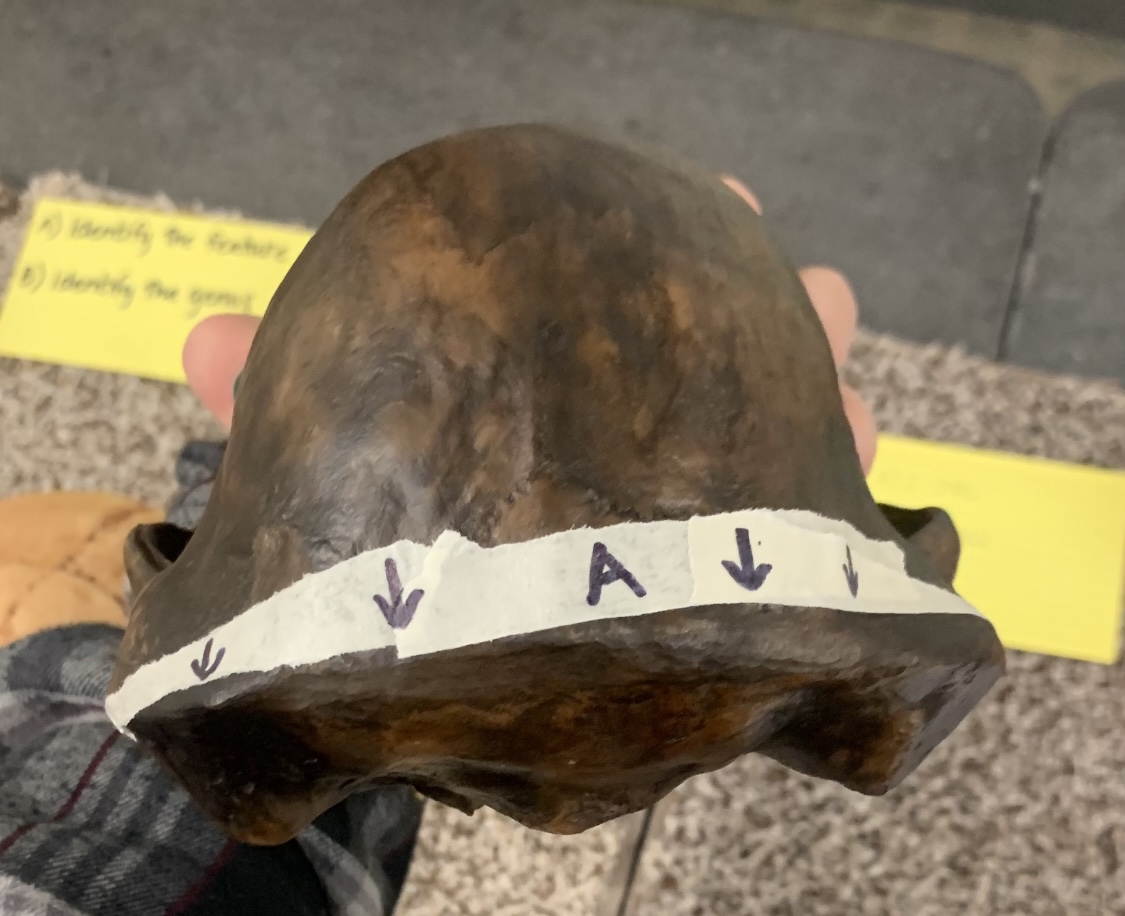

Identify the physical trait
C-TNC
95
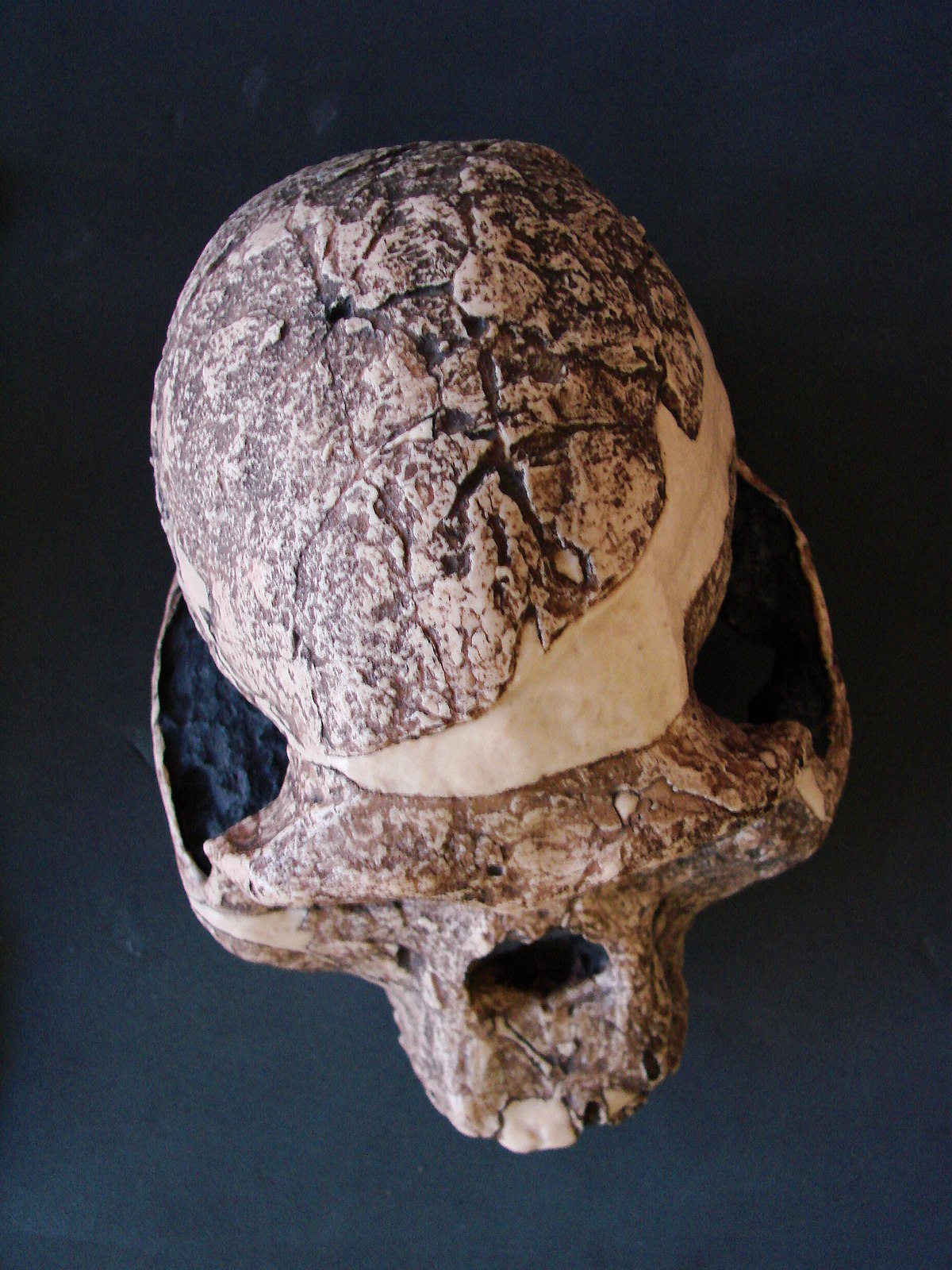
New cards
Identify the physical trait
post-orbital constriction
96
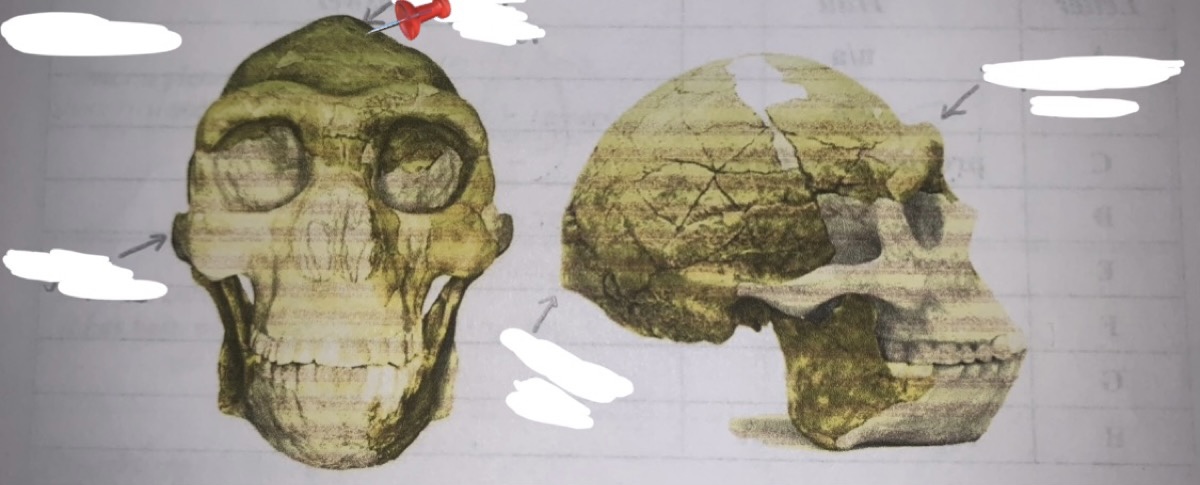
New cards
Identify the physical trait
sagittal keel
97
New cards
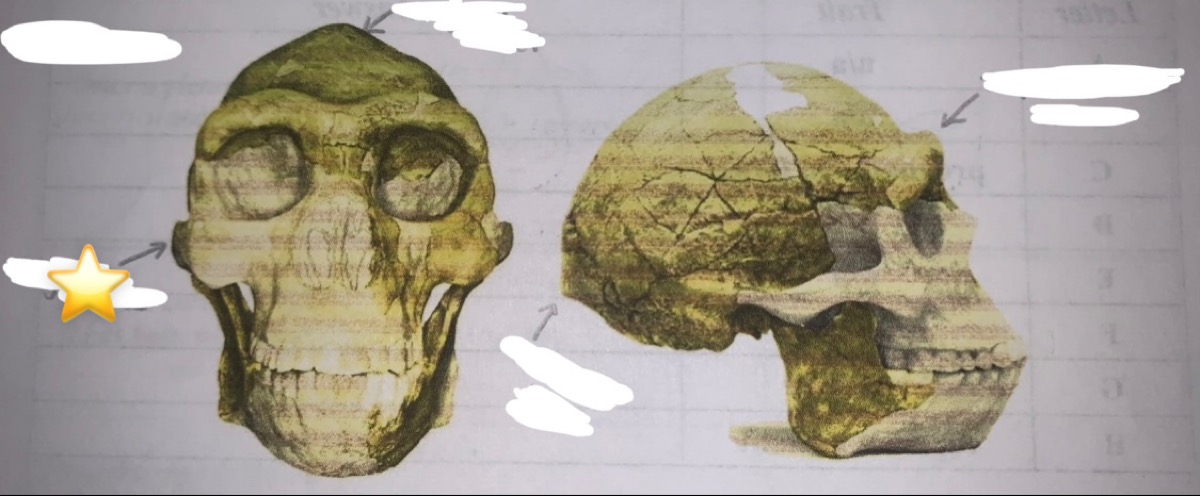
Identify the physical trait
angular torus
98
New cards
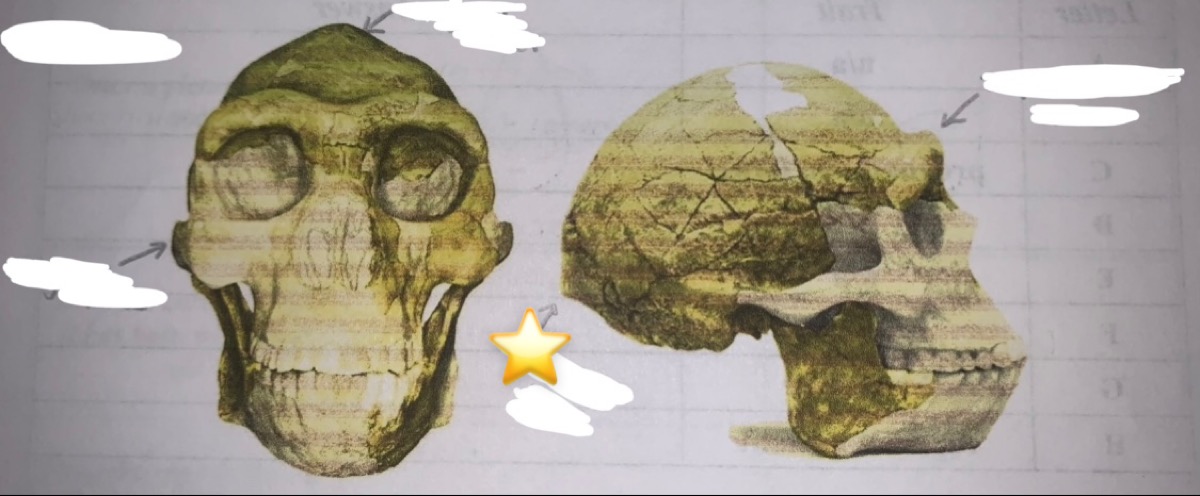
Identify the trait
occipital torus
99
New cards
What arch does the blue line represent?
transverse arch
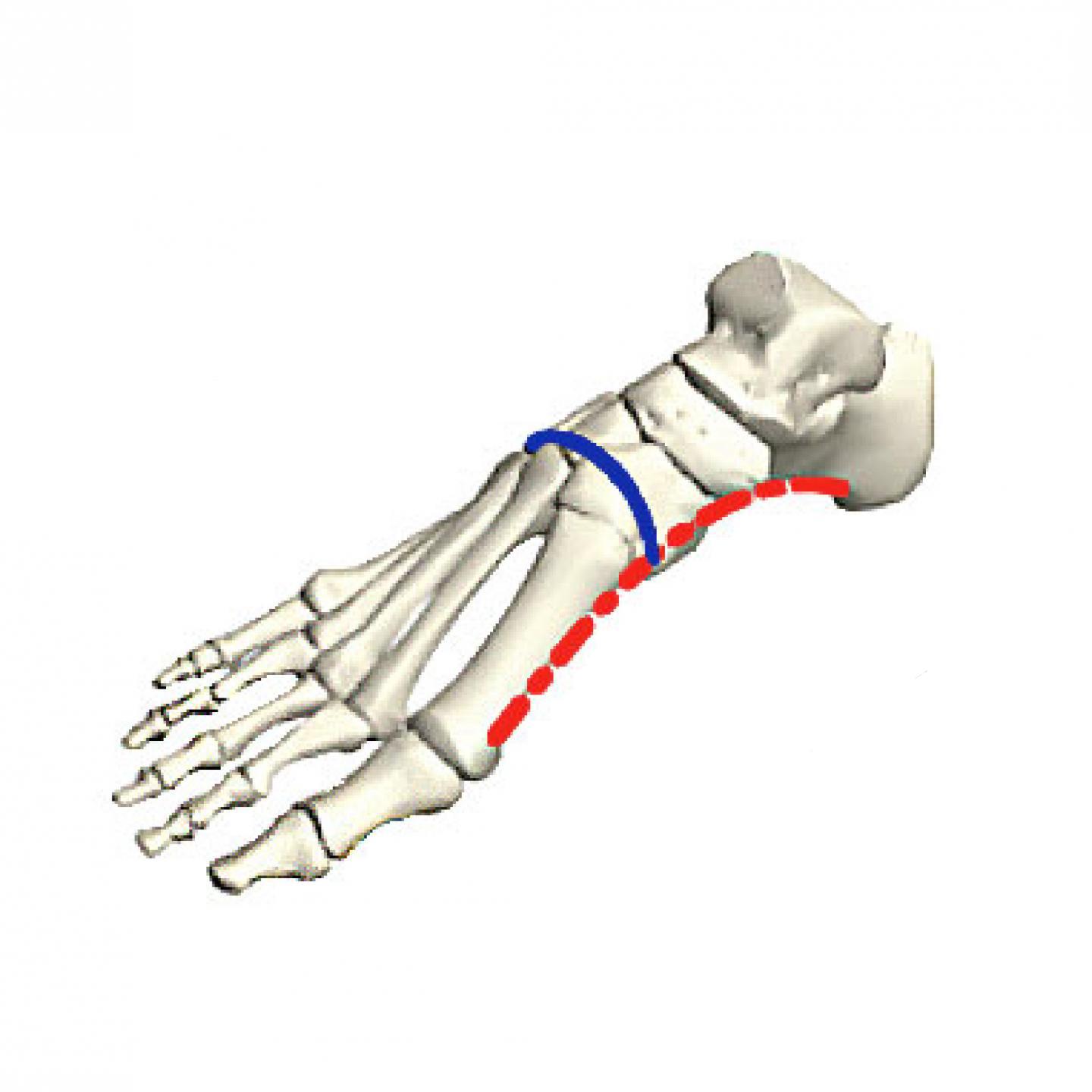
100
New cards
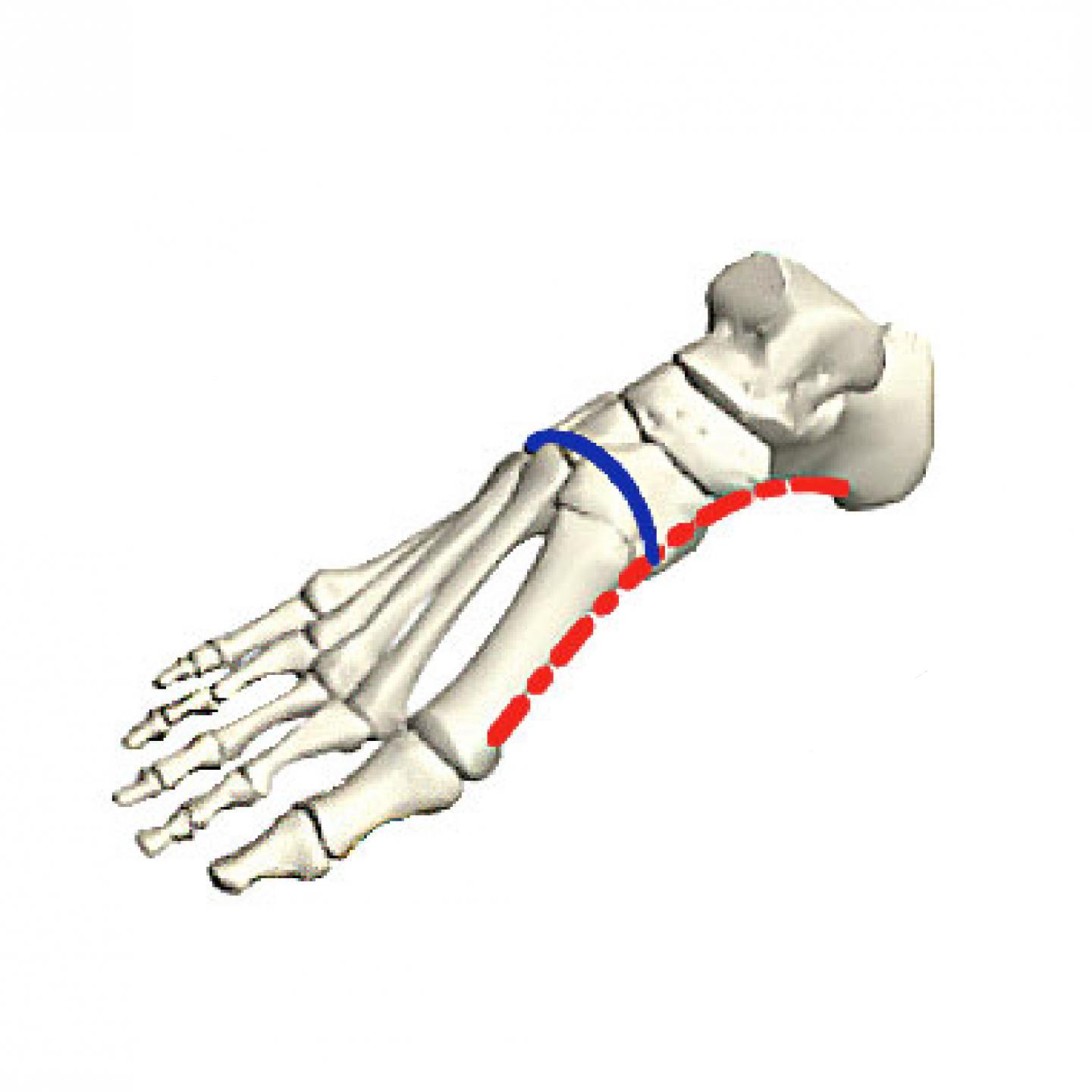
What arch does the red line represent?
longitudinal arch