Animal behaviour
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
animal behaviour paert of bio114
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what is Altruism
co operative behaviour - behaviour thats costs the individual but benefits others
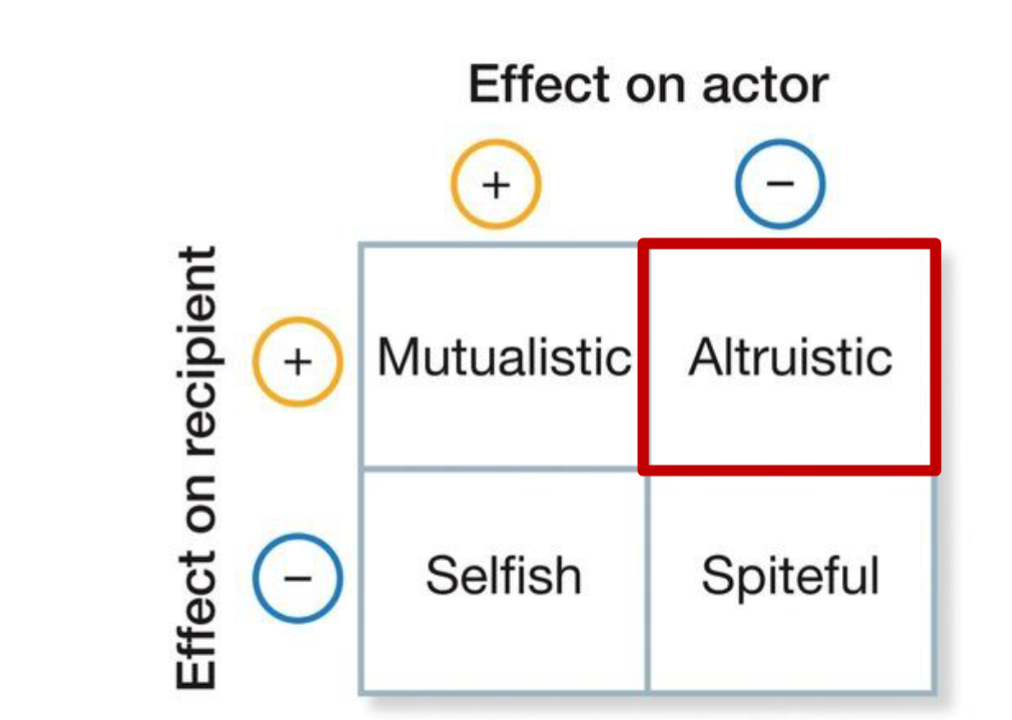
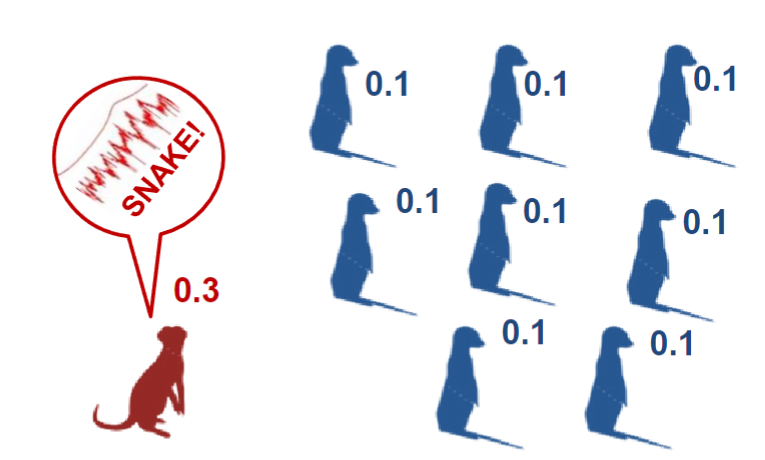
give an example of Altruism
one meercat sounding an alarm for the group
vampire bats sharing food with those unsucessful
dolphins helping injured pod members to the surface
give an example of a cost of grouping
increased competition
incresed energetic cost of movement
increased disease risk
give an example of the benefits to grouping
can be less vigilant but more likley to spot prey/predators
less likley to be captured
more efficiant in locating prey
more efficiant problem solvers
enables reduced energy cost of movement
defend larger territory
mating oppertunities
what are the different foraging strategies
generalists
specialists
hunters
ambush predators
grazers
browsers
scavengers
filter feeders
tool users
what are generalists
feed on a variety of food items and will exploit any food source in their environment. e.g. racoons
what are specialists
feed on specific types of food e.g. panda
what are hunters
predators that will stalk, chase and ambush prey e.g. lion
what are ambush predators
use camoflauge to ambuch prey e.g. crocodile
what are grazers
feed on grasses e.g. cow
what are browsers
feed on branches and leaves e.g. elephant
what are scavengers
feed on dead organic matter
what are filter feeders
passivley collect oragnisms like planton from the water column e.g. wales
what are tool users
use sticks and stones to manipulate food e.g. chimpanzees
what is optimal foraging theory (OFT)
a theory to understand animal foraging
who was the optimal foraging theory developed by
Robert Mac Arthur and Eric Pianka
what is energy maximisation
maximise energy gained per time spent foraging
what is time minimisation
minimise time spent foraging for other activities
what is risk sensitivity
take into account different risks per food source e.g. predation
what are the 3 optimal foraging models
marginal value - predicts optimal time to leave a resource patch based on diminishing returns
diet choice - predicts optimal diet composition by considering the energy and time handling of prey
patch use - predicts how organisms should allocate their time between patches
what is animal behaviour
the way animals physically and socially interact with their environment and surroundings
how is animal behaviour studied
repeatable, definable and recognisable units
what can hormones be stimulated by
temperture
day length
season
what are chemical senses
taste
smell
what are mechanical senses
touch
sound
pressure
vibration
what are electromagnetic senses
sight
what is Inate behaviour
developmental changes (not learning)
e.g. frogs learning how to swim and birds flying
what is single stimulus
non associative learning
no signal/cue
one action and response
habitualisation
sensitisation
what is stimulus-stimulus
associative behaviour
a warning before the behaviour
pavlovian conditioning
classical conditoning
what is response reinforce
associative behaviour
a reward or punishment after action
operant learning
instrumental learning
how do animals learn from each other
social cues (stimulus-stimulus)
evolved signals (response reinforce)
imitation
teaching
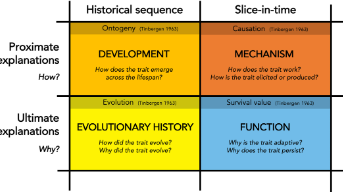
what are tinbergerns 4 questions?
ontogeny
causation
eveloution
survival value
what are the three main ways to avoid being eaten
defend
pretend
team up
types of defence (anti-predator behaviour)
wepeon
signal
e.g. skunk spray
types of pretend
mullerian mimicry
batesian mimicry
pretence (deceptive behaviour e.g. play dead)
how do animals team up to avoid predators
collective defence (loud calls)
collective escape
what is the ‘arms race’
ongoing cycle of adaptation between predators and prey
what is proximate
close in space of time (hormones and environmental factors that may predict behaviour)
how
what is ultimate
end of a process (evolution and natural selection)
why
what are the ways you can record behaviour
point focal sampling
continious focal sampling
what is agression
a defensive posture or attack either through threat or competition
what are the reasons for agression
defence
courtship/reproduction/parental care
recource competition (inter/intraspecific)
territorality
how can animals signal agression
olfactory (smell)
auditory
visual
what are the benefits of play
improve wellbeing
decrease in self destructive behaviours
develop physical and phycological skills for unexpected events
increase versatility movements
forms relationships
costs of play
energetic cost
danger from predators
injury (rarely serious)
play is poorly studied and difficult to observe
what are the types of play
object
locomotor
social
how do storms affect sea birds
at the nest - increases nest failure rates
at sea - seabird strandings
what is one of the first responses to environmental change
movement
what are the technological developments for tagging and marking
ringing
marking
pit tags
VHF
ARGOS
GPS
what is the definition of movement
a change in the spatial location of the whole individual overtime
what is marginal value
predicts optimal time to leave a resource patch based on diminishing returns
what is diet choice
predicts optimal diet composition by considering the energy content and handling time of prey
what is patch use
predicts how organisms should allocate their time between patches