9. Cellular Respiration
life is work
living cells require energy from outside sources to do work
the work of the cell includes assembling polymers, membrane transport, moving and reproducing
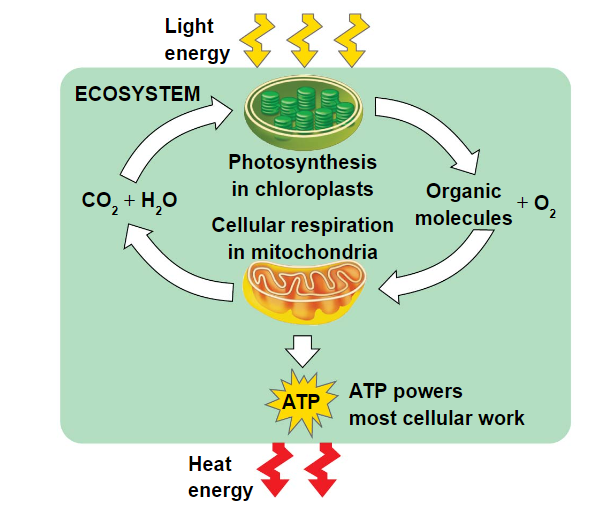
animals can obtain energy to do this work by feeding on other animals or photosynthetic organisms
energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat
the chemical elements essential to life are recycled
photosynthesis generates O2 and organic molecules (like glucose), which are used in cellular respiration
cells use chemical energy stored in organic molecules to generate ATP which powers work
catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
- catabolic pathways release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules
- electron transfer plays a major role in these pathways
- these processes are central to cellular respiration
catabolic pathways and ATP production
- the breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic
- fermentation is partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2
- aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP
- anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2
- when there isn’t enough oxygen for muscle cells to perform cellular respiration, they will cramp up
- cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration
- although carbohydrates, fats and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose
redox reactions
the transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules
this released energy is ultimately used to synthesize ATP
chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called oxidation-reduction reactions
in oxidation, a substance loses electrons or is oxidized
in reduction, a substance gains electrons or is reduced
LEO says GER
- lose electrons = oxidation
- gain electrons = reduction
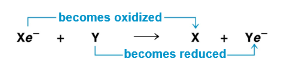
the electron donor is called the reducing agent
the electron receptor is called the oxidizing agent
some redox reactions do not transfer electrons but change the electron sharing in covalent bonds
- eg. methane + O2
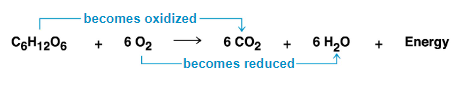
glucose is the initial electron donor
carbon dioxide is the initial electron receptor
oxygen becomes the final electron acceptor
- during ETC to produce water
oxidation of organic fuel molecules during cellular respiration
- during cellular respiration, the fuel (glucose) is oxidized and O2 is reduced
- organic molecules with an abundance of hydrogen are excellent sources of high-energy electrons
- energy is released as the electrons associated with the hydrogen ions are transferred to oxygen, a lower energy state
stepwise energy harvest via NAD and the ETC
in cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps
electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme
as an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration
NADH, the reduced form of NAD+ represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP
NAD+ + 2H+ + 2e- = NADH + H+
NADH has the ability to make 3 ATP
NAD+ is being reduced
coenzyme FAD+ will pick up 2e- and 3H+ to form FADH
- FADH can make 2 ATP
NADH passes the electrons to the electron transport chain
unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction
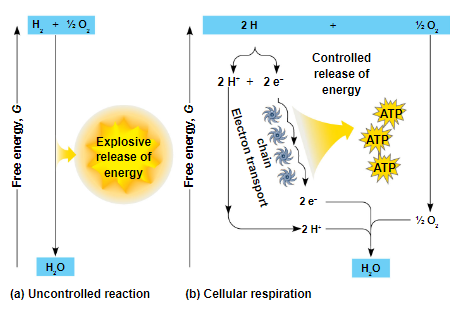
^^O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energy-yielding tumble^^
the energy yielded is used to regenerate ATP
NADH returns to NAD+ after transporting electrons
the stages of cellular respiration
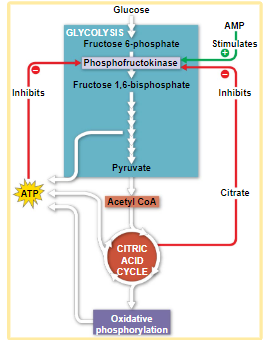
glycolysis - breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules
Krebs cycle - complete breakdown of glucose
oxidative phosphorylation - most of ATP synthesis
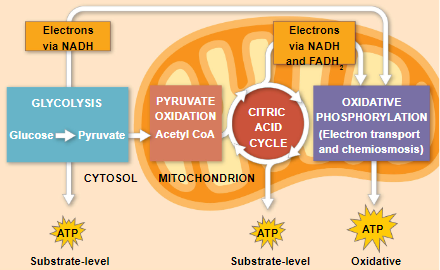
- glycolysis happens in the cytosol
- electron transport chains and cellular respiration occur along the inner membrane and waves
- oxidative phosphorylation is when ATP is released from ETC from the coenzymes being reduced (NADH and FADH)
- the process that generates almost 90% of the ATP is called oxidative phosphorylation because it is powered by redox reactions
- the smaller amount of ATP is formed in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle by substrate-level phosphorylation
- substrate-level phosphorylation produces ATP by itself, without going through coenzymes NADH and FADH
- oxidative phosphorylation is when ATP is made through coenzymes NADH and FADH in the ETC
- for each molecule of glucose degraded to CO2 and water by respiration, the cell makes 32 - 36 ATP
glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate
- glycolysis (sugar splitting) breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
- glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and has two major phases
- energy investment phase
- energy payoff phase
- glycolysis occurs whether or not O2 is present
- this is because prokaryotes who don’t have organelles also use glycolysis for energy
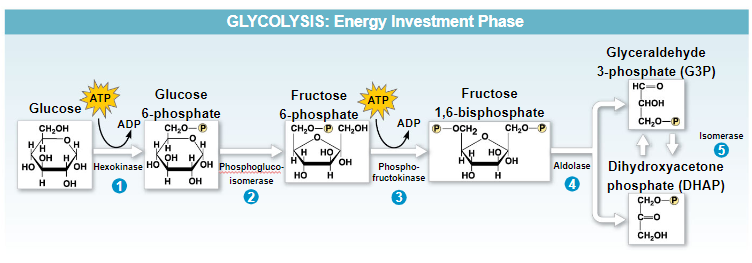
steps of glycolysis
ATP is used to add phosphorus to glucose using hexokinase → glucose 6-phosphate
phosphoglucoisomerase creates an isomer of glucose 6-phosphate → fructose 6-phosphate
ATP is used to add another phosphorus using phosphofructokinase → fructose 1,6-biphosphate
aldolase converts fructose 1,6-biphosphate into 2 potential products → glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
- G3P is an acetone and can move on in glycolysis
- DHAP is an aldehyde and needs to be converted into G3P to move on
* Everything is doubled from now on *
- isomerase can convert DHAP and G3P to each other depending on what is necessary
- G3P is converted to 1,3-Biphosphoglycerate and ^^produces 2 NADH^^
- 1,3-biphosphoglycerate is converted to 3-phosphoglycerate using phosphoglycerokinase and ^^produces 2 ATP^^
- phosphoglyceromutase is used to convert 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate
- enolase is used to convert that to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and water is produced
- pyruvate kinase converts that to pyruvate and ^^produces 2 ATP^^
after pyruvate is oxidized, the krebs cycle completes the oxidation
- in the presence of O2, pyruvate enters a mitochondrion (in eukaryotic cells), where the oxidation of glucose is completed
- before the krebs cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
- this is carried out by a multienzyme complex that catalyzes three reactions
- oxidation of pyruvate and ^^release of CO2^^
- reduction of NAD+ to ^^produce 2 NADH^^
- combination of the remaining 2-carbon fragment and coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA
- 2 ATP are used in pyruvate oxidation
the krebs cycle
the citric acid cycle or krebs cycle completes the breakdown of pyruvate to CO2
the cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate generating ^^1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH^^ for EACH pyruvate (glucose would have 2)
- 24 ATP in total
each acetyl-CoA is fed into the cycle separately and ^^converted into 2 CO2 (4 total)^^
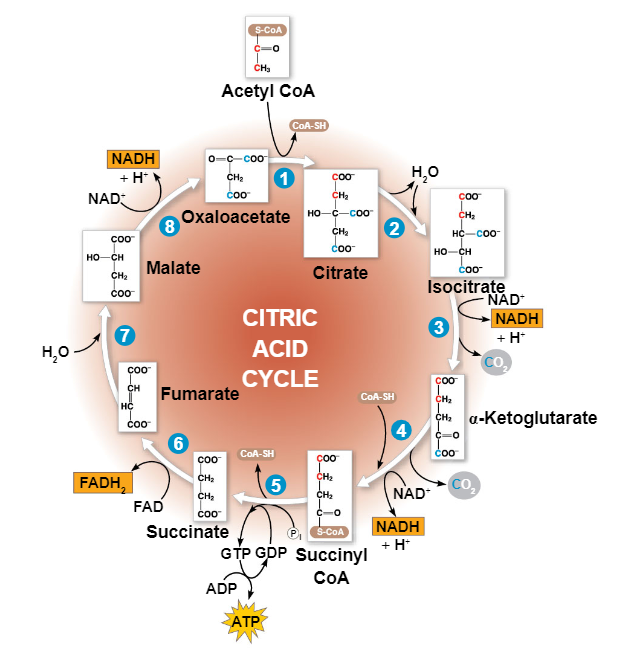
ending molecule of Krebs cycle is oxaloacetate
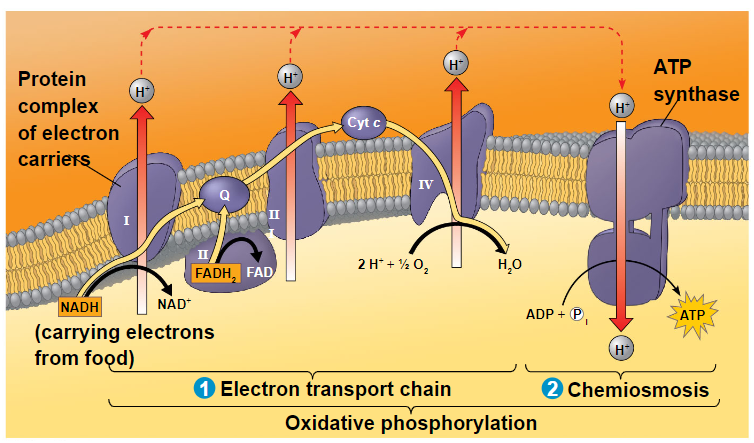
during oxidative phosphorylation chemiosmosis couple electron transport to ATP synthesis
- following glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, NADH and FADH account for most of the energy extracted
- these 2 electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation
the pathway of electron transport
- the electron transport chain is in the inner membrane (cristae) of the mitochondrion
- most of the chain’s components are proteins which exist in multiprotein complexes
- electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O
- electron carriers alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons
- electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH to the electron transport chain
- electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2
- the electron transport chain generates no ATP directly
- it breaks the large free-energy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts
- the energy released as electrons are passed down the ETC is used to pump H+ from the matrix to the intermembrane space
- H+ then moves down its concentration gradient back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex ATP synthase
- H+ moves into the binding sites on the rotor of ATP synthase causing it to spin in a way that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
- this is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
- certain electron carriers in the ETC accept and release H+ along with the electrons
- in this way, the energy stored in a H+ gradient across a membrane couple the redox reactions of the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis
- the H+ gradient is referred to as a proton-motive force
accounting of ATP production by cellular respiration
- during cellular respiration, most energy flows in this sequence
- glucose → NADH → ETC → proton-motive force → ATP
- about 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration making about 32-36 ATP
- the rest of the energy is lost as heat
- 3 reasons why the # of ATP is not exact
- photophosphorylation and the redox reactions are not directly coupled; the ratio of NADH to ATP molecules is not a whole number
- ATP yield varies depending on whether electrons are passed to NAD or FAD in the mitochondrial matrix
- the proton-motive force is also used to drive other kinds of work
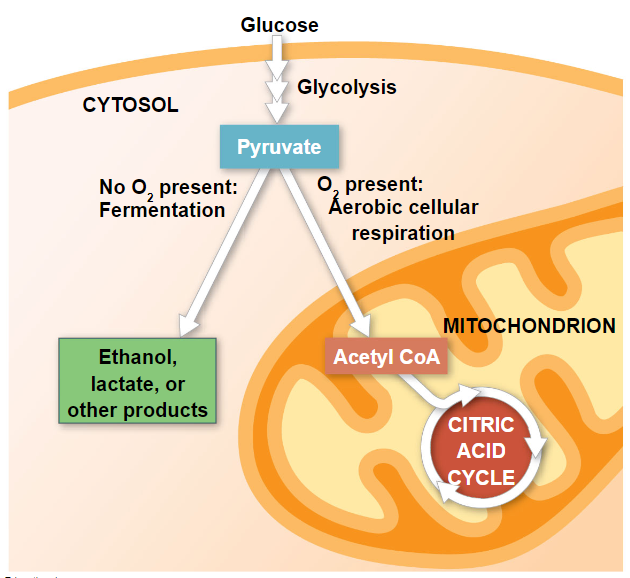
fermentation and anaerobic respiration produces ATP without oxygen
- most cellular respiration depends on electronegative oxygen to pull electrons down the transport chain
- without oxygen, the electron transport chain will cease to operate
- in that case, glycolysis couples with anaerobic respiration or fermentation to produce ATP
- anaerobic respiration uses an ETC with a final electron acceptor rather than oxygen
- eg sulfate
- fermentation uses substrate-level phosphorylation instead of ETC to generate ATP
- eg. sourdough - sour because of lactic acid
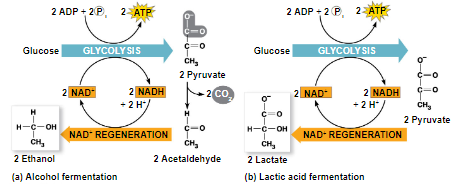
types of fermentation
fermentation consists of glycolysis plus reactions that regenerate NAD which can be reused by glycolysis
2 common types are alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
alcohol fermentation - pyruvate is converted to ethanol in 2 steps
- first releases CO2 from pyruvate
- second produces NAD and ethanol
alcohol fermentation by yeast is used in brewing, winemaking, and baking
lactic acid fermentation - pyruvate is reduced by NADH forming NAD and lactate as end products with no release of CO2
lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt
human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentations to generate ATP during strenuous exercise when O2 is scarce
in alcohol fermentation, if there is not enough yeast, it will make acetic acid (eg. balsamic vinegar)
comparing fermentation with anaerobic and aerobic respiration
- all use glycolysis (net 2 ATP) to oxidize glucose and harvest the chemical energy of food
- in all three, NAD is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis
- the processes have different mechanisms for oxidizing NADH to NAD
- fermentation uses and organic molecule like pyruvate of acetaldehyde to act as a final electron acceptor
- cellular respiration transfers electrons to the ETC
- cellular respiration produces 32 ATP per glucose molecule
- fermentation produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule
- obligate anaerobes carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2
- yeast and bacteria are facultative anaerobes, meaning that they survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration
- in a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic road that leads to 2 alternative catabolic routes
the evolutionary significance of glycolysis
- it is an ancient process
- early prokaryotes used glycolysis to produce ATP before O2 accumulated in the atmosphere
- used in both cellular respiration and fermentation
- the most widespread metabolic pathway
- occurs in the cytosol so does not require organelles
glycolysis and krebs cycle connections
- glycolysis and krebs are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways
versatility of catabolic pathways
- catabolic pathways funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration
- glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbs
- proteins that are used for fuel must be digested to amino acids and their amino groups must be removed
- fats are digested to glycerol and fatty acids
- they are too big to enter mitochondria without being broken down
- fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yields acetyl CoA, NADH and FADH
- an oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate
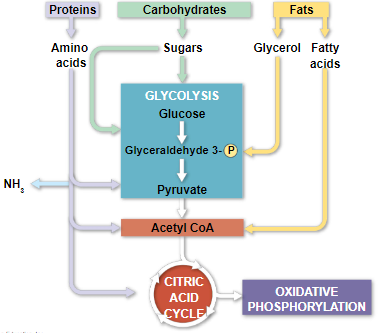
biosynthesis (anabolic pathways)
- the body uses small molecules from food to build their own proteins
- these small molecules may come directly from food, glycolysis or the krebs cycle
regulation of cellular respiration via feedback mechanisms
- feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for metabolic control
- if ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down
- control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in catabolic pathways