[MDCU] Heart disease in pregnancy
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the most common cause of heart disease in pregnancy?
Rheumatic heart disease
Changes in pregnancy
Cardiac output
Heart rate
Vascular resistance
Blood pressure
Osmotic pressure
Cardiac output ↑
Heart rate ↑
Vascular resistance ↓
Blood pressure ↓
Osmotic pressure ↓
Cardiac output reaches peak at GA ___
Immediately postpartum
Blood pressure reaches nadir at GA ___
GA 24-26 weeks
In pregnancy, heart and apex displace ___
Heart = upward & left
Apex = lateral
Larger cardiac silhouette
Syncope is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Abnomal = syncope with exertion
Syncope with exertion is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Normal = syncope
Dizzy spells is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Easy fatigability is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Chest pain related to exertion is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Normal = dyspnea
Dependent edema in pregnancy is normal if occurs at ___
3rd trimester
Dependent edema in pregnancy is abnormal if occurs at ___
1st & 2nd trimester
Rales in lower lung is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Engorged neck vein is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Cardiomegaly is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Cyanosis and clubbing finger is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Diastolic murmur is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Systolic murmur grade ___ in pregnancy is normal
Systolic murmur grade <=2
Systolic murmur grade ___ in pregnancy is abnormal
Systolic murmur grade ≥3
S3 gallop is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
S3 gallops = heard during early diastolic filling, caused by vibrations of ventricular wall as flow suddenly decelerated
S4 gallop is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Abnormal
Venous hums is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Venous hum is a benign phenomenon caused by the normal flow of blood through the jugular veins.
Internal mammary flow murmur is (normal / abnormal) in pregnancy
Normal
Which 5 conditions are considered WHO class IV risk of cardiovascular diseases?
Pulmonary artery hypertension
Severe ventricular dysfunction (NYHA 3, 4, LVEF <30%)
Severe left heart obstruction
Previous peripartum cardiomyopathy with residual left heart dysfunction
Marfan syndrome with aortic dilation >40 mm
What are 4 risk factors associated with CARPREG score?
Prior cardiac events
Baseline NYHA class III & IV
Left heart obstruction
LVEF <40%
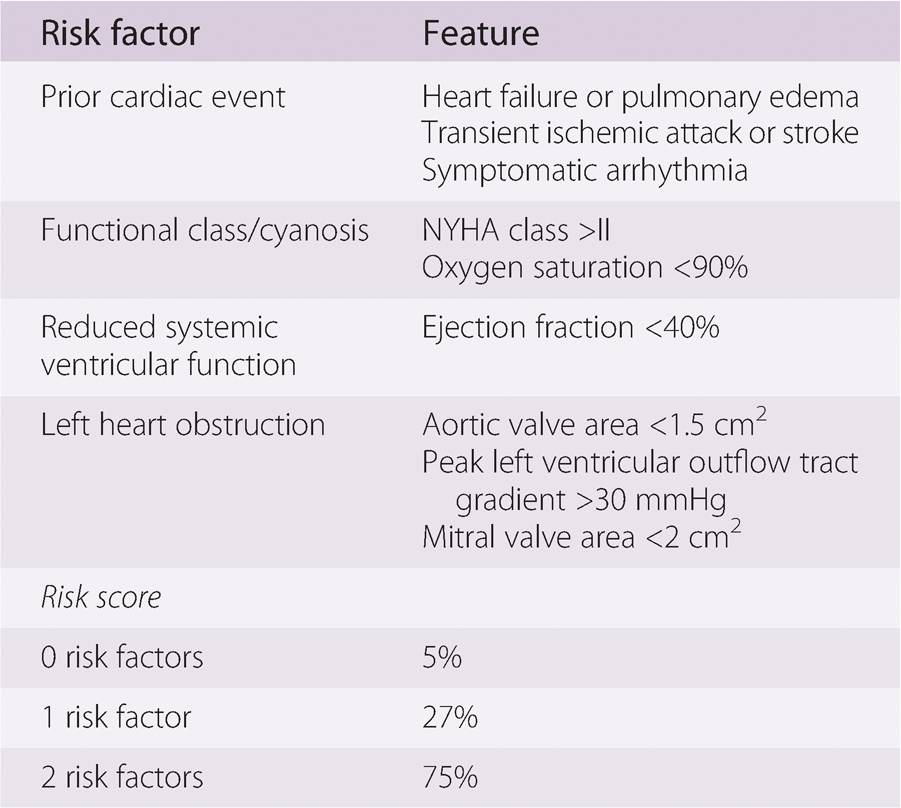
Left heart obstruction in CARPREG score is defined as:
Mitral valve area ___
Aortic valve area ___
Peak LV outflow tract gradient ___
Mitral valve area <2 cm2
Aortic valve area <1.5 cm2
Peak LV outflow tract gradient >30 mmHg
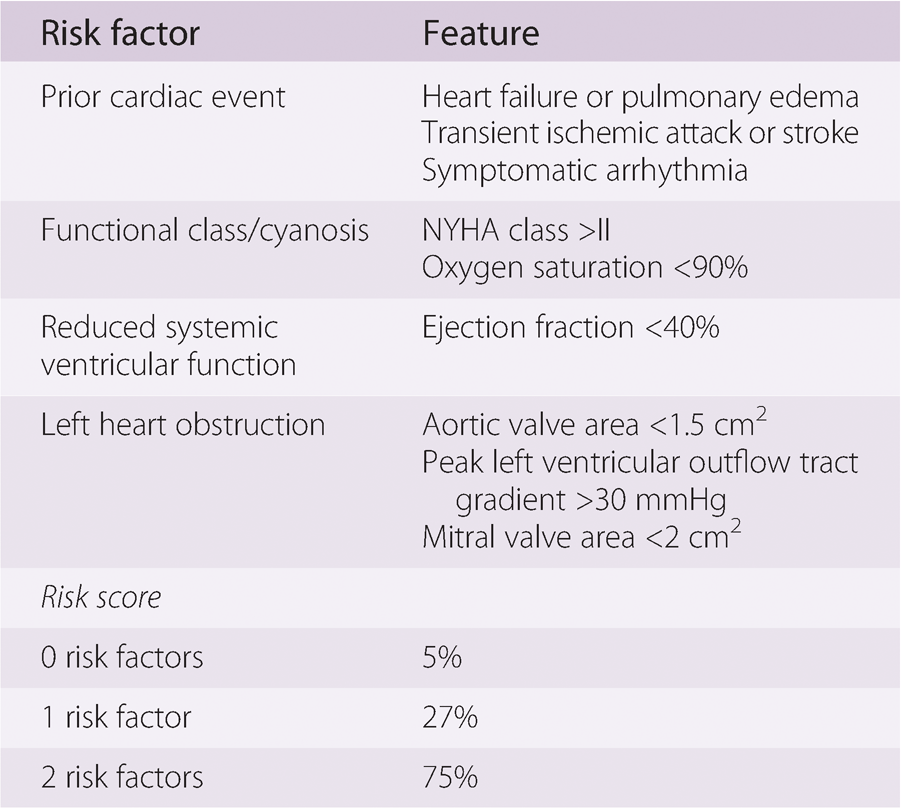
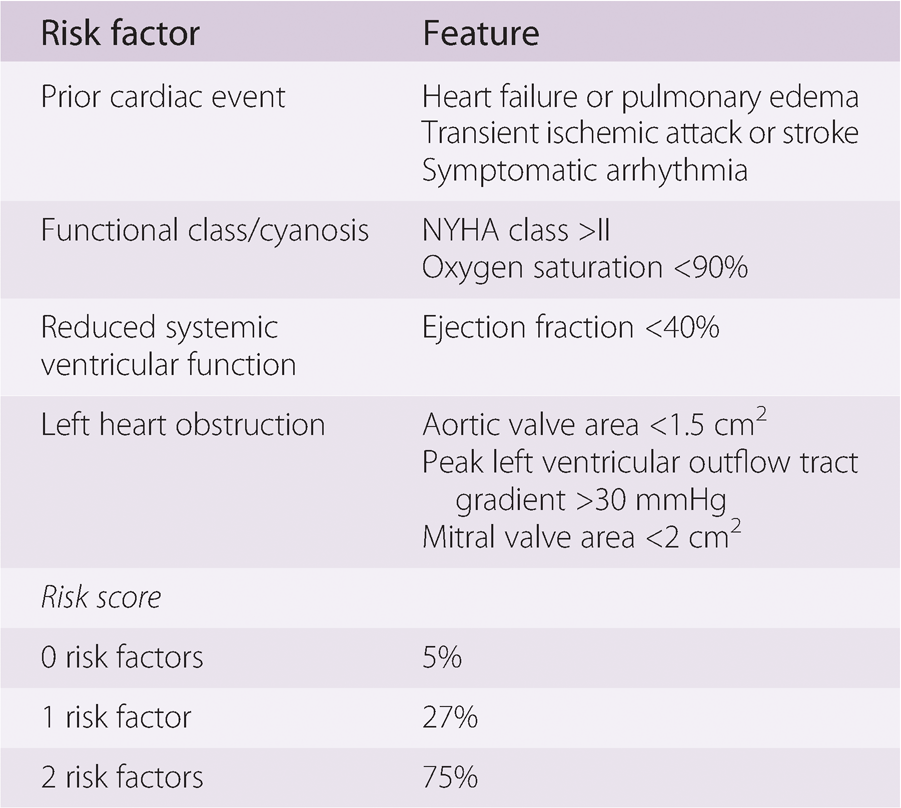
What are risks of maternal cardiac event during pregnancy in patients with CARPREG score of 0, 1 and 2?
0 risk = 5%
1 risk = 27%
2 risks = 75%
Risk for warfarin embryopathy significantly increases if dose ___
>5 mg/day
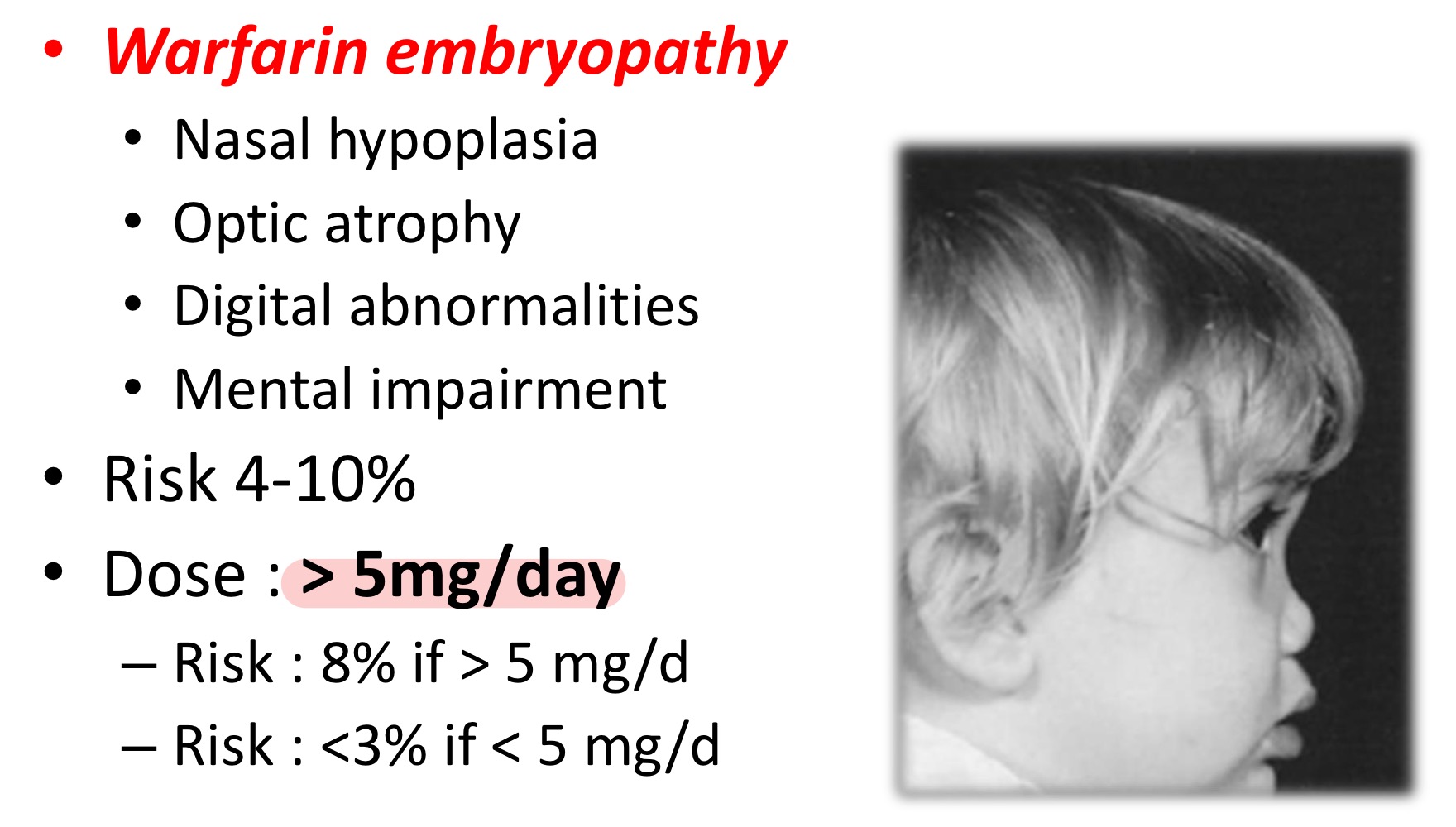
What are common presentations of warfarin embryopathy?
Nasal hypoplasia
Mental retardation
Optic atrophy
Digital abnormalities
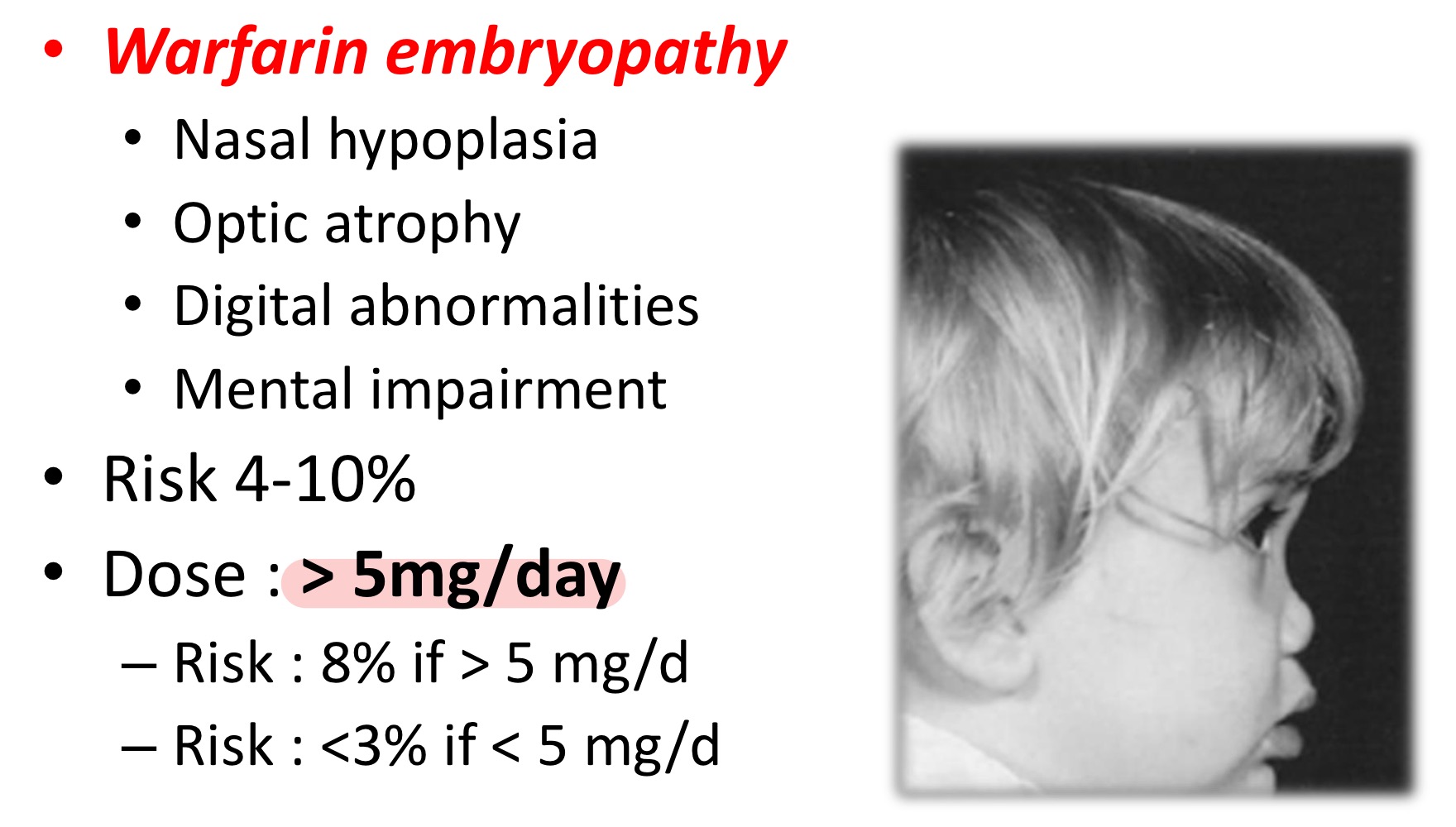
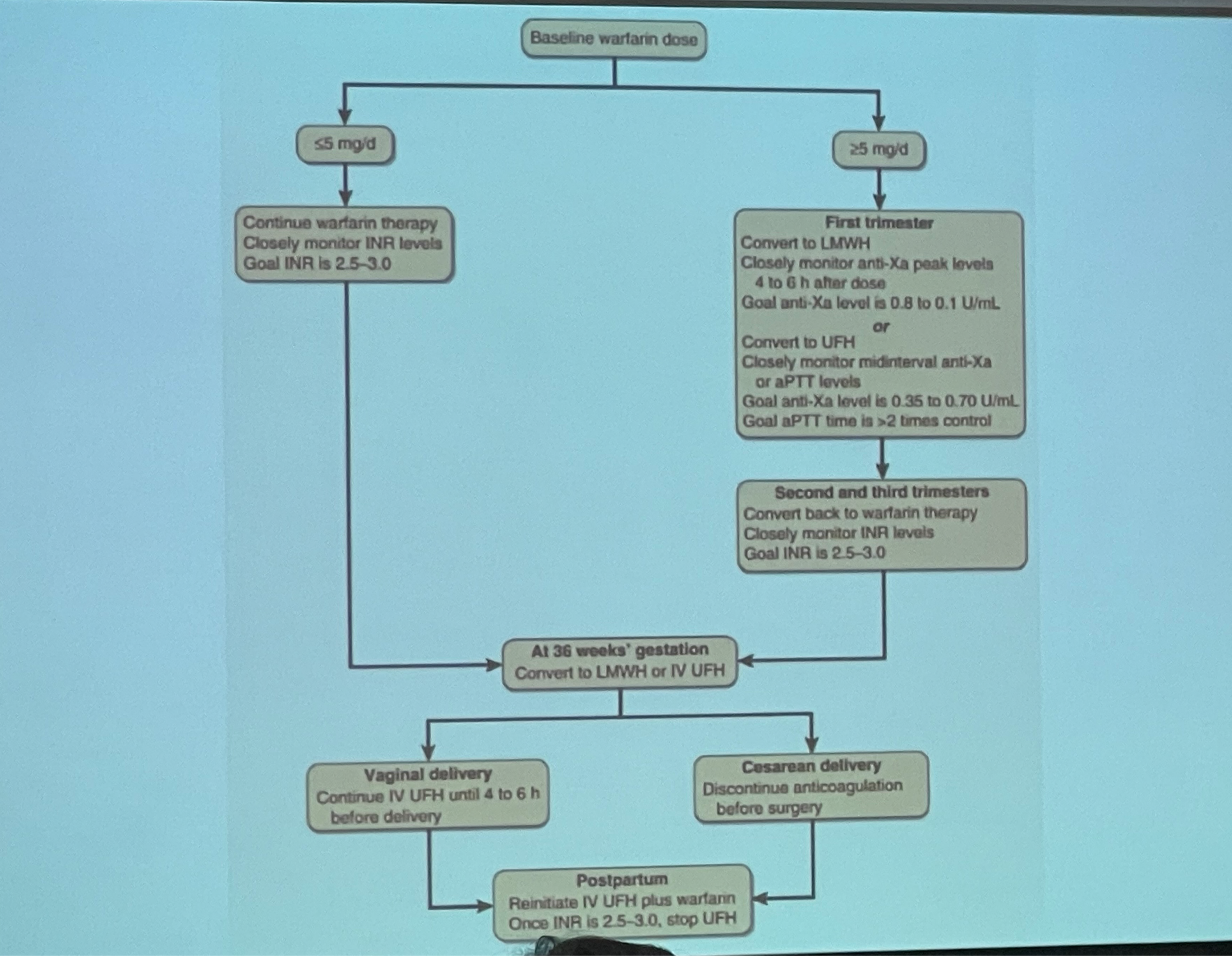
In pregnant women with baseline warfarin >5 mg/day, what is the appropriate anticoagulant in during 1st, 2nd, 3rd trimester?
1st trimester = LMWH (anti-Xa) / UFH (anti-Xa & aPTT)
2nd & 3rd trimester = switch back to warfarin
Switch again to LMWH/UFH at GA 36 weeks
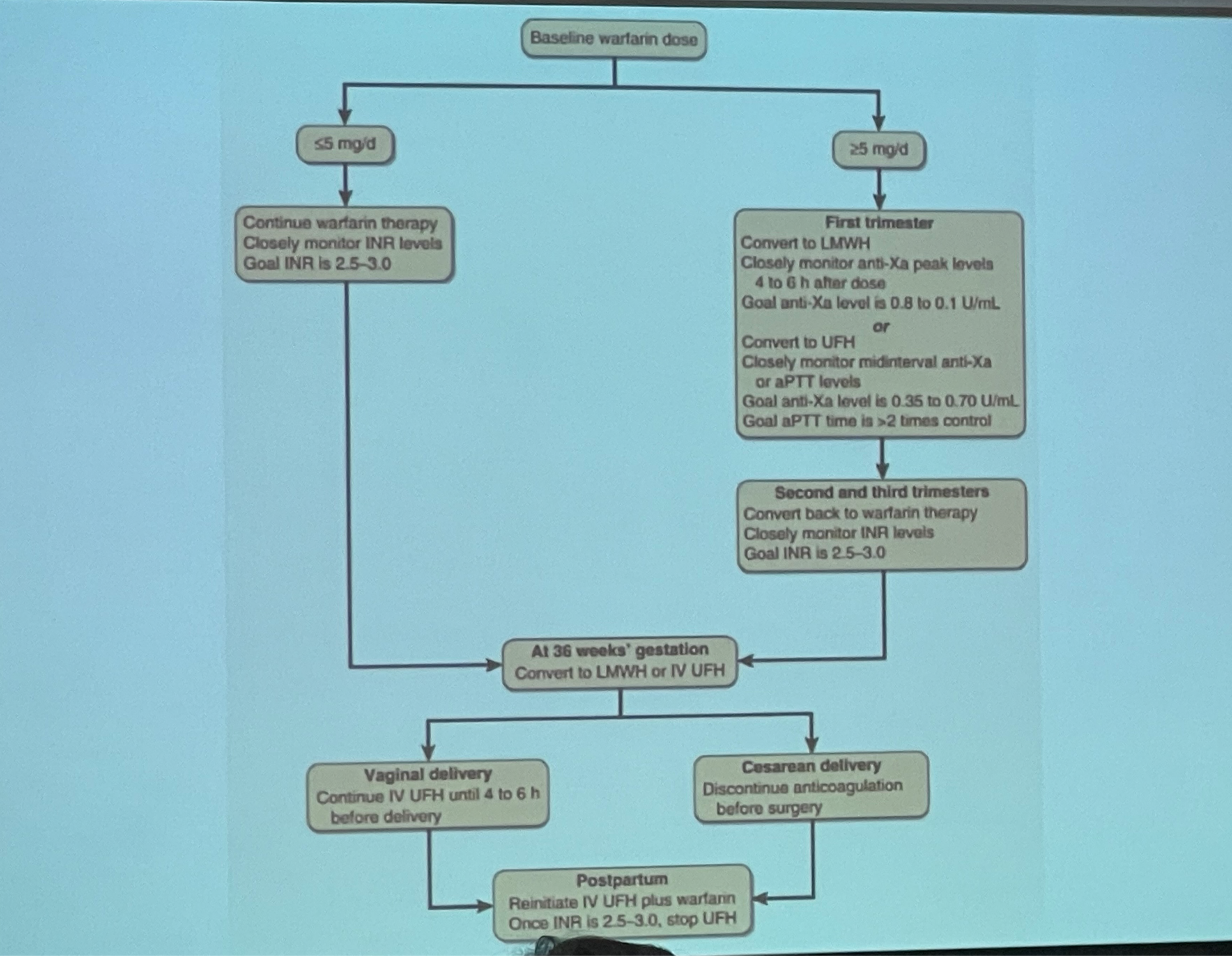
In pregnant women receiving warfarin, INR should be kept at ___
2.5 - 3.0
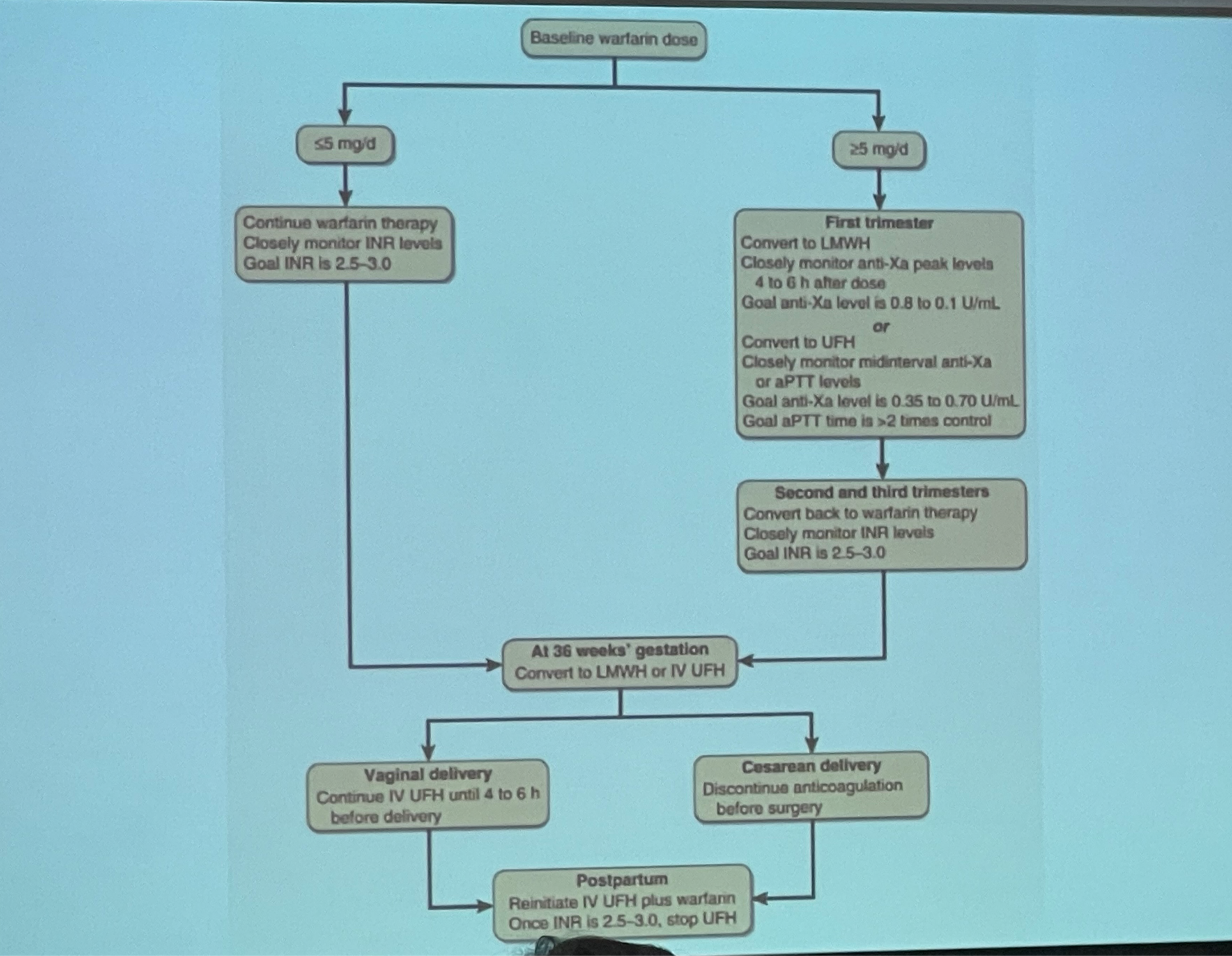
Which coagulogram parameter should be monitored in pregnant woman receiving LMWH and UFH?
LMWH = anti-Xa
UFH = anti-Xa & aPTT
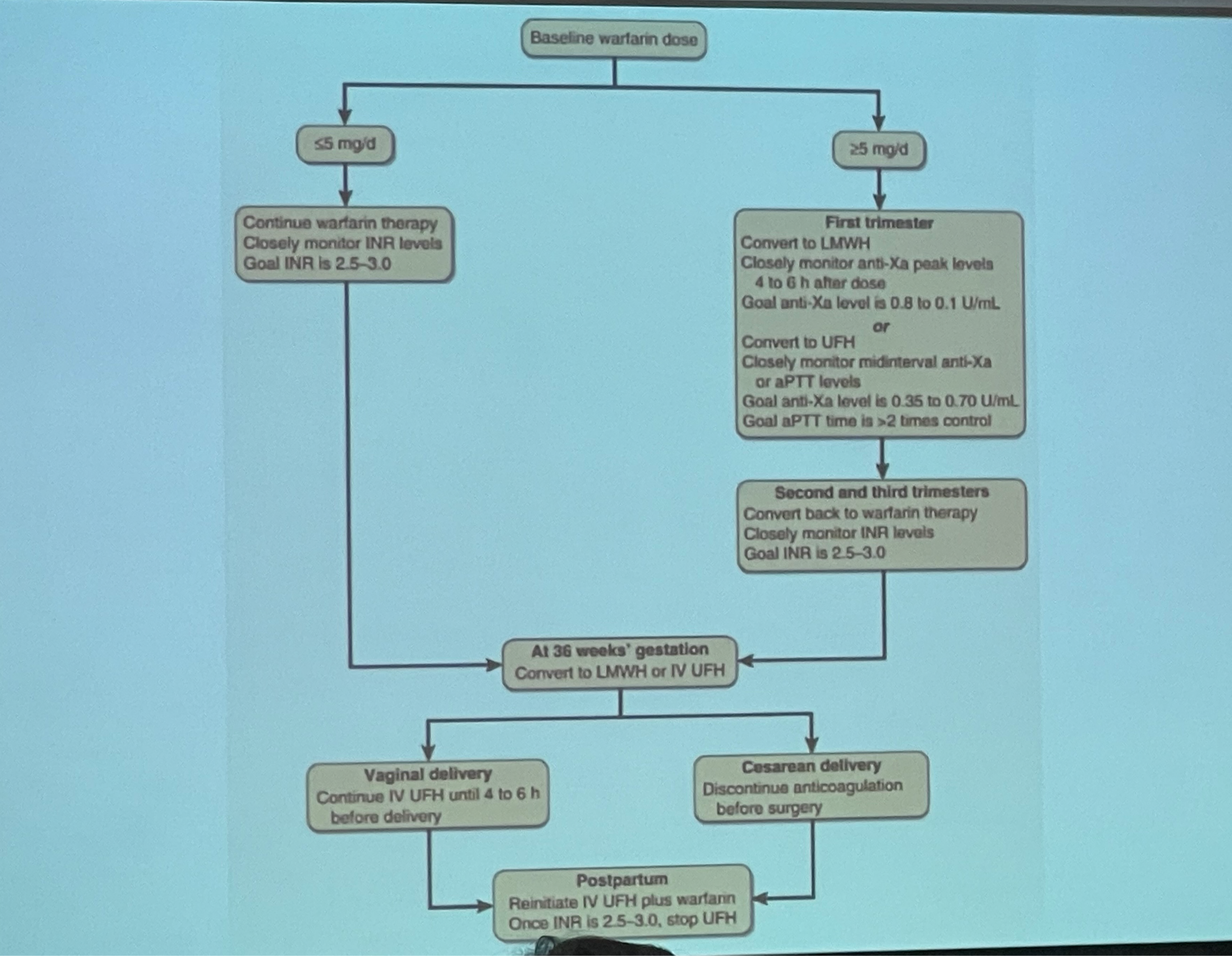
Which anticoagulant should be reinitiated post-partum?
IV UFH + warfarin
Once INR 2.5-3.0, stop UFH
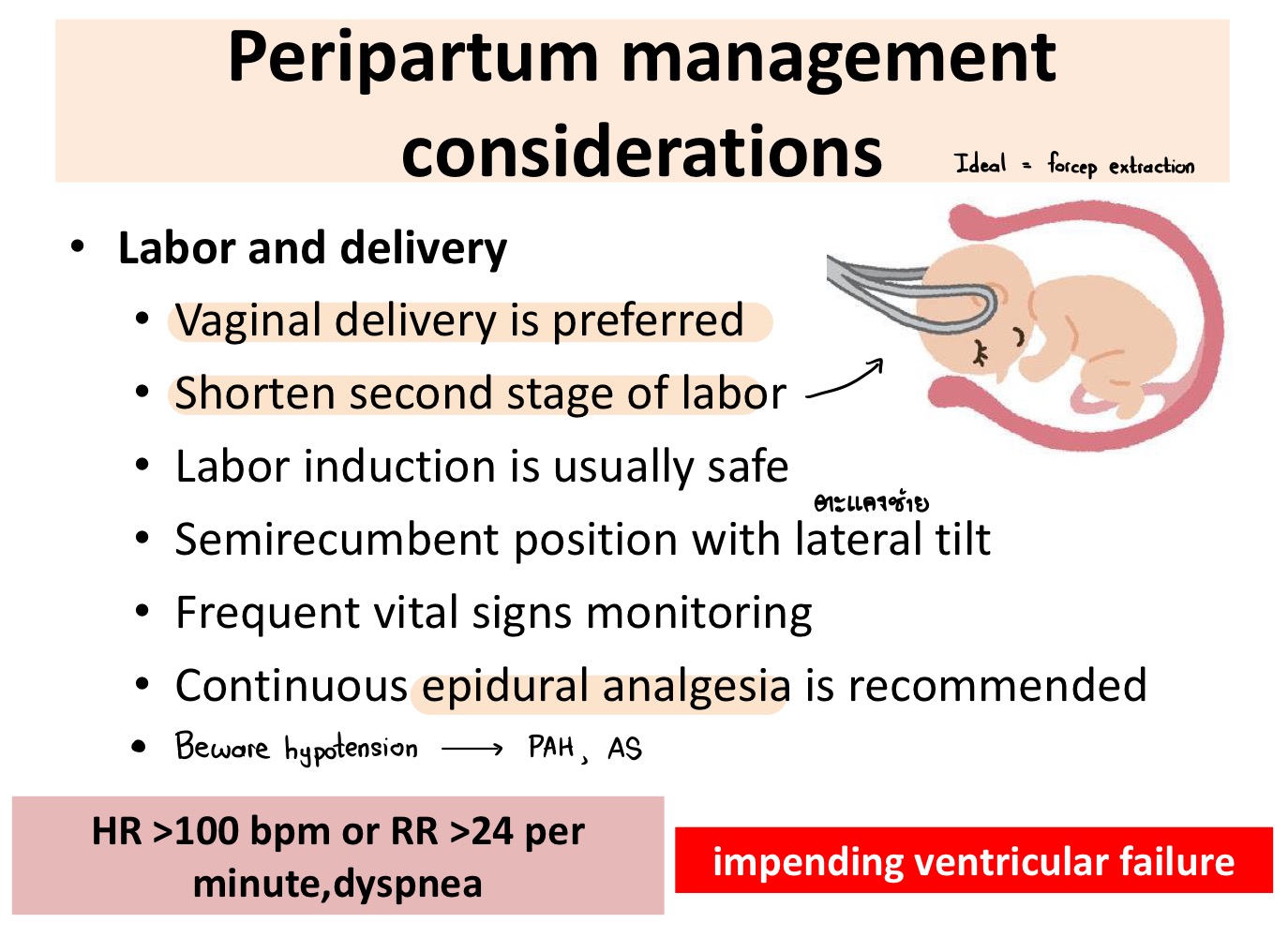
What method of delivery is preferred in pregnant women with heart disease?
Vaginal delivery + forceps extraction
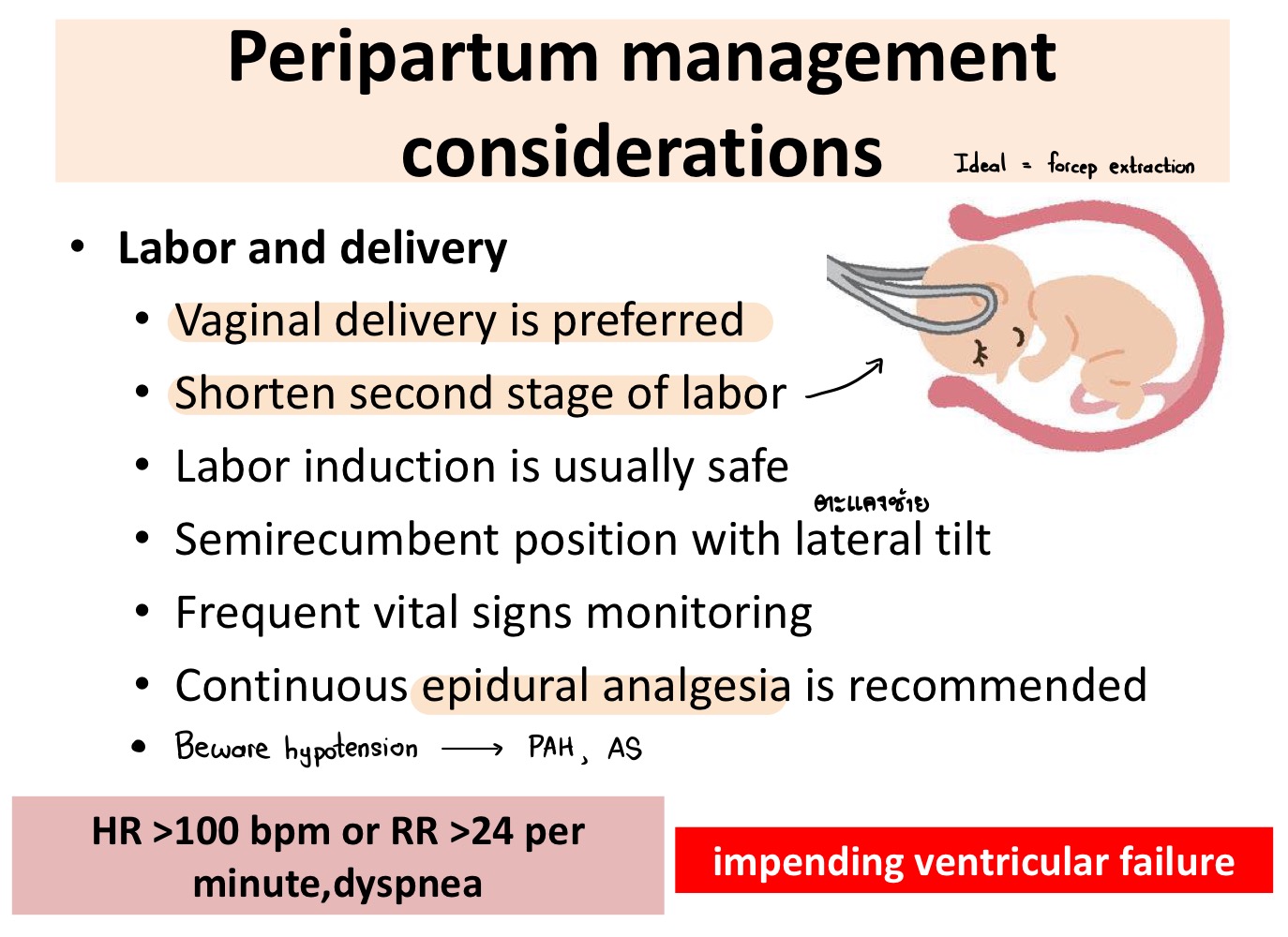
Which anesthesia is preferred in pregnant women with heart disease during delivery?
Epidural anesthesia
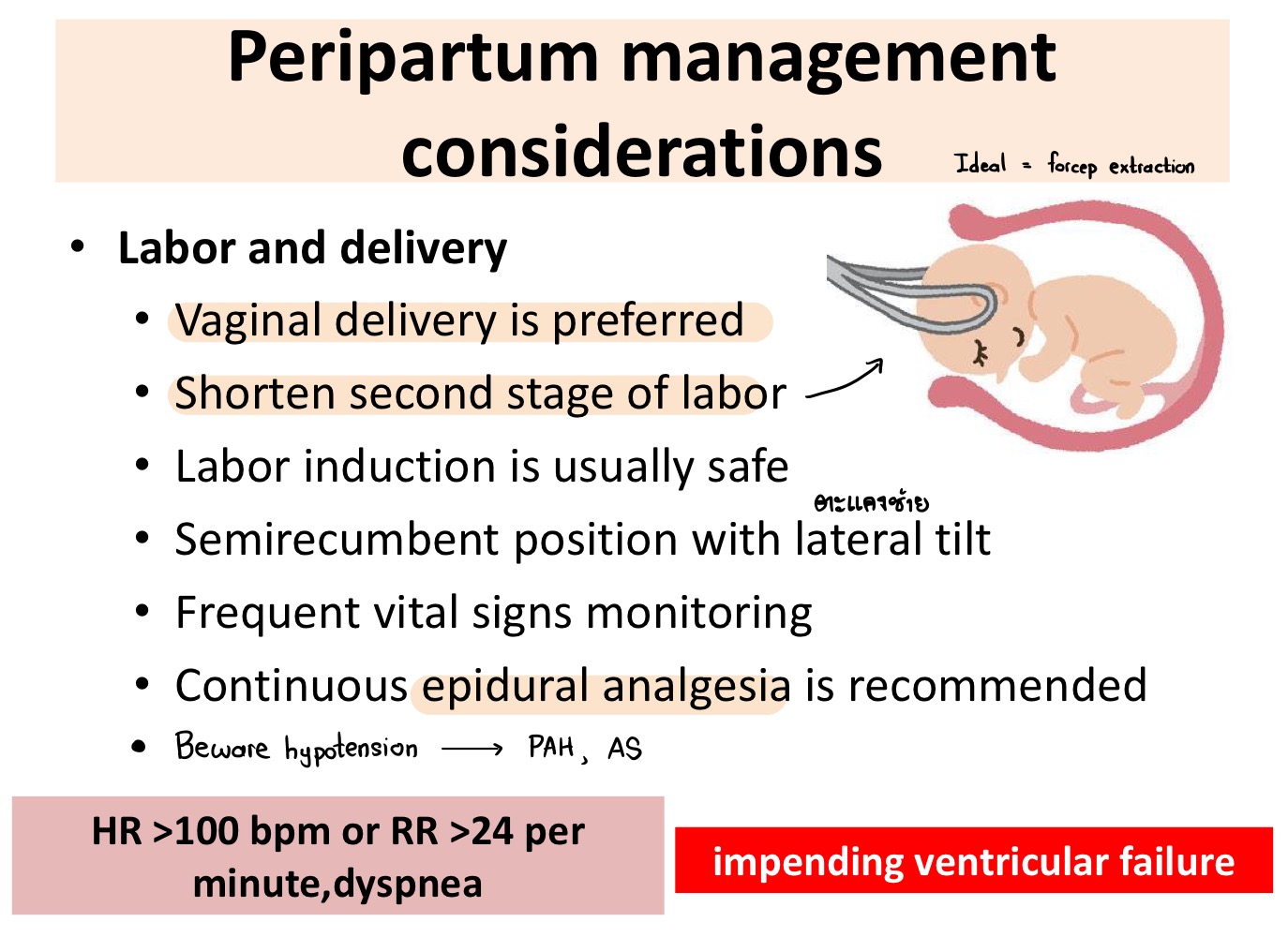
What are 3 signs of impending ventricular failure?
HR >100
RR >24
Dyspnea
Cardiac surgery, if lifesaving, should be done under:
Pump flow rate ___
Normothermic perfusion pressure ___
Hematocrit
Pump flow rate >2.5 L/min/m2
Normothermic perfusion pressure >70 mmHg
Hematocrit >28%
Patients underwent cardiac transplantation should postpone pregnancy for at least ___
At least 1 year
Risk of acute rejection ↓
Intensity of immunosuppressants ↓
What is the timing for tubal resection in postpartum woman with heart disease?
Delayed up to days 2-3 to ensure stabilized hemodynamics
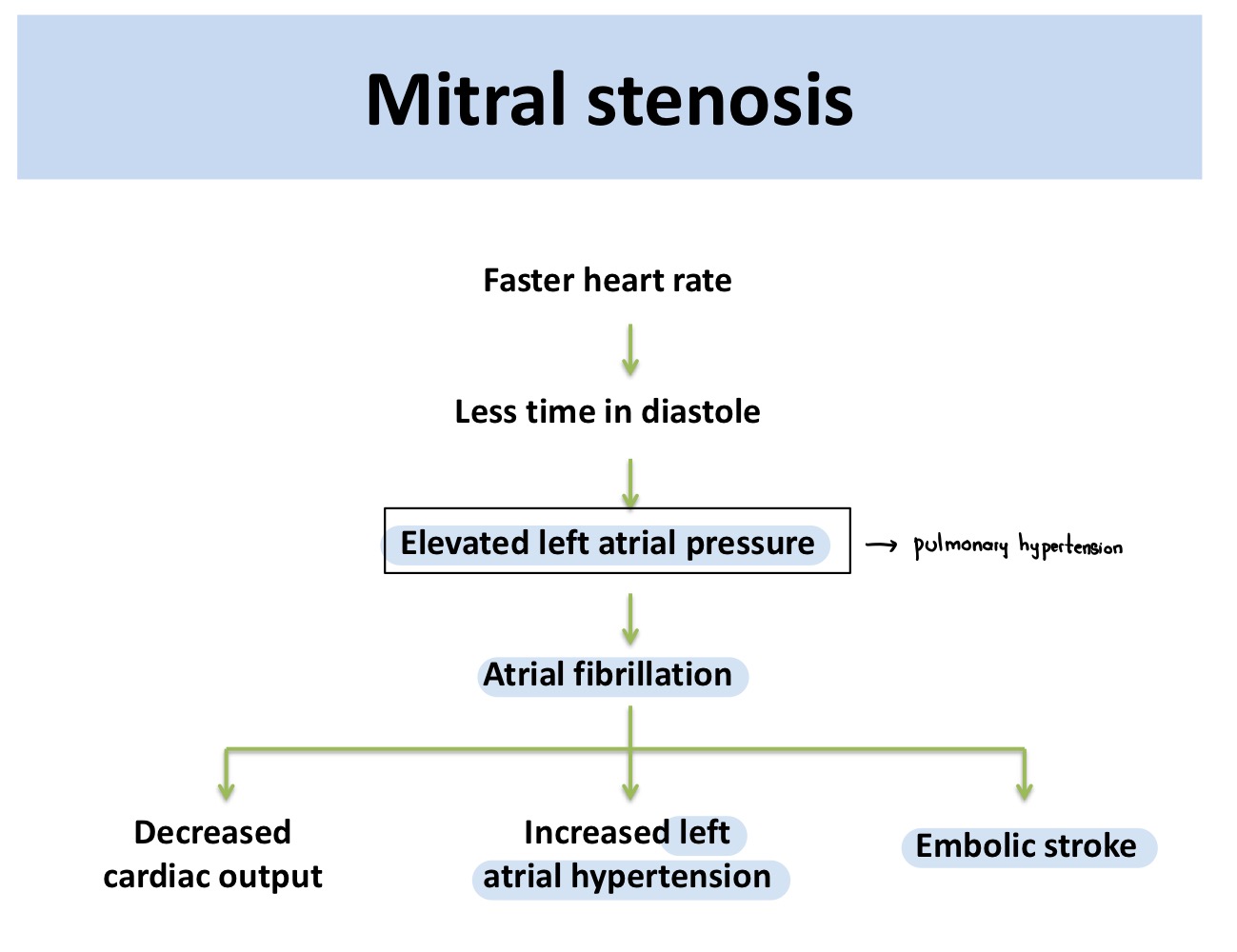
Symptoms of mitral stenosis will start to develop after valve area ___
<2.5 cm2 (normal 4 cm2)
Which valvular defect is associated with Lutembacher’s syndrome?
Congenital ASD + mitral stenosis
Atrial fibrillation results from mitral stenosis by ___
Elevated left atrial pressure
Therapeutic anticoagulants should be used in mitral stenosis in which cases?
Persistent atrial fibrillation
LA thrombus
History of emboli
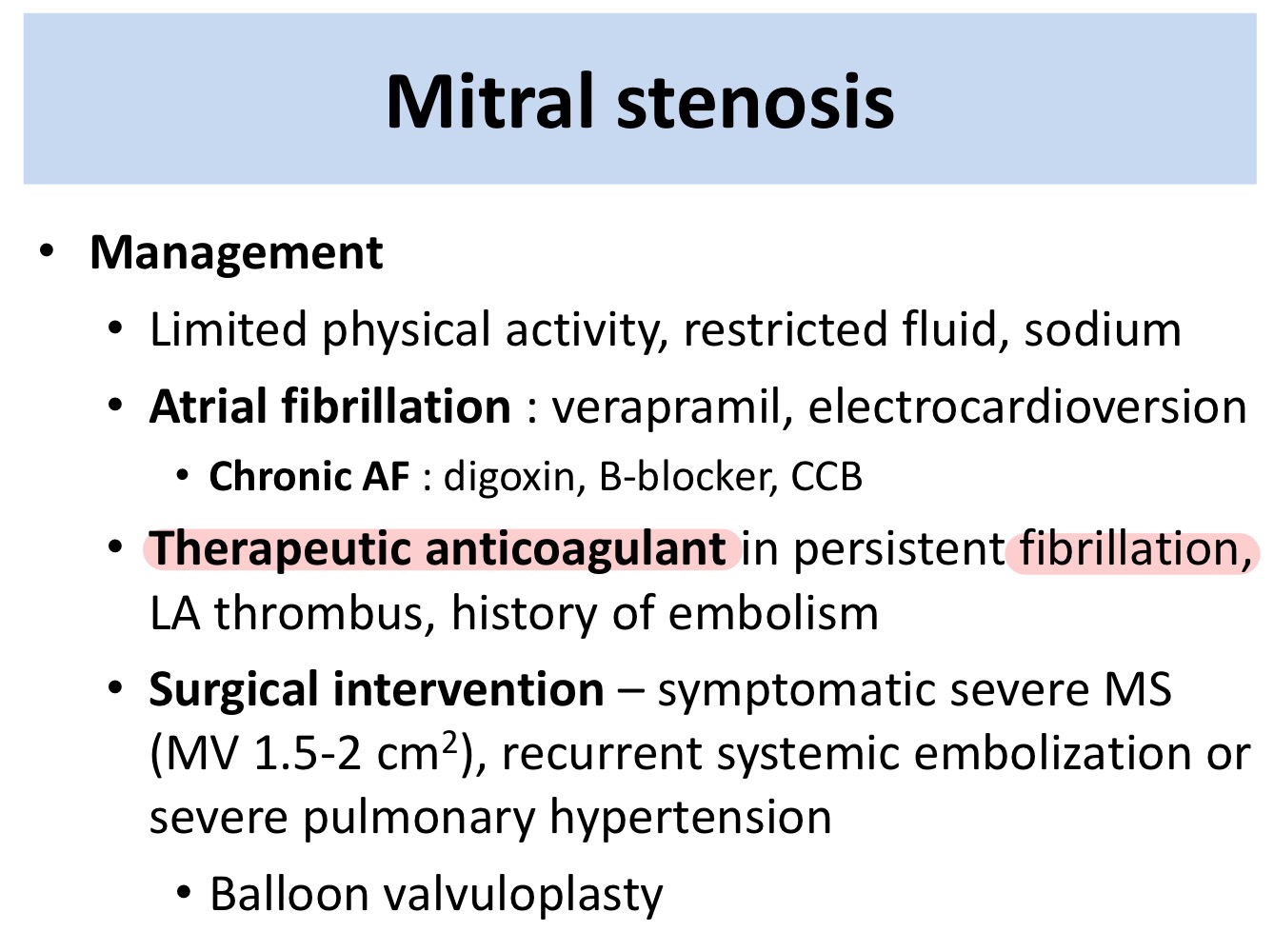
What is the surgery used to treat mitral stenosis?
Balloon vulvuloplasty
Severe mitral stenosis
Severe pulmonary hypertension
Recurrent systemic embolization

What is the indications for balloon vulvuloplasty in mitral stenosis?
Recurrent systemic emboli
Severe mitral stenosis (A <1.5-2 cm2)
Severe pulmonary hypertension
What is the recommended route of delivery in patients with mitral stenosis?
Vaginal delivery + epidural anesthesia
Severe obstruction occurs when aortic valve area ___
<1 cm2 (normal 3-4 cm2)
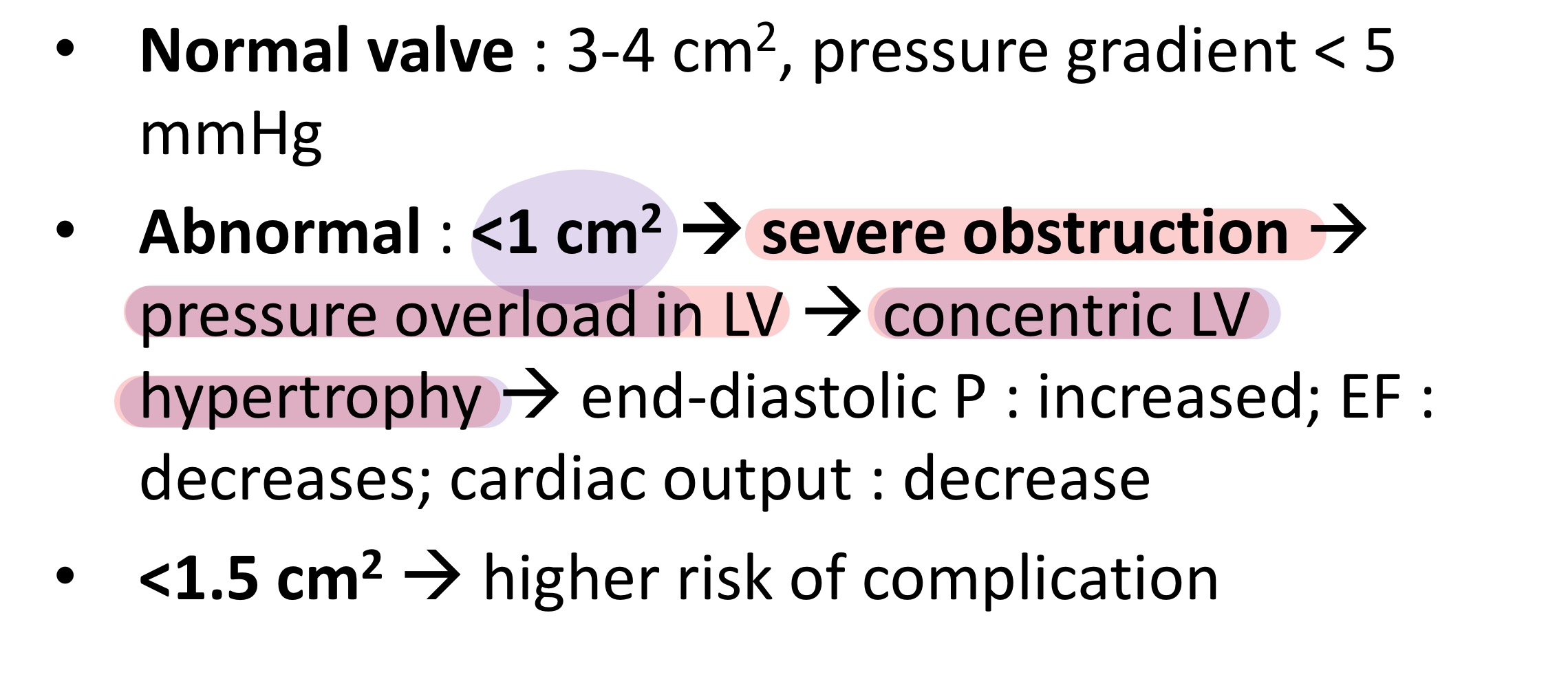
Aortic stenosis causes FGR and stillbirth by ___
Aortic stenosis —> cardiac output ↓ → uterine blood flow ↓
What is the recommended route of delivery in patients with aortic stenosis?
Vaginal delivery + epidural anesthesia + vasodilator
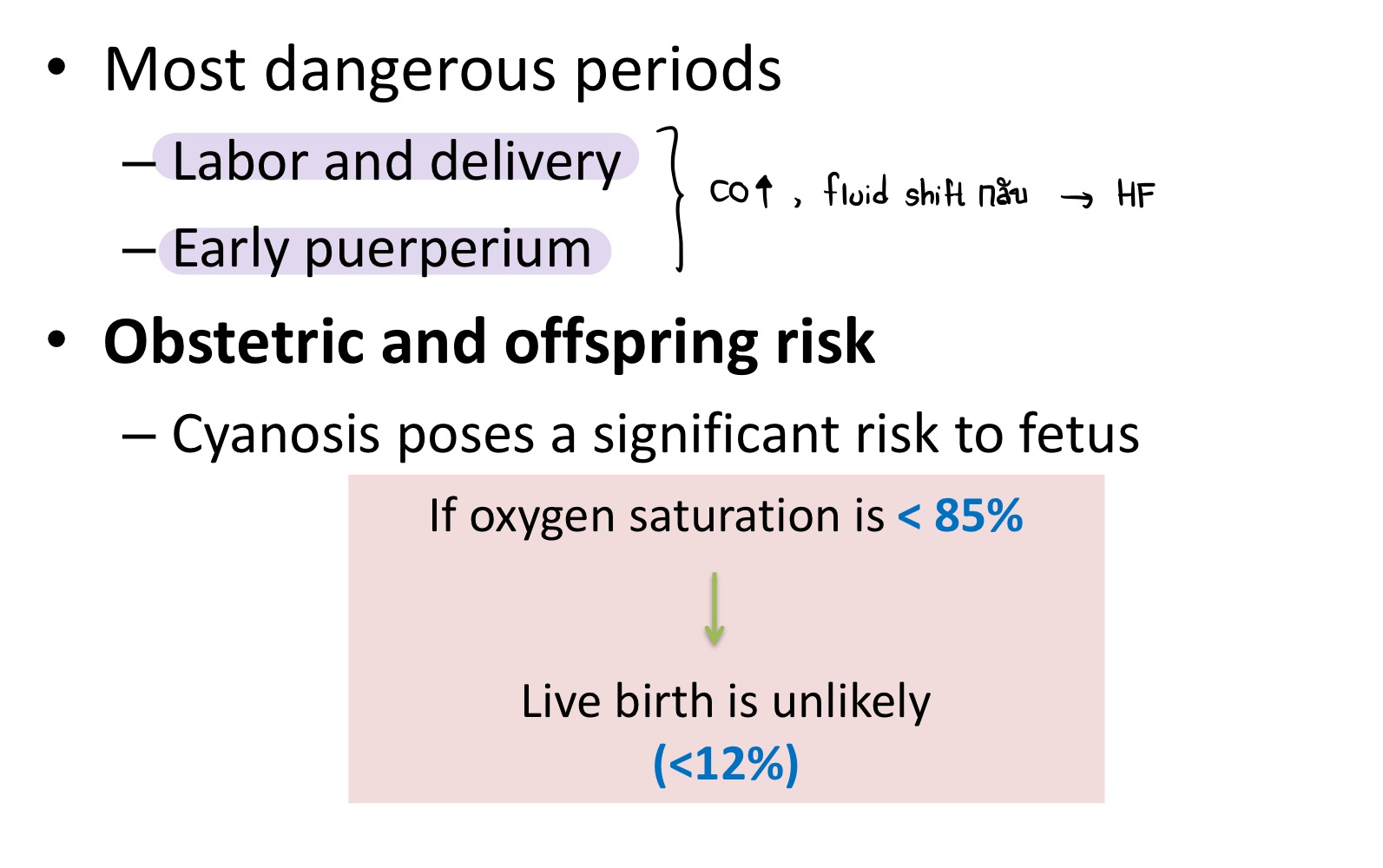
Which valvular disease is an absolute contraindication of pregnancy?
Eisenmenger syndrome
What is the criteria for the diagnosis of peripartum cardiomyopathy?
Heart failure occur last month of pregnancy - 5 months after delivery
Absence of prior heart disease
Absence of identifiable cause
LV systolic dysfunction
Which infection is a risk factor of peripartum cardiomyopathy?
Parvovirus B19, HHV 6, CMV, EBV
What is the antibiotic prophylaxis for infective endocarditis before vaginal & cesarean delivery?
Not recommended prophylaxis
Antibiotic prophylaxis regimen for infective endocarditis
Ampicillin 2 g IV /
Cefazolin 1 g IV /
Ceftriaxone 1 g IV
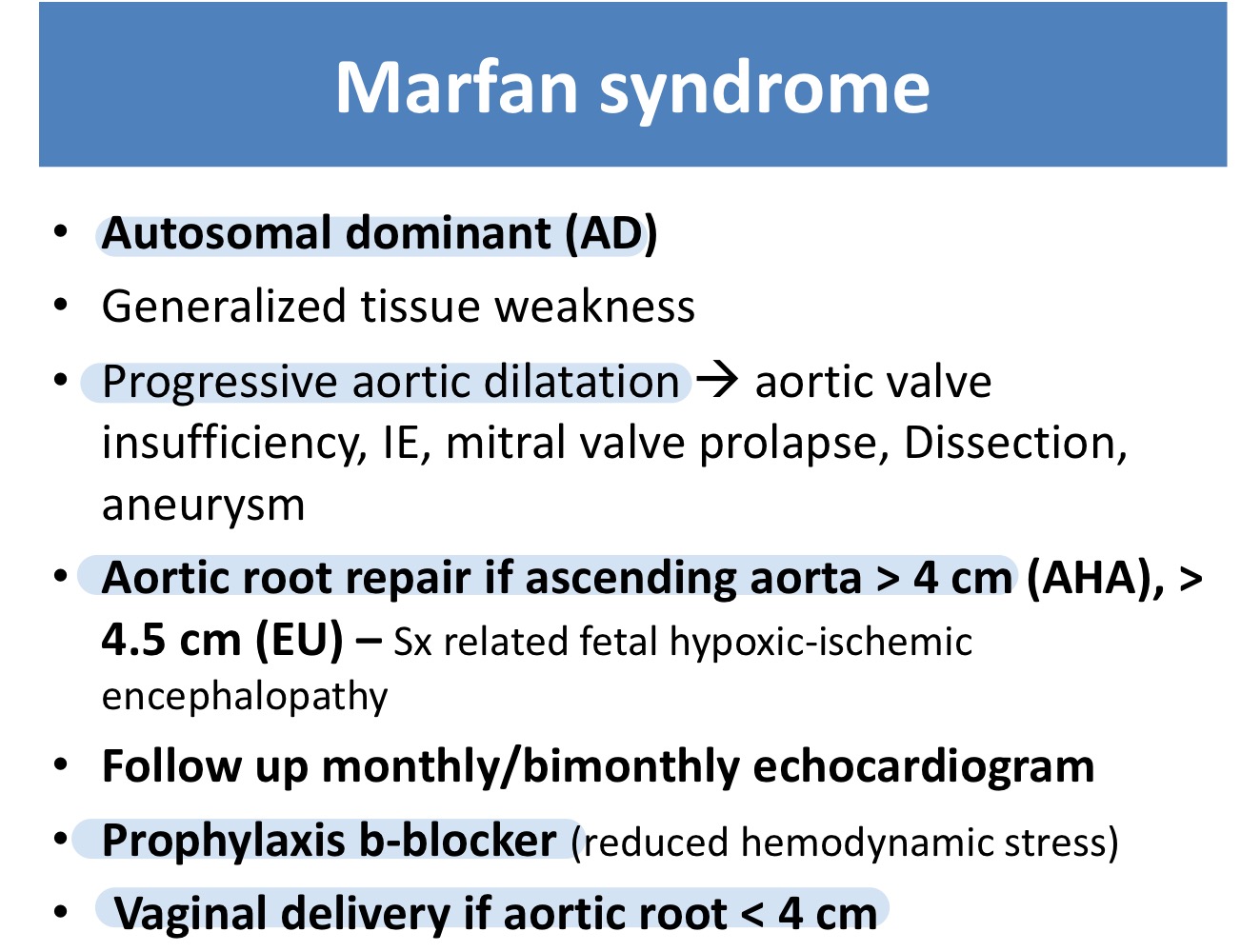
Marfan syndrome is a cause of which valvular disease?
Aortic insufficiency
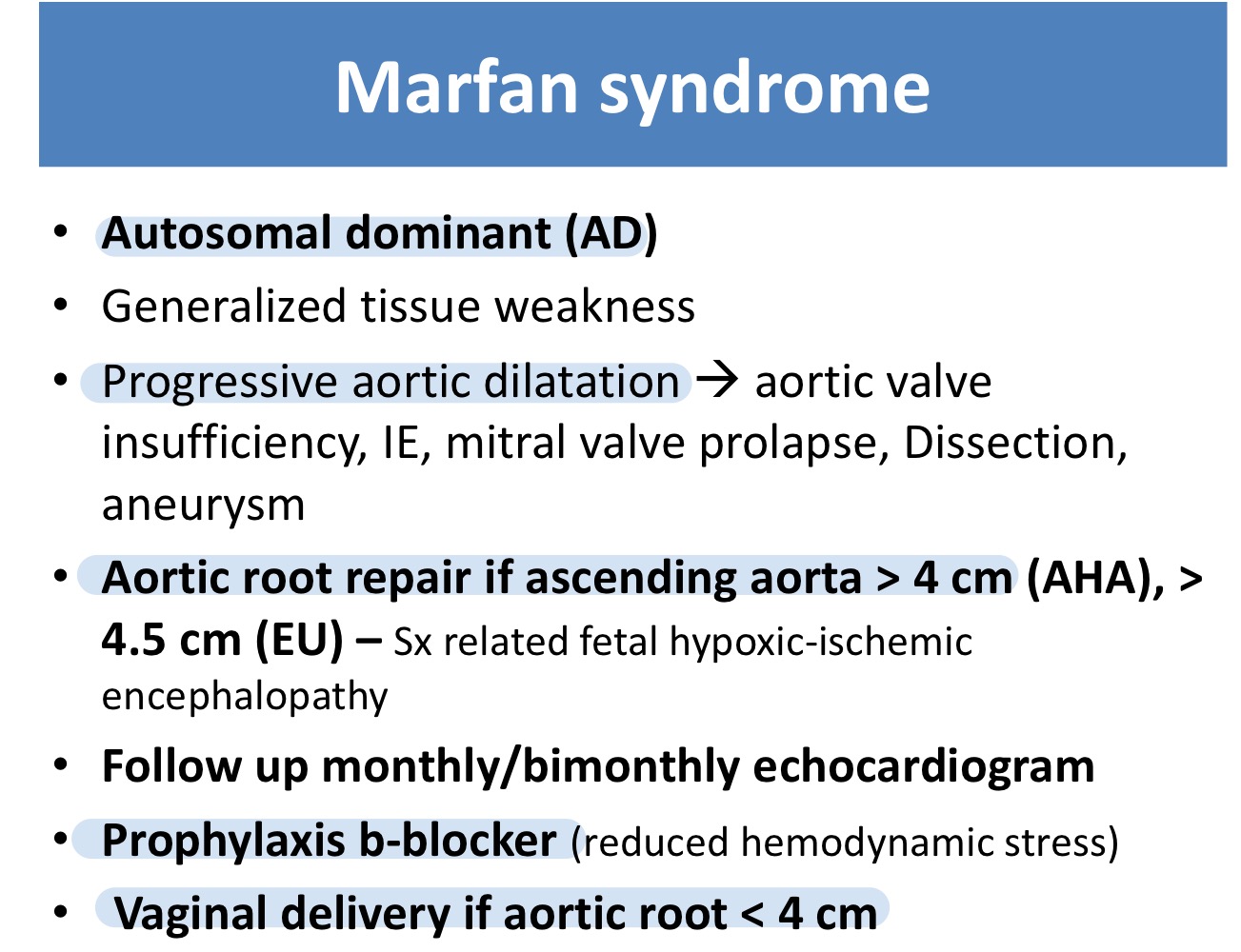
Aortic root repair should be done in Marfan syndrome if size of ascending aorta ___
>4 cm
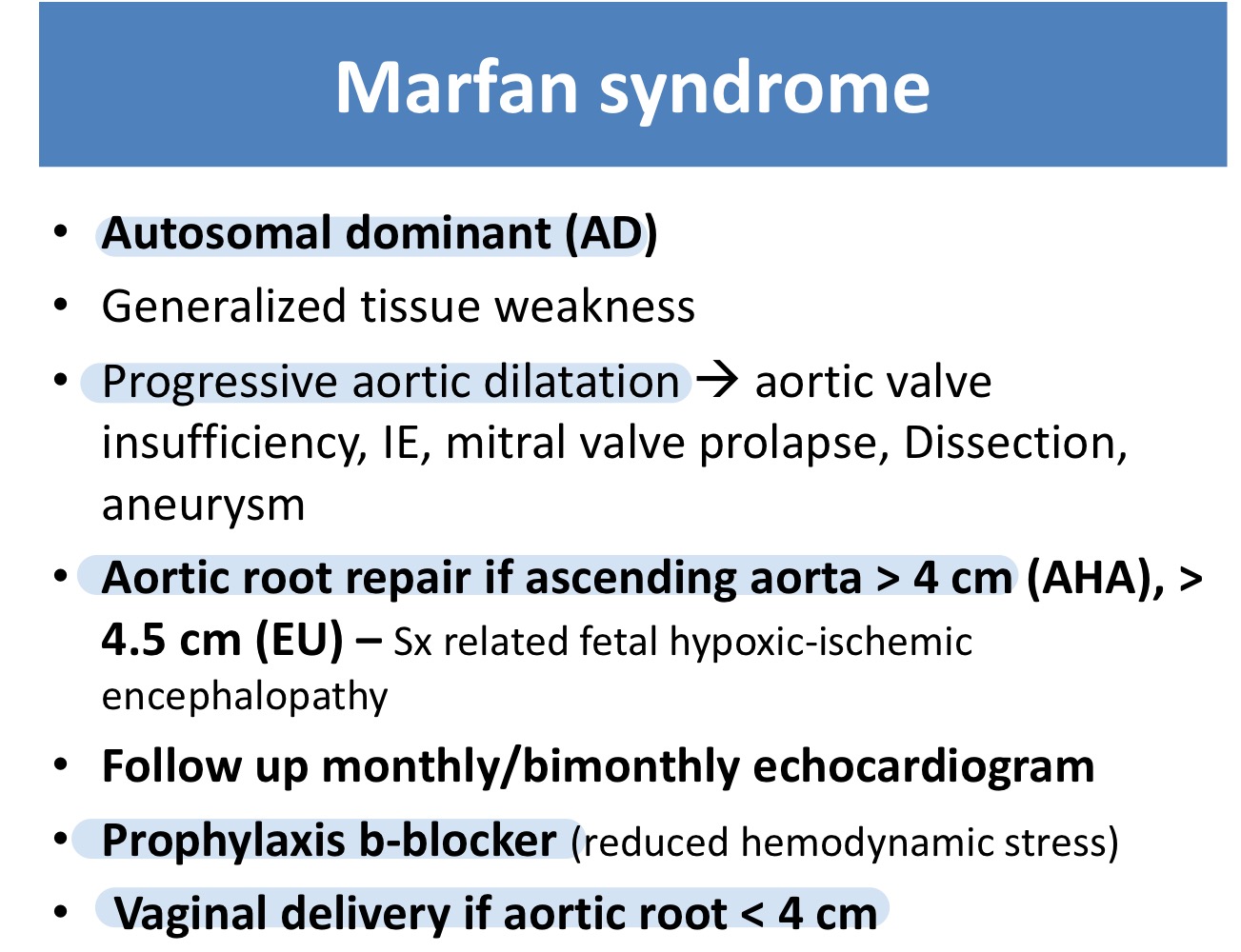
What is the prophylaxis drug for Marfan syndrome?
β-blocker