Biochemistry Two, Deguo Du Final Exam Notes
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all slides for exams 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Virtually all life on earth depends on energy ultimately from:
a. The power company
b. batteries
c. the green-house effect
d. the sun
e. activation energy
d. the sun
Which statement pertaining to the three basic systems is true?
a. open systems exchange matter with other open systems
b. open systems exchange matter with closed systems
c. the internal energy of an open system is always constant
d. a closed system can accept heat from an isolated system
a. open systems exchange matter with other open systems
Internal energy is all except:
a. a function that keeps track of heat transfer and work expenditure in the system
b. path dependent
c. referred to as a state function
d. commonly designated as E or U
b. path dependent
Under constant pressure condition, enthalpy change (deltaH) is:
a. the sum of heat absorbed and work
b. not a thermodynamic state function
c. a measure of disorder in a system
d. equal to the heat transferred (Q)
d. equal to the heat transferred (Q)
Entropy, S, is exactly zero at:
a. 25 Celsius
b. 0 Celsius
c. 25 Kelvin
d. 0 Kelvin
e. 38 Celsius
d. 0 Kelvin
For an irreversible process of the universe (which is also an isolated system), the entropy change (deltaS) is:
a. > 0
b. = 0
c. < 0
d. cannot determine
a. > 0
If the enthalpy change for 2A --> B is deltaH1 and 2A --> 3C is deltaH2, then for the transformation B --> 3C, the enthalpy change is:
a. deltaH1 + deltaH2
b. deltaH1 - deltaH2
c. 2deltaH2 - 3deltaH1
d. deltaH2 - deltaH1
d. deltaH2 - deltaH1
All describe modified standard state for a thermodynamic parameter in biological systems except:
a. designated with a prime ( ' ) symbol
b. H+ ion of 10^-7 M
c. 10^-6 M for matters in solutions
d. 1 atm for gases
c. 10^-6 M for matters in solutions
High energy compounds exhibit large negative free energy of hydrolysis. Which of the following is not a high energy compound?
a. acetyl phosphate
b. Glucose-1-phosphate
c. 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerate
d. phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
e. ATP
b. Glucose-1-phosphate
Which of the following statements about ATP is not true?
a. it is used for storage of the energy in the cell
b. it has two phosphoanhydride bonds
c. ATP is usually complexed with Mg2+
d. ATP is usually a thermodynamically unstable molecule
a. it is used for storage of energy in the cell
The chemical reason for the large negative DeltaG^o' value for ATP hydrolysis is:
a. electrostatic repulsion between negative charges is decreased in products
b. resonance stabilization is increased in products
c. competing resonance is reduced in products
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
Chemoheterotrophs require:
a. organic carbon sources and light
b. carbon dioxide and light
c. organic carbon sources and oxidation-reduction reactions
d. carbon dioxide and inorganic compounds
e. carbon dioxide and oxidation-reduction reactions
c. organic carbon sources and oxidation-reduction reactions
Which of the following is the major advantage of a multi-enzyme complex?
a. it's large size enables it to span an entire membrane
b. the product of one enzyme is passed directly to the next enzyme without the possibility of diffusion
c. multi-enzyme complexes are much less likely to be inhibited
d. none of the above
c. the product of one enzyme is passed directly to the next enzyme without the possibility of diffusion
For the following types of molecules, the one with the least reduced state of carbon is:
a. Aldehyde
b. Hydrocarbon
c. CO2
d. Alcohol
e. carboxylic acid
c. CO2
Many of the catabolic pathways converge to the common intermediate:
a. alanine
b. acetyl-CoA
c. lactic acid
d. glucose
e. carbon dioxide
b. acetyl-CoA
What coenzyme would be required in the following reaction?
a. ADP
b. thiamine pyrophosphate
c. biotin
d. lipoic acid
e. coenzyme A
c. biotin
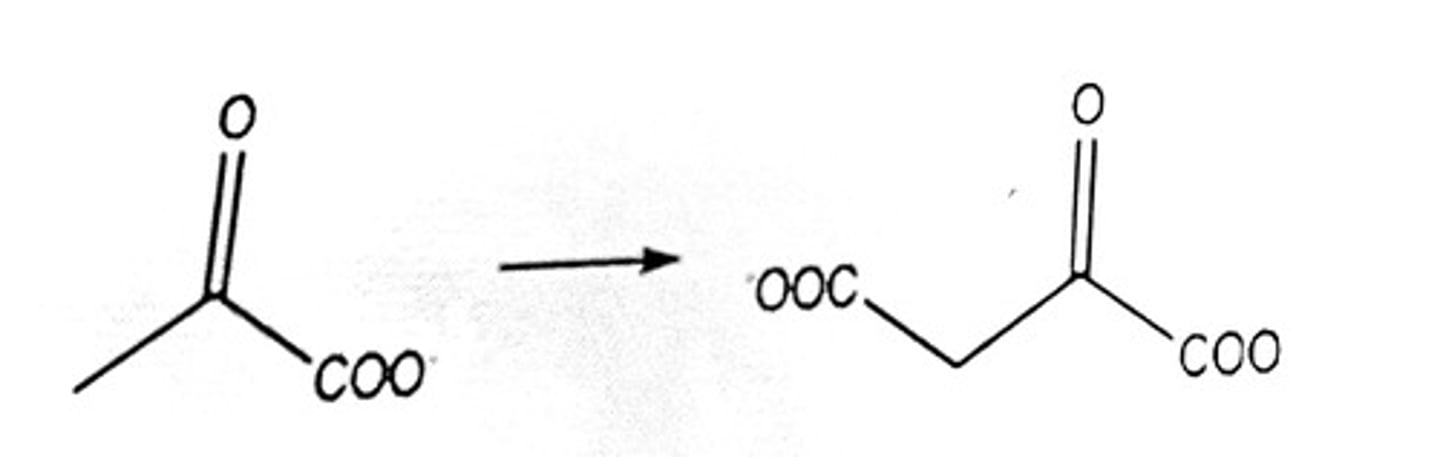
Characteristics of anabolism are:
a. energy yielding
b. energy requiring
c. break covalent bonds
d. form covalent bonds
e. reduction of NAD+
f. oxidation of NADPH
a. a,d,f
b. a,c,e
c. b,d,f
d. b,c,f
c. b,d,f
Which vitamin is essential to vision?
a. A
b. C
c. D2
d. B12
e. B1
a. A
All of the coenzymes listed participate in electron transfer except:
a. FAD
b. biotin
c. NAD+
d. vitamin C
e. FMN
b. biotin
Which vitamin catalyzes a variety of reactions involving amino acids?
a. cyanocobalamin
b. Vitamin C
c. Pyridoxal phosphate
d. folic acid
c. Pyridoxal phosphate
Which of the following is not true regarding flavins?
a. FAD and FMN both contain ribitol and isoalloxazine ring
b. the reduced form is colorless, the oxidized form is yellow
c. flavins can only transfer one electron
d. FAD is not a dinucleotide
c. flavins can only transfer one electron
A possible function of NADPH is to:
a. provide reducing equivalents to synthesize glucose from CO2
b. carry electrons from anabolic reactions
c. provide a source of hydrogens for oxidative biosynthesis
d. be reduced by hydride ions to form NAD+
a. provide reducing equivalents to synthesize glucose from CO2
In eukaryotic cells the glycolysis is carried out in:
a. cell membrane
b. mitochondria
c. cytoplasm
d. cell nucleus
c. cytoplasm
For the first five steps of glycolysis, the appropriate sequence of enzymes is:
A. phosphofructokinase
B. hexokinase/glucokinase
C. fructose bisphosphate aldolase
D. Phosphoglucoisomerase
E. triose phosphate isomerase
a. A, C, B, E, D
b. B, C, D, E, A
c. D, B, C, A, E
d. B, D, A, C, E
e. B, D, E, C, A
d. B, D, A, C, E
In the first steps of glycolysis, glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate. This product:
a. can freely cross the plasma membrane
b. cannot easily cross the plasma membrane because of its larger size
c. cannot easily cross the plasma membrane because of its net charge
d. can only take part in glycolysis metabolic pathway in cells
c. cannot easily cross the plasma membrane because of its net charge
Glucokinase has a Km value of 10.0 mM whereas hexokinase has a Km value of 0.1 mM. This is consistent with which of the following?
a. glucokinase acts on glucose at low concentrations
b. glucokinase acts on glucose only at high glucose concentrations
c. glucokinase phosphorylates most of the glucose at low glucose levels
d. hexokinase acts on glucose only at high levels of glucose
e. hexokinase acts at about half-maximal velocity at glucose concentrations of 4-5 mM
b. glucokinase acts on glucose only at high glucose concentrations
For phosphofructokinase:
a. low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits
b. high ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates
c. high ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits
d. low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates
e. ATP and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate both inhibit the enzyme
d. low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates
The second intermediate of glycolysis with high free energy of hydrolysis more negative than that of ATP is:
a. glucose-6-phosphate
b. PEP
c. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
d. dihydroxyacetone phosphate
e. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
b. PEP
In the second half of the glycolytic pathway, ___ ATP molecules are produced and with the offset of ___ ATPs consumed in the first half, the net yield is ___ ATPs per glucose.
a. four, four, zero
b. four, two, two
c. two, two, four
d. two, one, one
e. four, one, three
b. four, two, two
Pyruvate kinase can be allosterically inhibited by:
a. pyruvate
b. AMP
c. ATP
d. glucose
e. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
c. ATP
NADH, ____ and ____ are products of glycolysis, and the NADH must be recycled to ____ before it becomes limiting in glycolysis.
A. ATP; pyruvate; NAD+
B. NAD+; ATP; pyruvate
C. ATP; NAD+; ATP
D. ATP; pyruvate; lactate
E. None are true
a. ATP; pyruvate; NAD+
Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction forming an ene-diol intermediate?
a. glucokinase
b. aldolase
c. phosphoglycerate mutase
d. phosphoglucoisomerase
e. phosphoglycerate kinase
d. phosphoglucoisomerase
The most common form of hemolytic anemia can be the result of a genetic defect in:
a. hexokinase
b. phosphoglycerate mutase
c. pyruvate kinase
d. phosphoglycerate mutase
e. triose-phosphate isomerase
c. pyruvate kinase
phosphorylation of Fructose-6-P to form fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate:
Fructose-6-P + Pi - fructose-1,6-bisphosphate +H2O deltaG°prime = 16.3 kJ/mol.
In glycolysis, the reaction is coupled with ATP, and the standard free energy of hydrolysis of ATP is -30.5 kJ/mol.
ATP + HO -> ADP + Pi deltaG°prime = -30.5 kJ/mol
Write the coupled reaction of phosphorylation of Fructose-6-P in glycolysis, and calculate the standard free energy and the equilibrium constant (Keq) of the reaction. (all values in the question are obtained at 25°C).
Fructose-6-P + ATP --.. > fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP
deltaG°prime = deltaG°prime (1) + deltaG°prime (2) =- 14.2 kJ/mol
=-RTIn(Keq)
Keq = exp (-deltaG°prime/RT) = 308
Name the enzymes that catalyze reactions where ATP is synthesized.
Phosphoglycerate kinase
Pyruvate kinase
Name the enzymes that catalyze reactions where ATP is consumed.
(Also be able to circle the arrows of steps where NADH is made and put boxes around arrows that are regulated steps.)
Hexokinase
phosphofructokinase
What is the net yield of ATP made anaerobically in the conversion of one glucose to pyruvate? (don't include those generated from NADH). Give a number as your answer.
2 ATP
Suppose you discover a mutant yeast whose glycolysis pathway is shorter because of the presence of a new enzyme that catalyzes the reaction:
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G-3-P) + H2O + NAD+ --> 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG) + NADH + H+
What is the net yield of ATP made anaerobically in the mutant yeast in the conversion of 1 glucose pyruvate by this shorted pathway? (Don't include those generated from NADH) and give a number as your answer.
0 ATP
In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis occurs in the ___ and the TCA cycle reactions take place in ___.
a. mitochondria, mitochondria
b. cytoplasm, mitochondria
c. cytoplasm, cytoplasm
d. mitochondria, ribosomes
e. cytoplasm, ribosomes
b. cytoplasm, mitochondria
In the TCA cycle, carbon enters the cycle as ____ and exits as ____ with metabolic energy captured as ____, ____ and ____.
a. malonate, water, NADH, ATP, NADPH
b. acetyl-CoA, CO2, NADH, ATP, NADPH
c. succinyl-CoA, CO2, ATP, NADH, NADPH
d. acetyl-CoA, CO2, ATP, NADH, FADH2
e. malonyl-CoA, water, NADH, FADH2, ATP
d. acetyl-CoA, CO2, ATP, NADH, FADH2
Place these enzymes in the correct sequence for the TCA cycle:
a. aconitase
b. succinyl-CoA synthetase
c. fumarase
d. alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
a. a, b, c, d
b. b, c, a, d
c. a, d, b, c
d. c, d, b, a
c. a, d, b, c
The number of carbon atoms of acetate lost as CO2 during the first turn of the TCA cycle is/are:
a. 0
b. 0.5
c. 1
d. 2
a. 0
The only reaction of the citric acid cycle that provides substrate level phosphorylation is catalyzed by:
a. malate dehydrogenase
b. citrate synthase
c. isocitrate dehydrogenase
d. succinyl CoA synthetase
d. succinyl CoA synthetase
Which of the following is the correct sequence of processes in the oxidation of glucose?
a. Krebs cycle, glycolysis, electron transport
b. Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport
c. Electron transport, Krebs cycle, glycolysis
d. Krebs cycle, electron transport, glycolysis
b. Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport
The coenzymes listed below are associated with a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex except:
a. FAD
b. TPP
c. lipoic acid
d. NADP+
d. NADP+
Which statement below is not correct regarding regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase:
a. ATP inhibits it
b. NAD+ activates it
c. Acetyl CoA inhibits it
d. Phosphorylation activates it
d. Phosphorylation activates it
The anaplerotic reactions associated with the TCA cycle are a result of the:
a. use of many of the TCA cycle intermediates in biosynthesis
b. oxidative nature of the TCA cycle
c. decarboxylation reactions
d. production of GTP and reduced enzymes
e. irreversible nature of some of the TCA cycle reactions
a. use of many of the TCA cycle intermediates in biosynthesis
Enzymes of the TCA cycle are in the matrix of the mitochondria except one which is located in the inner mitochondria membrane. Name the enzyme.
a. citrate synthase
b. succinate dehydrogenase
c. malate dehydrogenase
d. a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
e. fumarase
b. succinate dehydrogenase
All are true statements for the glyoxylate pathway except:
a. has one CO2 producing reaction
b. consumes two acetyl-CoA molecules per turn
c. has the net production of succinate
d. bypasses the oxidative decarboxylation steps of the TCA cycle
a. has one CO2 producing reaction
All are characteristics of inner mitochondrial membranes except:
a. contains specific transport proteins
b. membrane lipids have mostly unsaturated fatty acids
c. folds into cristae
d. is permeable to most molecules and ions
d. is permeable to most molecules and ions
Reduction involves the ___ of electrons and reactions for which the standard cell potential is ___ are spontaneous under standard conditions.
a. loss, negative
b. loss, positive
c. gain, negative
d. gain, positive
d. gain, positive
What is the standard reduction potential for the reaction of transferring one electron from cytochrome bL (Fe2+) to cytochrome bH (Fe3+)?
cytochrome bL(Fe3+) + e- --> cytochrome bL (Fe2+) delta epsilon = -0.1V
cytochrome bH (Fe3+) + e- --> cytochrome bH(Fe2+) delta epsilon = 0.05V
a. 0.05 V
b. 0.15 V
c. -0.05V
d. -0.15V
b. 0.15V
the final electron acceptor in the elctron transport chain is
a. O2
b. H2O
c. cytochrome C
d. coenzyme Q
a. O2
All of the following are membrane bound except:
a. cytochrome a/a3
b. Fe-S centers
c. cytochrome c
d. cytochrome c1
e. coenzyme Q
c. cytochrome c
The complex in the electron transport chain, which does not have a direct link to ubiquinone in some form is:
a. complex 1
b. complex 2
c. complex 3
d. complex 4
d. complex 4
Which of the following is a two-electron carrier?
a. Copper center in complex IV
b. Fe-S
c. NADH
d. cyt a3
e. cyt c
c. NADH
Where does the energy that drives ATP synthesis in mitochondria come from?
a. the proton gradient
b. high energy molecule
c. the electron gradient
d. the oxidation states of the complexes
e. molecular oxygen
a. the proton gradient
All are characteristics of Boyer's binding change mechanism except:
a. There are three active subunits in ATP synthase to catalyze ATP synthesis
b. Each active site contains three different conformations
c. The reactants and intermediates pass through the three subunits sequentially to finally make one ATP
d. one conformation state of the active site can allow release of the newly synthesized ATP
c. the reactants and intermediates pass through the three subunits sequentially to finally make one ATP
Which of the following is not a feature of oxidative phosphorylation?
a. direct transfer of phosphate from a substrate molecule to ADP
b. An electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
c. a membrane bound ATP synthase
d. a protonmotive force
a. direct transfer of phosphate from a substrate molecule to ADP
All are properties of uncouplers except:
a. they dissipate the proton gradient
b. their function will lead to the increase of ATP/ADP ratio
c. they are hydrophobic molecules
d. heat is produced during the function of uncouplers
b. their function will lead to the increase of ATP/ADP ratio
Chloroplasts consist of a folded inner membrane called the ___, which is organized into paired folds called ___.
a. thylakoid membrane, stroma
b. lamellae, thylakoid membrame
c. thylakoid membrane, lamellae
d. stroma, thylakoid membrane
e. lamellae, stroma
c. thylakoid membrane, lamellae
Properties of photosystem II include all except:
a. conducts light-driven O2 evolution
b. absorbs mainly at 680 nm
c. passes electrons directly to NADP+
d. does not directly pump protons crossing the membrane
c. passes electrons directly to NADP+
Via PSI and PSII, electrons ultimately flow from ___ to ___
a. NADPH, O2
b. NADP+, water
c. water, NADP+
d. O2, NADPH
c. water, NADP+
Which of the following does not happen in cyclic phosphorylation?
a. ATP is produced
b. photosystem I reaction center is active
c. electron transport occurs in the photosynthetic membranes
d. light energy is utilized
e. NADPH is formed
e. NADPH is formed
___ protons are absorbed to drive the evolution of 1 O2 in eukaryotic photosynthesis.
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
e. 8
e. 8
The structure of chlorophyll is:
a. two fatty acid chains and a glycerol backbone
b. one fatty acid chain and a glycerol backbone
c. a benzene ring structure and a long hydrocarbon chain
d. a porphyrin ring and a long hydrocarbon chain
d. a porphyrin ring and a long hydrocarbon chain
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules?
a. split water and release oxygen to the reaction center chlorophyll
b. harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction center chlorophyll
c. synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi
d. transfer electrons to ferredoxin and then NADPH
e. concentrate photons within the stroma
b. harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction center chlorophyll
In the electron transport chain of photosynthesis, the electron carrier molecule plastocyanin (PC) has a very similar function as the ___ molecule in oxidative phosphorylation.
a. ubiquinone
b. rieske protein
c. cytochrome c
d. cytochrome a3
e. cytochrome c1
c. cytochrome c
All are correct statements about reactions of the Calvin cycle except:
a. ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP
b. NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
c. an intermediate is 3-phosphoglycerate
d. some of the enzymes are shared by glycolysis
b. NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
The appropriate sequence of events for activation of rubisco is:
A. carbamylation of E
B. ribulose-1,5 bisphosphate released from E
C. rubisco activase
D. Mg2+ binding
E. light flash
a. C, E, D, A, B
b. C, D, A, B, E
c. B, C, D, A, E
d. E, B, C, D, A
e. E, C, B, A, D
e. E, C, B, A, D
The C4 pathway is used to
a. deliver oxygen to cells
b. carry CO2 to bundle sheath cells
c. increase photorespiration
d. none of the above
b. carry CO2 to bundle sheath cells
Consider a complete oxidative degradation of one acetyl-CoA molecule in mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. How many CO2 will be released and how many ATP/GTPs will be made? (Show steps for ATP/GTP)
2 Co2 released
1 ATP/GTP, 3 NADH (3 x 2.5 = 7.5)
1 FADH2 (1.5)
total: 10
The figure (photo of light absorption) shows absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a. Based on the figure and general knowledge, explain why leaves of many plants are green.
Chlorophyll absorbs certain wavelengths of light within the visible light spectrum. As shown, chlorophyll absorbs light in every region except green, which is reflected, making the plant appear green.
Cytochrome c protein, which contains a large central heme group, is oxidized and reduced during electron transport. Chlorophyll, with a structure reminiscent of heme, is a crucial light absorber and can also be oxidized and reduced during photosynthesis. Explain and compare the chemical mechanisms of these two molecules for transferring electrons.
In cytochrome c, the iron at the center of the heme group is responsible for electron transfer in the oxidation reduction reaction (Fe3+ + e- = Fe2+)
Chlorophyll has a porphyrin like heme but with Mg instead. The Mg++ does not change the oxidation state during excitation. Electrons are promoted from pi to pi* orbitals in the conjugated aromatic part of the molecule after absorbing one proton, donating one electron to another acceptor. It then receives one electron (e.g. from H2O) and returns to the ground state.
The primary energy storage form of lipid is ___ and it is normally stored in the ___.
a. sphingolipid, liver
b. cholesterol, muscles
c. monoacylglycerol, adipocytes
d. triacylglycerols, adipocytes
d. triacylglycerols, adipocytes
___ carries long chain fatty acyl groups across the ___ membrane.
a. biotin, intestinal
b. carnitine, plasma
c. CoA-SH, plasma
d. Carnitine, inner mitochondrial
e. TPP, outer mitochondrial
d. Carnitine, inner mitochondrial
The first oxidation in the B-oxidation of saturated fatty acids is catalyzed by __ and is the conversion of ___.
a. B-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a primary alcohol to an aldehyde
b. acyl CoA dehydrogenase, a carbon-carbon single bond to a carbon-carbon double bond
c. acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, a secondary alcohol to a ketone
d. B-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid
e. acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, an aldehyde to a ketone
b. acyl CoA dehydrogenase, a carbon-carbon single bond to a carbon-carbon double bond
The first three reactions in the B-oxidation of saturated fatty acids produce:
a. 2 moles of NADH
b. 2 moles of FADH2
c. 2 moles of ATP
d. 1 mole of both NADH and FADH2
d. 1 mole of both NADH and FADH2
For the complete oxidation of a saturated fatty acid with 16 carbons, how many times must the B-oxidation cycle be repeated?
a. 4
b. 6
c. 7
d. 8
e. 16
c. 7
Which statement is incorrect concerning the activation of a fatty acid (attachment of a fatty acid to CoA)?
a. It involves formation of a high energy thioester bond
b. activation is accompanied also by the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi
c. An acyl-adenylate intermediate is formed
d. Hydrolysis of ATP produces AMP and PPi with the further hydrolysis of PPi to drive this reaction to completion
b. Activation is accompanied also by the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi
To oxidize for the fatty acid molecule shown, what enzymes are needed in addition to the enzymes needed for B-oxidation?
CH3-(CH2)3-CH=CH-(CH2)3-C (db O)- Onegative
a. 2, 4 dienoyl-CoA reductase only
b. enoyl-CoA isomerase only
c. both enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4 dienoyl CoA reductase
d. no additional enzymes are needed besides the normal ones for B-oxidation
b. enoyl-CoA isomerase only
Propionyl CoA is a product of B oxidation of __ and is ultimately converted to the TCA cycle intermediate, ___.
a. odd-chain fatty acids, pyruvate
b. even-chain fatty acids, isocitrate
c. odd-chain fatty acids, succinyl CoA
d. even-chain fatty acids, succinate
c. odd-chain fatty acids, succinyl CoA
Which of the following correctly describes the sequence of events for the conversion of a fatty acid to Co2?
a. carnitine shuttle, activation to acyl CoA, B-oxidation, TCA cycle
b. activation to acyl CoA, B oxidation, carnitine shuttle, TCA cycle
c. activation to acyl CoA, carnitine shuttle, B oxidation, TCA cycle
d. TCA cycle, activation to acyl CoA, B-oxidation, carnitine shuttle
c. activation to acyl CoA, carnitine shuttle, B oxidation, TCA cycle
What are the three most common ketone bodies?
a. acetone, butyrate, and acetyl CoA
b. acetoacetate, hydroxyacetone phosphate, and butyrate
c. acetone, B hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate
d. acetoacetate, acetyl CoA, and acetone
c. acetone, B hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate
Which of the following about peroxisomal B-oxidation is not correct?
a. electrons go to O2 directly to produce H2O2
b. Yields same amount of Acetyl CoA compared with mitochondria B-oxidation
c. Yields more ATP compared with mitochondria B-oxidation
d. The first step is catalyzed by Acyl-CoA oxidase
c. Yields more ATP compared with mitochondria B-oxidation
Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of:
a. glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors
b. glycogen from glucose
c. pyruvate from glucose
d. fatty acids from glucose
e. glucose from fatty acids
a. glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors
The major tissues carrying out gluconeogenesis are the ___ and ___.
a. brain, muscles
b. muscles, kidneys
c. liver, kidneys
d. liver, Red blood cells
e. red blood cells, brain
c. liver, kidneys
All are substrates for gluconeogenesis except:
a. glycerol
b. lactate
c. serine
d. pyruvate
e. all of the above can be substrates of gluconeogenesis
e. all of the above can be substrates of gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is not simply reversal of glycolysis since two pyruvate to glucose requires ___ of combined ATP and GTP.
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 5
e. 6
e. 6
All of the enzymes of gluconeogenesis may be found in cytosol except ___ which is only found in mitochondria:
a. PEP carboxykinase
b. pyruvate carboxylase
c. fructose-1,6,-bisphosphate
d. glucose-6-phosphate
b. pyruvate carboxylase
Which molecule below can inhibit the fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase?
a. AMP
b. acetyl CoA
c. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
d. citrate
a. AMP
The endoplasmic reticulum bound enzyme that hydrolyzes glucose-6-phosphate to glucose in liver is:
a. glucose oxidase
b. hexokinase
c. phosphoglucomutase
d. glucose-6-phosphatase
d. glucose-6-phosphatase
Limit dextrins are degraded by the action of ___.
a. a amylase
b. B amylase
c. debranching enzyme
d. gluconolactonase
c. debranching enzyme
Glycogen synthase is inhibited by:
a. ATP
b. glucose-6-phosphate
c. caffeine
d. phosphorylation
d. phosphorylation
Insulin in the bloodstream is a response to increased blood glucose and:
a. stimulates gluconeogenesis
b. inhibits glycolysis
c. stimulates glycogen synthesis in muscle and liver
d. stimulates glycogen breakdown in liver
c. stimulates glycogen synthesis in muscle and liver
Which of the following is not the product of the pentose phosphate pathway?
a. compound with 4 carbon
b. compound with 3 carbon
c. compound with 5 carbon
d. compound with 7 carbon
e. compound with 8 carbon
e. compound with 8 carbon
How many NADPH can be made via degradation of one glucose molecule via pentose phosphate pathway?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 4
e. 5
c. 2
Fatty acid synthase differs from B-oxidation in all of the following ways except:
a. occurs in cytosol
b. uses NADPH for reductive reactions
c. has acyl carrier protein linked intermediates
d. all of the above are true
d. all of the above are true
Which of the following cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane?
a. citrate
b. acetyl CoA
c. Malate
d. Pyruvate
b. acetyl CoA
The main sources of NADPH for fatty biosynthesis are:
a. TCA cycle
b. oxidative phosphorylation
c. malic enzyme and the pentose phosphate pathway
d. the conversion of OAA to malate by malate dehydrogenase
e. glycolysis
c. malic enzyme and the pentose phosphate pathway