Mechanical Ventilation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what is a benefit of using heating high flow nasal cannula (HHFNC)?
no mask; therefore, the patient is more comfortable & able to speak & eat
when is HHFNC indicated?
- pneumonia
- hypoxemia
- NC > 10 lpm
- peds (bronchectasis)
what is the flow rate w/ HHFNC?
up to 40 lpm
- allowing for flush of deadspace gas = decreased WOB & RR
w/ HHFNC, O2 can be titrated between _______.
21-100%
w/ HHFNC, gas can be heat to 37*, what does this allow for?
improved secretion clearance
when is BiPAP indicated?
for hypercapnic & hypoxic respiratory failure
BiPAP ___________ the patient's spontaneous breathing
augments
what are the initial settings for BiPAP?
- IPAP: 15 cm H2O
- EPAP: 5 cm H20
- Rate: 12 bpm
- O2: 100% & titrate
does BiPAP control the patient's breathing like mechanical ventilation does?
NO, it is AUGMENTING what the patient is doing on their own
what is ▵P?
breath size/volume
increasing rate on BiPAP over ___ can cause asynchrony
20
should you use restraints on someone who is on BiPAP?
NO; CONTRAINDICATED!
CPAP alone may __________ WOB, but changing to BiPAP will give an inspiratory boost & may decrease WOB
increase
when is CPAP indicated?
- OSA
- pulmonary edema
- lung recruitment w/o hypercapnia
- if pt forgot theirs at home
oxygenation & ventilation issues usually go hand in hand when on BiPAP - due to what?
interface leaks & medication limitations
troubleshooting the patient on BiPAP:
- increase O2%
- change ▵P
- adjust rate
- titrate settings
- change mask
- assess for leaks
- assess pt triggers
- pain/sedation titration
- improve pt comfort
- change in medical or mental status
- time for mechanical ventilation?
should NIV (CPAP or BiPAP) be used in extreme hypoxemia?
NO
1 multiple choice option
should HHFNC be used for post-op patients?
NO
1 multiple choice option
consider these things in your decision to choose NIV or HHFNC:
- level of consciousness (GCS score)
- able to protect airway?
- acidotic?
- extreme hypoxia or hypercapnia?
- intubation may be the best option!
what should be monitored in a patient on mechanical ventilation?
- O2
- are they breathing? (assisted or controlled breath?)
- secretions (amount, color, consistency)
- PIP (trend this value, peak vs plateau)
what is the 1st parameter that you should increase when a patient is sick/respiratory status declines or decrease when they improve?
O2
what is positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)?
applied at end of expiration (air trapping on purpose)
- improves oxygenation & ventilation
how does PEEP improve oxygenation (PaO2) & ventilation (PaCO2)?
by opening & recruiting collapsed alveoli
PEEP also improves PaO2 by ___________ O2 into the blood
"pushing"
side effects of PEEP:
- decreased systemic blood pressure, CO, or venous return to the heart
- barotrauma (injury due to excessive pressure)
- increased ICP
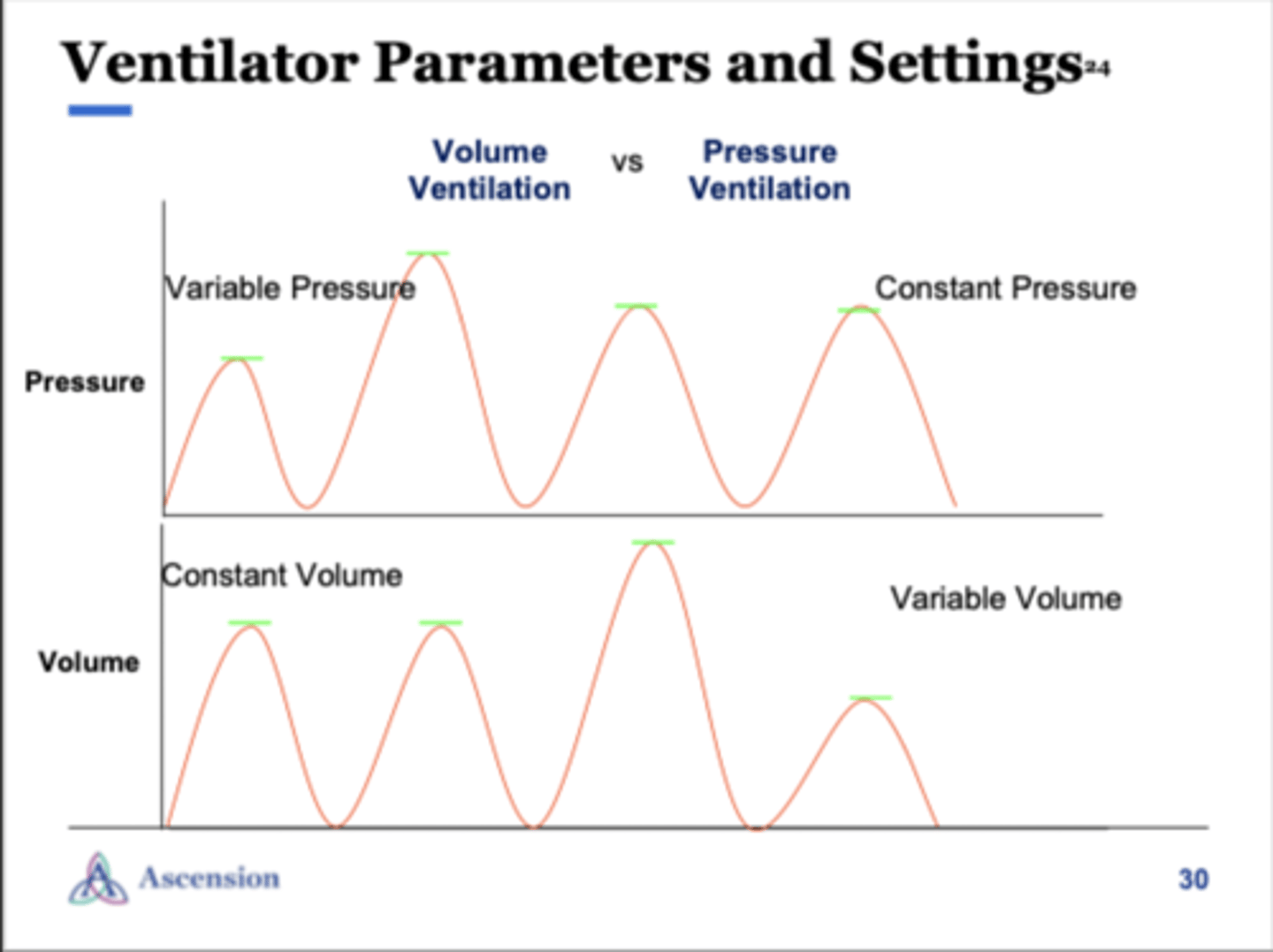
ventilator parameters & settings
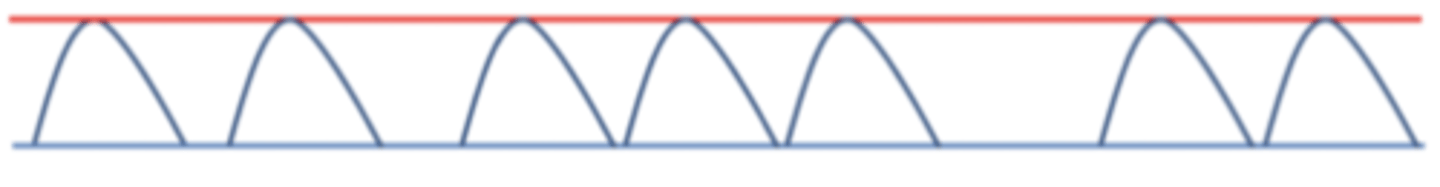
A/C VC+ =
assist control & volume control + flow
ventilator settings:
A/C VC+
A/C PC
spont/PS
what does assist control (A/C) mean?
- every breath given to the patient is the "right" breath
- there is a set target inspiratory volume which supports spontaneous breaths by the patient
- set vent rate is a minimum RR for patient
- each breath guaranteed at a set target volume
improved synchrony between ventilator & patient =
decreased sedation = less time on vent = less time in ICU
what does volume control (VC+) mean?
preset tidal volume is delivered at a set rate
- guaranteed volume in the presence of changing lung compliance
- variable flow to meet pt's inspiratory flow demands
A/C PC =
assist control & pressure control
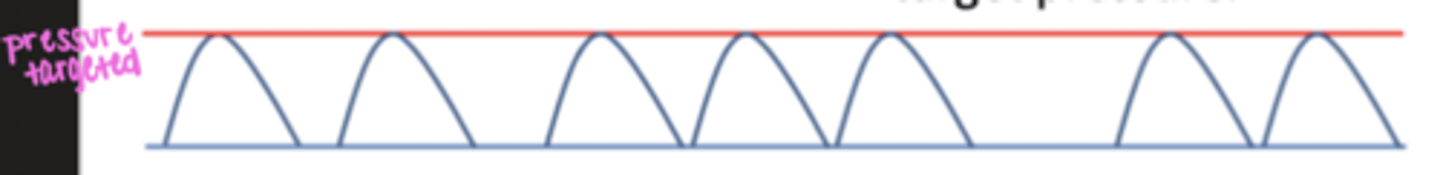
what does pressure control (PC) mean?
ventilator delivers a breath to a set pressure & rate
- variable volumes & flow to meet pt's inspiratory demands
- inspiratory time is set/constant
spont/PS =
spontaneous mode w/ pressure support
what does spontaneous mode (spont) mean?
- ventilator set to rate of 0
- pressure support used to augment tidal volume (Vt/volume w/ each breath)
- PATIENT MUST HAVE A STABLE RESPIRATORY DRIVE
- ventilation will kick in during periods of apnea as a safety net
what does pressure support (PS) mean?
supports & augments patient's inspiratory effort
- pt controls RR, flow, volume & inspiratory time (IT)