Pathophysiology of Sleep Disorders: Neurotransmitters and Brain Regions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the role of caffeine in relation to adenosine?
Caffeine acts as an antagonist of adenosine.
What neurotransmitter is primarily involved in the inhibitory signaling of the brain?
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter.
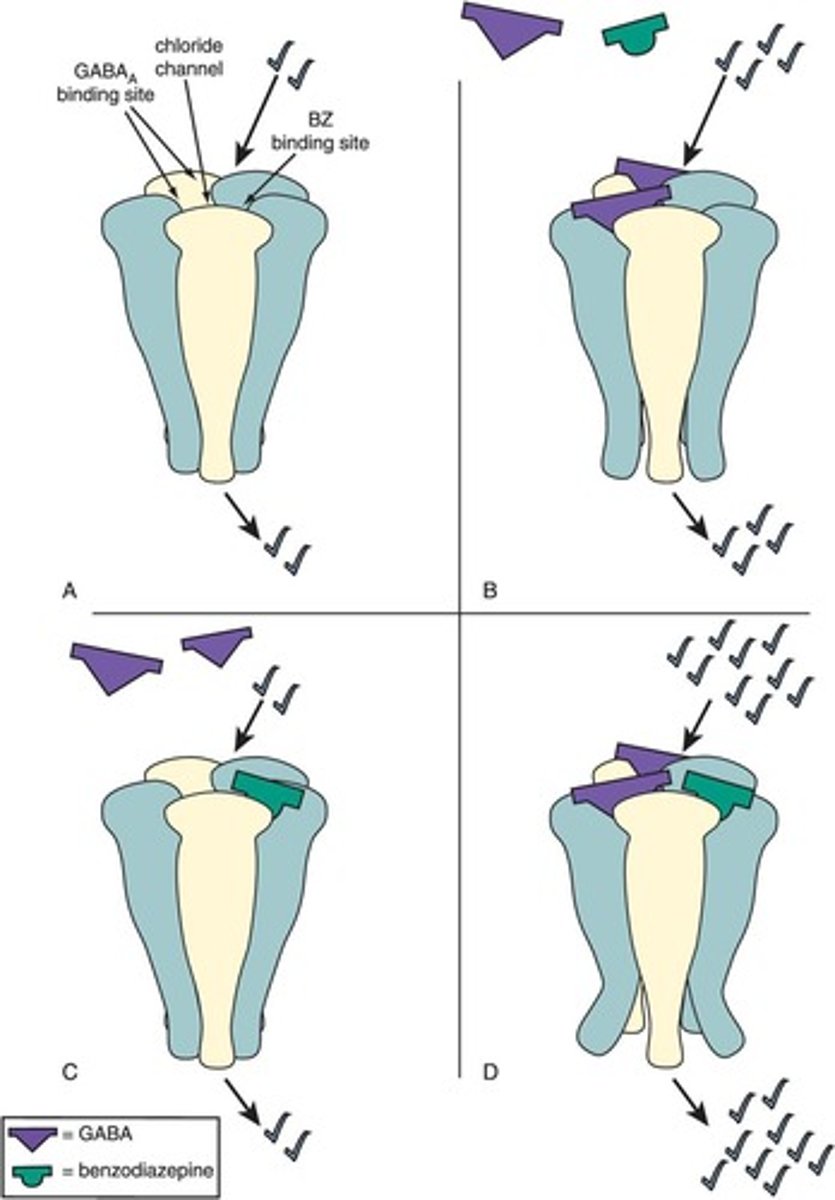
What happens when GABA and benzodiazepines (BZs) bind to their receptors?
The combination leads to more Cl- influx than either GABA or BZ alone, enhancing inhibitory effects.
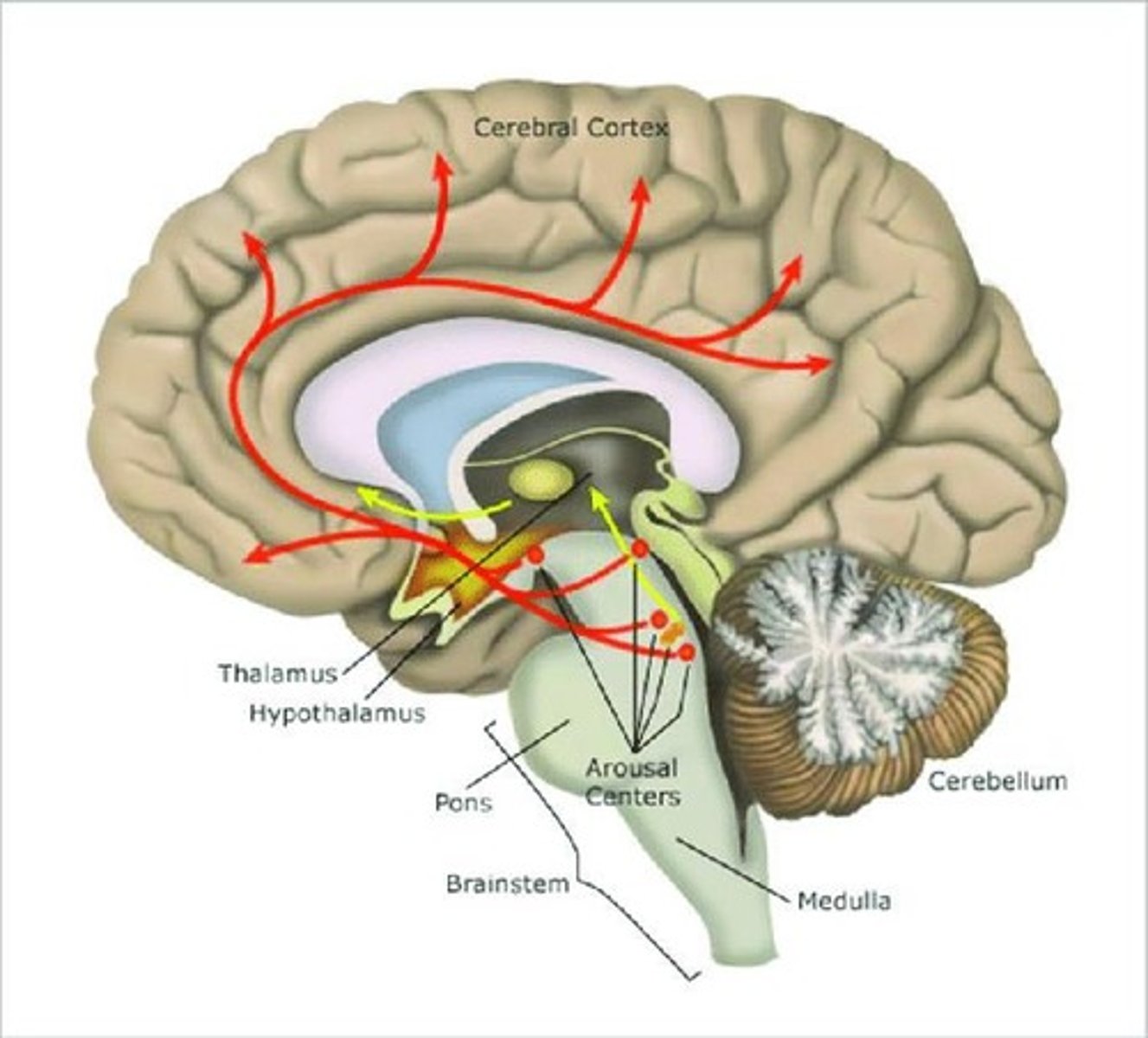
What is the significance of the arousal spectrum in sleep disorders?
Cognitive dysfunction can arise from both too little and too much arousal, affecting cortical neuron activity.
What neurotransmitters are involved in the arousal spectrum?
Five neurotransmitters, including histamine, orexin, and acetylcholine, are involved.
What is the function of orexin in the brain?
Orexin is a neuropeptide that promotes wakefulness.
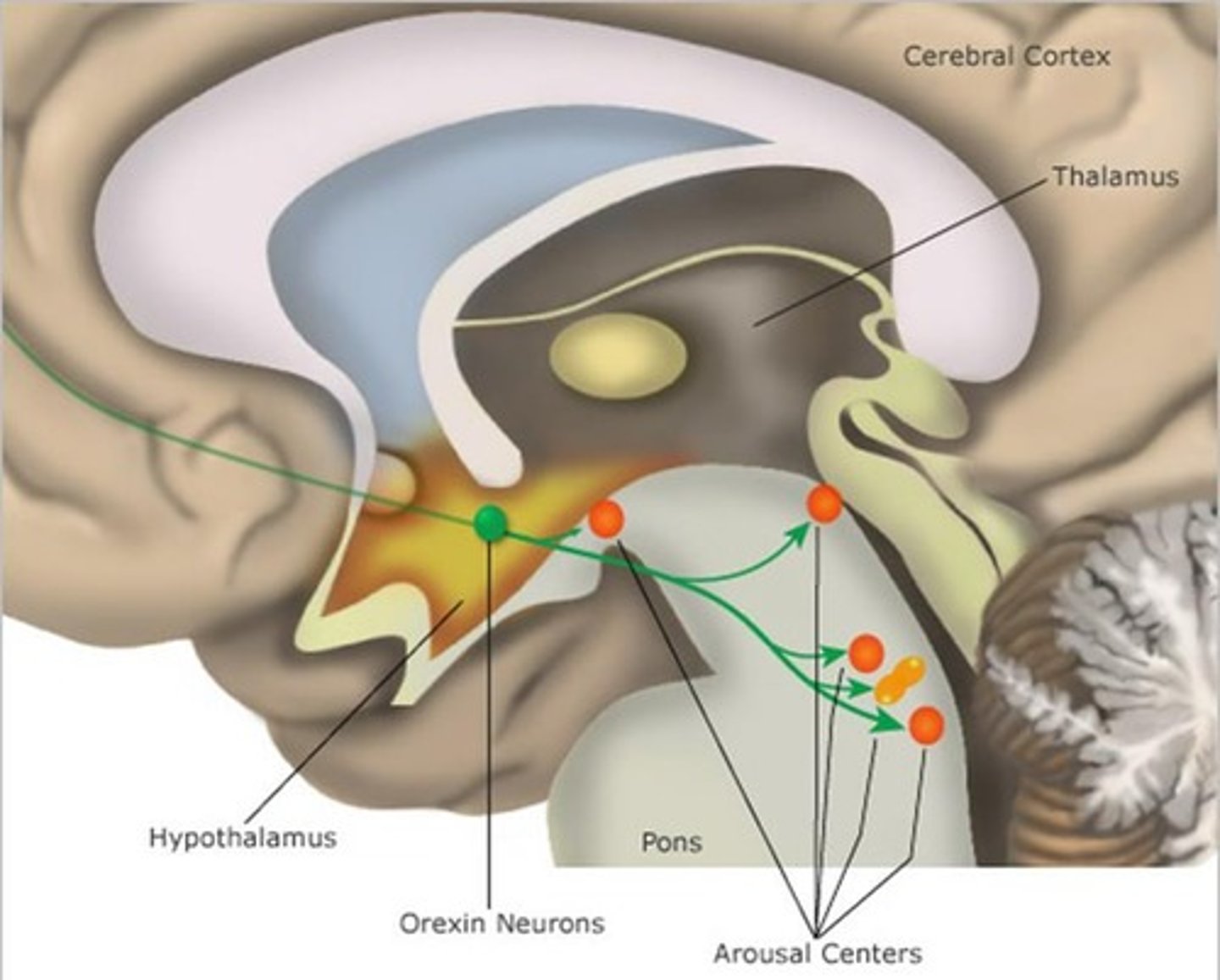
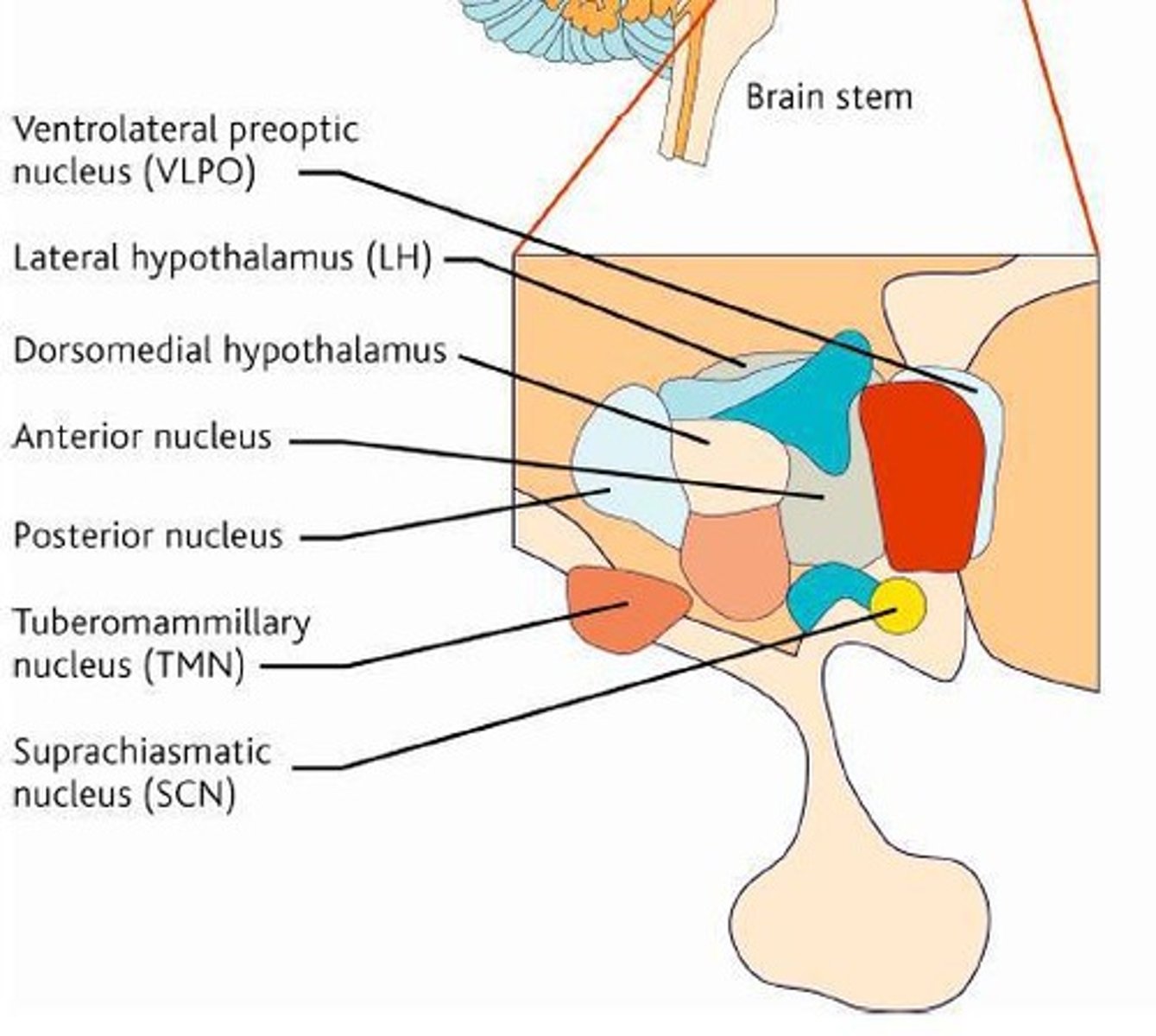
How does the hypothalamus affect sleep/wake regulation?
The hypothalamus contains nuclei that regulate sleep/wake states, including the release of melatonin.
What is the effect of antihistamines like diphenhydramine on sleep?
Antihistamines inhibit histamine release, which can promote sleep.
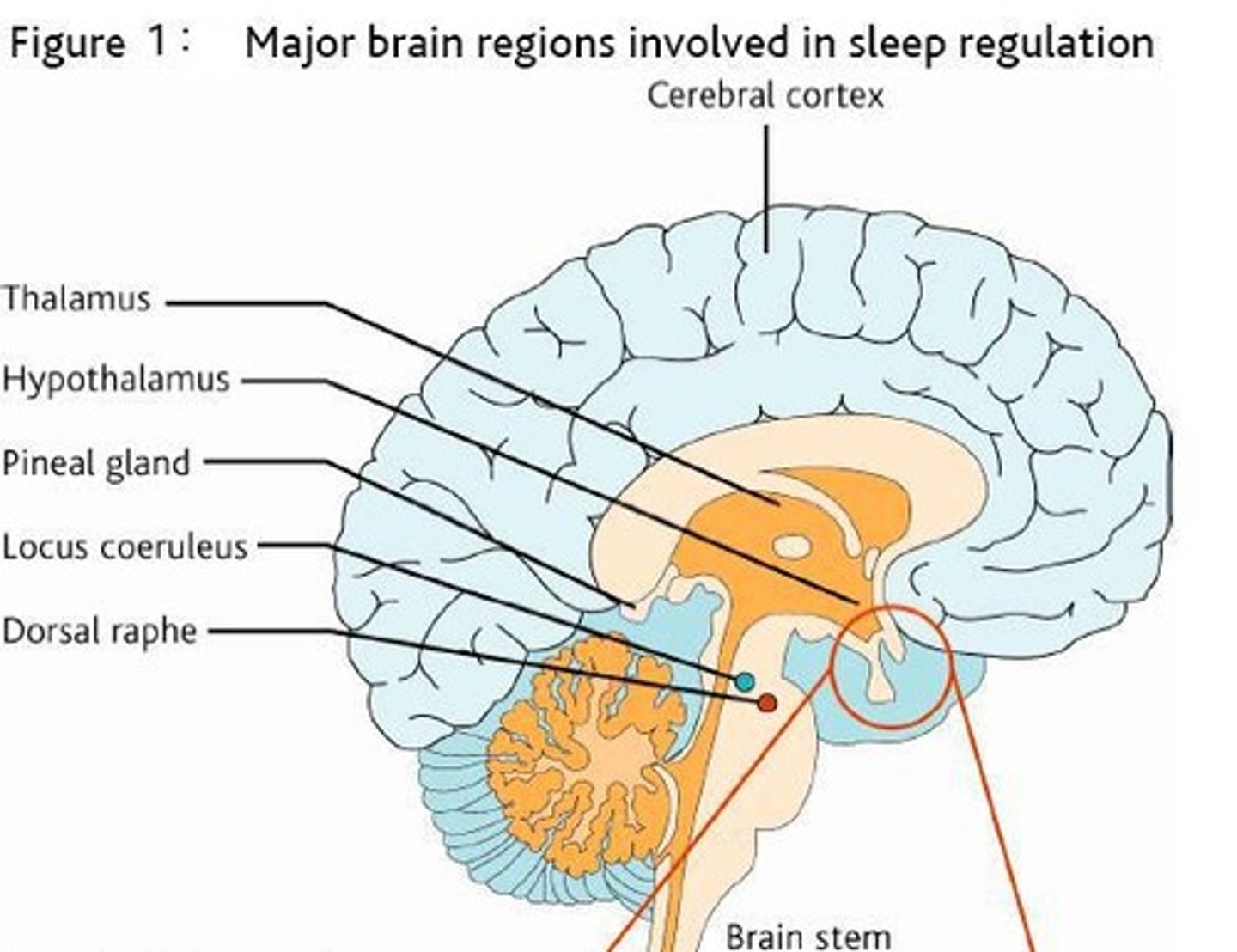
What is the role of the reticular activating system (RAS) in sleep?
The RAS is involved in regulating arousal and wakefulness.
What occurs when GABA is released in the context of sleep?
GABA release inhibits wake-promoting neurons, facilitating sleep.
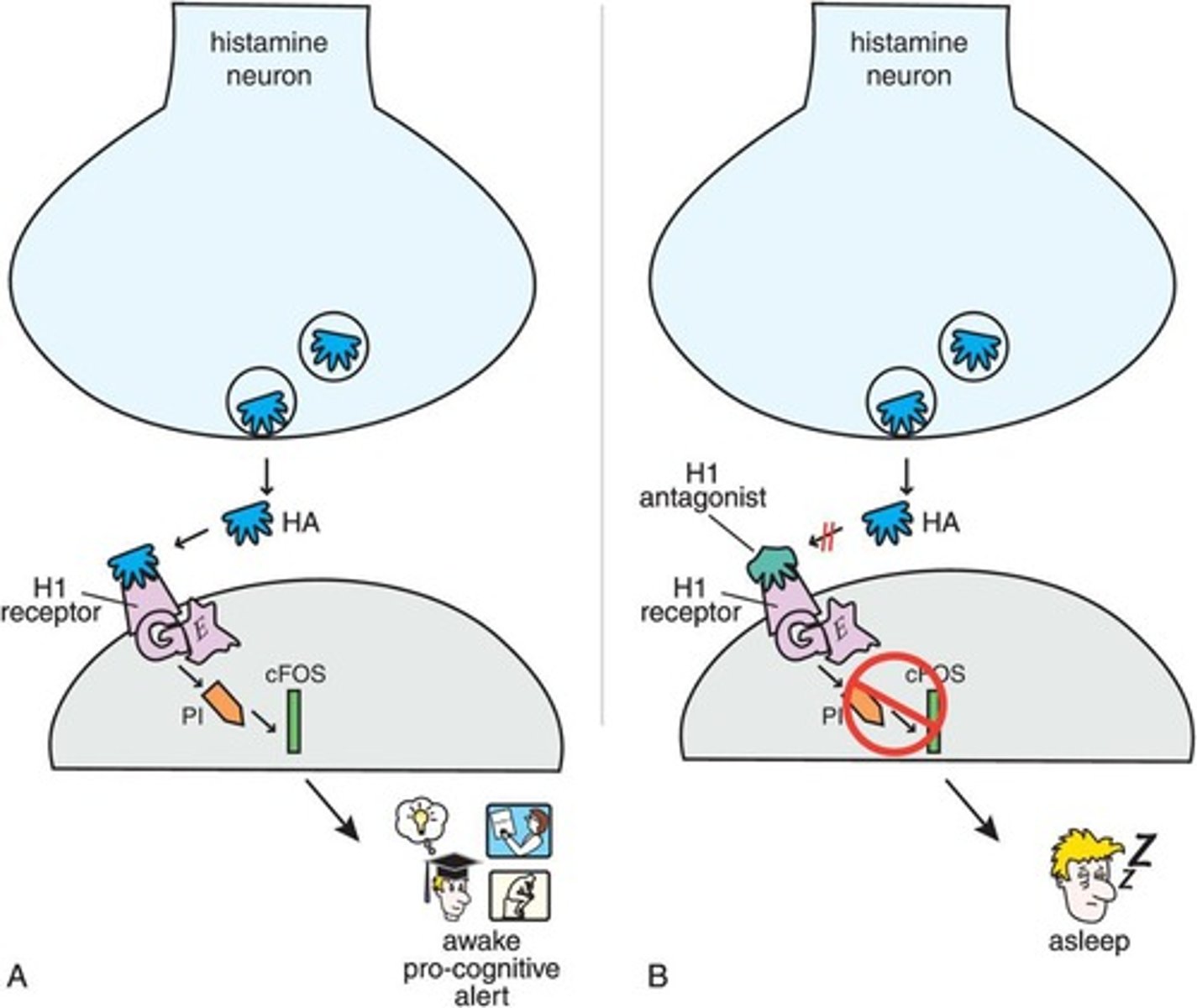
What is the relationship between histamine and sleep?
Histamine promotes wakefulness, and its inhibition can facilitate sleep.
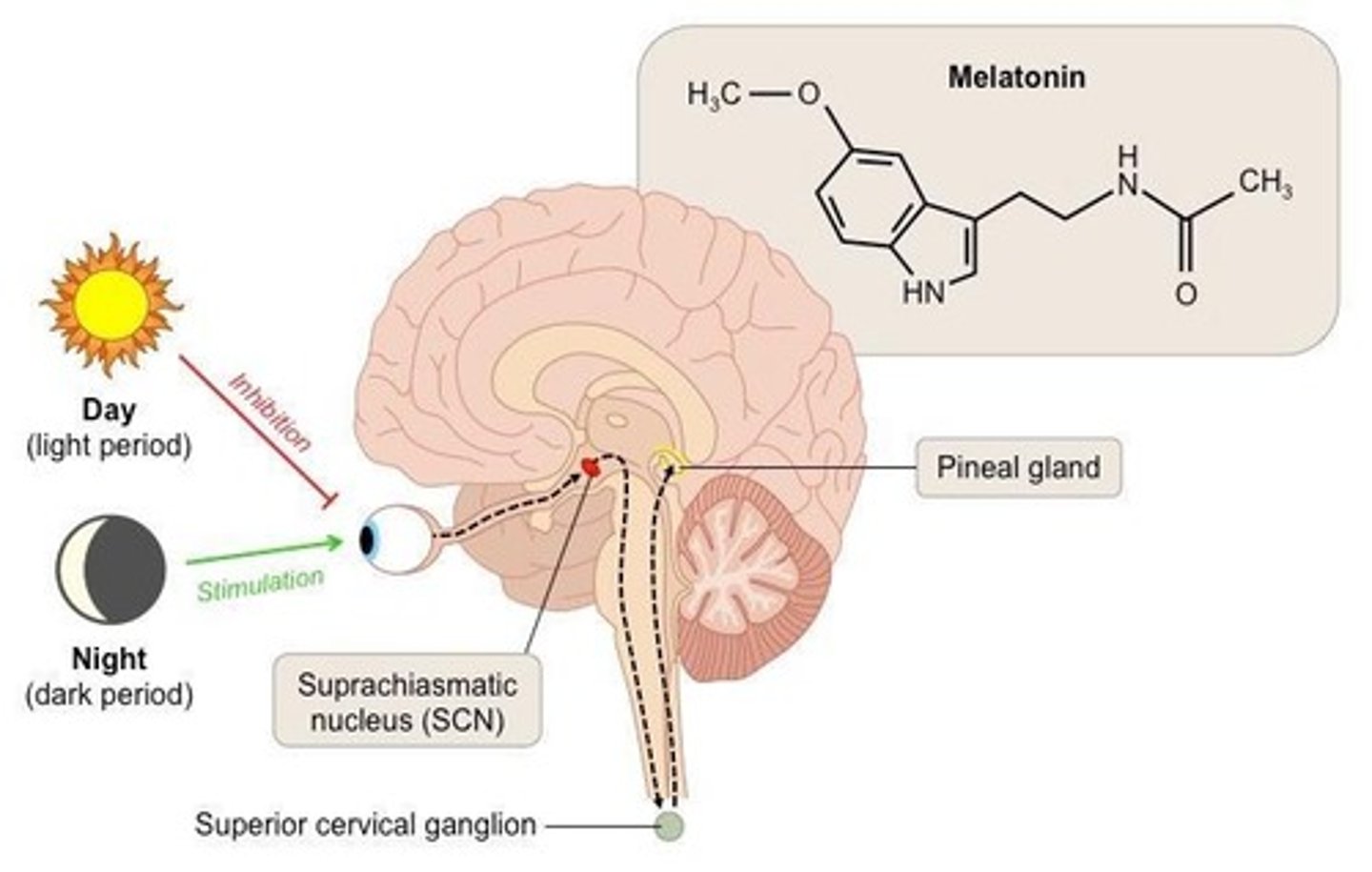
What is the impact of melatonin on sleep?
Melatonin release promotes sleep and is regulated by the hypothalamus.
What is the pathophysiology of narcolepsy related to orexin?
Narcolepsy is characterized by decreased orexin neurons in the hypothalamus, which promotes wakefulness.
What does the term 'positive allosteric modulators' (PAMs) refer to in sleep pharmacology?
PAMs, such as BZs and Z drugs, enhance the effect of GABA at its receptors.
What is the effect of too much neuronal activity on cortical neurons?
Excessive activity can make cortical neurons out of tune, similar to having too little activity.
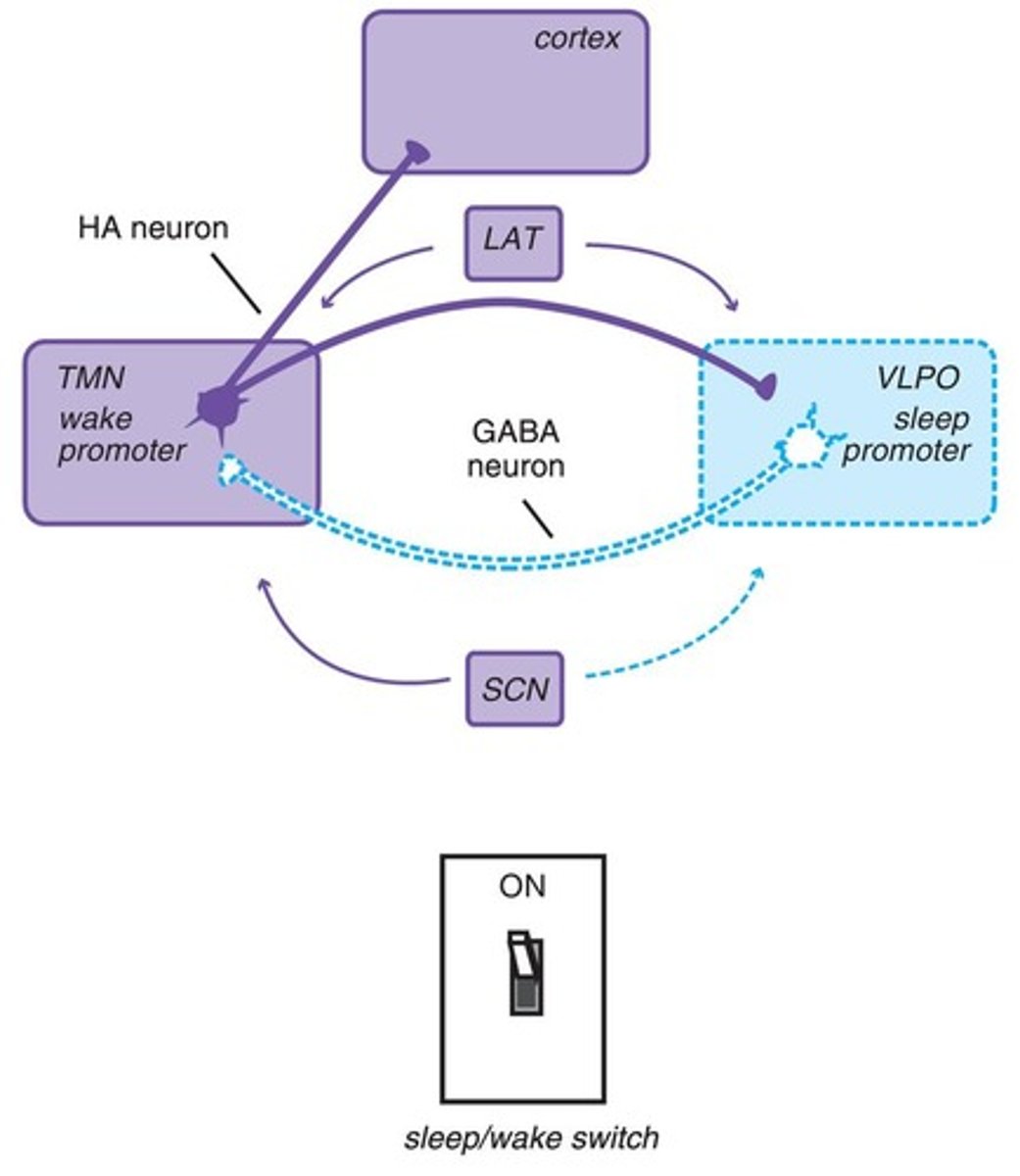
What is the function of the sleep/wake switch in the brain?
The sleep/wake switch regulates the transition between sleep and wakefulness.