Chapter 13
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
**__**__**___ _____**__ have a physical presence; they can be seen and touched.
Tangible assets
2
New cards
\
______ _______ are rights or privileges. They cannot be seen or touched.
______ _______ are rights or privileges. They cannot be seen or touched.
Intangible assets
3
New cards
\: Sometimes called plant assets or fixed assets. We depreciate these assets over their useful life.
Property, Plant, and Equipment
4
New cards
\: Land is considered a component of Property, Plant, and Equipment. It has an infinite life, and as such, land is not subject to depreciation.
Land
5
New cards
\: Mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, timber stands, coal mines, and stone quarries are some examples of natural resources. We deplete these assets over their useful life.
Natural Resources
6
New cards
\: patents and copyrights. Amortize the cost of each over its useful life.
Intangible Assets with Identifiable Useful Lives
7
New cards
\: renewable franchises, trademarks, and goodwill. The cost of these assets is not expensed unless it can be shown that there has been an impairment in value.
**Intangible Assets with** ***Indefinite*** **Useful Lives**
8
New cards
Buildings
* Purchase price
* Sales taxes
* Title search and transfer document costs
* Realtor’s and attorney’s fees
* Remodeling costs
* Sales taxes
* Title search and transfer document costs
* Realtor’s and attorney’s fees
* Remodeling costs
9
New cards
**Equipment**
* Purchase price (less discounts)
* Sales taxes
* Delivery costs
* Installation costs
* Costs to adapt for intended use
* Sales taxes
* Delivery costs
* Installation costs
* Costs to adapt for intended use
10
New cards
Land
* Purchase price
* Sales taxes
* Title search and transfer document costs
* Realtor’s and attorney’s fees
* Costs of removal of old buildings
* Grading costs
* Sales taxes
* Title search and transfer document costs
* Realtor’s and attorney’s fees
* Costs of removal of old buildings
* Grading costs
11
New cards
The life cycle of operational assets has four phases in a continuous loop that are used to account for and define the operational asset throughout its lifetime. These functions, in order, are:
1. Acquiring funding
2. Buying the asset
3. Using the asset
4. Retiring the asset
12
New cards
Depreciation refers to the **_____** __of the cost of a fixed asset (PP&E) to__ ____**_** over the years the organization expects to use it ***(expense deferral)***
Allocation; Expense
13
New cards
***______*** is a generic term referring to the spreading out of a cost over a period of time
Ammortization
14
New cards
The __**____ _____**__ of accounting requires that firms use depreciation and amortization
matching principal
15
New cards
As a long-term asset is **__**__, we allocate a portion of the original cost as an__ ____**_** in each year
Used; expense
16
New cards
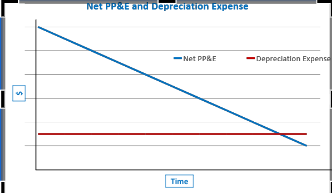
This graph demonstrates what happens under the __**________**__ method
Straight-line
17
New cards
Assets are depreciated based on their **_____**
cost
18
New cards
*Asset valuation for depreciation:*
*Includes costs incurred to put the asset* ***____ ___***
*Includes costs incurred to put the asset* ***____ ___***
into use
19
New cards
*Ordinary repairs and maintenance are* ***________***
Expensed
20
New cards
*Extraordinary repairs, replacements, additions, and improvements are* ***________***
capitalized
21
New cards
*Expensed means the costs are charged to the __*__*__ _____*__ *in the period they are incurred*
income statement
22
New cards
Capitalized means they are added to the value of the asst and depreciated over the asset’s __*____ ____*__
remaining life
23
New cards
*Depreciable Base*
*This is the full amount that will be depreciated* ***_***__*___ ___ ___*__*of the asset*
Cost - Salvage Value
*This is the full amount that will be depreciated* ***_***__*___ ___ ___*__*of the asset*
Cost - Salvage Value
over the life
24
New cards
*Accumulated Depreciation*
*The total amount of depreciation taken on an asset* __***__ __***__
*Shown on the balance sheet, reduces* ***_*__*__ ____*__**
*The total amount of depreciation taken on an asset* __***__ __***__
*Shown on the balance sheet, reduces* ***_*__*__ ____*__**
to date; Net PPE
25
New cards
*Depreciation Expense*
* *The depreciation taken in the* __***____ ___***__
* *Shown on the income statement, reduces* ***_*__*__ ____*__**
* *The depreciation taken in the* __***____ ___***__
* *Shown on the income statement, reduces* ***_*__*__ ____*__**
*current period; net income*
26
New cards
\: The same amount is depreciated each accounting period.
**Straight-line method**:
27
New cards
\: Produces more depreciation expense in the early years of an asset’s life, with a declining amount of expense in later years.
Double-declining-balance
28
New cards
\: Produces varying amounts of depreciation in different accounting periods depending upon the number of units produced.
Units-of-production
29
New cards
There are many depreciation methods, and some are more **____** than the straight-line method (accelerated)
aggressive
30
New cards
Similar to the various inventory costing methods (*FIFO/LIFO; we’ll discuss later*), different methods can produce ____ _____acct numbers!
Significantly different