EVDS-1660 - History of Culture, Ideas and Environment: chapter 1
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
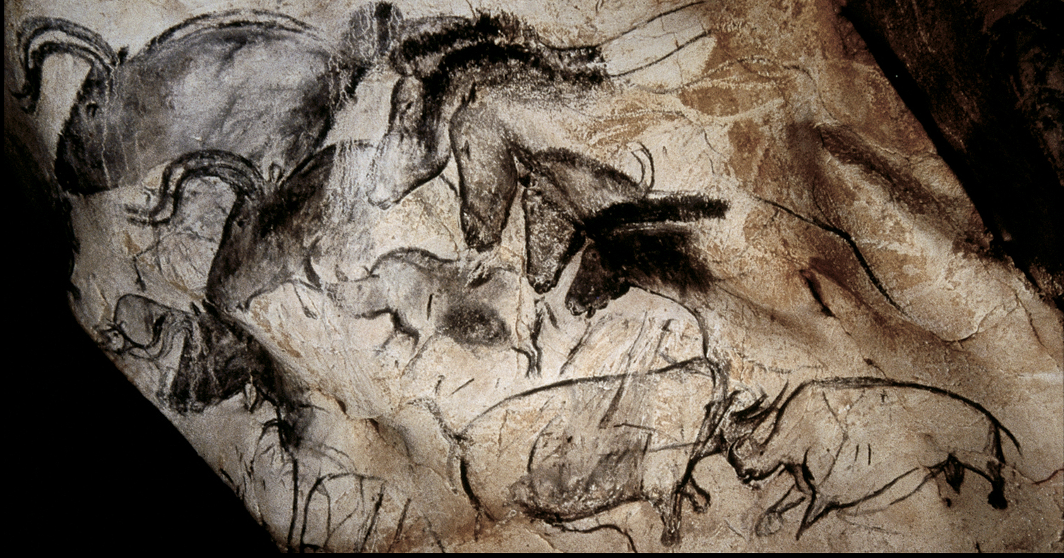
WALL PAINTING WITH HORSES, RHINOCEROSES, AND AUROCHS
Chauvet Cave. Vallon-Pont-d'Arc, Ardèche Gorge, France.
c. 32,000-30,000 BCE. Paint on limestone.
Charcoal for drawing rhinos are radiodated, to be 32,410 years old plsr or minus 720 years
Paleo
Earliest known sites of prehistoric cave paintings,
Image illustrate grazing, running, or resting animals such as wild horses,, bisons, mammoths,bears, panthers, owls, deer, aurochs, woolly rhinoceroses and wild goats(i bex)
Include both male and women handprints
geometric marking:Grids, circles, dots
Child like Footprints in cave lead to a “room” full of bear skulls
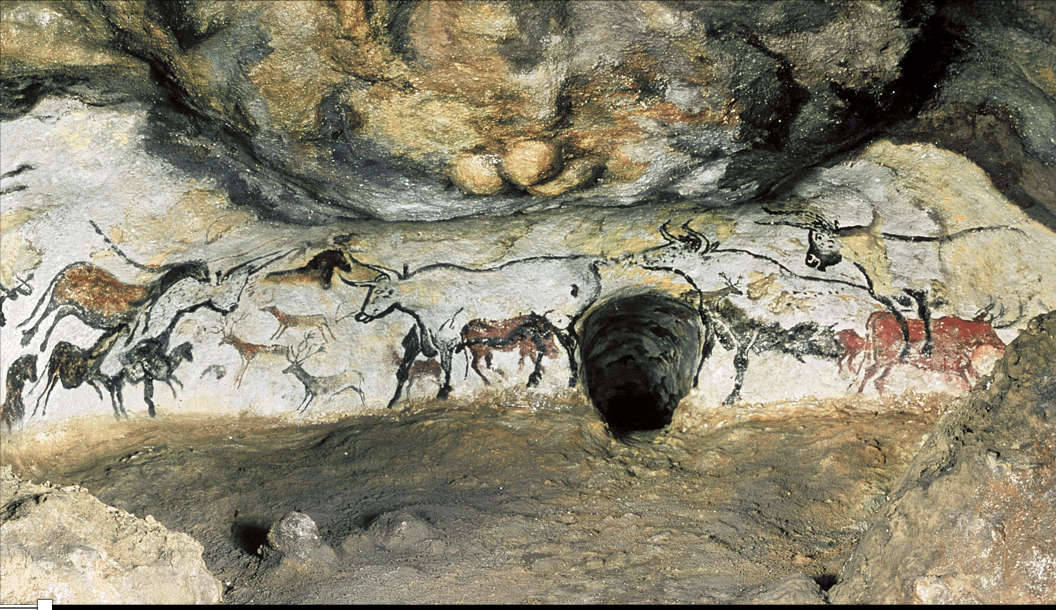


Lascaux: HALL OF BULLS
Lascaux Cave. Dordogne, France. c. 15,000 BCE.
Paint on limestone, length of largest auroch (bull) 18' (5.50 m).
Sites now closed off because off visitors bringing in heat, humidity, exhaled carbon dioxide
Paleo
The best-known cave paintings, southern france
Animals are emphasized by their most characteristic features and rendered in a
composite pose =with hooves, eyes, and horns seen from the front but bodies and heads in profile
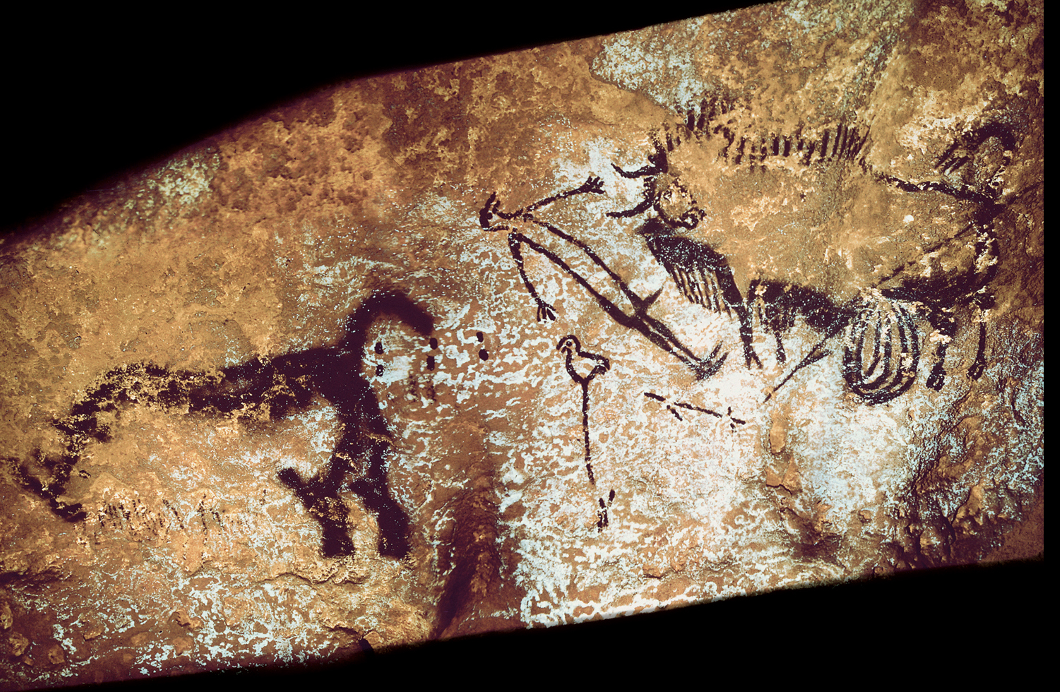

BIRD-HEADED MAN WITH BISON
Shaft scene in Lascaux Cave. c. 15,000 BCE.
Paint on limestone,

Paleo
Only painting in the cave that seems to tell a story-storytelling
Stylistically different from the other painting at Lascaux
A figure-most likely a hunter, male-with a head of a bird/wearing a bird’s-head mask-appears to be lying on the ground-Bison above him-below him lie a staff and a spear thrower-outer end carved in the shape of a bird-spear through the bison hindquarter-bison will soon die and is disemboweled- on the left a rhinoceros seems to run off-
Unknowns: If it is a myth, actual event, vision of shaman -and why the male is portrayed as a stick figure compared to the detailed animals
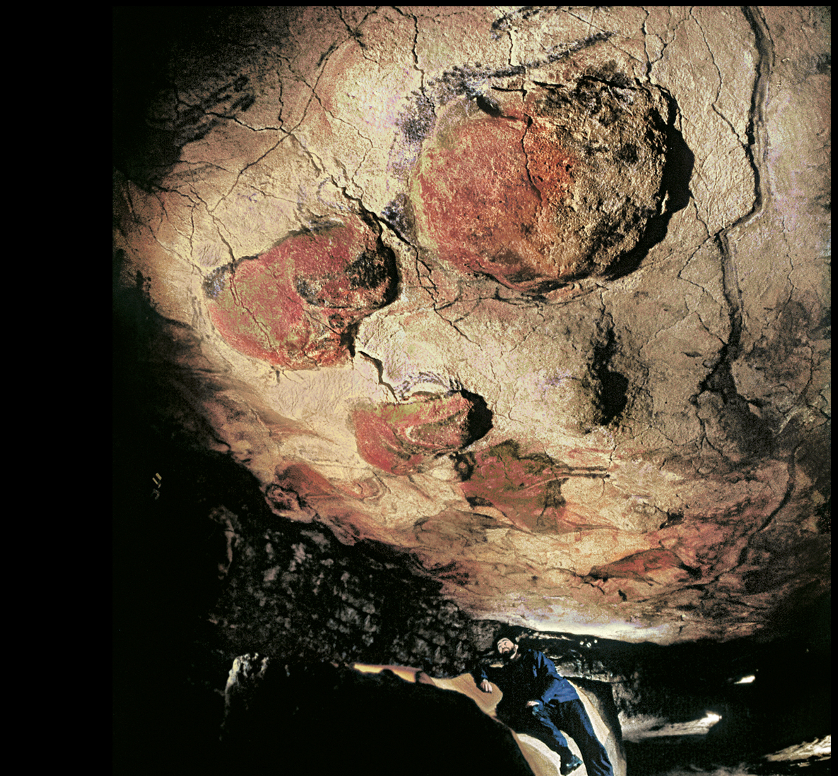
BISON
Ceiling of a cave at Altamira, Spain. c. 12,500 BCE.
Paint on limestone, length approx. 8'3" (
Paleo
1st to be discovered and attributed to the upper paleolithic period
used the natural curve(irrigulation) of the cave to carve, sculptural effects
Herd of bison: used red and brown ocher to paint large areas of the animals shoulders, backs, flanks
In black and brown to sharpened the contours of the rocks and added details of the leg, tails, heads, and horns
mixed yellow and brown iron based ocher to make red tones which came from charcoal or manganese
What is Relative Dating?
Relationship among objects in single excavation or among several sites
EX: Pottery types A,B,and ,C follow eachother chronologically in one site that knowledge can be applied to another site
What is Absolute dating?
determine a precise span of calendar years in which the artifacts was created
What is radiometric dating?
Method of absolute dating, which radioactive materials have disintegrated over time
what is Potassium-argon dating?
Measure the decay of radioactive isotope into a stable isotope of argon, reliable with material over one million years ago
what is Uranium-thorium dating?
measures the decay of uranium into thorium in the deposits f calcium carbonate that covers the surface of cave walls, determining the minimum age of paintings under the crust
What is Thermo-luminescence dating?
measure the irridation of the material subjected to fire,like pottery and the soil in which it is found in, determined my the luminescence produced when the sample is heated
What is Electron spin resonance?
uses magnetic feild and microwave irradiation to date the material such as tooth enamel and the soil around it
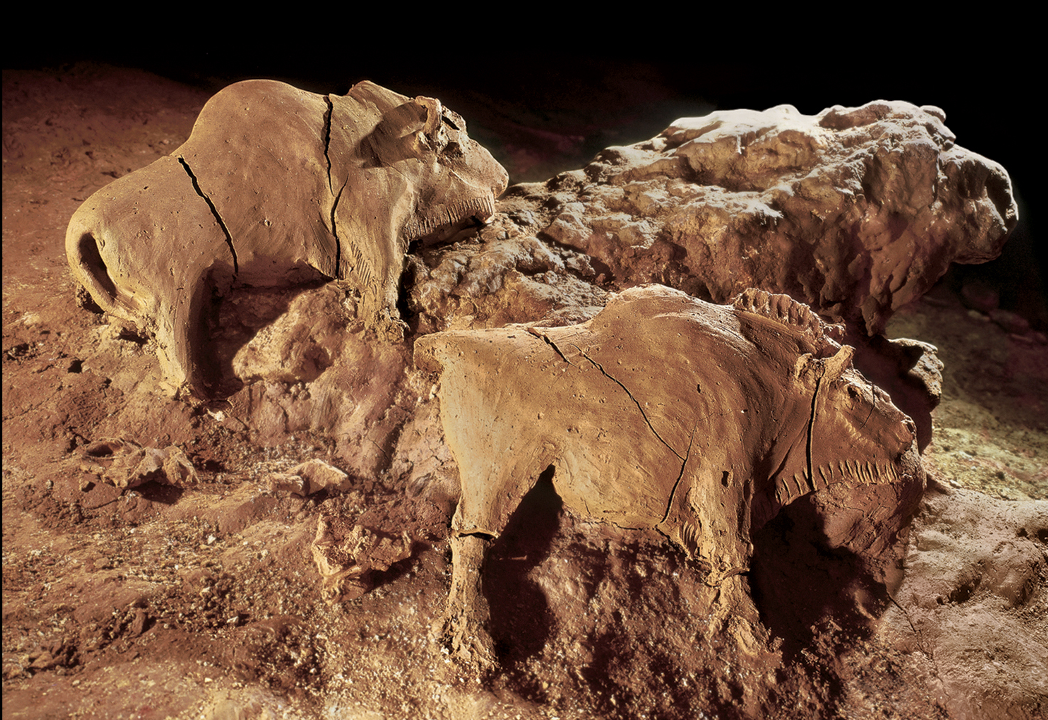

BISON
Le Tuc d'Audoubert, France. c. 13,000 BCE.
Unbaked clay, length 25" (63.5 cm) and 24" (60.9 cm).
Paleo
Example of high relief,
emphasis on the broad masses of the meat bearing flanks and shoulders
So life like because: creator engraved short parallel line below their necks, representing shaggy coats
Group rites took place because of the small footprints on the clay floor
what are the three phases of the Paleolothic period?
lower=older
upper/middle=most recent
transitional/middle=Meso’middle”

SPOTTED HORSES AND HUMAN HANDS
Pech-Merle Cave. Dordogne, France. Horses 25,000-24,000 BCE; hands c. 15,000 BCE. Paint on limestone, individual horses over 5' (1.5 m) in length
Prehistoric
First spray paint= spraying paint from the mouth
prehistoric art and painters painted what they saw
-two horses back to back on the wall of a chamber, the head follows the natural shape of the rock
-black dots surround portions of its contours and fill most of its body, which though to be decorative but actually was popular species at the time
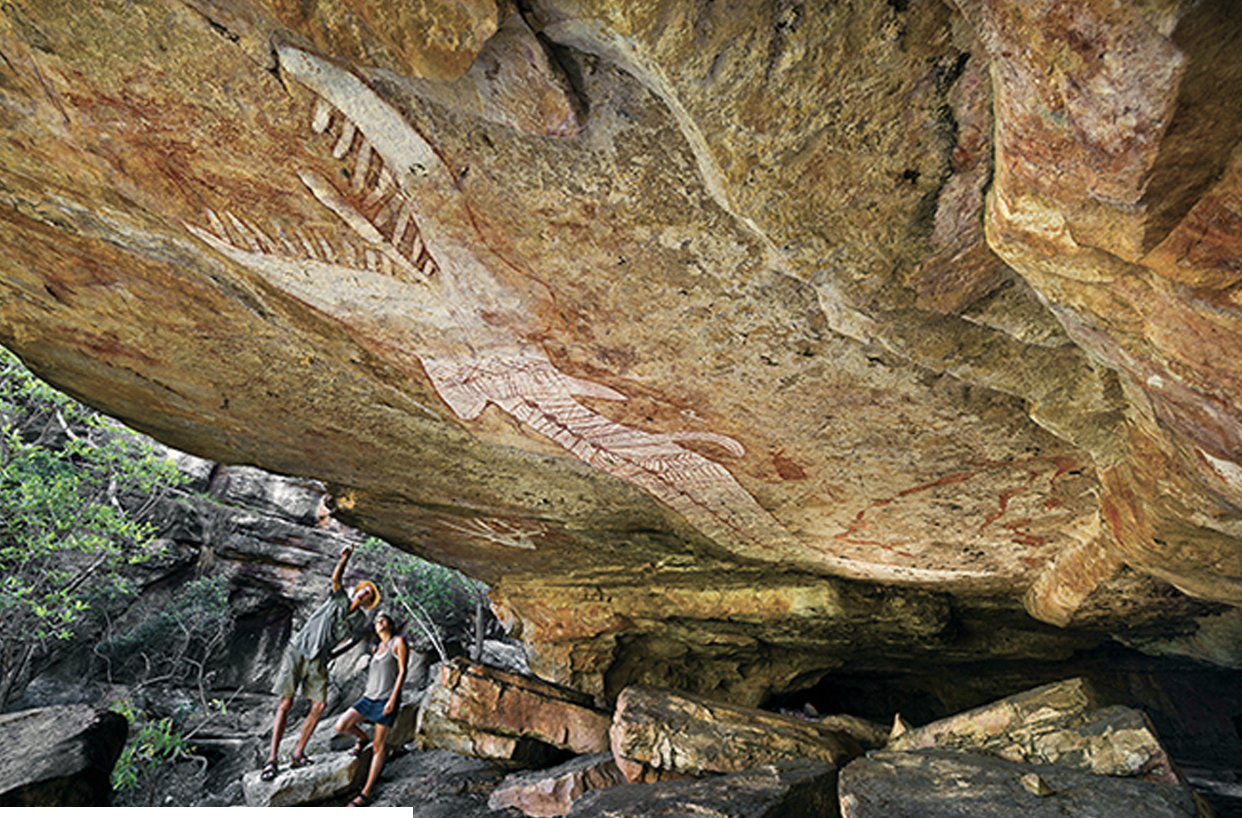

RAINBOW SERPENT ROCK
prehistoric
Painters left their own hand prints around the art
rainbow serpents play a role in rituals and legends of the creation of of human beings, the generation of rains, storms, floods, and the reproductive power of nature and people
What’s pre-history?
language before the written word
BCE=before common Era
BC=exclusive
CE=common Era

homo sapiens appeared when?
Homo sapiens sapiens appeared when?
vast movement of ppl happened when?
Study of prehistoric art happened when?
400,000 years ago
120,000 years ago
100,00-35,00 years ago
200 years ago
Paleolithic stands for what
Neolithic stands for what
paleo”old” and lithos”stone”
Neo”new” and lithos”stone”
what sets modern humans from our predecessors?
Make and understand art
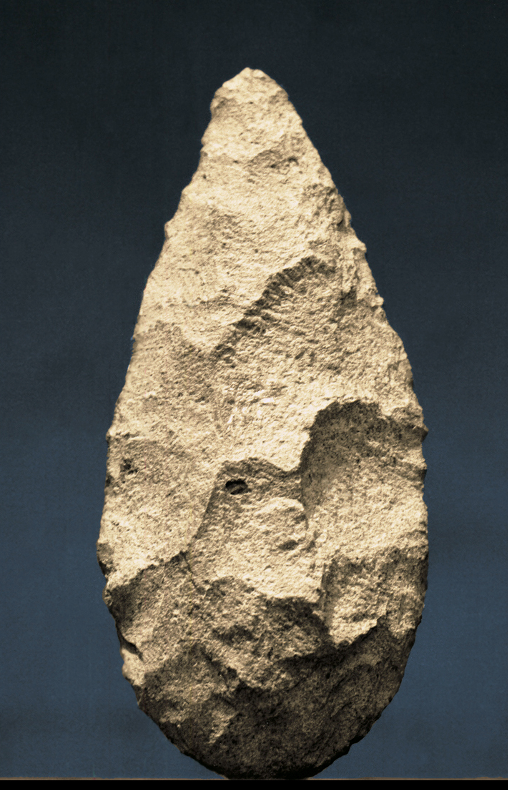

PALEOLITHIC HAND-AXE
From Isimila Korongo, Tanzania. 60,000 years ago.
Stone, height 10"

The making of images, or "art," is a hallmark of the Upper Paleolithic period.
Early tools in the Lower Paleolithic period were made by chipping or flaking.
used: to cut animal skin and meat, break bones for bone marrow, cut wood and plants
represents the evolution to create and object to complete a task

performance + process
hanges form tools to tools with art,
Multi step process
Social function: multiple were found suggest to announce an individuals skill and status withen their community
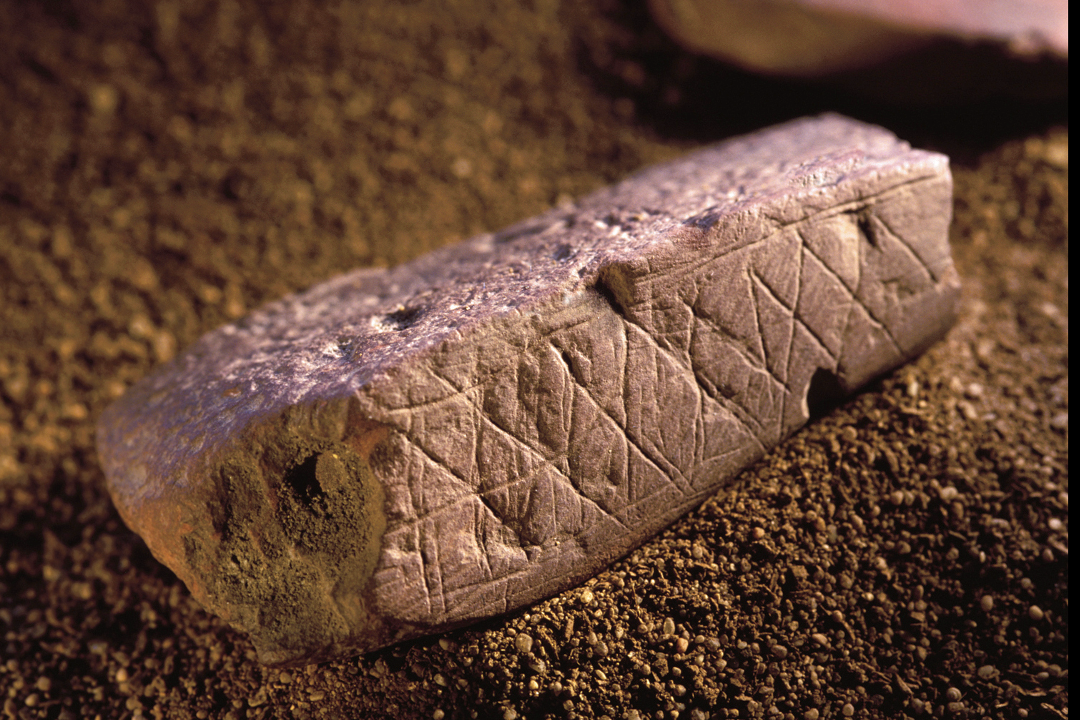

DECORATED OCHER
From Blombos Cave, southern Cape coast, South Africa.
75,000 years ago

Paleo
Used to draw patterns and art , used on bodies, colour shell or tool ornements

RECONSTRUCTION DRAWING OF MAMMOTH-BONE HOUSES
Ukraine. c. 16,000-10,000 BC

Upper Paleo
example of early architecture, mammoth tusks for roof support and door openings, inside fire pit,
What is sculpture in the round VS relief sculpture
Round: self contained, three dimensional-
Relief: stone, bone,ivory-surrounding material is contained to form a backround

LION-HUMAN
From Hohlenstein-Stadel, Germany. c. 30,000-26,000 BCE.
Mammoth ivory, height 11-5/8" (29.6 cm).
Ulmer Museum, Ulm, Germany

Paleo
Anthropomorphic = human + animals, important , creative, shows advancement by not copying what the the painters saw in nature
Showed different ideas of humans and what it’s meant to be human and how we’re distinct from animals
a foot tall

An example is the human figure with a feline head, which was created not by copying directly by nature, but combining a unique half-human, half-beast
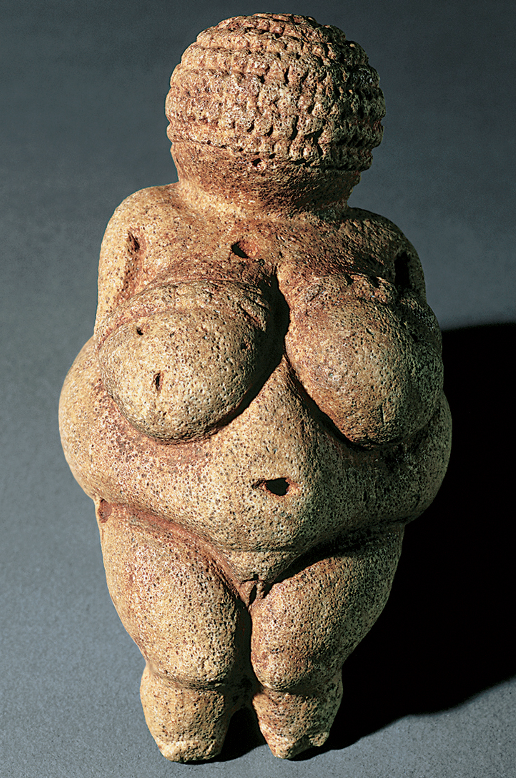


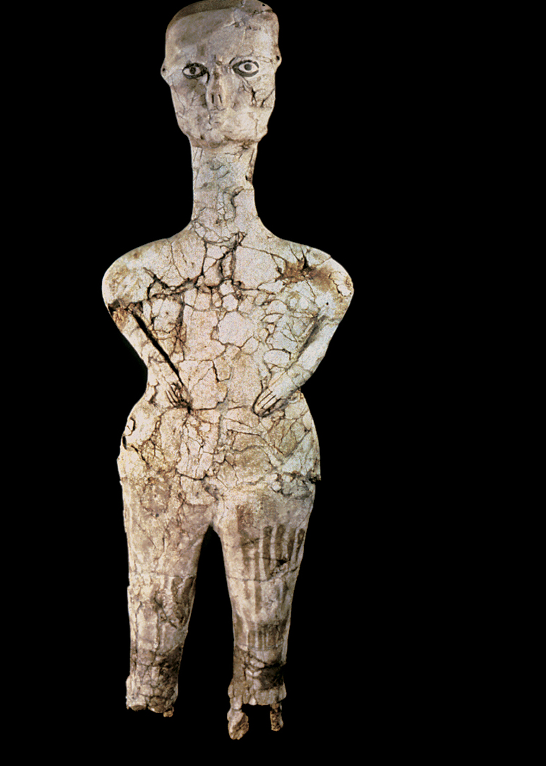
WOMAN FROM WILLENDORF
Austria. c. 24,000 BCE. Limestone,

Upper Paleo
Female figures
Red ocher, imestone ,
Good fortune, well fed, fertile, reprsentational quality(good luck, fertility, gift) , child bearing hips, unimportant face,
Was found in multiple region
Used for communication to different groups: mating or friendly
largets production of these figurines happend when climate conditions were the worst and a need for interaction and alliance
Pantheon , goddess
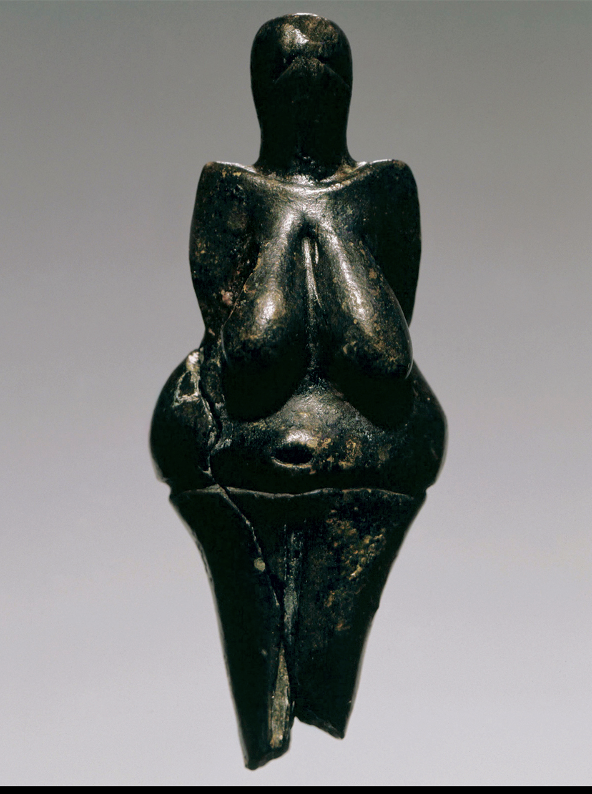


WOMAN FROM DOLNÍ VĔSTONICE
Moravia, Czech Republic. 23,000 BCE.
Fired clay, 4-1/4" × 1-7/10" (11 × 4.3 cm).
Moravske Museum, Brno, Czech Republic.

Paleo
use of Fire for making, out of water and soil-specific cecipe then putting in a kiln to bake ,
Expecting the figures to explode before but did not happen as the figures turned out great
performance and process at the rawrest and earliest form

WOMAN FROM BRASSEMPOUY
Paleo
Shows head/memory image- egg shape in a long neck, wide nose, strong bowline to show deep eyes
an abstraction which is abstract art, reduction of shape and size yet still recognizable forms , not to be exact replications of nature
When did sophisticated cave paintings start?
40,000 years ago
Prehistoric Wall Painting technique
Micheal Lorblanchet
-Using animal fat lamp→ chewed a piece of charcoal to dilute with water and saliva→ blew out on the surface of the wall→ using hand as stencil→ a hole punched in leather to make a stencil
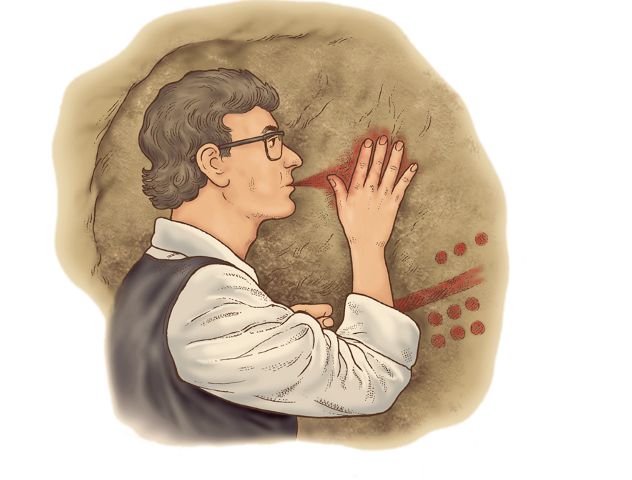
what three painting technique did the homo sapiens sapiens use
1)Spraying
2)Drawing with fingers or blocks of ocher
3) daubing with paintbrush made out of hair or moss
other thre stages:
1)engraved line using flakes or flint2)colour wash of ocher and maganese 3)final engraving to emphasize shaped and detail
What is the meaning of cave paintings?
What else was found in the caves
Humans have an aesthetic impulse,
Depends on cultural views and who advances them
social function and aesthetics and culturally relative
Products of rites to strengthen clans bonds and of ceremonies to enhance the fertility of animals used for food-theory denied because animals portrayed were not the same as being hunted
sympathetic magic
places of worship and initiation rituals
Painting are found deep in cave so only the privileged could see them
Upper Paleo understanding: Shamanism→ belief that certain ppl(shaman) can travel outside their bodies to meditate between the living and spirit
Instrumental peice were found
What signified the starting of the Neolithic period?(social and cultural changes of the neolithic period)
The gradual ending of the Ice Age affected the distribution, density, and stability of plant, animal, and marine life.
People exerted increasing control over land and resources, changing the economy and community interactions.
origin of plant and animal domestication

What makes Neolithic architecture different?
Ppl developed an attachment to the land, w/ settlement came a new type of social life
![<p><span>RECONSTRUCTION drawing OF LEPENSKI VIR HOUSE/SHRINE<br>Serbia. 6000 BCE. [Fig. 01-15]</span></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7b614c54-5986-4d88-861f-adf31b4adf0d.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>Neo</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bca3ef33-6d6f-41d8-aaac-161540c5da7c.png)
RECONSTRUCTION drawing OF LEPENSKI VIR HOUSE/SHRINE
Serbia. 6000 BCE. [Fig. 01-15]

Neo
made out of mud, clay, wooden post, branches-set on stone foundation
burials found beneath
Little sign of domestication of plants and animals
![<p><span>HUMAN-FISH SCULPTURE<br>From Lepenski Vir, Serbia. c. 6300-5500 BCE. [Fig. 01-16]</span></p><p>Neo</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c15b2246-5eed-4573-94a9-55b4e3502853.png)
HUMAN-FISH SCULPTURE
From Lepenski Vir, Serbia. c. 6300-5500 BCE. [Fig. 01-16]
Neo
found in homes, confusing combination of architecture and nondomesticated economy, we think it was temporary habitations where ppl carried out special rites and activities linked to death and the natural and wild worlds
A HOUSE IN ÇATALHÖYÜK
Reconstruction drawing. Çatalhöyük, Turkey. c. 7400–6200 BCE.
Illustration: John Gordon Swogger, originally published in Ian Hodder, The Leopard's Tale: Revealing the Mysteries of Çatalhöyük. London: Thames & Hudson, 2006., fig. 5.8.
[Fig. 01-17

Neo
Long lasting architecture, home to 3000ppl , made out of mud brick and held with mortar
Important because: use of early architecture; the sensational art that was found in the building
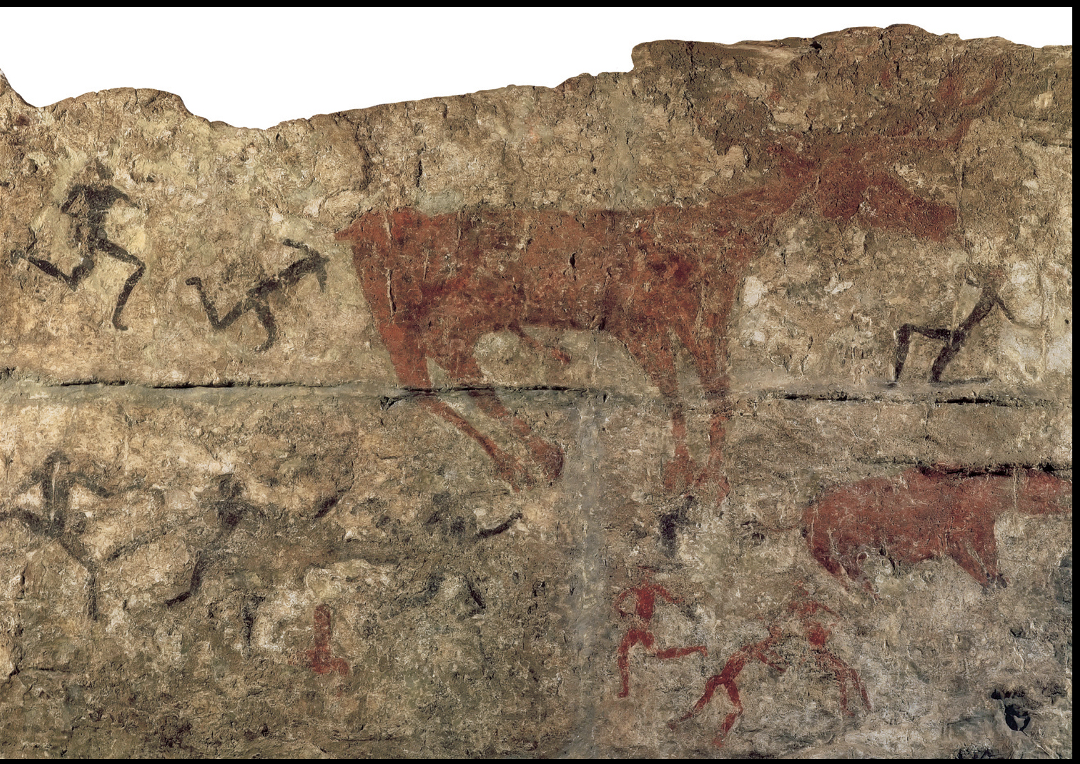
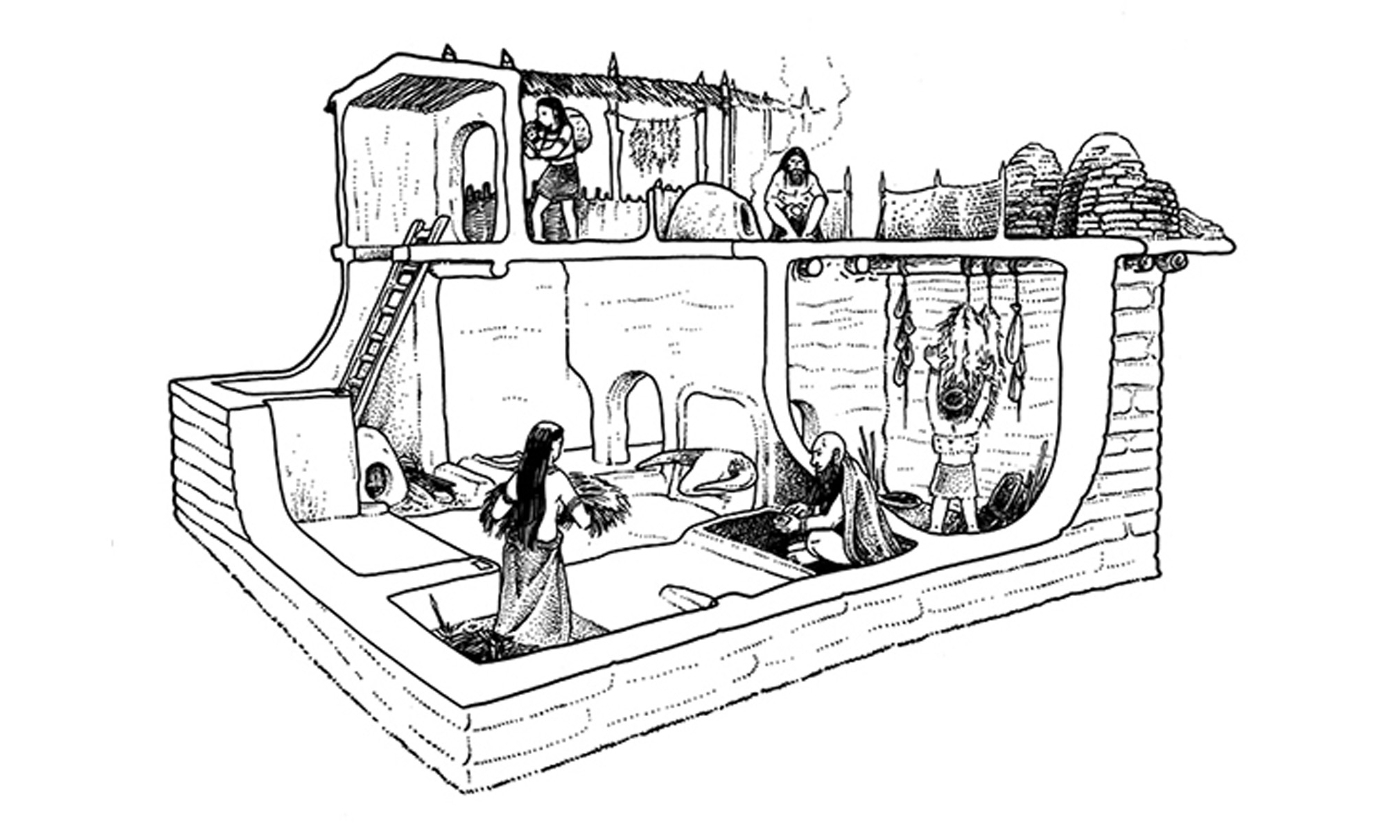

MEN TAUNTING A DEER (?)
Detail of a wall painting from Çatalhöyük, Turkey. c. 6000 BCE.
Museum of Anatolian Civilization, Ankara, Turkey. [Fig. 01-17
Neo
Huge horned wild animal ,deer maybe, surrounded by small humans maybe jumping or running, taunting or baiting w/ animals
![<p><span>SESKLO STONE-FOUNDATION HOUSE<br>Sesklo, northern Greece. 6500 BCE. [Fig. 01-18]</span></p><p>Neo</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/35c76980-41e9-43cc-8bd0-36fea44acdd9.png)
SESKLO STONE-FOUNDATION HOUSE
Sesklo, northern Greece. 6500 BCE. [Fig. 01-18]
Neo
Stone based, and long lasting structure and other parts of the village mud clay and wooden buildings
Neolithic architecture terms Çatalhöyük:
Ridgepole
Wattle and daub
thatch
a horizontal beam along the ridge of a roof
wall material
Plant material such as reeds or straw tied over the framework of poles
![<p><span>TOMB INTERIOR WITH CORBELING AND ENGRAVED STONES<br>Newgrange, Ireland. c. 3000-2500 BCE. [Fig. 01-19]</span></p><p>Neo</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c1e65599-fb9d-47cb-ac58-0f6a10a56465.png)
TOMB INTERIOR WITH CORBELING AND ENGRAVED STONES
Newgrange, Ireland. c. 3000-2500 BCE. [Fig. 01-19]
Neo
Megalithic, these structures associated with death, death and burial as a fundamental, death is viewed as theatre, monument as stage, grave goods as props, celebrnts and mourners as actors,
engineers for the transportation, alignment , shaping of the stone
Megalithic architecture terms:
Dolmen and Post line and lintel
Capstones
Cairn
passage grave
Corbeled vault
construction with two upright posts support a horizontal element, the lintel
a stone fixed on top of something, typically a wall.
artificial hill
narrow, stone-line passaeways led to a large room at the center
arched structure that spans an interior space
![<p><span>STONEHENGE FROM THE AIR<br>Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England. c. 2900-1500 BCE. [Fig. 01-20]</span></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7b877a8d-cbb7-4fe6-9218-aea3acde69a7.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>Neo</p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/243b23ef-ec16-409a-9ba6-c3df9981306b.png)
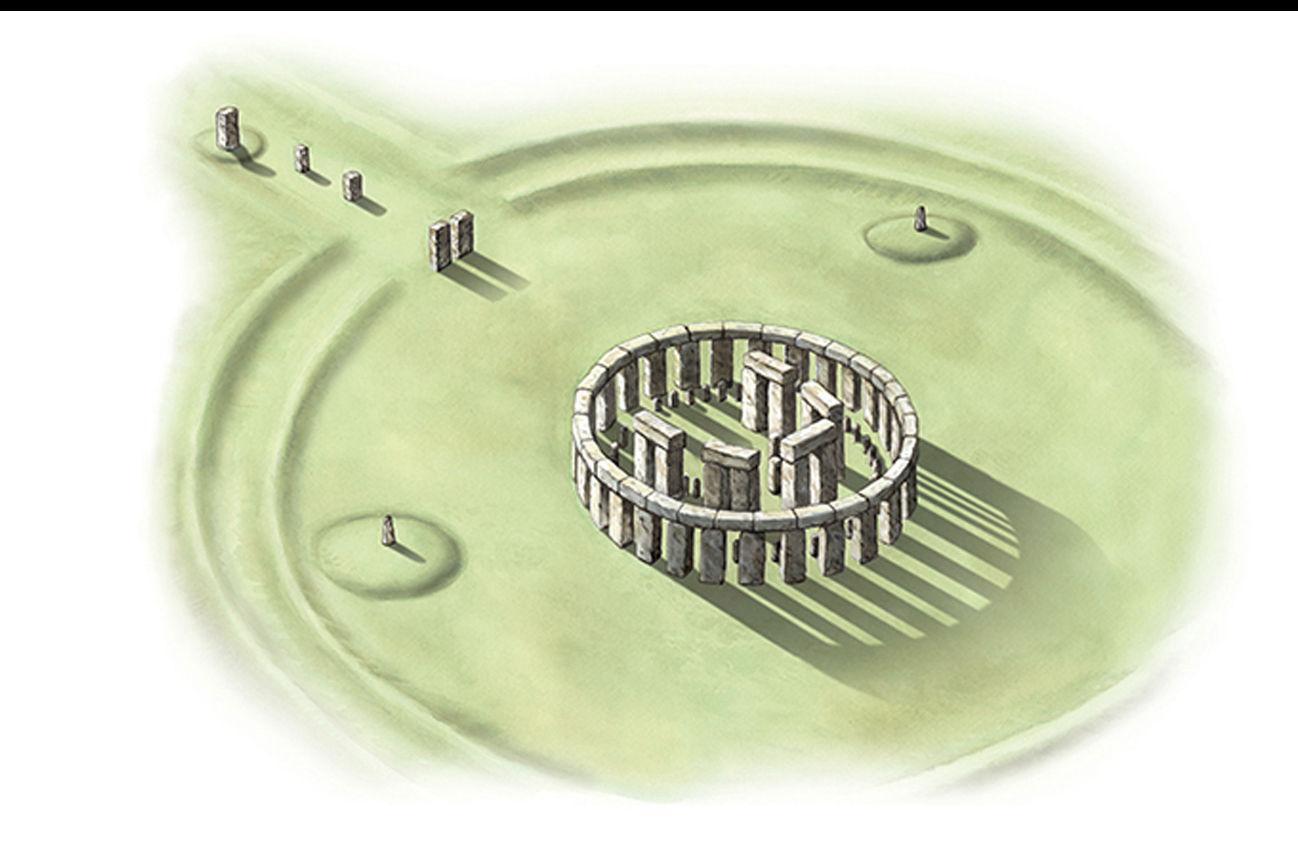
STONEHENGE FROM THE AIR
Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire, England. c. 2900-1500 BCE. [Fig. 01-20]

Neo
compasse used
8 diff phases of construction-Neo→ bronze age
Started as a ceremony burial → bluestone was reanranged in arc→ circle of sarsen→ blustone rearanged with sarsen → dominated by horshoe shape with five sand stones(lintels)
Mortise and tenon joints
Different type of stone along different times of construction → bluestone in early phases were not locally available, therefore transported from afar shows powerful connection w/ homeland
Ceremonies linked to death and burial because of the neerby settlements(built of wood),Astrological alignment which takes planning and knowledge, in tuned with sciences and astrology,
![<p><span>RECONSTRUCTION DRAWING OF DURRINGTON WALLS<br>The settlement at Durrington Walls, near Stonehenge, southern England. 2600 BCE.<br>Private collection. </span><span data-name="copyright" data-type="emoji">©</span><span> Historic England/Bridgeman Images. [Fig. 01-24]</span></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5c094e88-b5db-44d8-be4f-bd5b325d72d4.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>Neo</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3ebebbc5-1c93-4e34-9733-f8c252dce2c0.png)
RECONSTRUCTION DRAWING OF DURRINGTON WALLS
The settlement at Durrington Walls, near Stonehenge, southern England. 2600 BCE.
Private collection. © Historic England/Bridgeman Images. [Fig. 01-24]

Neo
Walls and stonehenge are connected to the avon river by banked avenues, connected worlds of the living(walls) and dead(stonehenge)
Ceramic terms
clay based:
Ceramic=inclusive term of pottery
Pottery= includes all baked-clay except porcelain
porcelain=most refine product of ceramic
Earthenware=fired800 degree
Stoneware= fired and 1200-1400 degrees
pottery fragment/potsherds=serve as dating key and reconstructing human living and trading pattern
![<p>EARLY POTTERY FROM JAPAN'S JOMON CULTURE<br>12,000 BCE. [Fig. 01-24] left</p><p>Neo</p><p>EARLY POTTERY FROM THE FRANCHTHI CAVE, GREECE<br>6500 BCE. [Fig. 01-25]right</p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/50f81365-8090-4566-a81b-72bc0ed8a788.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>neo</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5cdb0138-588c-478a-a078-a7e375717310.png)
EARLY POTTERY FROM JAPAN'S JOMON CULTURE
12,000 BCE. [Fig. 01-24] left
Neo
EARLY POTTERY FROM THE FRANCHTHI CAVE, GREECE
6500 BCE. [Fig. 01-25]right

neo
Pottery is advancing, slowly seeing ceramics
, unsure why,
Early stages of pots used for ceremonies(medicinal/narcotic plants) later on used for eating and cooking
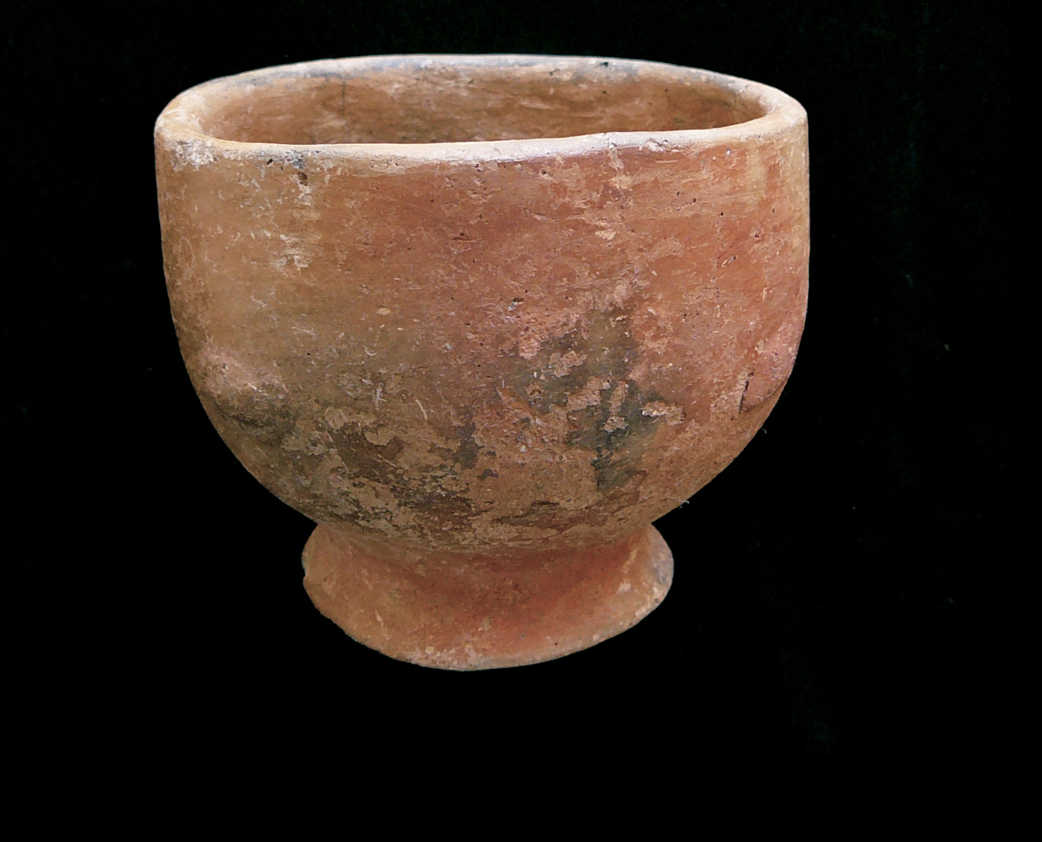


FIGURES OF A WOMAN AND A MAN
Fwomen:Stability,continuity of family, body shows she is watching the smoke come form earth,worrying about holes in the roof, worrying about her partner, comuning w/ heaven
man: slim, masisve legs and shoulder, thoughtfullness,weariness,boredon or sorrow
neo
HUMAN FIGURE
Toys,portraits,votives, ceremonial functions
Cowrie shells outline with bitumen,nostriles defines,mouths are discreet and tightlipped, clothes and other feature were painted on the body, used the same plaster for walls to coat the figures,
Impression is of living breathing individuals who are unable to speak. Statues burried in pits while humna are in houses, statues are represnetd wide and awake
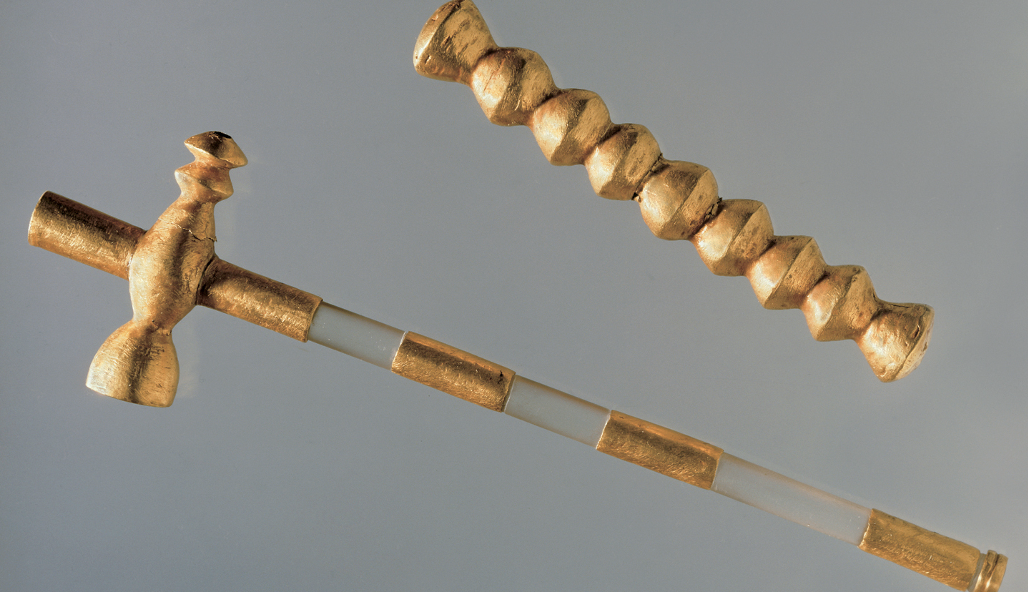
![<p><span>GOLD-ADORNED FACE MASK<br>From Tomb 3, Varna I, Bulgaria. Neolithic, 3800 BCE.<br>Terra cotta and gold. Archaeological Museum, Plovdiv, Bulgaria. [Fig. 01-28]</span></p><p>right: <span>GOLD SCEPTERS<br>From Varna, Bulgaria. 3800 BCE.<br>National Museum of History, Sofia, Bulgaria. [Fig. 01-29]</span></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/10c769f5-2a60-4033-bcff-e91a47b90d09.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>Neo</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f9d99ee1-3fa3-4520-be6b-7f013ee6d6ac.png)
GOLD-ADORNED FACE MASK
From Tomb 3, Varna I, Bulgaria. Neolithic, 3800 BCE.
Terra cotta and gold. Archaeological Museum, Plovdiv, Bulgaria. [Fig. 01-28]
right: GOLD SCEPTERS
From Varna, Bulgaria. 3800 BCE.
National Museum of History, Sofia, Bulgaria. [Fig. 01-29]

Neo
Metallurgy=metal work, gold copper,
left: no skeleton present, body was presented by a clay mask with gold adornments
right:for ceremonial purposes

what is the Bronze age?
The introduction of metal work
Copper was an abundant but relatively nonfunctional metal beyond representational use.
The alloy bronze proved to be a stronger substance vital to the development of weapons, therefore vital to the shift in power bases of communities to those who had the resources to make bronze.

![<p><span>ROCK ART: BOAT AND SEA BATTLE<br>Fossum, northern Bohuslän, Sweden.<br>Bronze Age, c. 1500-500 BCE. [Fig. 01-30]</span></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/304ac16e-35cb-4381-b4b4-1584e1c68162.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p>bronze age</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/df68571b-70d8-4938-8392-8ef9bab9dddd.png)
ROCK ART: BOAT AND SEA BATTLE
Fossum, northern Bohuslän, Sweden.
Bronze Age, c. 1500-500 BCE. [Fig. 01-30]

bronze age
-connects sky, earth, and sea, visualization of a three part nature of the universe OR
-between water and earth marking a boundary between the living and spirits
Prehistoric artists created representations of human figures using a variety of media, styles, and techniques. Compare two examples drawn from different times and places by discussing the relationship between style or technique and expressive character.

Woman from willendorf- Austria,24000BCECarved from limestone- same expressive character of fertile women(produce strong children), well fed,wide hips, with big breast and hips, used for trading andnon-verbal communication, seem to be used for mating between groups, forming an alliance, faceless
vs
Woman from Dolní Věstonnice-Czech republic-23000BCE- fired clay made from water and soil, fire Kiln
What are the common motifs found in cave paintings such as those at Lascaux and Altamira? Summarize the current theories about their original meaning and purpose.

used the natural shape of the stone or rock, animal based paintings, herd of animals, bison in both areas,
Lascaux-hall of bulls
Altamira bison
Many examples of prehistoric art and architecture express relationships between the living and the dead. Discuss how this theme is evoked in one work of architecture and one example of sculpture discussed in this chapter. Why do you think this theme was so important?
Stone henge
Stonehenge, Architecture,
Cave paintings and its relation to shamans(travel outside world and meditate between exsisting world and spirits and Votiv figurines ex Figures of man and woman
How did the emergence of ceramics and metallurgy transform art making in the Neolithic era? Select and analyze a work discussed in the chapter that was made in one of these new media and discuss the unique properties of the medium

new medium of extraordinary potential for shaping and decorating durable object, marked a shift from textiles, skin,and wooden containers to a multistep process of making and firing ceramics
Ex: Mettalurgy for artifacts(gold adorned face mask) in the cemetaries could be an explanation of the more powerful individuals