EKG Interpretation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Electrocardiogram
Records cardiac electrical activity.
Same heartbeat, different view.
Depolarization
The electrical impulse that activates the heart to contract.
Repolarization
The heart muscle relaxes.
P-Wave
Atrial depolarization (atria contracting)
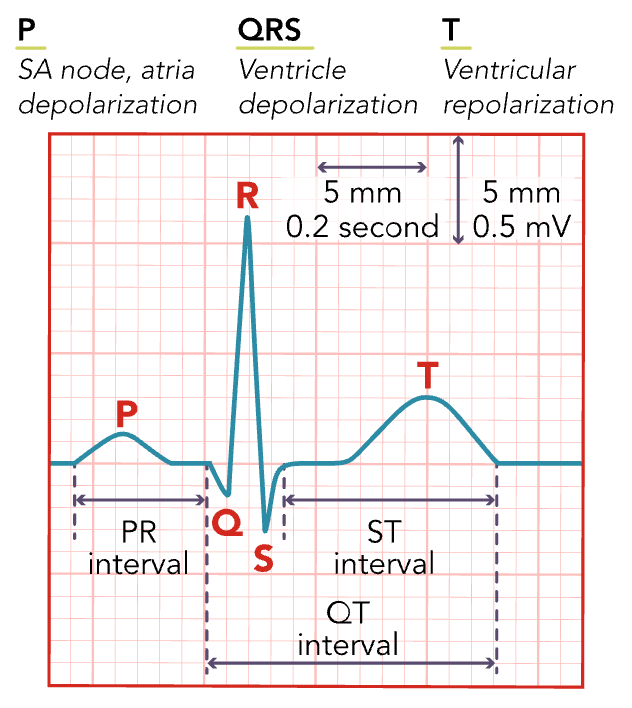
PR Interval
Related to the rate of cardiac impulse transmitted from the AV node. The time from when the P starts until the QRS starts.
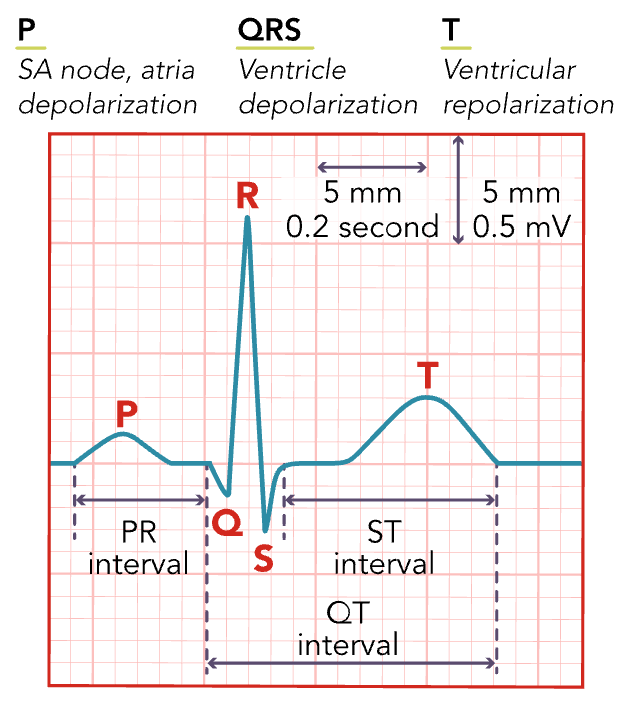
QRS Complex
Ventricular depolarization (ventricle contracting)
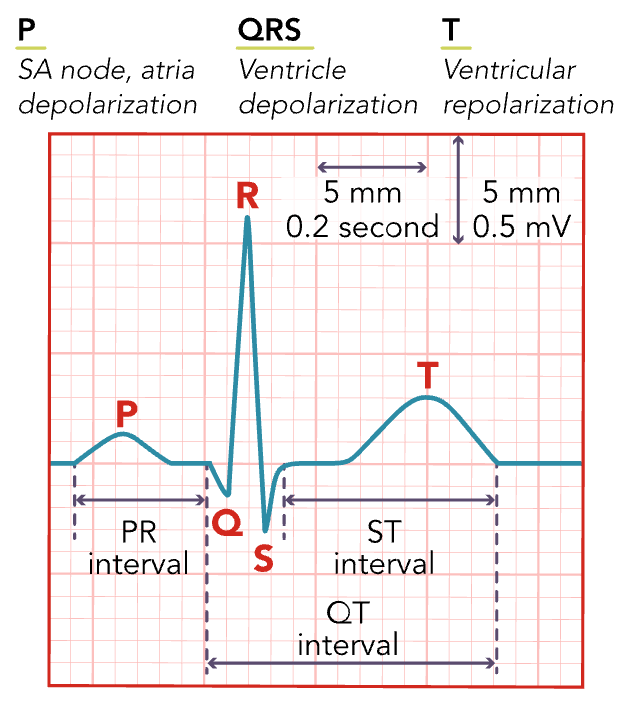
ST Segment
Follows ventricular depolarization and occurs prior to the start of ventricular repolarization.
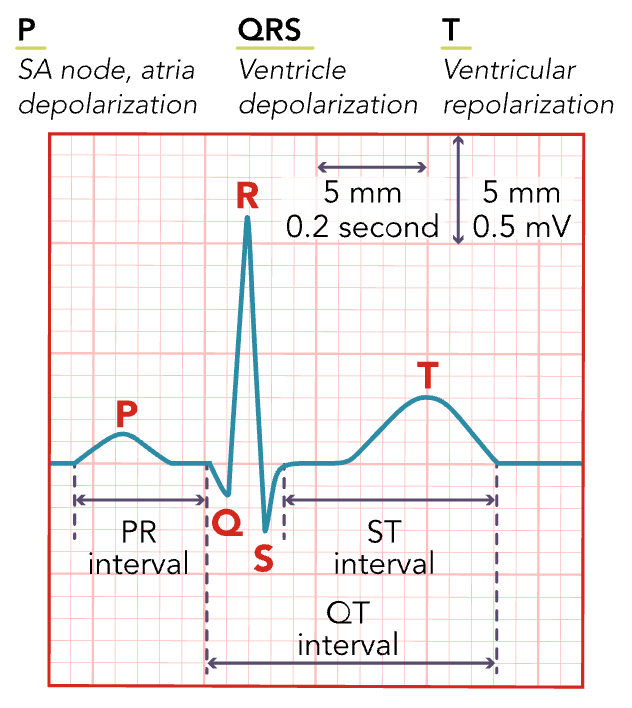
T Wave
Ventricular repolarization is occurring.
QT Interval
The time for ventricular repolarization to complete. (can be effected by certain medications)
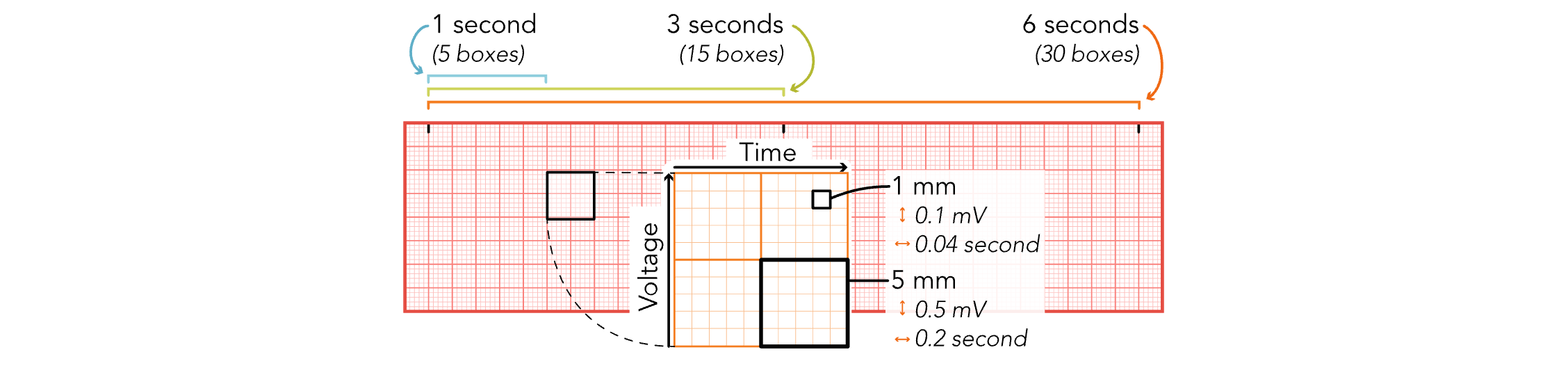
EKG Strips - 5 Large Boxes
Equals 1 Second
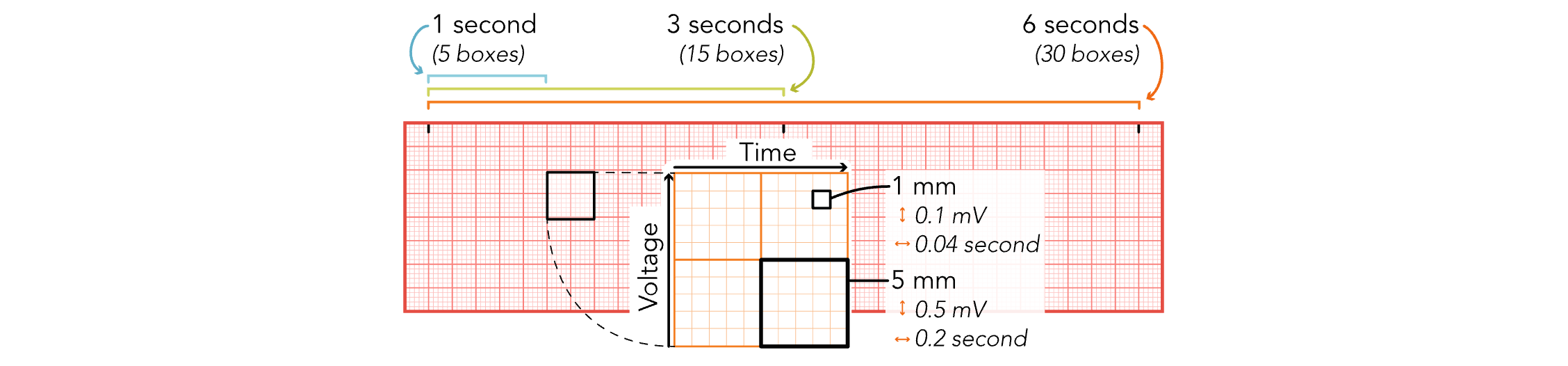
EKG Strips - 15 Large Boxes
Equals 3 Seconds
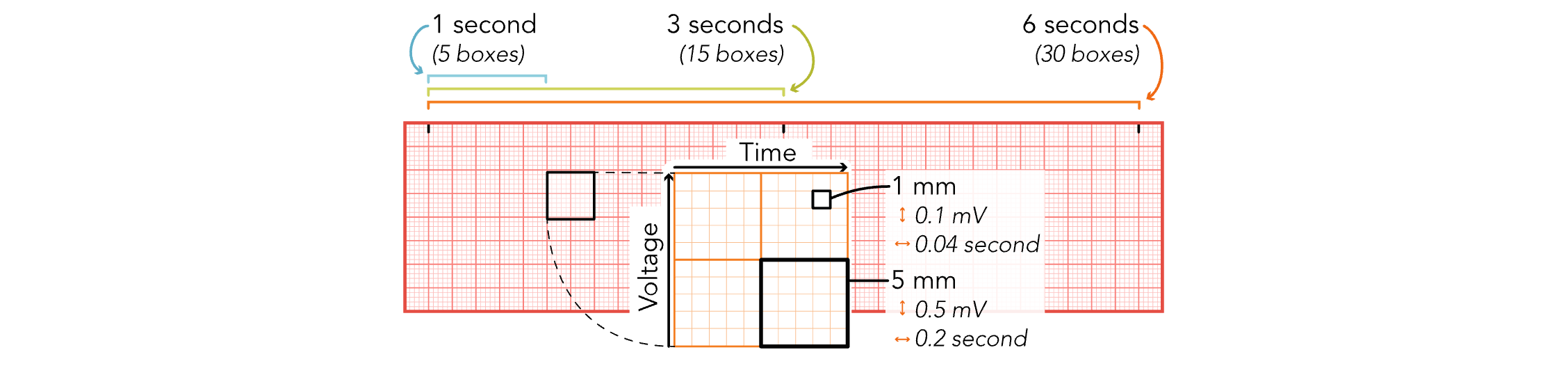
EKG Strips - 30 Large Boxes
Equals 6 Seconds
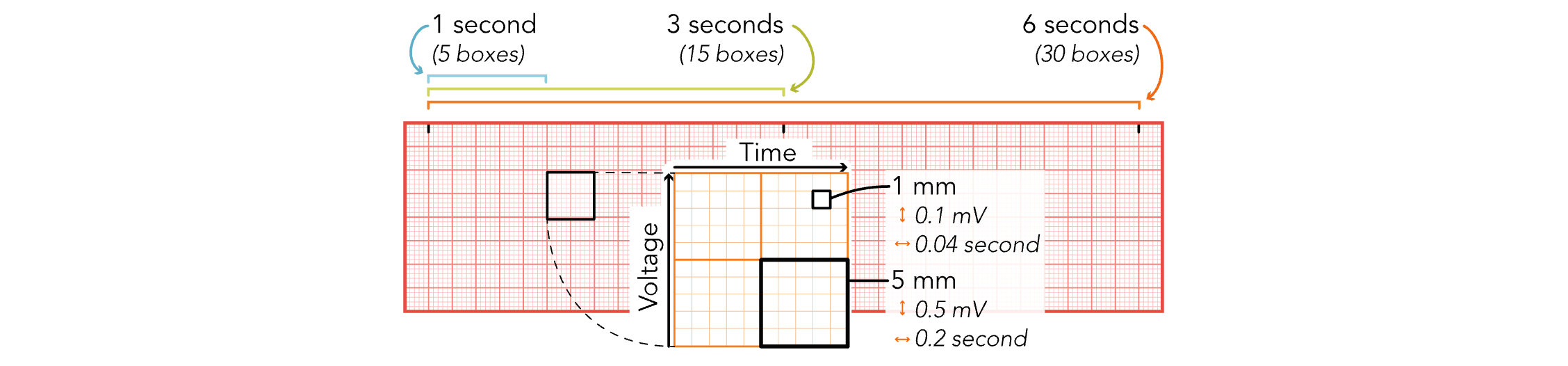
EKG Strips - 1 mm (Small Boxes)
Equals 0.04 Seconds
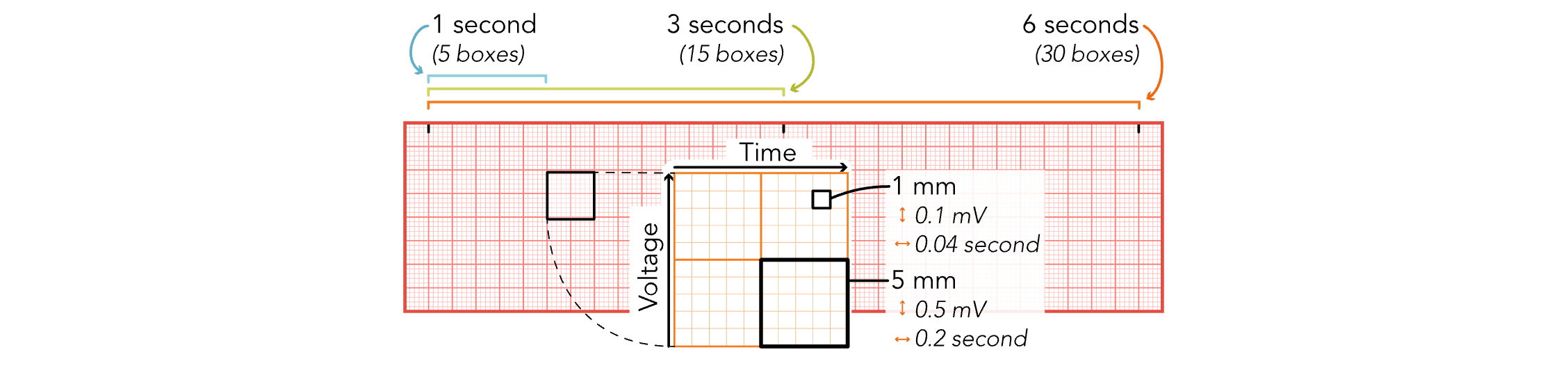
EKG Strips - 5 mm (Small Boxes)
Equals 0.2 Seconds
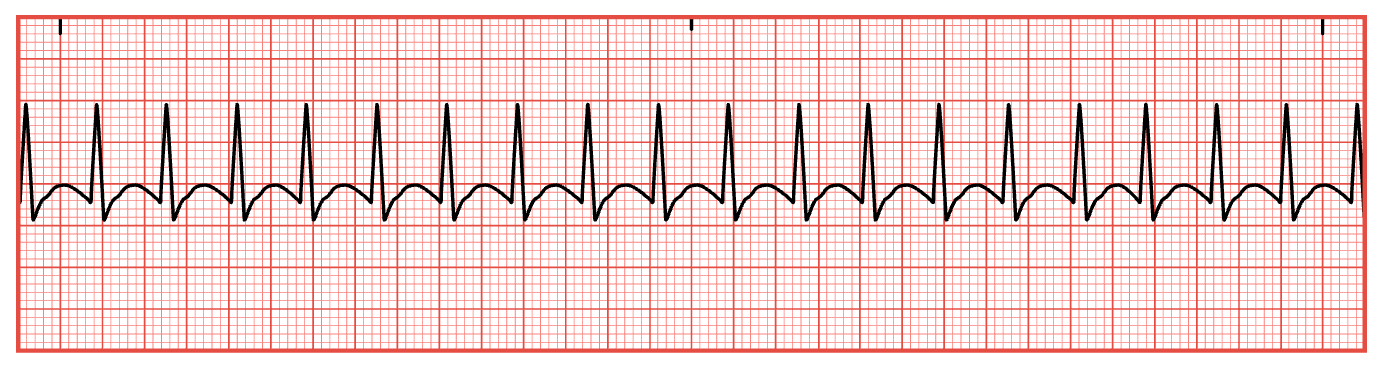
7 QRS Complexes in 6 Sec
7 X 10 = 70 bpm
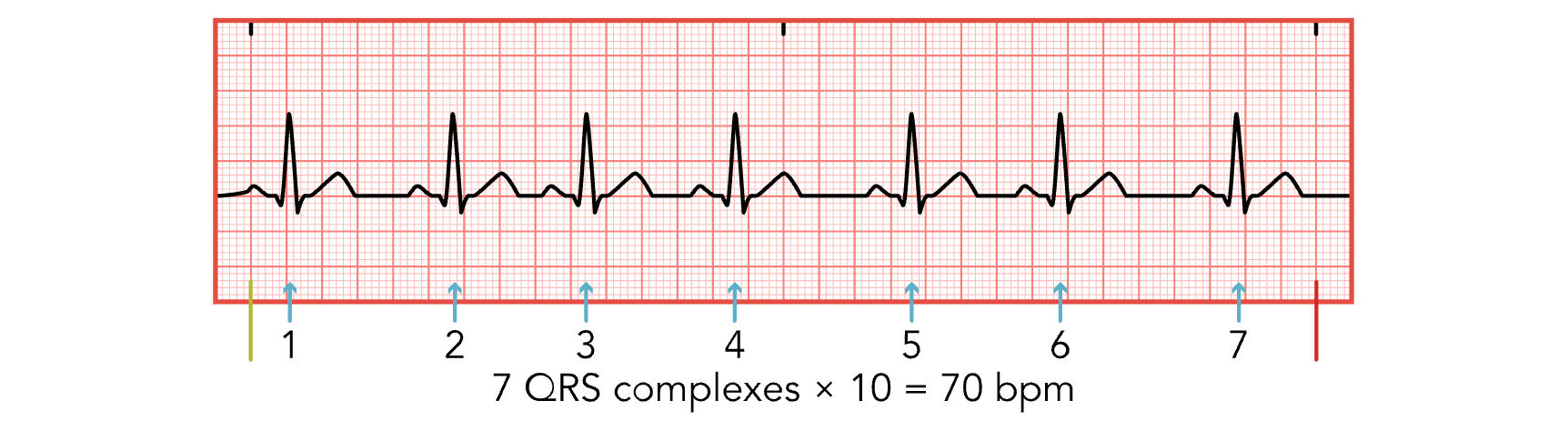
Step 1 for ECG Analysis
Calculate heart rate.
Count R spikes for 6 seconds and multiply by 10.
Step 2 for ECG Analysis
Determine if the heart rhythm is regular.
Are the Rs evenly spaced?
Step 3 for ECG Analysis
Assess for P waves.
Is it there and is it married to the QRS?
Step 4 for ECG Analysis
Measure the PR interval.
Normal: 0.12-0.2 seconds
Step 5 for ECG Analysis
Measure the duration of the QRS complex.
Is it there? Is it wide?
Normal: 0.08-0.12 seconds
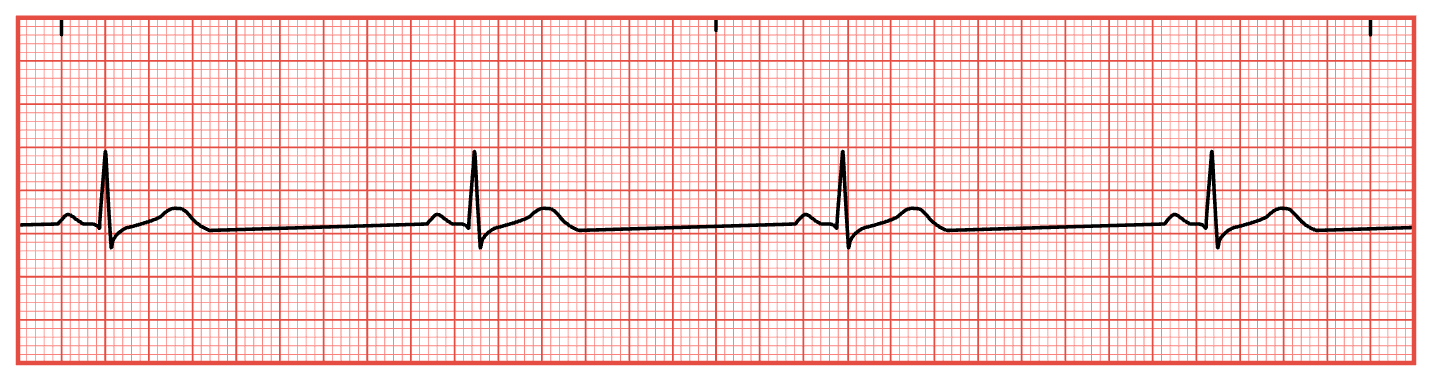
Sinus Bradycardia
BPM < 60
Asymptomatic or symptomatic
Fatigue
Increased SOB
Dizziness
Fall precautions for symptomatic bradycardia!!
Unstable clients
IV atropine 1 mg repeat every 3-5 minutes not to exceed a total of 3 mg.
Monitor for changes in heart rate
Temporary transcutaneous pacemaker if client continues to remain unstable and symptomatic
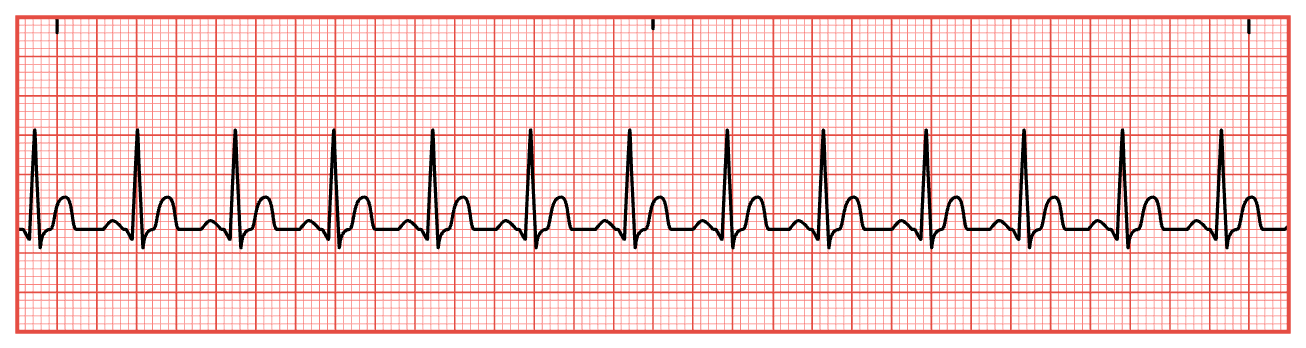
Sinus Tachycardia
BPM > 100
Palpitations
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Elevated temperature
Chest pain
Difficulty breathing
If symptomatic: decrease physical intensity or activities. Change position slowly!
Administer Medications as ordered
Adenosine
Betablockers (metoprolol)
Catheter Ablation
Performed to destroy the abnormally excited cardiac cells responsible for increased heart rate
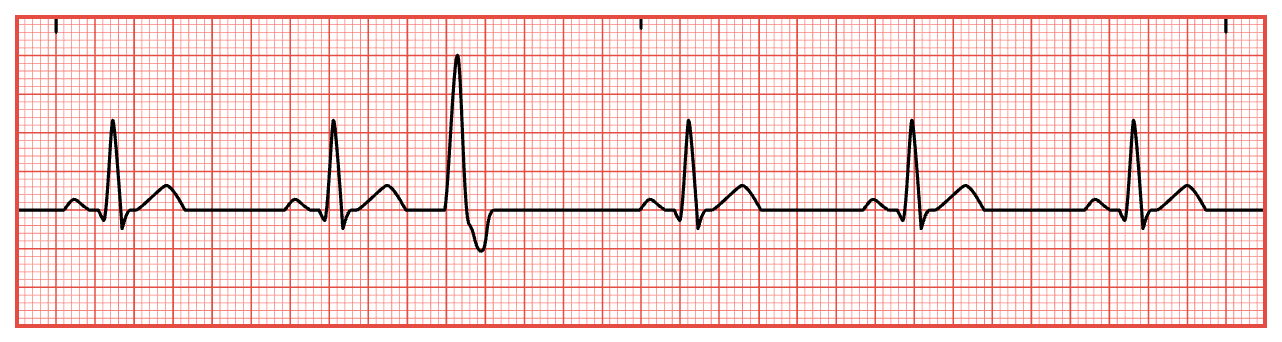
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
Bigeminy & Trigeminy
Bigeminy — every other beat is a PVC
Trigeminy — every third beat is a PVC;
ECG: Wide, bizarre QRS not preceded by a P wave; Missing p-wave where the PVC occurs
Symptoms:
Palpitations
Lightheadedness
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Potential causes for PVCs:
Potassium
Magnesium
Thyroid levels
PVCs can be normal and may occur often in healthy clients.
Client teaching to minimize or prevent PVCs
Smoking cessation
Minimize alcohol
Eliminate illicit drug use
Reduce caffeine intake
Premature Atrial Contractions
The P wave associated with PAC may be hidden or unidentifiable
The PR interval may be shortened less than 0.12 or unmeasurable
Usually have no manifestations but may feel fluttering in the chest
PACs are frequently asymptomatic & do not pose a safety risk to the client.
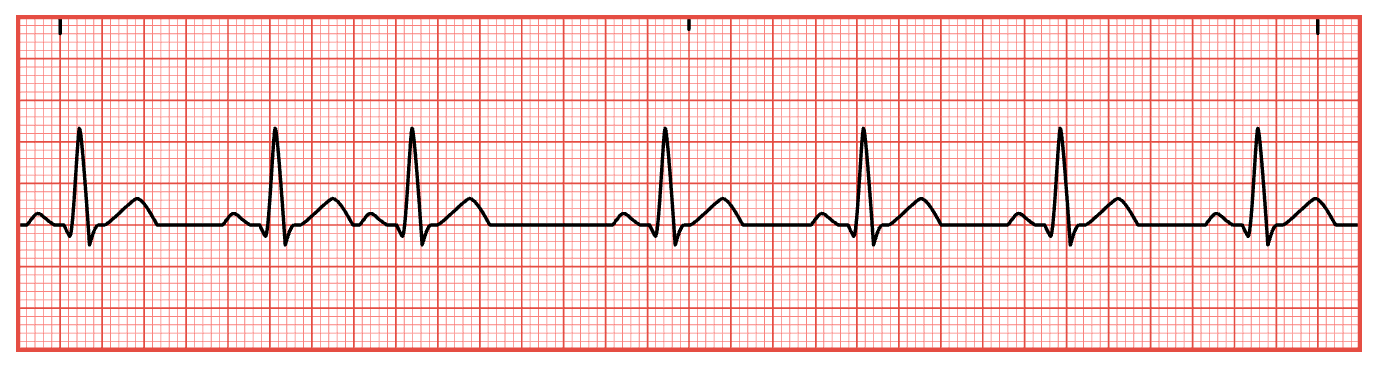
First-Degree Heart Block
Regular rhythm with a wide PR interval
Contribute to first degree heart block
Diets high in sodium, cholesterol or triglycerides
Lifestyle modification
Avoid smoking, alcohol consumption and eat a healthy low-cholesterol diet
Avoid excessive fatigue
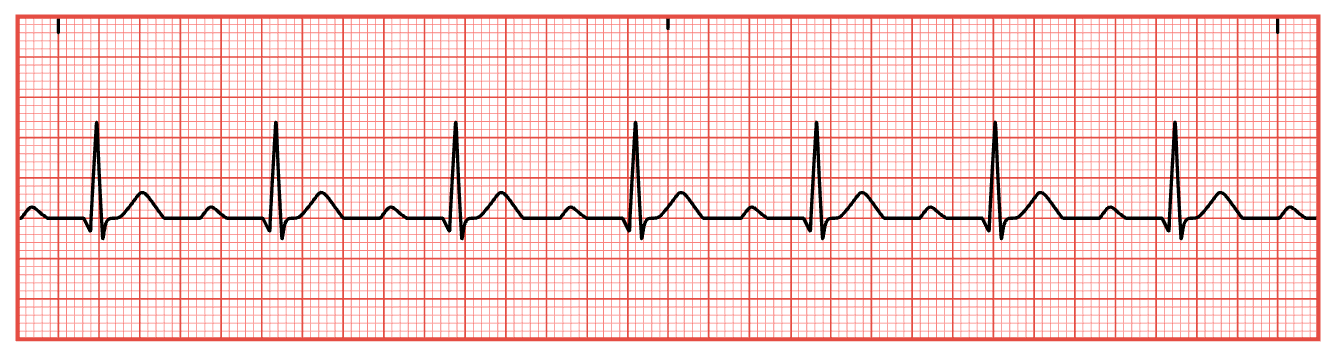
Atrial Fibrillation
NOT A SHOCKABLE RHYTHM
Confirm diagnosis: a-fib is an ECG.
P waves replaced by atrial activities between QRS complexes
HR is fast, irregular, and weak.
Rate can be (60 to 100) or increased (100 to 200)
Asymptomatic or Symptomatic
Irregular pulse
Heart palpitations
Increased heart rate
Chest discomfort
Shortness of breath (At rest or with activity)
Fatigue
Dizziness/Lightheadedness/Syncope
Safety:
Client at risk for stroke & Risk for spontaneous bleeding
Education:
Report manifestations
Take medications as prescribed
Bleeding precautions
Healthy lifestyle modifications
Avoid stimulants
Avoid herbal supplements
Treatment - Rhythm control
Electro cardioversion
Catheter ablation
Anticoagulants
Diet modification
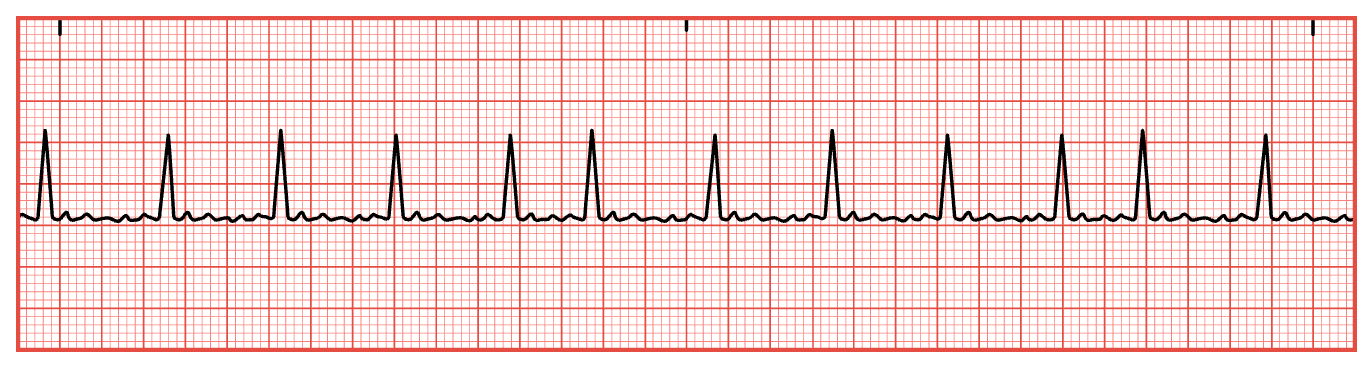
Atrial Flutter
Often regular and looks like a saw
Lightheadedness
Palpitations
Hypotension
Dizziness
Chest discomfort
Shortness of breath
Same for atrial flutter as it is for a-fib.
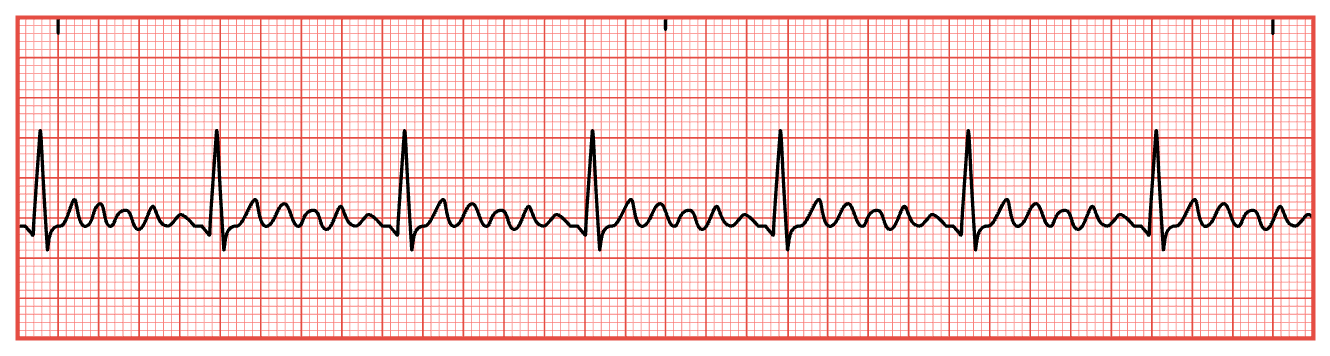
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Can’t measure a PR interval
QRS is skinny
Manifestations may present suddenly
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Syncopal episodes
Hypotension
Shortness of breath
Palpitations
Increased risk of falls
Vagal maneuvers
IV adenosine 6 mg IV over 1 to 3 seconds then flush with 20 mL NS
If no change give a repeat dose of 12 mg followed by 20 mL NS
Adenosine will the heart rate: have a defibrillator on hand